Похожие презентации:
Cytology, embryology, General histology
1. Lecture 3
Cytology, embryology,General histology
Lecture 3
Tissues.
1. Epithelial tissue.
2. Definition
• Tissues -- groups of cells organisedto perform one or more functions.
3. Please, note and write down:
4 basic types of tissues:• Epithelial (Epithelium)
• Connective
• Muscular
• Nervous
4.
Please, note and write down:There are two main types of Epithelial Tissue:
1. Covering and lining
2. Glandular
5.
Please, note and write down:Covering and lining epithelia lie on the free
surface:
- cover outer body surfaces (i.e. skin) and
- line inner body surfaces:
-- lumen of hollow organs (i.e. intestine)
-- cavities (i.e. peritoneal cavity),
-- blood vessels,
-- ducts (in glands),
-- tubules (in kidneys).
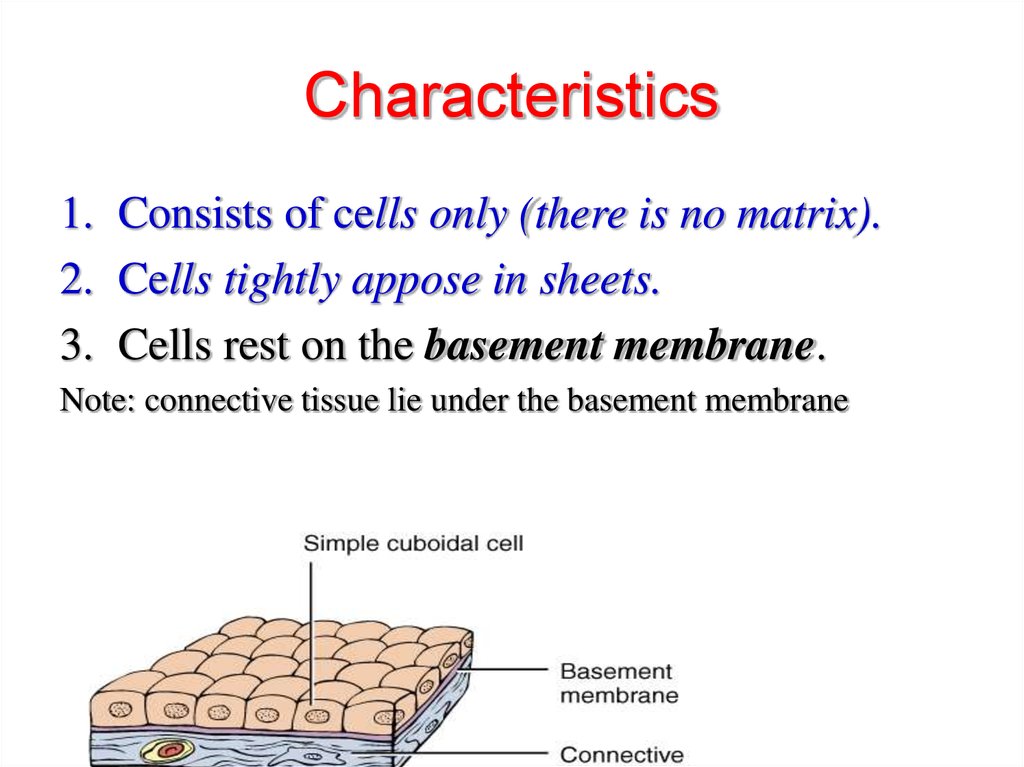
6. Characteristics
1. Consists of cells only (there is no matrix).2. Cells tightly appose in sheets.
3. Cells rest on the basement membrane.
Note: connective tissue lie under the basement membrane
7. Importance :
• Epithelium create a selective barrierbetween the organism and its external
environment:
any substances must pass through the epithelial
cell, not between them.
8. Please, note and write down:
Two types of surface epithelia:• epithelium is simple, when it is one cell
layer thick
• and stratified when it is two or more cell
layer.
9. Maine functions
• protection• diffusion or absorption or excretion =
exchange
10. Another functions
Characteristics.3. polarity - cells have 2 surfaces :
the apical or free surface - towards the lumen or
outside world
the basal surface, closest to the basement
membrane
4. Epithelia are avascular, do not contain blood
vessels, but are nourished by diffusion of
substances from capillaries in underlying
connective tissue.
