Похожие презентации:
Astronomy from Space
1. Astronomy from Space
Samara UniversityMay 22, 2018
Dr Jordi L. Gutiérrez
Department of Physics
Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya
jordi.gutierrez@upc.edu
2. Skeleton
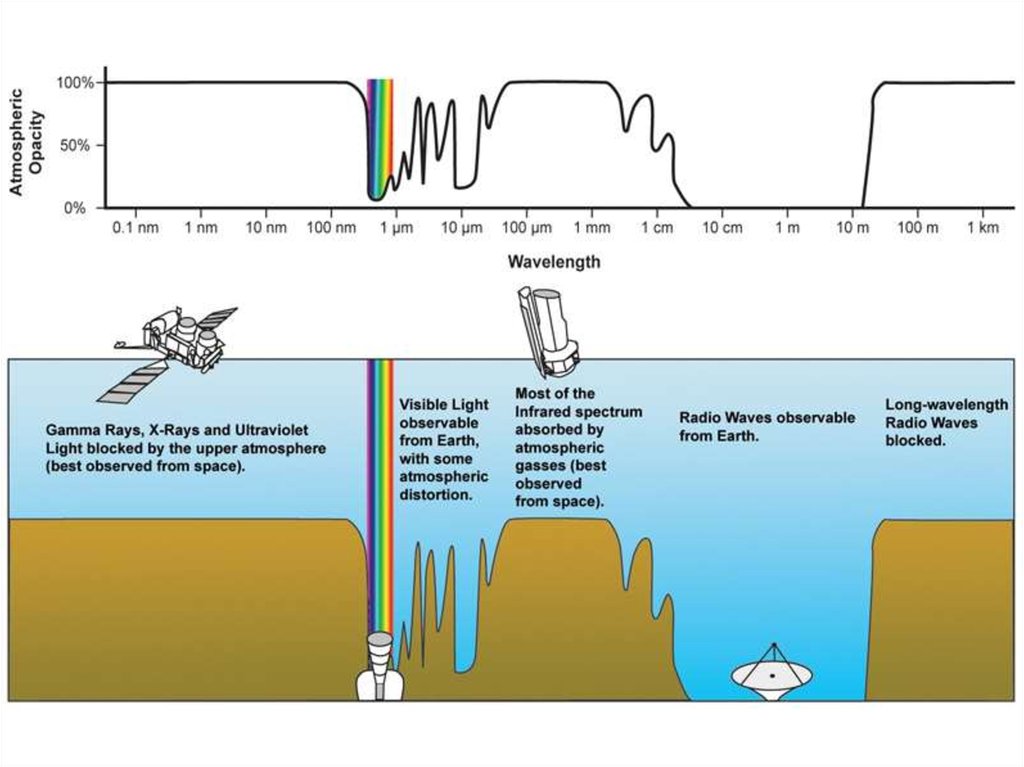
Why space astronomy?The atmosphere filters and distorts the incoming
light:
- Some parts of the EM spectrum are completely blocked
