Похожие презентации:
Culture of Ancient East
1.
Lecture 2Culture of Ancient East
1. Peculiarities of the Ancient Eastern
Culture
2. The specificity of Ancient Indian culture .
3. The specificity of Ancient China culture.
2.
3.
Peculiarities of the Ancient Eastern way of life andphilosophy
Intelligent interruption
1. Traditionalism & conservatism;
2. Cyclic attitude to the time and history
3. Practical orientation
4. Closely connected with religion;
5. Cognition = the content and the way of spiritual
development;
6. Orientation to the authority of the Teacher,
Guru;
4.
1. Traditionalism & conservatism;2. Cyclic attitude to the time and history;
3. Practical orientation;
5.
4. Closely connected with religion;5. Cognition = the content and the way of spiritual
development;
6. Orientation to the authority of the Teacher,
Guru;
6.
Ancient India- The oldest – 4000 years B.C. (Mohenjo-Daro &
Harappa)
very developed cities – 2-storied houses, strictly
planned streets, ceramic tubes under ground, the most
developed canalization system
pictography (400 special pictures) + syllabic signs
7.
2. The specificity of Ancient Indian culture.Periods of Ancient Indian culture:
- Who were the founder of the Indian culture?
- Dravidians
- Arians – nomads, cattle breeders – no cities,
villages+fortified points
І period - The Vedic period (II – I thousand years B.C.).
Sruti – (“smth. that was heard”)
Vishnu)
Rigveda – hymns;
Yajurveda – texts for priests;
Samaveda – song to the god Sama;
Atharvaveda – spells.
other texts – Upanishad & Brahman.
Smriti – (“smth. that was remembered”)
Ramayana & Mahabharata (Krishna and Rama – avatar of
8.
Indian religion are:polytheistic – 33 -333-3339
henotheistic
animism - the soul is immortal.
Samsara -the birth - death – birth
Karma causal dependence
Most popular gods are
- Indra - Varuna –
- Agni
- Kama
9.
Concepts that are the basement for Indian culture1) Rita
Karma
- sum of good and bad actions that can
influence the fate;
2) Casts –
- closed social group;
legend about Purusha
10.
3) Ahimsa – “not to injure”– do no harm, non violence;
11.
4) Samsara- endless circle of life and death;
5) Nirvana
- highest spiritual state that can possibly be
achieved;
12.
II period – Brahmanic period (10 – 6 century B.C.)- transformation of the Karma concept:
law of retribution;
- Karma can be changed by requests & prayers;
- Brahmanism as a stage of development of
Hinduism and major religion.
13.
Features of Brahmanism1. Recognition of all the Vedic gods;
2. The main divine triad - the Trimurti:
Brahma - Supreme - God-the Creator;
Vishnu - God the preserver;
Shiva - God-destroyer
.
14.
Philosophical schools = DARSHANAAstika
Confirming
Nastika
Denying
15.
- The Orthodox schools. They recognize theauthority of the Veda and to some degree based
on their texts (Sankhya, Yoga, Mimansa, Vedanta,
Nyaya) - III century BC. - II century BC.
- The Unorthodox schools, they deny the preceding
tradition (Buddhism, Jainism) - about the VI
century BC.
16.
17.
18.