5. It is frequently mitotically active
11. Characteristics.
Shape of cells:• Squamous.
• Cuboidal.
• Columnar.
12.
Please, note and write down:The morphology of the epithelium
correlates with its function:
• - Epithelia involved in secretion or absorption
are typically simple.
• -- Stratified epithelia usually impermeable
and protective
13.
Simple Squamous Epithelium– lines blood vessels (endothelium), closed body
cavities (mesothelium), alveoli in the lungs
– Function: controls diffusion, osmosis and filtration
14. Please, note and write down: The morphology of the epithelium correlates with its function:
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium• lines tubules and ducts
15.
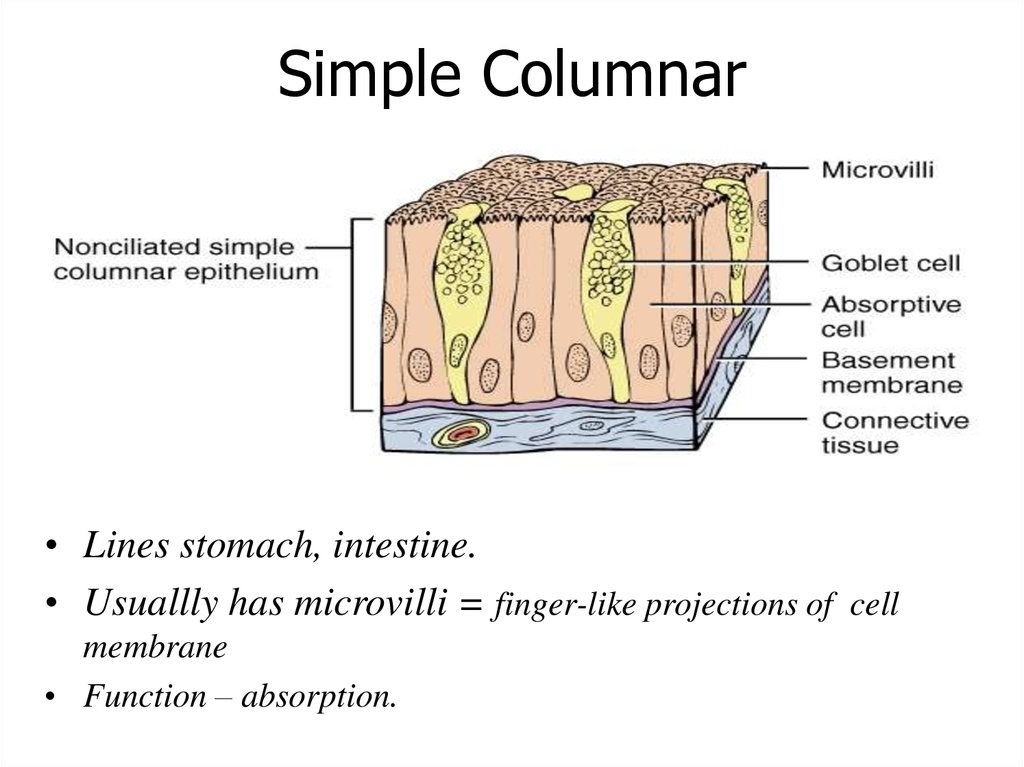
Simple Columnar• Lines stomach, intestine.
• Usuallly has microvilli = finger-like projections of cell
membrane
• Function – absorption.
16.