by the atmosphere
- Others are only partially so
- In the visible spectrum, the atmosphere severely
distorts de wave fronts (seeing)
- An analogue phenomenon happens at radio
wavelengths due to the ionosphere
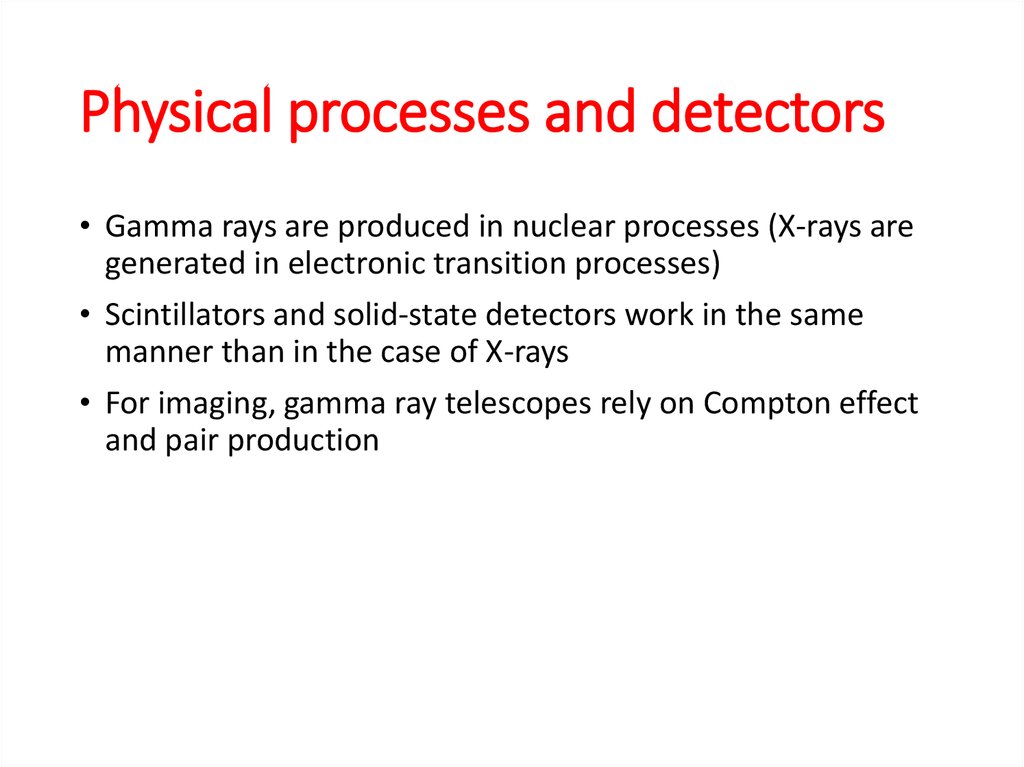
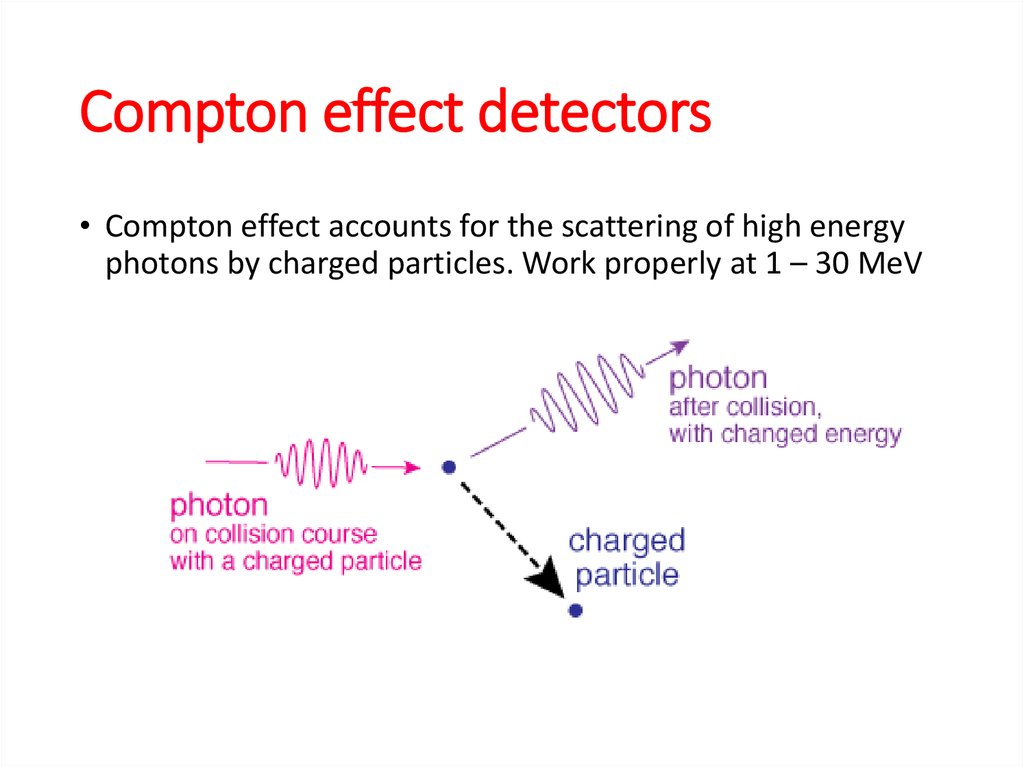
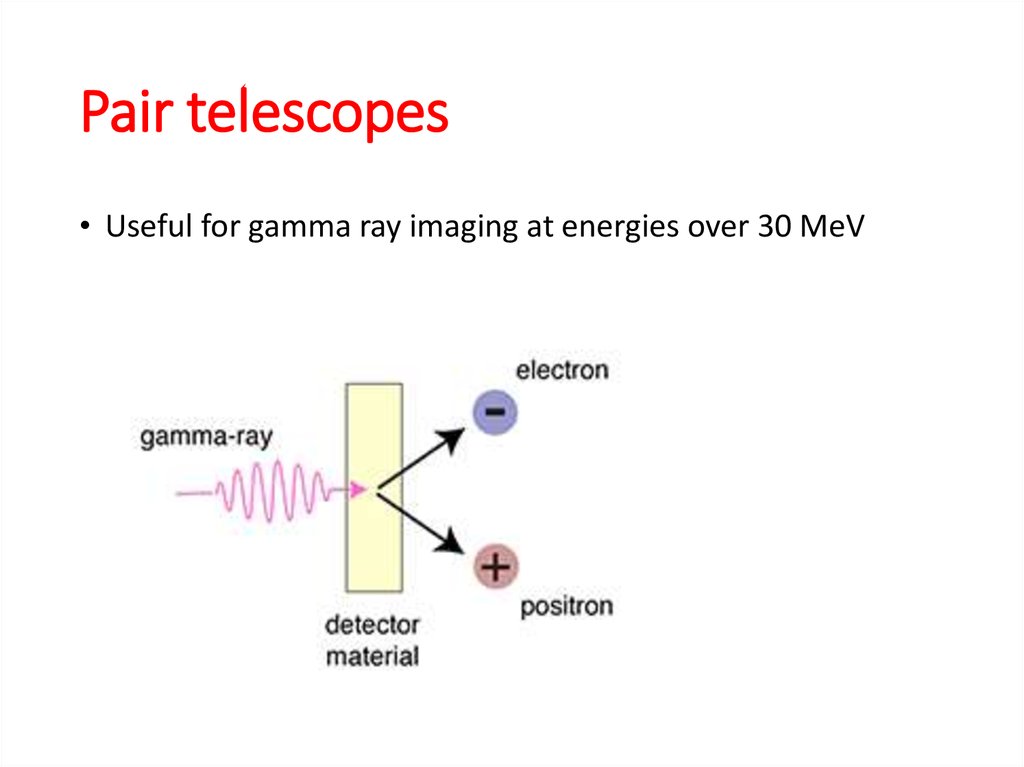
3. Why space astronomy?
4.
