Похожие презентации:
Consumer behaviour
1. Consumer behaviour
2.
23.
34.
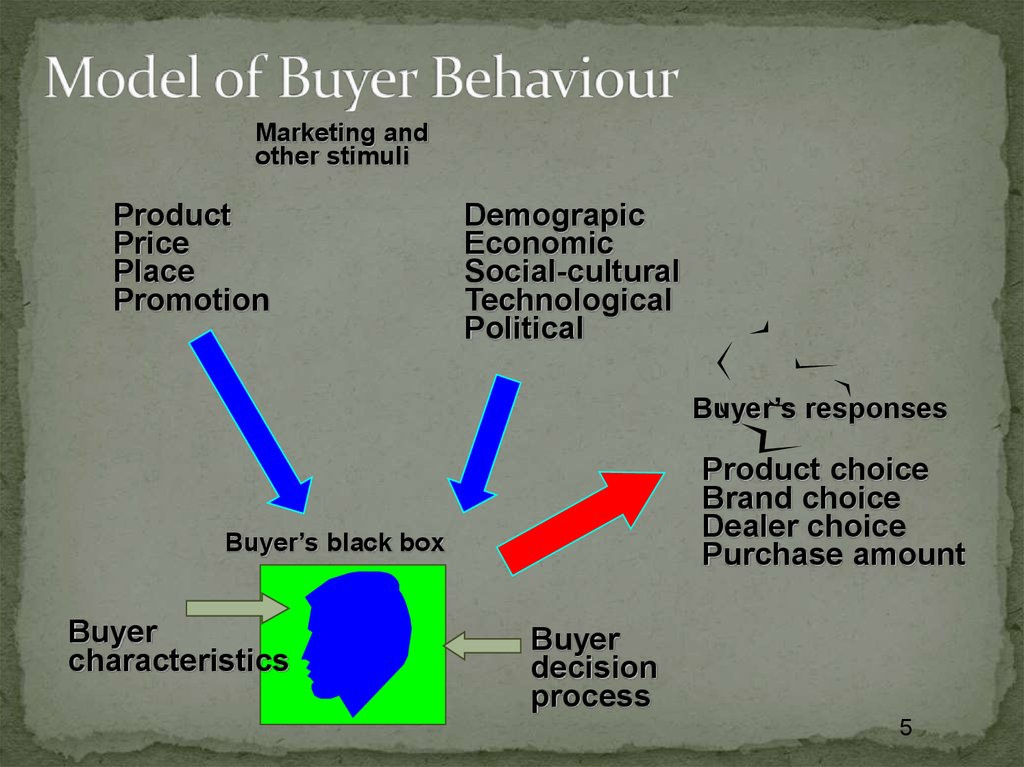
45. Model of Buyer Behaviour
Marketing andother stimuli
Product
Price
Place
Promotion
Demograpic
Economic
Social-cultural
Technological
Political
Buyer’s responses
Product choice
Brand choice
Dealer choice
Purchase amount
Buyer’s black box
Buyer
characteristics
Buyer
decision
process
5
6. What is consumer behaviour?
Consumer behaviour is the process that individualsor groups go through to select, purchase, use and
dispose of goods, services, ideas or experiences to
satisfy their needs and desires.