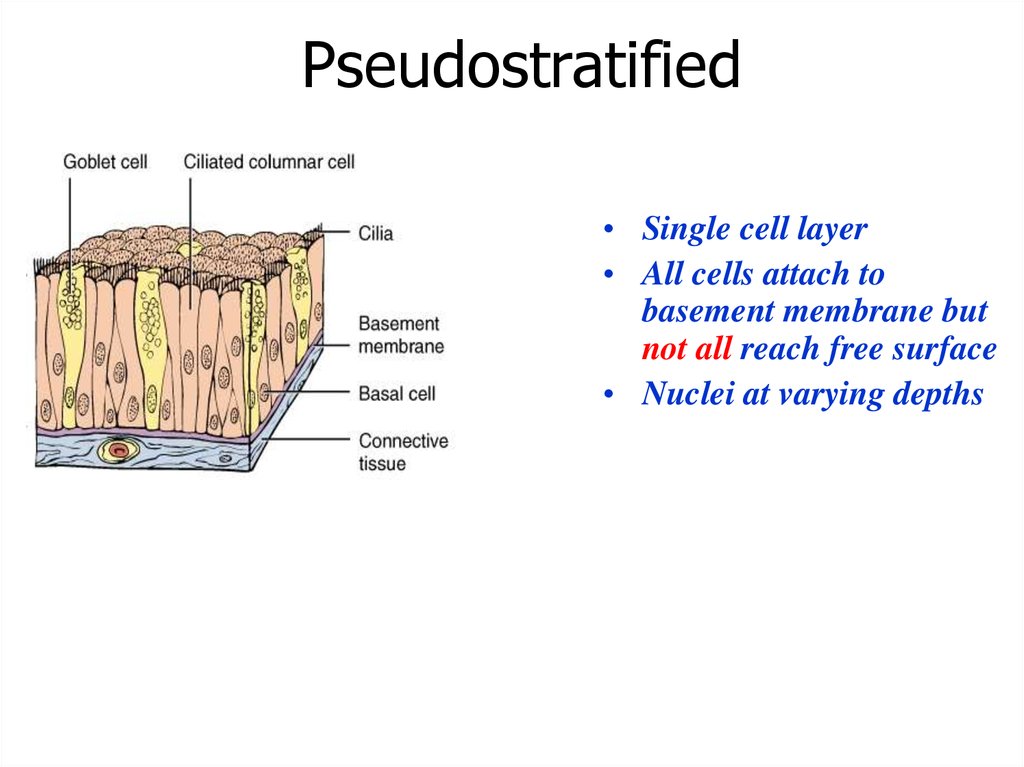
Pseudostratified• Single cell layer
• All cells attach to
basement membrane but
not all reach free surface
• Nuclei at varying depths
17.
Stratified squamousEpithelium
Several cell layers thick,
Surface cells flat
2 types:
Keratinized = surface
cells dead and filled with
keratin
– Example - Skin
• Nonkeratinized = no
keratin in moist, living
cells at apical surface
– Example - Cornea
18.
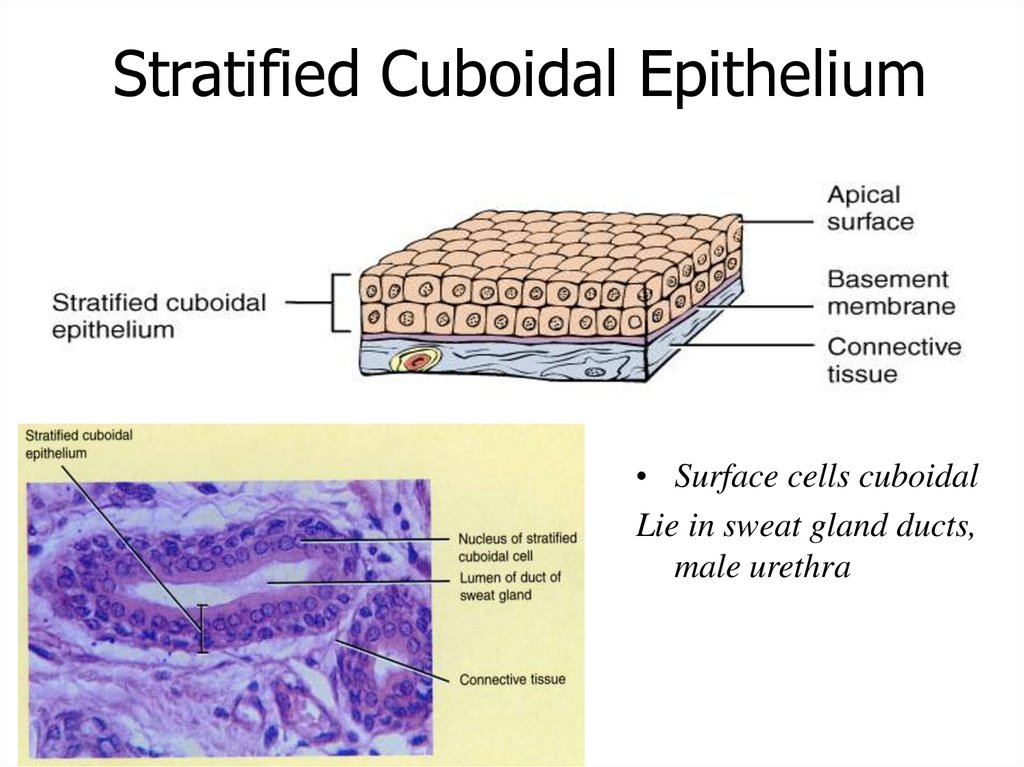
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium• Surface cells cuboidal
Lie in sweat gland ducts,
male urethra
19.