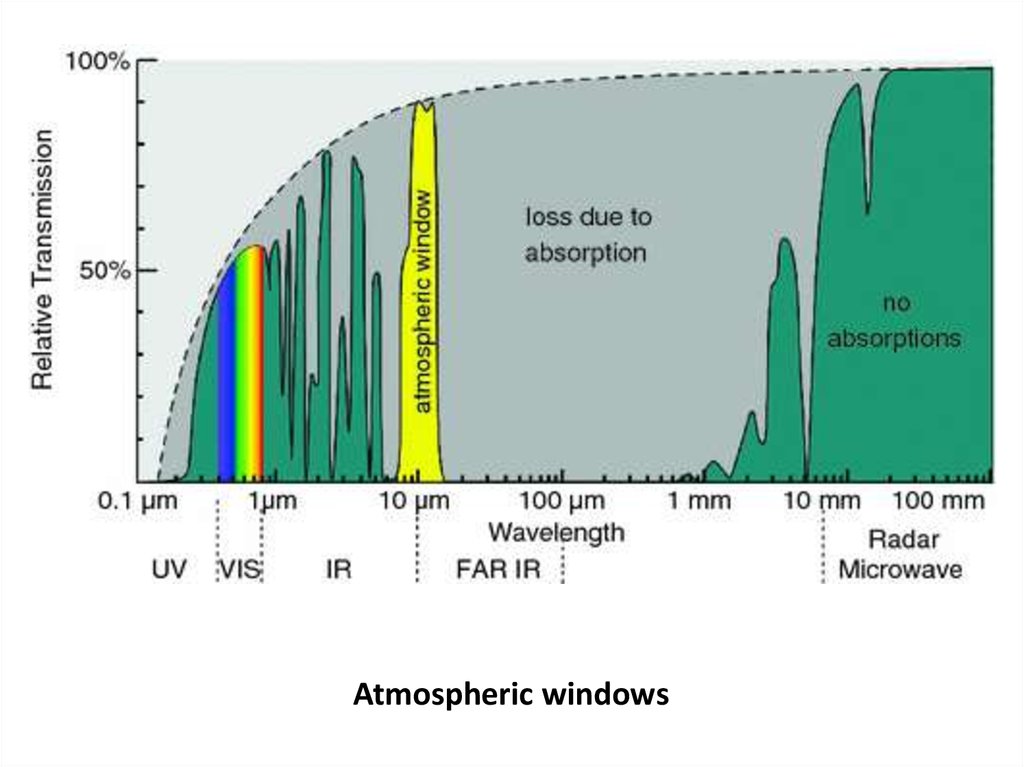
Atmospheric windows5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
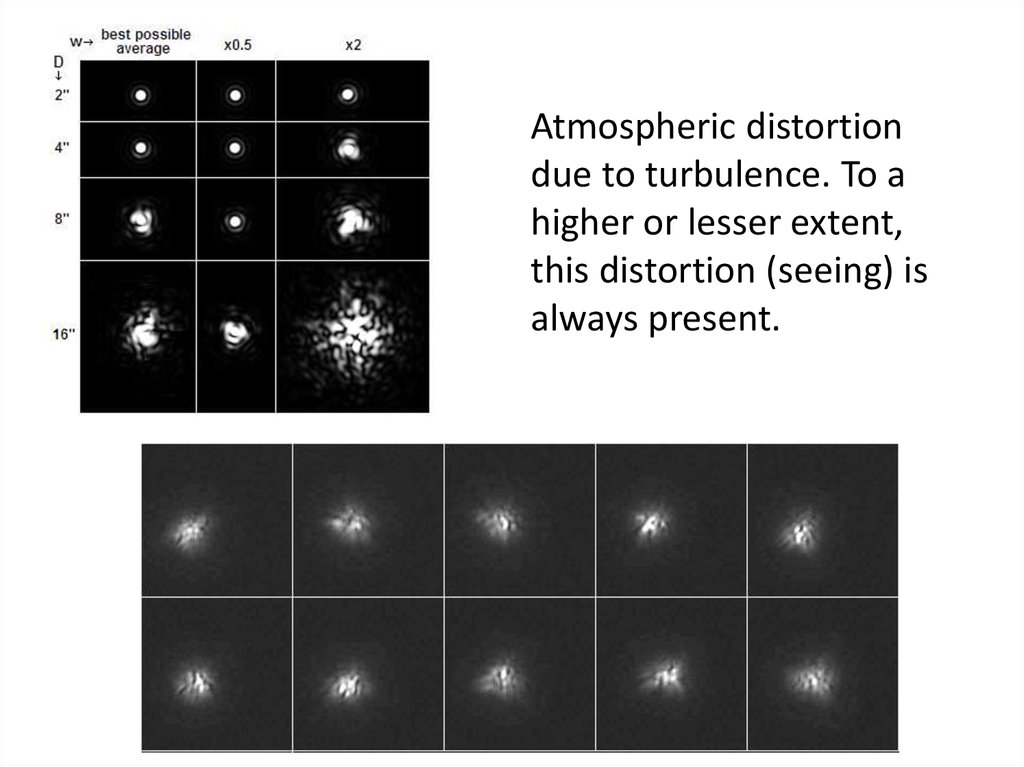
Visible12.