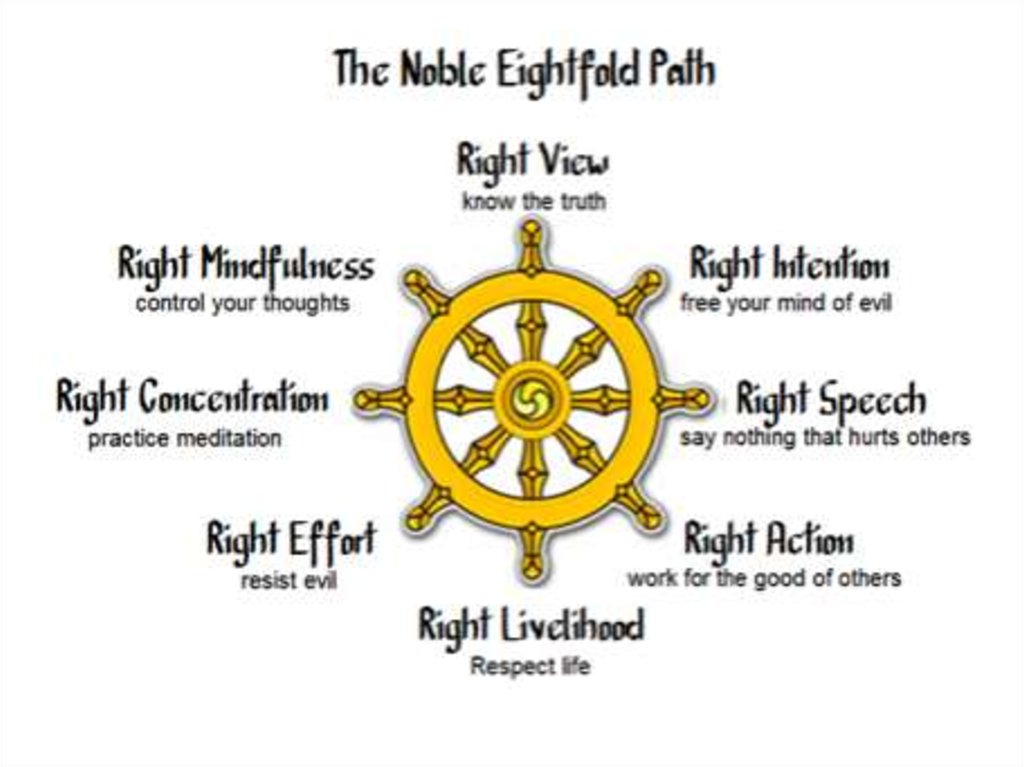
The origin and development of Buddhism.- The most ancient in the world - 6-5 centuries BC.
- 400 million + 1 million monks;
- Northern India
- the doctrine of the Dharma – Sanskrit "the nature of
all things; the way it is“
- The teachings of Buddha
precepts (teachings)
84 thousand
19.
- The most non-religious religionphilosophy
there’s NO
- God-creator;
- God-judge;
- Teaching about mind – that perceives and
realizes;
Buddhism = mind exercises + everyday tips
20.
Goals are- liberation from suffering,
- inner peace,
- the disclosure of the quality of the
mind for the benefit of all beings.
21.
The History Of Buddhism:- Shakyamuni
5 century BC city of Kapilavastu the only son - 3 sages
ruler
spiritual leader
- 29 years behind Palace walls
4 signs
the sick man
the old man
the dead man
the monk
22.
- The first sermon - Deer Grove - the first disciples - 5ascetics
- The first turning of the wheel of Dharma
Hinayana (Small vehicle);
- The second turning of the wheel of Dharma
Mahayana (the Great vehicle);
- The third turning the wheel of Dharma
Vajrayana (Diamond vehicle);
- Died at 80
"Don't trust anyone's word,
even Buddha’s, check all the
teachings with the help of experience.
Be your own guiding light!"
23. It is the world's largest book " - pagoda Khutodo To read this "book", a man needs 450 days. There are 729 pages. They are not
It is the world's largest book " - pagoda KhutodoTo read this "book", a man needs 450 days.
There are 729 pages.
They are not made from paper, but from white marble.
24. Myanmar (Burma)
25.
26.
27.
28.
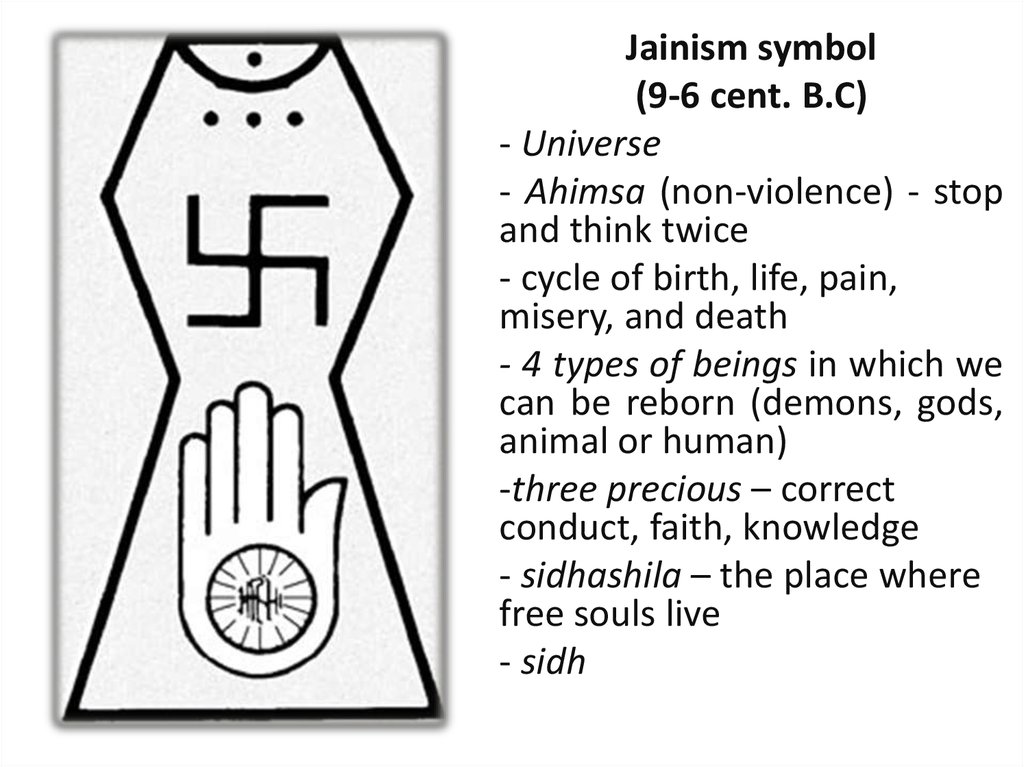
Jainism symbol(9-6 cent. B.C)
- Universe
- Ahimsa (non-violence) - stop
and think twice
- cycle of birth, life, pain,
misery, and death