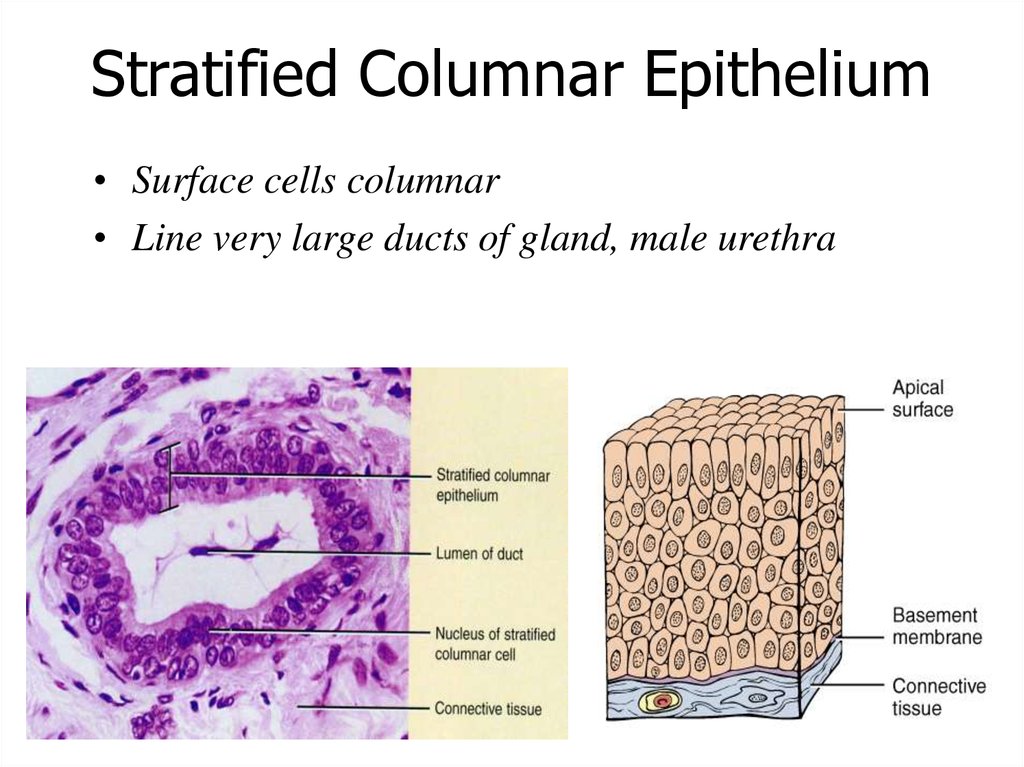
Stratified Columnar Epithelium• Surface cells columnar
• Line very large ducts of gland, male urethra
20.