Atmospheric distortiondue to turbulence. To a
higher or lesser extent,
this distortion (seeing) is
always present.
13. Visible
14.
CCD cameras• Charge Coupled Devices are based on the photoelectric
effect. Resulting electrons are stored in capacitors
• These capacitors are disposed in 2D, and are able to hand
over their charge to the one in the neighbouring line
• CCD chips have efficiencies of ~70%, and sport a linear
behaviour
• They have a noise due to finite temperature (dark current)
• Ionizing particles generate similar signals as photons.
15.
16. CCD cameras
CCD cameras. Pre-processing• The pre-processing of the image is as follows:
clean image =
(raw image −bias) −(dark −bias)
flat −bias
• After this processing, images are prepared for scientific data
exploitation
17.
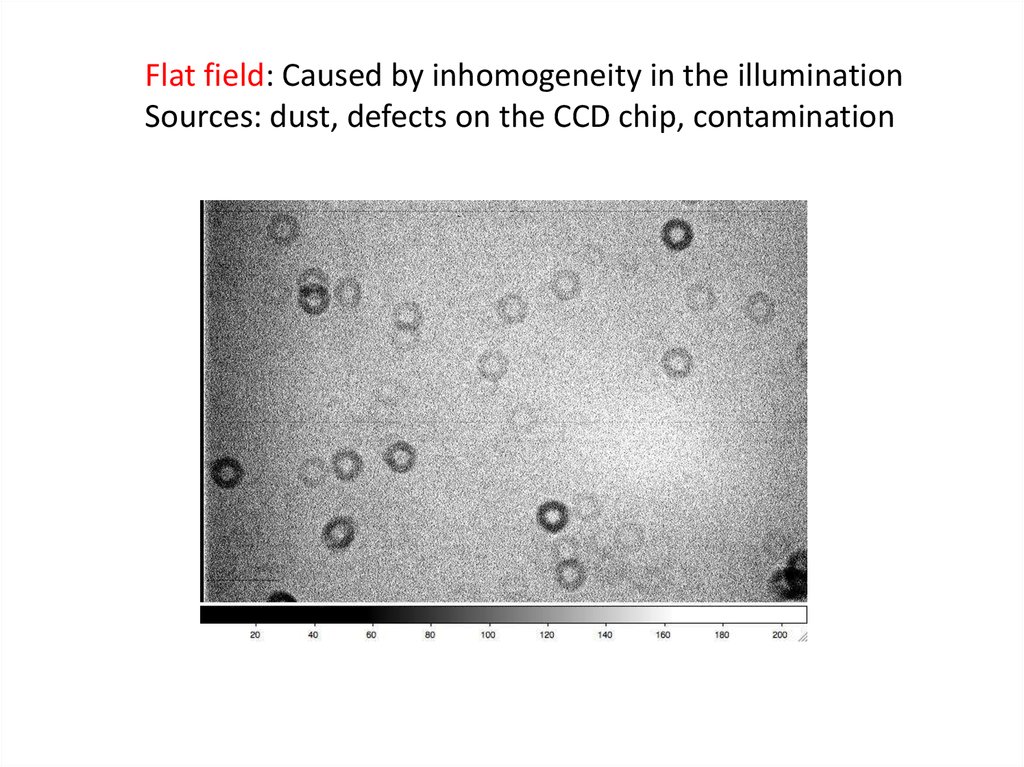
Flat field: Caused by inhomogeneity in the illuminationSources: dust, defects on the CCD chip, contamination
18. CCD cameras. Pre-processing
Dark field: Caused by thermal noise. The longer the exposure,the higher the electron counts. Extra problem: hot pixels
Solution: low temperature
19.
20.
21.
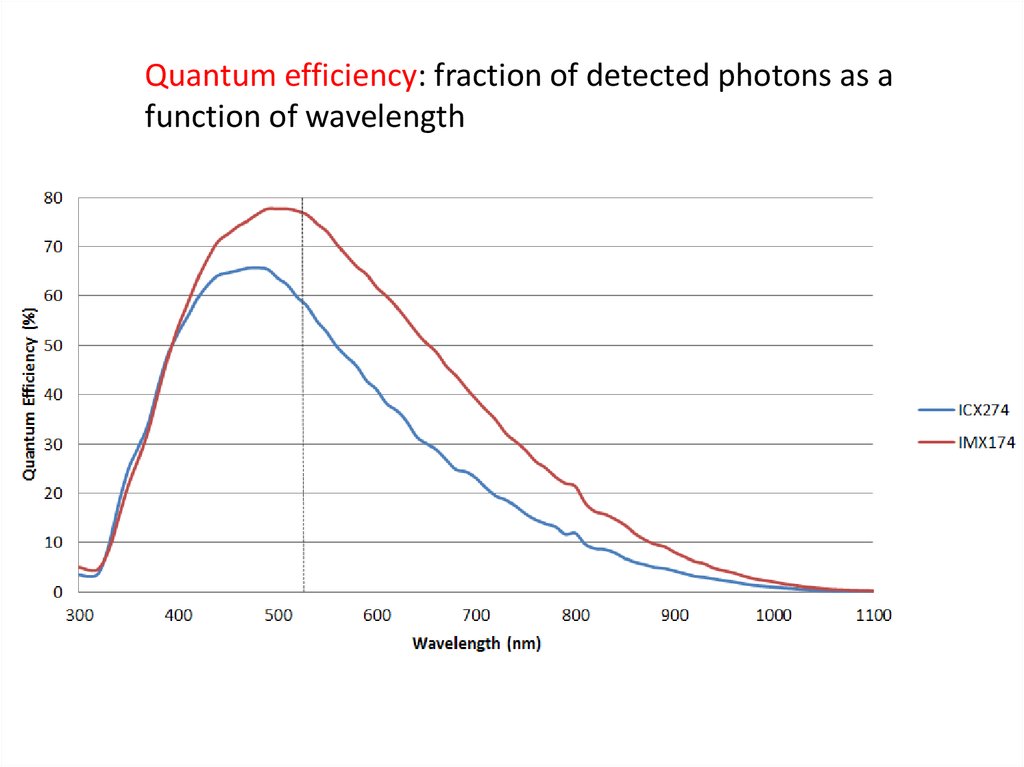
Quantum efficiency: fraction of detected photons as afunction of wavelength
22.