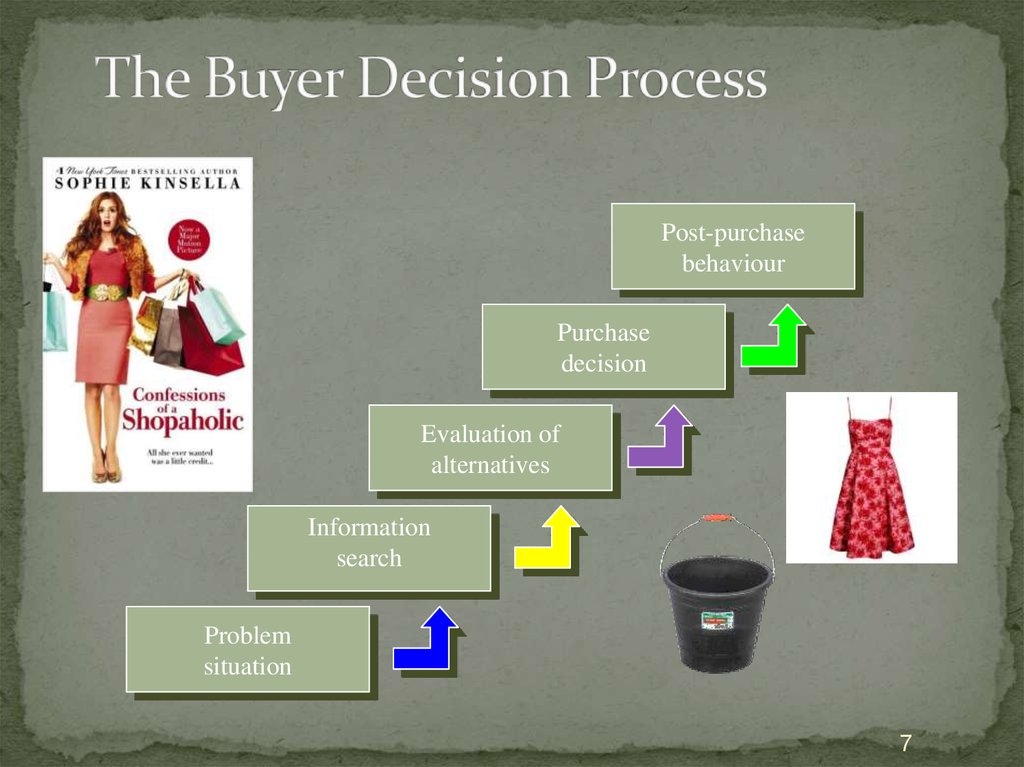
7. The Buyer Decision Process
Post-purchasebehaviour
Purchase
decision
Evaluation of
alternatives
Information
search
Problem
situation
7
8.
Problem recognition occurs whenever a consumerrecognises a difference between the current state
and the ideal or desired state.
9. Step 1: What’s my problem?
Personalexperience
Websites
Friends
Advertising
10. Step 2: What information is there about alternative solutions?
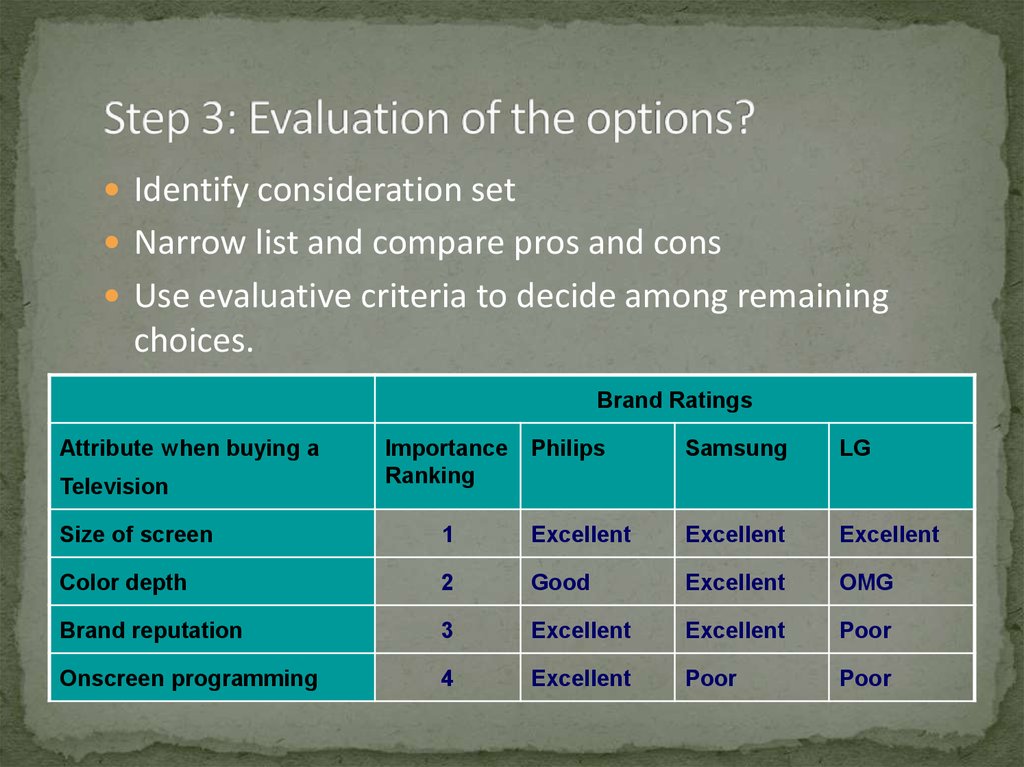
Identify consideration setNarrow list and compare pros and cons
Use evaluative criteria to decide among remaining
choices.