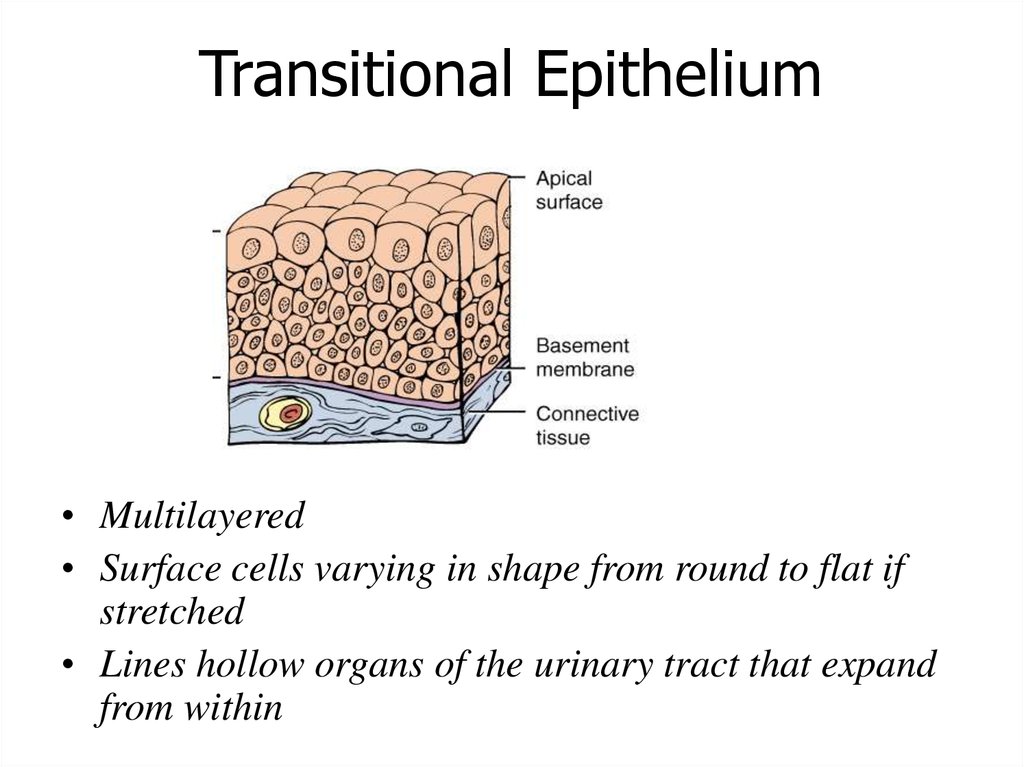
Transitional Epithelium• Multilayered
• Surface cells varying in shape from round to flat if
stretched
• Lines hollow organs of the urinary tract that expand
from within
21.
GLANDULAR EPITHELIA• - form glands.
• Function – secretion = synthesis and
releasing of substances.
22.
There are two types of gland in the body:exocrine and endocrine.
• Exocrine glands
secrete through ducts
or directly onto an
surface (skin or cavity
of inner organs).
• Endocrine secrete
hormones into the
bloodstream.
23. Please, note and write down: !! The morphology of an epithelium often correlates with its function:
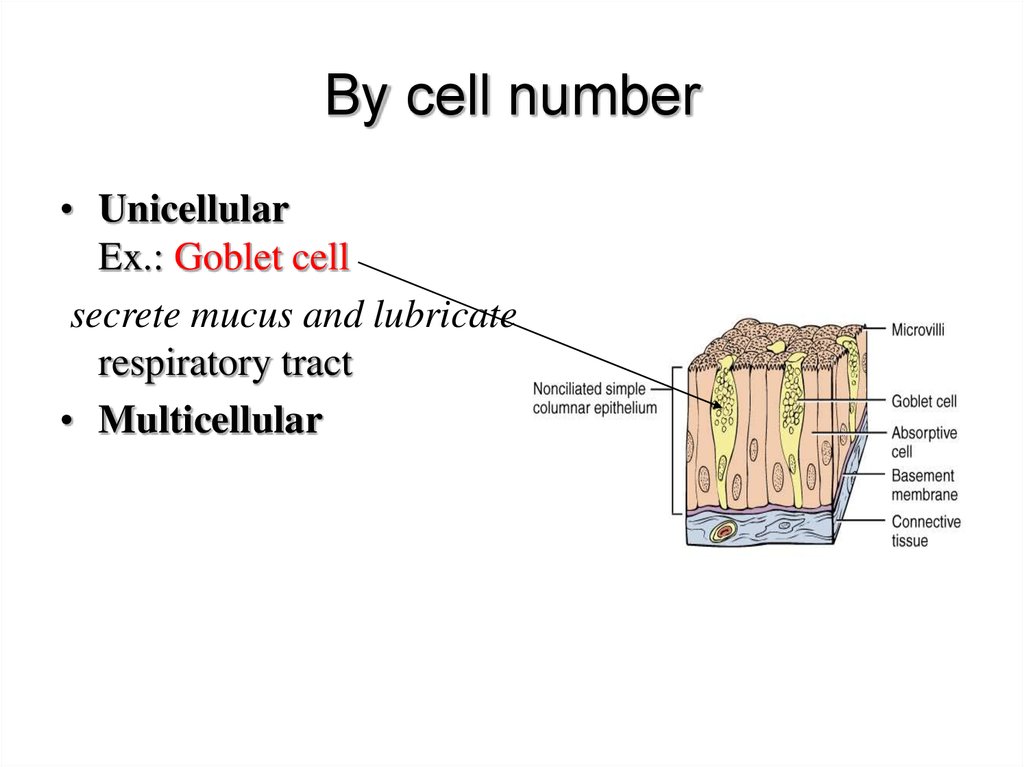
By cell number• Unicellular
Ex.: Goblet cell
secrete mucus and lubricate small and large intestine,
respiratory tract
• Multicellular
24. GLANDULAR EPITHELIA
Two type of secretionof Exocrine Glands
• Mucous - viscous, slimy
(mucus lines and lubricates cavities of
all inner hollow organs)
• Serous - watery
Ex.: exocrine pancreas (enzymes),
sweet gland,
Fluid in serous cavities, joints.