Filters• CCD cameras are monochromatic.
• To obtain colour information, there are sets of standard
filters.
23.
24. Filters
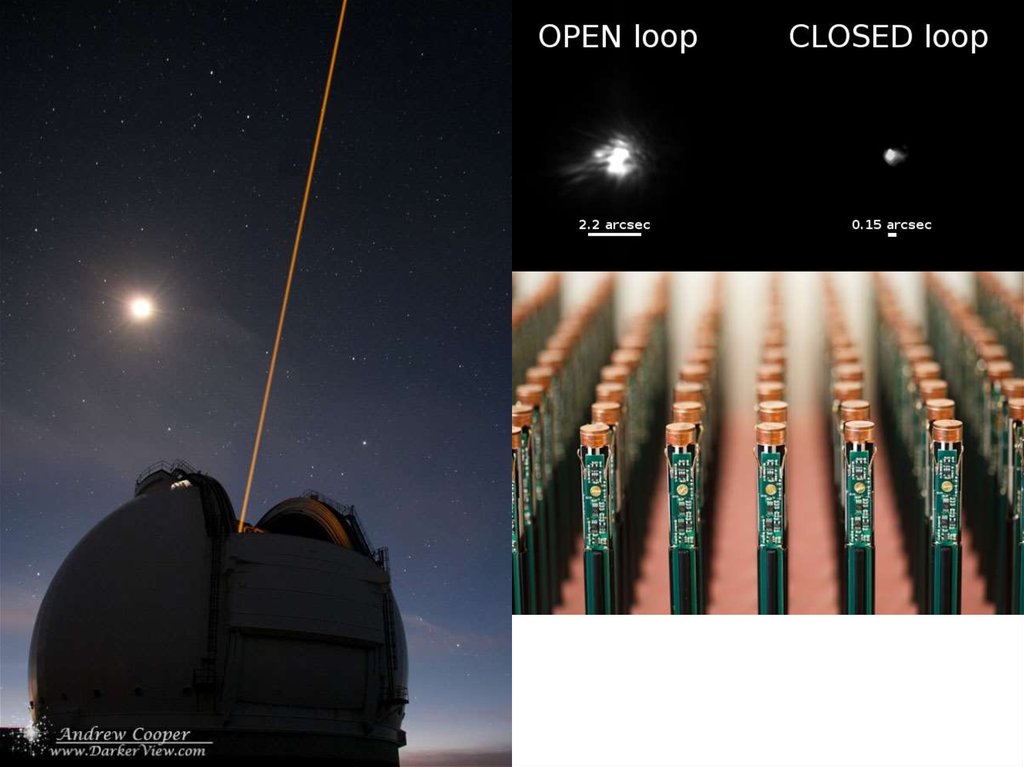
Adaptive optics• Adaptive optics are a family of methods to improve the
resolution of ground based telescopes
• The basis is to “deform” the main mirror of the telescope in
order to keep the images of stars as point-like as possible
• Sometimes, the observatory creates an “artificial star” by
means of a laser. This artificial star is used as a reference for
the adaptive optics system
25.
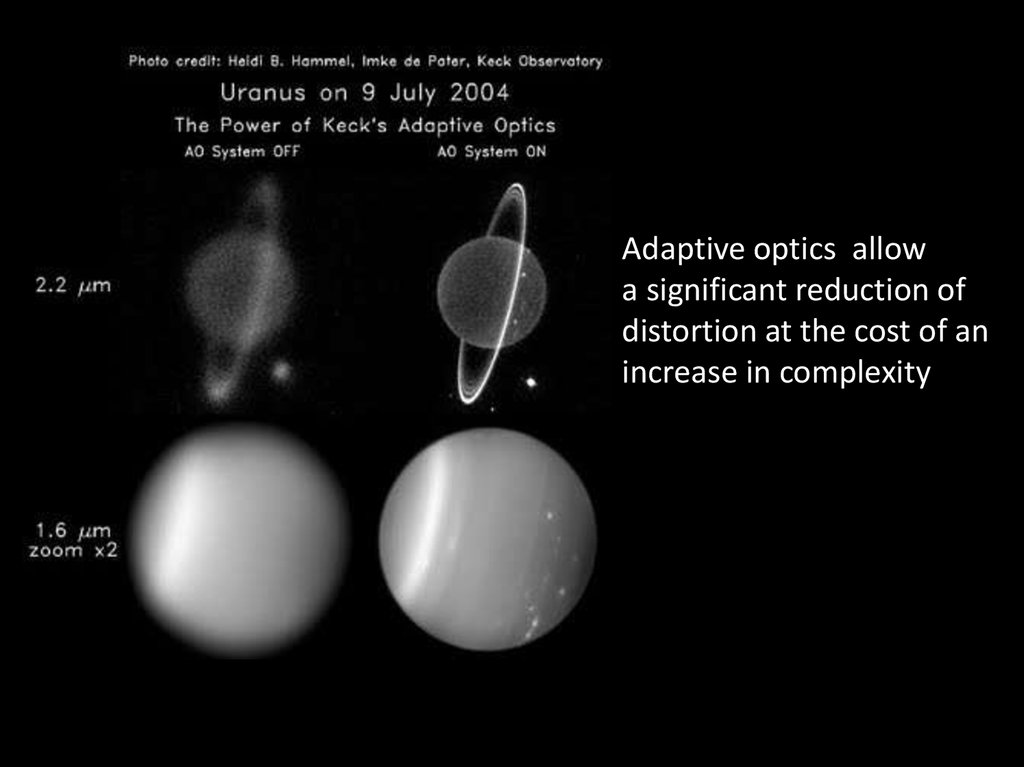
26. Adaptive optics
allowa significant reduction of
distortion at the cost of an
increase in complexity
27.