- 4 types of beings in which we
can be reborn (demons, gods,
animal or human)
-three precious – correct
conduct, faith, knowledge
- sidhashila – the place where
free souls live
- sidh
29.
30.
3. The specificity of philosophical knowledge ofAncient China.
The first Ancient Chinese ideas - VII cent. ВС
«Book of Changes»,
«Book of Songs»,
«the Book of History»
Features:
- the geographical;
- moral and political orientation.
- the reference to «the wise men»,
- the most influential schools - Confucianism and
Taoism.
31.
Confucianism - concentration on the ethical andphilosophical issues.
The founder is Confucius, the VI - V centuries BC
The main goal is education of the
person in the course of respect
(esteem) to the society, its laws
and traditions, i.e. the upbringing
of the individual for the society.
Central idea – the concept of the Noble Man (цзюнь
цзы ).
Social relations = Family relations
32.
Watch the episode and answer the questions:1. Specify years od birth/death of Confucius.
2. How he formulated the golden rule of ethics?
3. What concepts were put as a basis for
Confucianism?
4. Why is Confucianism is treated more as a
philosophy/social doctrine than a religion?
5. To whom his teaching was addressed?
33.
Taoism. The founder Lao Tzu (the «Old wise man» or«Old child») VI - V centuries BC.
Basic notion:
Tao understood as
≪way≫ i.e. the
natural course of things
or the impersonal
Universal law, ruling
over nature and society.
34.
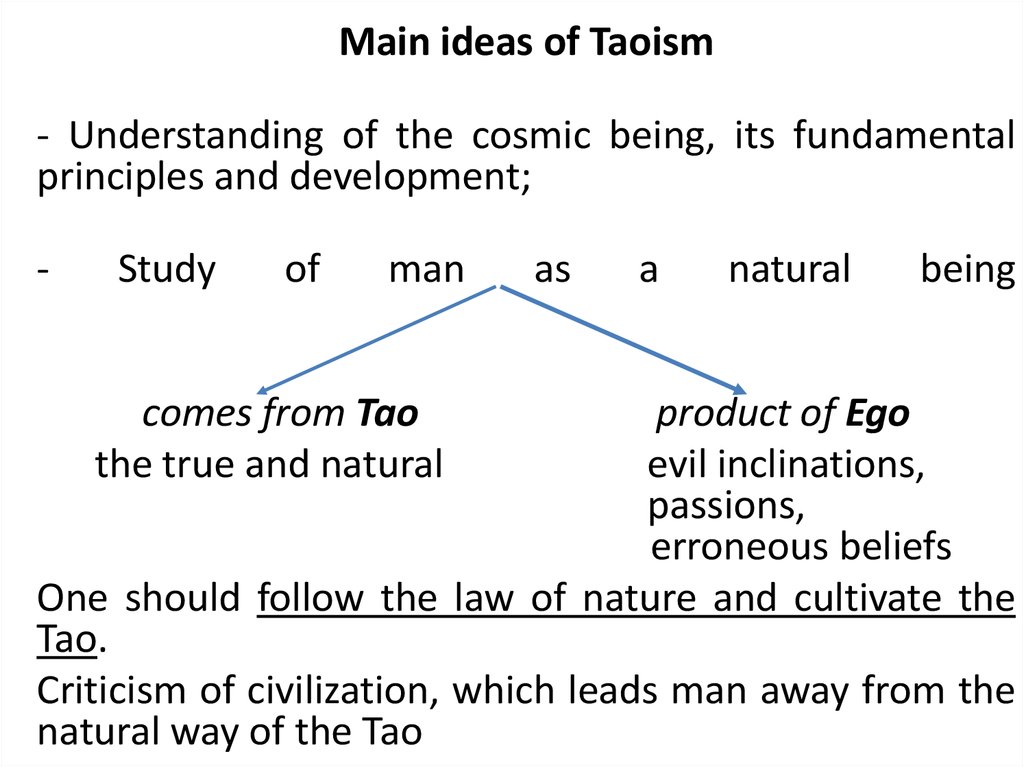
Main ideas of Taoism- Understanding of the cosmic being, its fundamental
principles and development;
-
Study
of
man
comes from Tao
the true and natural
as
a
natural
being
product of Ego
evil inclinations,
passions,
erroneous beliefs
One should follow the law of nature and cultivate the
Tao.