25. GLANDULAR EPITHELIA
26. There are two types of gland in the body: exocrine and endocrine.
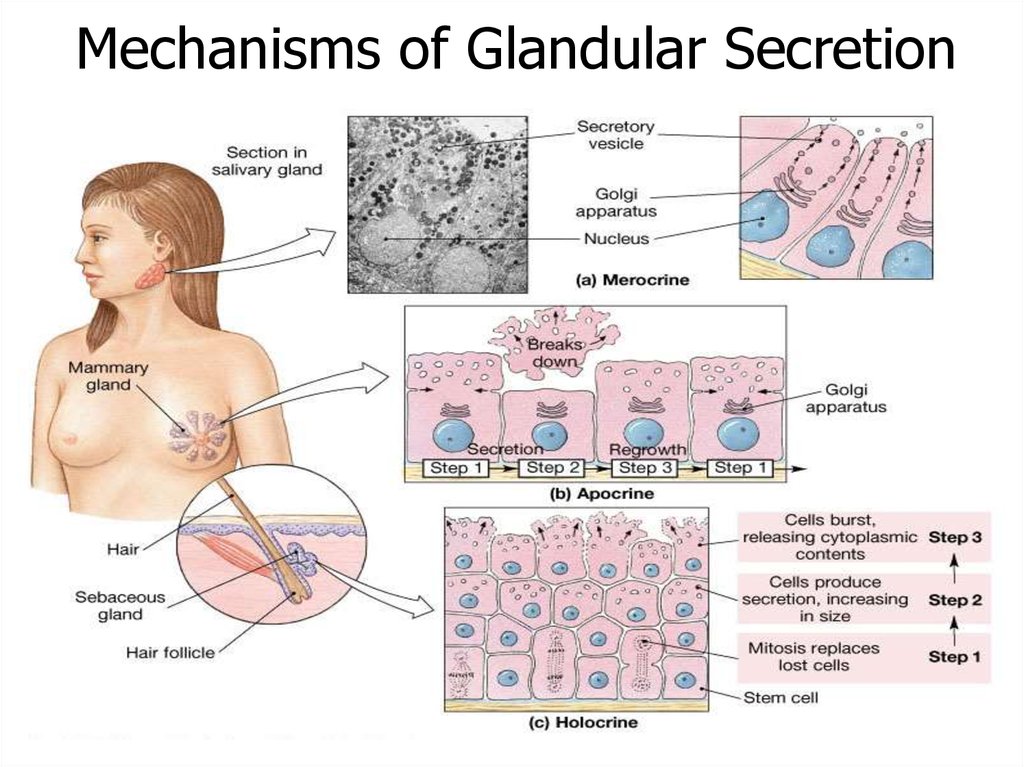
3 types of secretion mechanism:Merocrine (= eccrine)
Apocrine
Holocrine
27. By cell number
Merocrine (most common):Secretory granules fuse
with the apical
plasma membrane
and are secreted
into the lumen of
the gland.