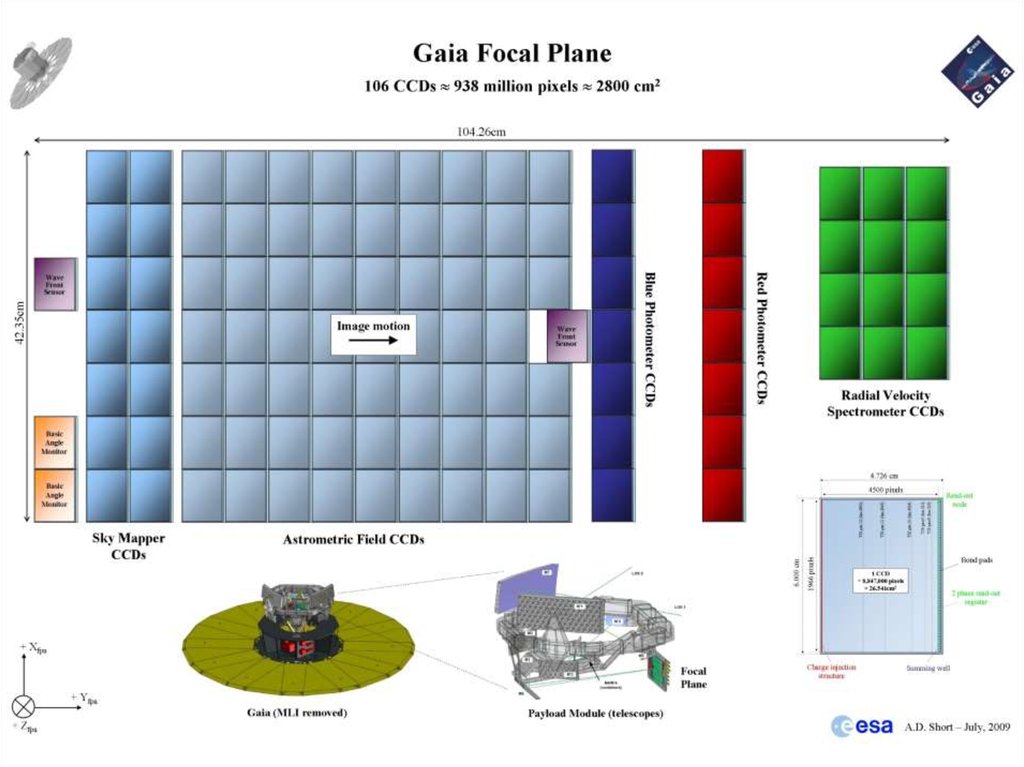
Gaia – ESA cornerstone mission L1• Gaia is gathering information (position, parallax, brightness,
and spectra) of 1.7 billion objects
• It will generate 53 TB of data
• The Payload Data Handling System pre-processes the
information gathered on-board to reduce the amount of
data relayed to the ground
• The mission will last 5 years (up to 2019)
• Launched with a Soyuz-Fregat from Kourou
28.
29. Gaia – ESA cornerstone mission L1
30.
31.
32.
Map of the sky generated with Gaia’s DR2 (includes 1.7 billion objects)Gaia DR2
33.