Criticism of civilization, which leads man away from the
natural way of the Tao
35.
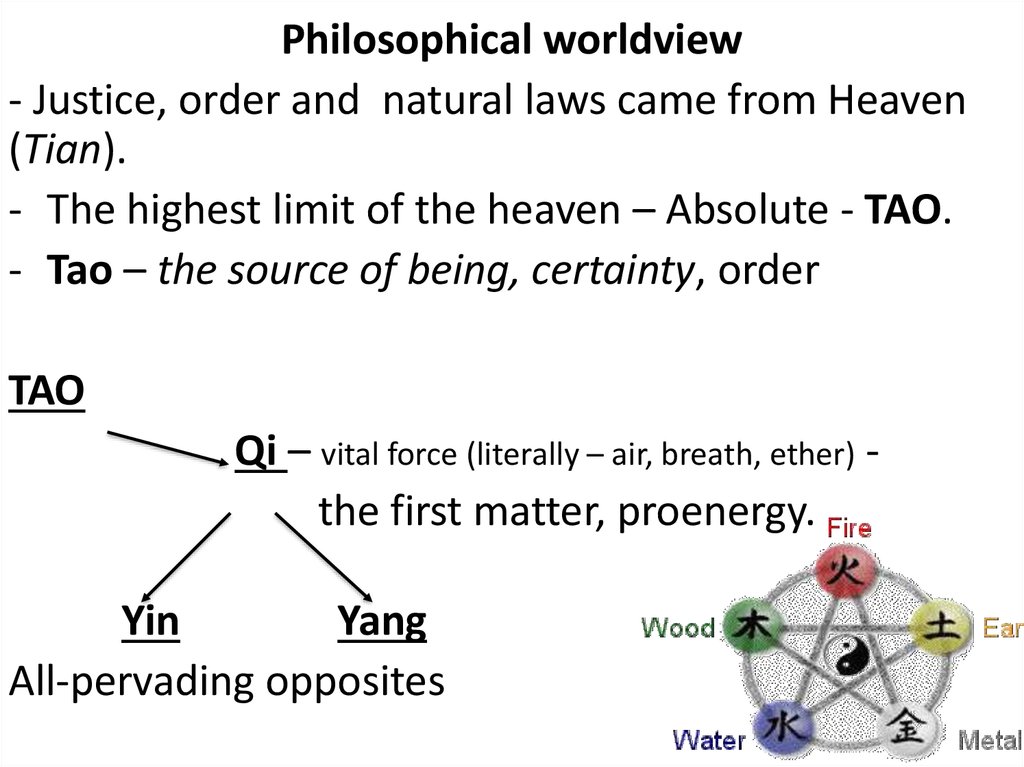
Philosophical worldview- Justice, order and natural laws came from Heaven
(Tian).
- The highest limit of the heaven – Absolute - TAO.
- Tao – the source of being, certainty, order
TAO
Qi – vital force (literally – air, breath, ether) the first matter, proenergy.
Yin
Yang
All-pervading opposites






























 История
История