28. 2 portions of gland: Parenchyma and Stroma
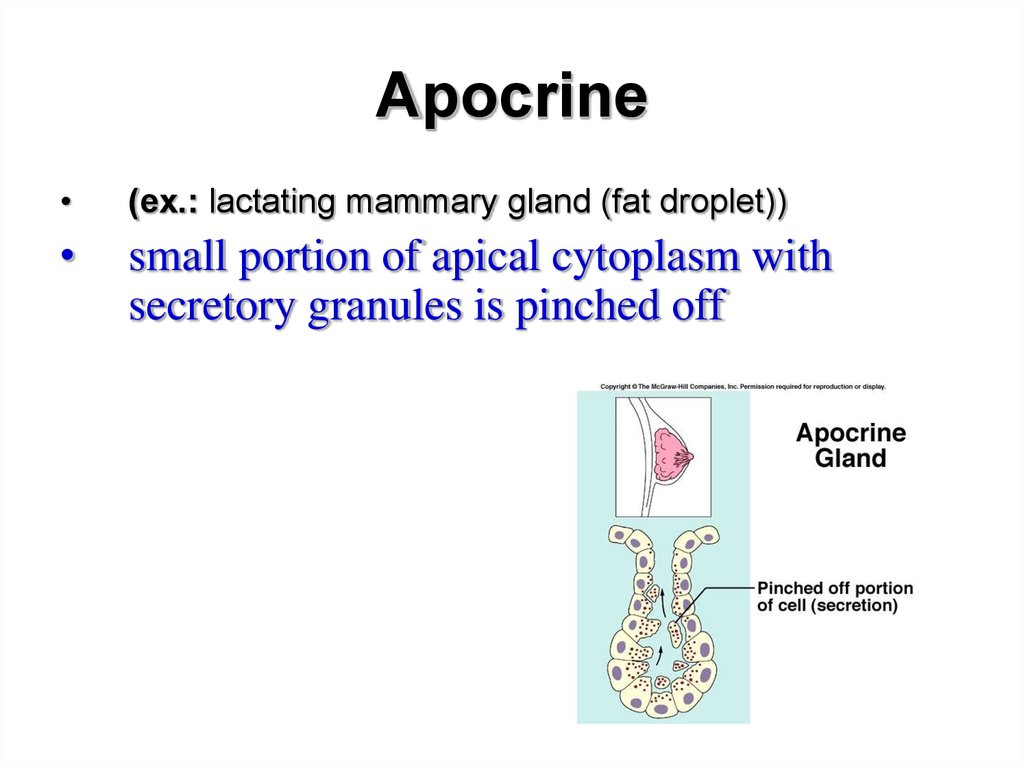
Apocrine(ex.: lactating mammary gland (fat droplet))
small portion of apical cytoplasm with
secretory granules is pinched off
29. Two type of secretion of Exocrine Glands
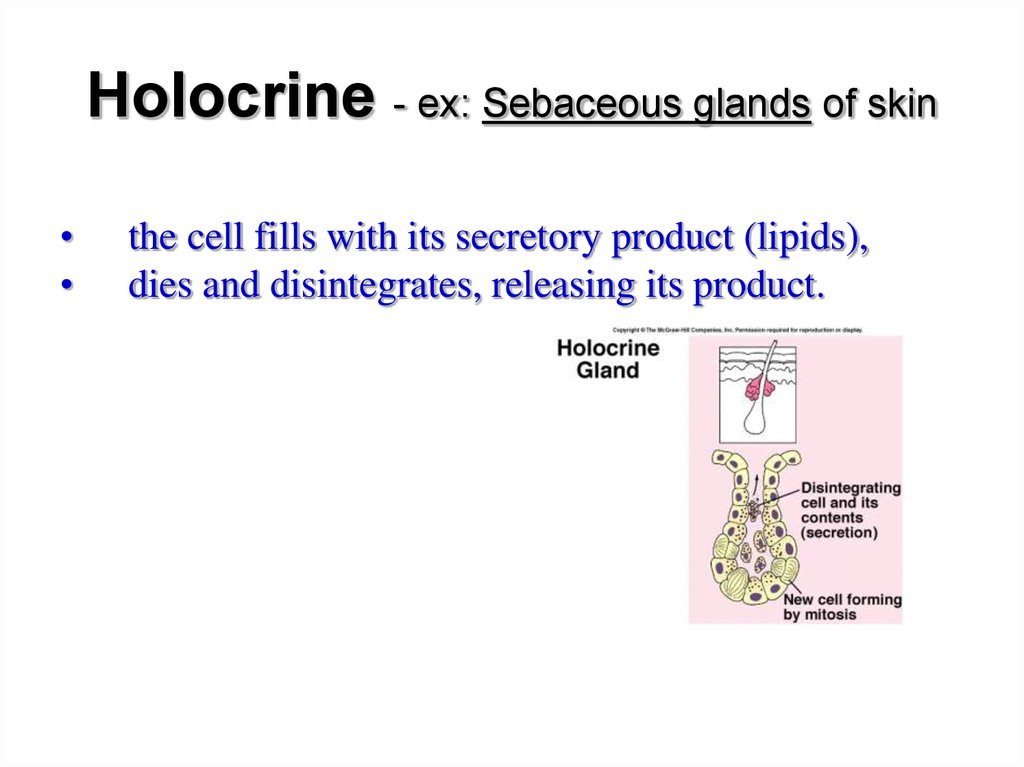
Holocrine - ex: Sebaceous glands of skinthe cell fills with its secretory product (lipids),
dies and disintegrates, releasing its product.