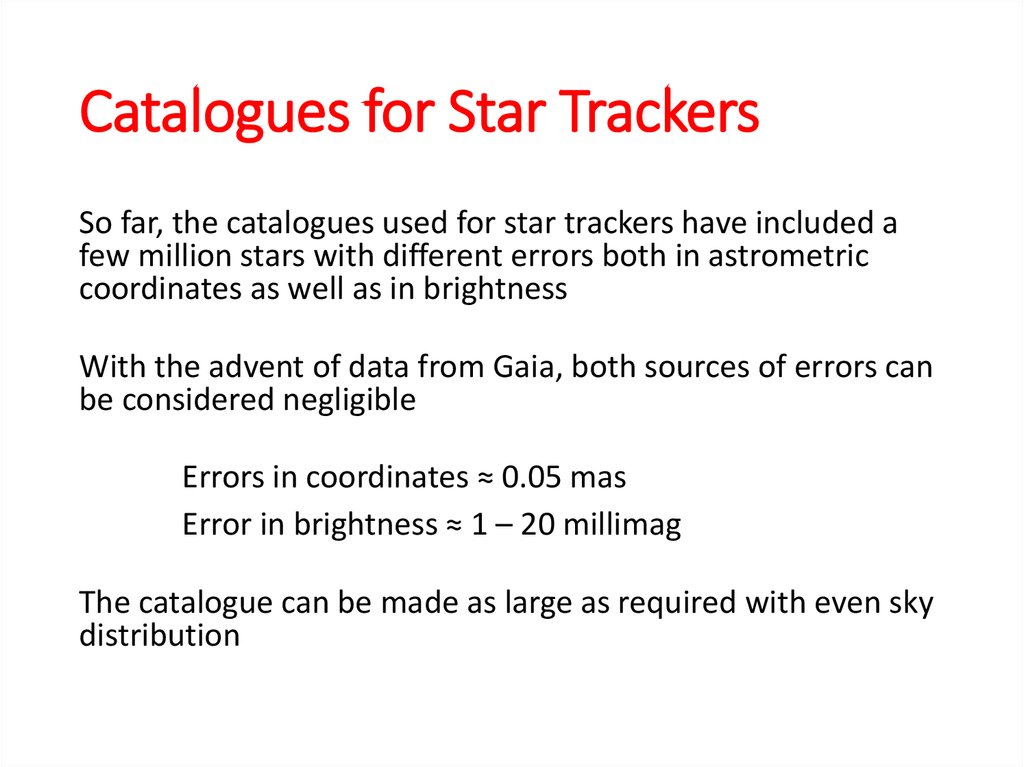
Catalogues for Star TrackersSo far, the catalogues used for star trackers have included a
few million stars with different errors both in astrometric
coordinates as well as in brightness
With the advent of data from Gaia, both sources of errors can
be considered negligible
Errors in coordinates ≈ 0.05 mas
Error in brightness ≈ 1 – 20 millimag
The catalogue can be made as large as required with even sky
distribution
34.
35. Catalogues for Star Trackers
36.
Often, there is a prior on the pointing that allows a very significantreduction on the amount of calculations
37.
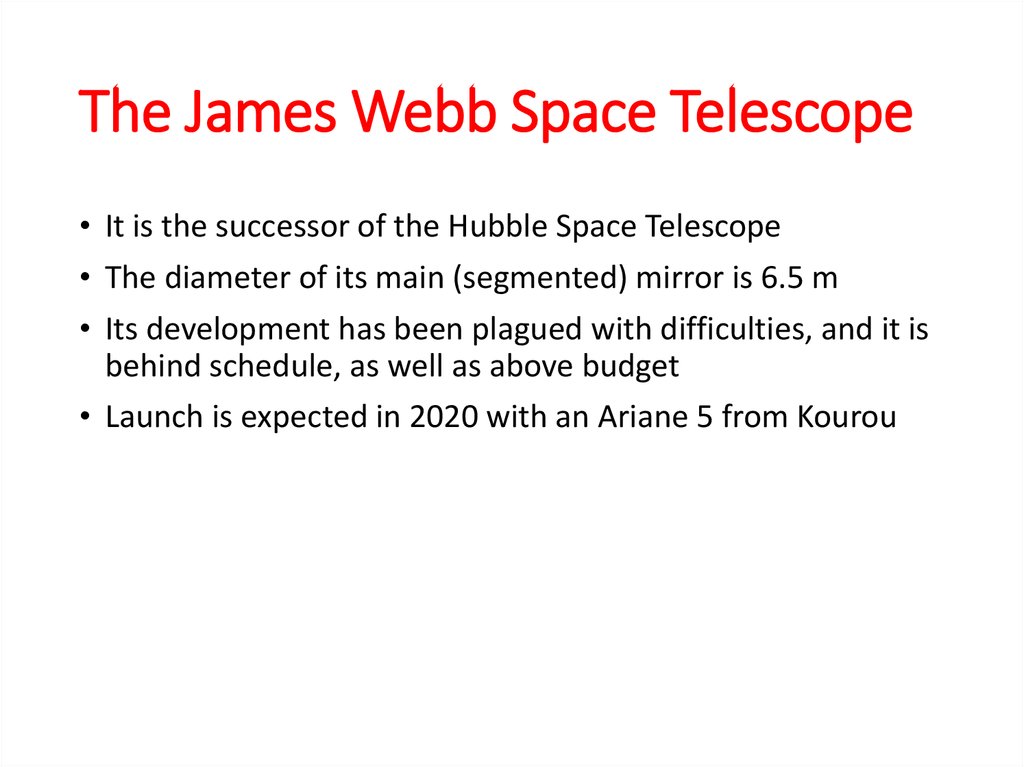
The James Webb Space Telescope• It is the successor of the Hubble Space Telescope
• The diameter of its main (segmented) mirror is 6.5 m
• Its development has been plagued with difficulties, and it is
behind schedule, as well as above budget
• Launch is expected in 2020 with an Ariane 5 from Kourou
38.
39. The James Webb Space Telescope
40.
41.
42.
Silly ideas also have an effect on Astronomy43.