Brand Ratings
Attribute when buying a
Television
Importance
Ranking
Philips
Samsung
LG
Size of screen
1
Excellent
Excellent
Excellent
Color depth
2
Good
Excellent
OMG
Brand reputation
3
Excellent
Excellent
Poor
Onscreen programming
4
Excellent
Poor
Poor
11. Step 3: Evaluation of the options?
Nespresso attempts to persuade consumersthat making the decision to buy Nespresso
coffee is beyond any doubt
12
12. NESPRESSO, WHAT ELSE?
13. Step 4: Making the final choice
Consumer satisfaction/dissatisfaction is determinedby the overall feelings or attitude a person has about
a product after purchasing and using it.
14. Step 5: Using and evaluating the purchase
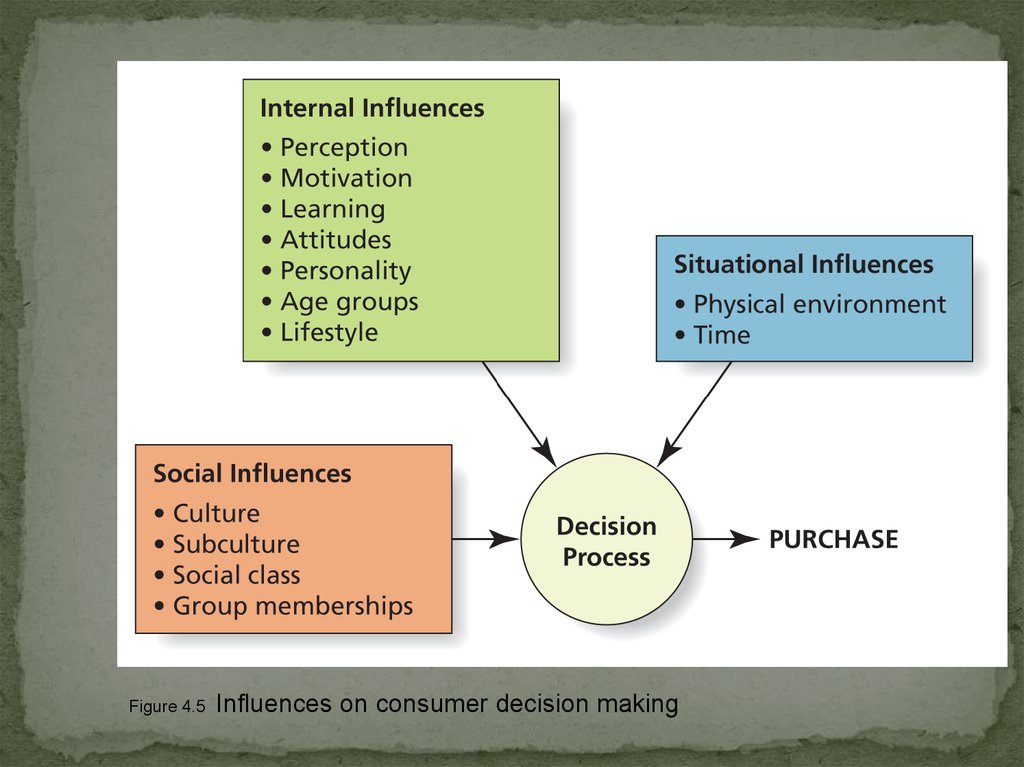
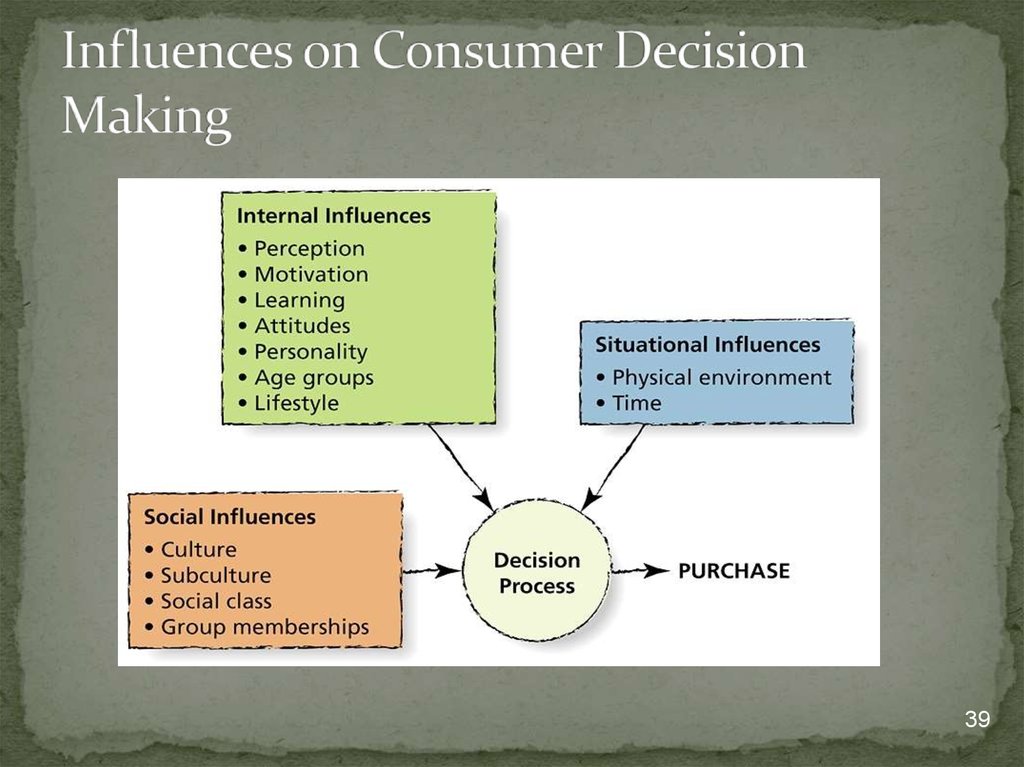
Figure 4.5Influences on consumer decision making
15.
MotivationPerception
Learning
Lifestyle
Attitudes
Age
Personality
16. Internal influences
1717. Perception
is the processby which people select,
organise and interpret
information.
18. What is perception?
19. Colours
Motivation is an internal state that drives us tosatisfy needs.
Once we activate a need, a state of tension exists
that drives the consumer to some goal that will
reduce this tension and eliminate the need.
20. Example perception
NEED FOR ACHIEVEMENTPlace a premium on products that
signify success (luxury brands,
technology products)
NEED FOR AFFILIATION
Want to be with other people
Focus on products that are used
in groups (alcoholic
beverages, sports bars)
NEED FOR POWER/CONTROL
NEED FOR UNIQUENESS
Control one’s environment
Assert one’s individual
identity
Focus on products that allow
them to have mastery
over surroundings
(muscle cars, loud boomboxes)
Enjoy products that focus on
their unique character
(perfumes, clothing)