30.
31. Classification of Exocrine Glands by type of secretion
Mechanisms of Glandular Secretion32. 3 types of secretion mechanism:
A Structural Classification of Exocrine Glands33. Merocrine (most common):
A Structural Classification ofExocrine Glands
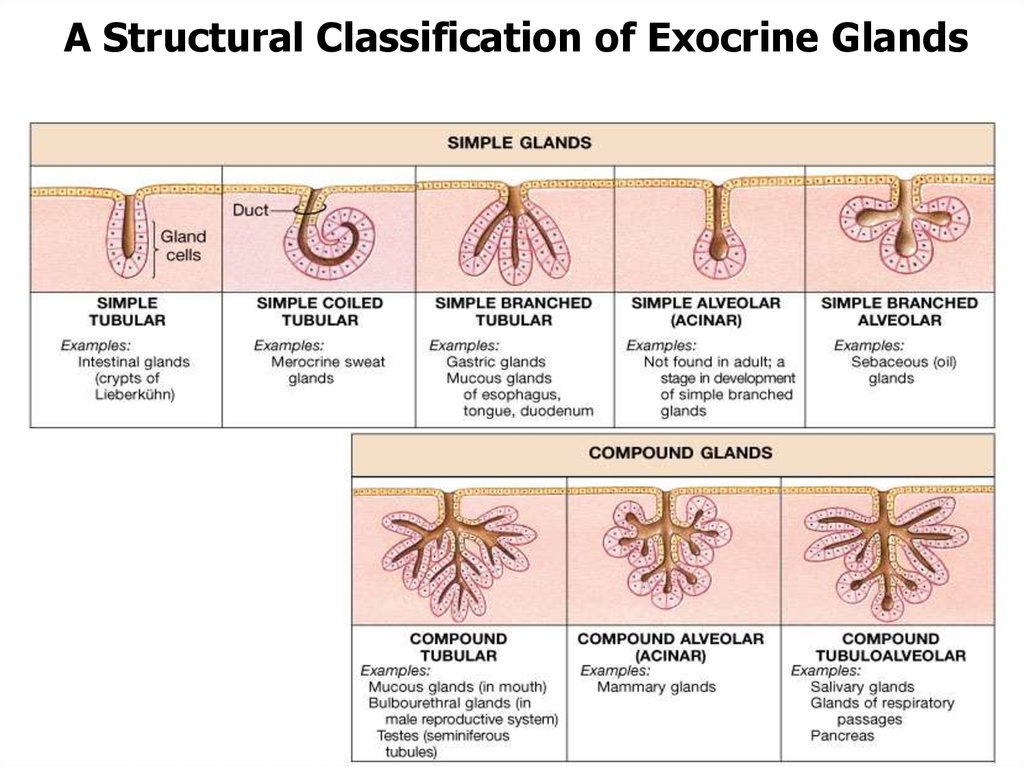
• By branching of duct exocrine glands may
be: simple (b-) or compound (b+)
• By shape of secretory ends – tubular or
alveolar (acinar)
• By branching of secretory ends exocrine
glands may be: branched (b+) or nonbranched (b-)





















 Биология
Биология