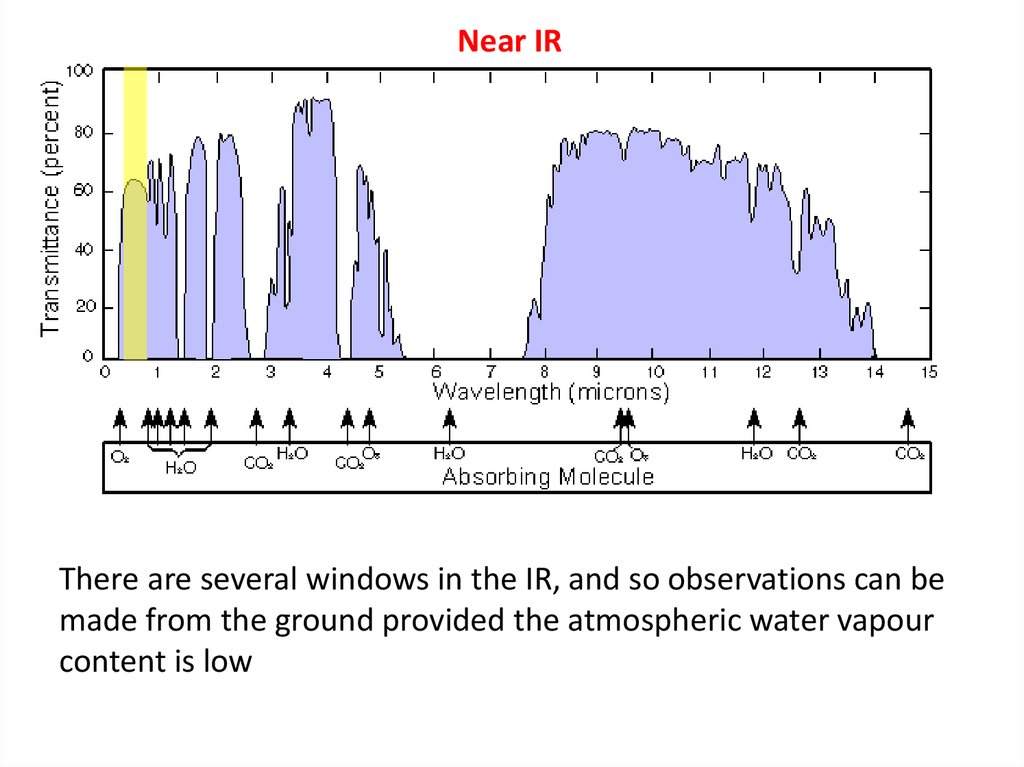
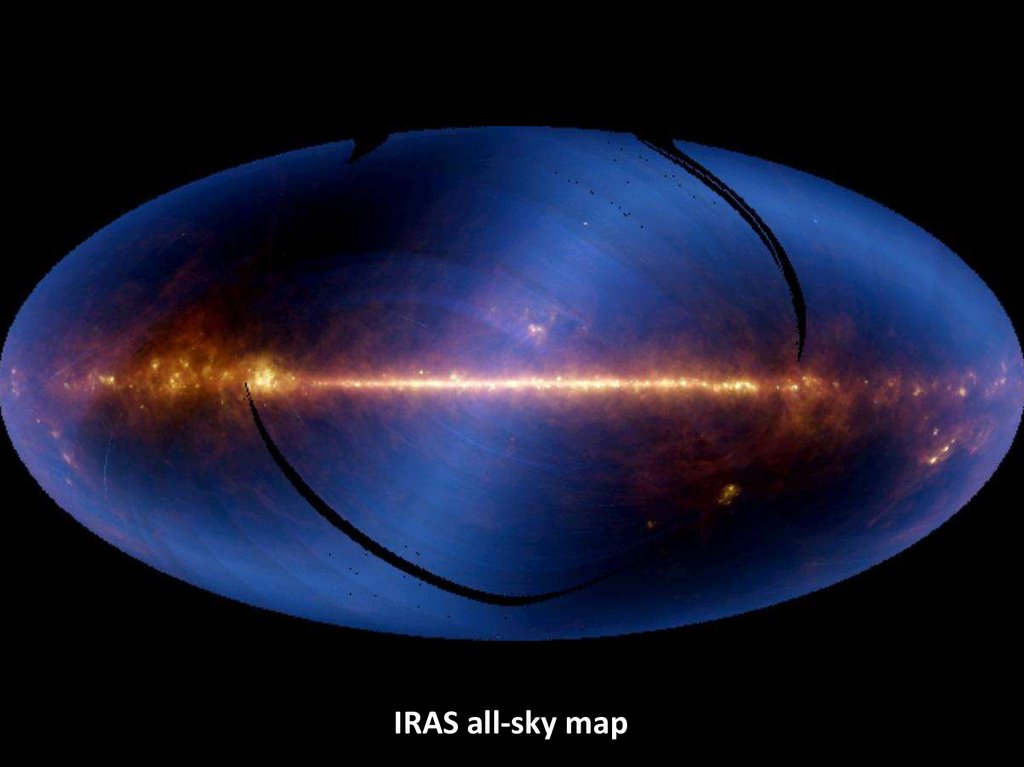
Infrared44.
Infrared telescopes• The IR Universe is dominated by low T processes, and then
our detectors and telescopes must be kept near a few K to
avoid thermal noise
• Wien’s displacement law teaches us that



























































 Астрономия
Астрономия Английский язык
Английский язык








