Похожие презентации:
The syllable as a phonetic and phonological unit. Types of syllables. Syllable patterns. Phonotactics
1. The syllable as a phonetic and phonological unit
Types of syllables. Syllable patterns.Phonotactics.
2. The syllable as a phonetic and phonological unit
• Sounds (phonemes) are the smallestsegments into which the speech
continuum is generally divided for
purposes of analysis, because these
units serve to differentiate words.
3. The syllable as a phonetic and phonological unit. Types of syllables. Syllable patterns. Phonotactics.
When we pronounce a syllable, thespeech organs, while producing a
consonant, take all the positions
necessary for the following vowel, for
example note the movements of the
tongue and the lips in /su:n/ “soon”,
/lu:z/ “lose”.
4. The syllable as a phonetic and phonological unit. Types of syllables. Syllable patterns. Phonotactics.
The syllable can be considered as both a phonetic and aphonological unit. As a phonetic unit the syllable is
defined in articulatory, auditory (perceptual) and acoustic
terms with universal application for all languages.
As a phonological unit the syllable can be defined and
described only with reference to the structure of one
particular language. The very term “syllable” denotes
particular ways in which phonemes are combined in a
language.
5. The approaches to defining a syllable
Two approaches to defining a syllable:The first approach defines the syllable as
sequence of segments. The syllable is a unit
consisting of 0 or more consonants followed
by a vowel followed by 0 or more consonants.
A vowel may be replaced by a syllabic
consonant.
6. The approaches to defining a syllable
The formula of a syllable:CnV Cn
where Cn = any number of
consonants
and V = vowel or syllabic
consonant.
7. The approaches to defining a syllable
The second approach defines syllables by theirsonority (or relative loudness). Some types of
phonemes appear to be more sonorous (louder)
than others.
8. The approaches to defining a syllable
Syllable is an element of speech that acts as a unit ofrhythm, and has internal structure. The constituent
parts are ONSET and RHYME, within the rhyme
we find the NUCLEUS and CODA. The
NUCLEUS is obligatory, other parts are optional.
The smallest syllable contains a nucleus only.
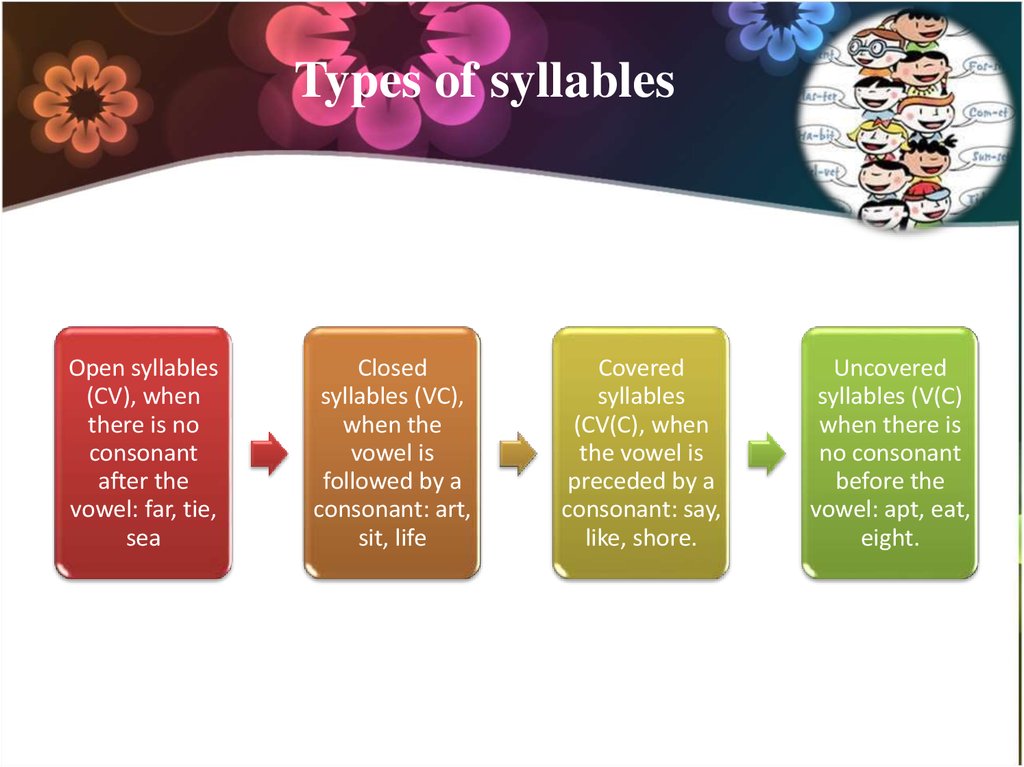
9. Types of syllables
Depending on the position of consonants (C) inrelation to the vowel (V), there are 4 types of
syllables:
10. Types of syllables
Open syllables(CV), when
there is no
consonant
after the
vowel: far, tie,
sea
Closed
syllables (VC),
when the
vowel is
followed by a
consonant: art,
sit, life
Covered
syllables
(CV(C), when
the vowel is
preceded by a
consonant: say,
like, shore.
Uncovered
syllables (V(C)
when there is
no consonant
before the
vowel: apt, eat,
eight.
11. Syllable patterns.
The fundamental syllable type in English is the closedsyllable, whereas in Russian it is the open syllable.
As to the presence, number and arrangement of
consonants there are 23 syllable patterns in English , such
as V, VC, CVC, CV, CCVC, CCVCC, CCCVC, CCCVCC etc.
The vowel may occur alone in a syllable or it may have up
to 3 consonants before it and up to 4 consonants after it.
The most frequent and fundamental pattern in English is
CVC.
12. Phonotactics
As a phonological unit, the syllablerequires a separate definition for each
individual language, because each
language has its own rules of
combining its phonemes into
syllables, or PHONOTACTICS.
13. Phonotactics.
In every language certain sound sequences arenot permitted. This is called called
‘phonotactic constraints’. English permit
more combinations of consonants than many
languages
14. Phonotactics.
Some combinations that don't occur inEnglish (e.g., syllable-initial /tl/) are
permissible in other languages (e.g.,
Polish, Russian).
When the English first attempt the initial
/kn/ of German KNABE (boy), they insert
a vowel and make it /kǝ’nɑ:bǝ/, i.e. three
syllables rather than two (as is for
Germans), because /kn/is no longer a
permissible initial sequence in English.
15. Phonotactics.
So, phonologically, thesyllable is a structural unit,
which consists of a vowel
(or a syllabic sonorant)
surrounded by consonants
in the numbers and
arrangements permitted by
a given language.











 Английский язык
Английский язык