21. What is motivation?
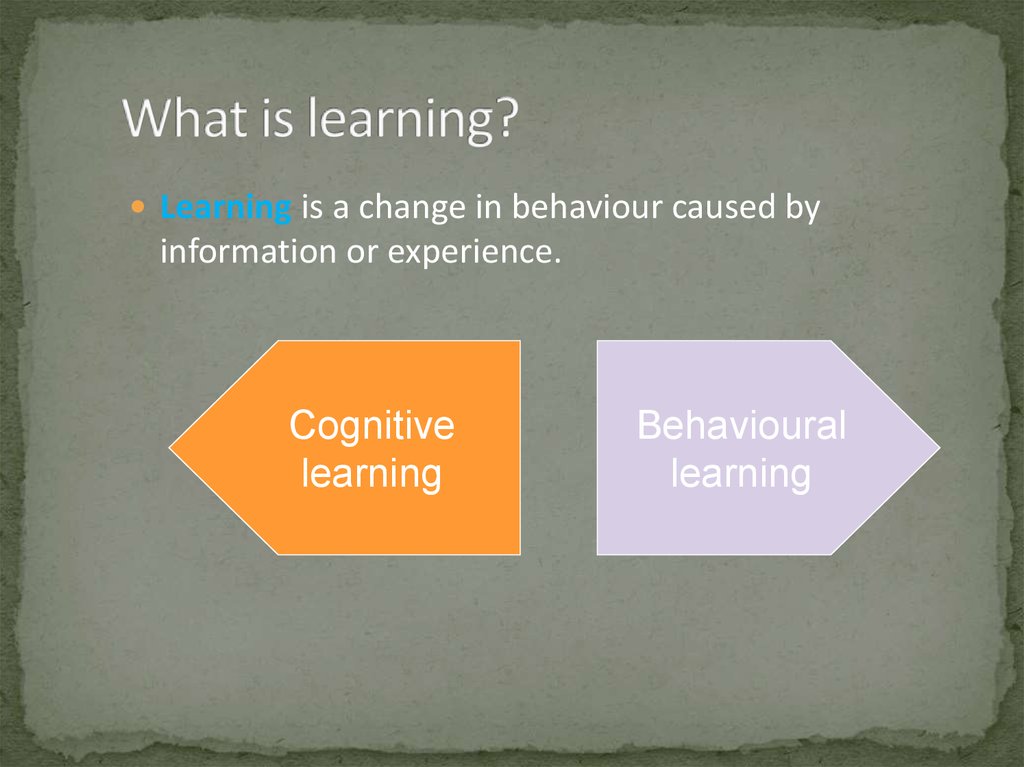
Learning is a change in behaviour caused byinformation or experience.
Cognitive
learning
Behavioural
learning
22. Motivation / Specific Needs
Observational learning occurs when people watchthe actions of others and note what happens to
them as a result.
23. What is learning?
Descriptive thought that a person holds aboutsomething
26
24. Consumer behavioural learning
Prentice-Hall, cr 2009Figure 7.4
7-27
25. What is observational learning?
Personality: a person’sunique psychological
makeup and how it
consistently influences the
way a person responds to
his/her environment
26. Beliefs
ChildrenTeens
Young adults
Middle-aged
Elderly
27. Attitudes
3028. Personality
A family life cycle expresses the stages throughwhich family members pass as they grow older.
29. Age groups
3230. Generations
3331. What is a family life cycle?
Culture is the values,beliefs, customs and
tastes produced and
valued by a group of
people.
A subculture is a group
with a distinctive set of
beliefs or characteristics.
32. Lifestyle
A reference group is a set ofpeople a consumer wants to
please or imitate.
Conformity is at work when
people change as a reaction to
real or imagined group
pressure.
33. Social influences
Society’s expectations regarding appropriate attitudes,behaviors, and appearance for men and women
37
34. Social influences
Physical environmentIn-store displays
Place-based media
Time
Season
Time available
Perceptions of time
poverty
35. Cultures and subcultures
3936. Group memberships
To listen consumers to understand their needs andwants
To make the ‘perfect’ product that will be successful
40





























 Психология
Психология Социология
Социология








