Похожие презентации:
Distinctive features of business culture in Аsia
1. DISTINCTIVE FEATURES OF BUSINESS CULTURE IN ASIA
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДДDARRYL CARLTON
2. Asia & The Pacific
Asia & The PacificRank
Country
—
World
1 United States
—
European Union
2 China (PRC)
GDP (billions of USD)
73,993,835
18,558,130
16,477,211
11,383,030
3 Japan
4,412,600
4 India
2,090,706
5 Canada
Rank
Country
GDP (billions of USD)
14 Malaysia
309,262
15 Singapore
294,560
16 Vietnam
201,361
17 New Zealand
169,922
18 Myanmar
74,012
1,552,386
19 Laos
13,359
6 Russia
1,324,734
20 Mongolia
11,652
7 South Korea
1,321,200
8 Australia
1,223,887
9 Indonesia
936,955
10 Republic of China (Taiwan)
508,849
11 Thailand
409,724
12 Hong Kong
322,429
13 Philippines
310,312
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДД
21 Brunei
9,097
22 Fiji
4,964
23 East Timor
2,100
24 Solomon Islands
1,202
25 Samoa
865
24 Tonga
414
DARRYL CARLTON
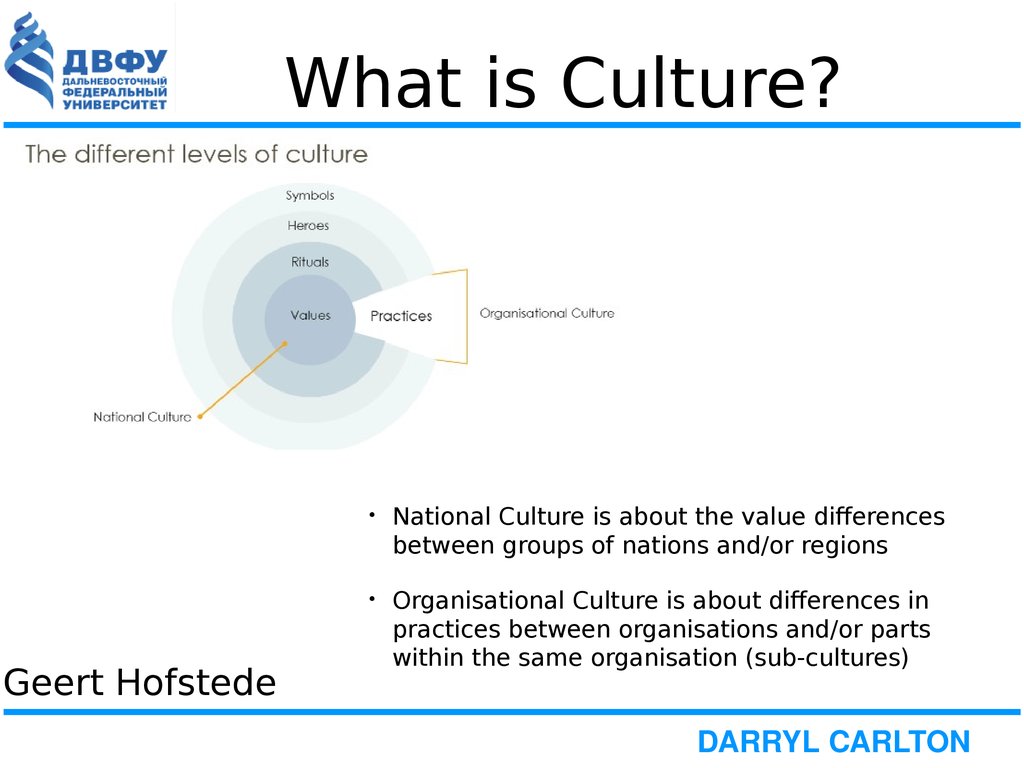
3. What is Culture?
Geert HofstedeДДДДДД ДДДДДДД
National Culture is about the value differences
between groups of nations and/or regions
Organisational Culture is about differences in
practices between organisations and/or parts
within the same organisation (sub-cultures)
DARRYL CARLTON
4. The National Culture Map
The National Culture
Map
culture is defined as the collective mental programming of the human mind which distinguishes
one group of people from another. This programming influences patterns of thinking which are
reflected in the meaning people attach to various aspects of life and which become crystallised
inPower
the Distance
institutions of a society
This dimension deals with the fact that all individuals in societies are not equal – it expresses the attitude of the culture towards these
inequalities amongst us. Power Distance is defined as the extent to which the less powerful members of institutions and organisations within a
country expect and accept that power is distributed unequally.
Individualism
The fundamental issue addressed by this dimension is the degree of interdependence a society maintains among its members. It has to do
with whether people´s self-image is defined in terms of “I” or “We”. In Individualist societies people are supposed to look after themselves
and their direct family only. In Collectivist societies people belong to ‘in groups’ that take care of them in exchange for loyalty.
Masculinity
A high score (Masculine) on this dimension indicates that the society will be driven by competition, achievement and success, with success
being defined by the winner/best in field – a value system that starts in school and continues throughout organisational life.
Uncertainty Avoidance
The dimension Uncertainty Avoidance has to do with the way that a society deals with the fact that the future can never be known: should we
try to control the future or just let it happen? This ambiguity brings with it anxiety and different cultures have learnt to deal with this anxiety
in different ways. The extent to which the members of a culture feel threatened by ambiguous or unknown situations and have created beliefs
and institutions that try to avoid these is reflected in the score on Uncertainty Avoidance.
Long Term Orientation
This dimension describes how every society has to maintain some links with its own past while dealing with the challenges of the present and
future, and societies prioritise these two existential goals differently. Normative societies. which score low on this dimension, for example,
prefer to maintain time-honoured traditions and norms while viewing societal change with suspicion. Those with a culture which scores high,
on the other hand, take a more pragmatic approach: they encourage thrift and efforts in modern education as a way to prepare for the future.
Indulgence
One challenge that confronts humanity, now and in the past, is the degree to which small children are socialized. Without socialization we do
not become “human”. This dimension is defined as the extent to which people try to control their desires and impulses, based on the way
they were raised. Relatively weak control is called “Indulgence” and relatively strong control is called “Restraint”. Cultures can, therefore, be
described as Indulgent or Restrained.
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДД
DARRYL CARLTON
5. CULTURAL DIMENSIONS
HTTPS://GEERT-HOFSTEDE.COM/COUNTRIES.HTML
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДД
DARRYL CARLTON
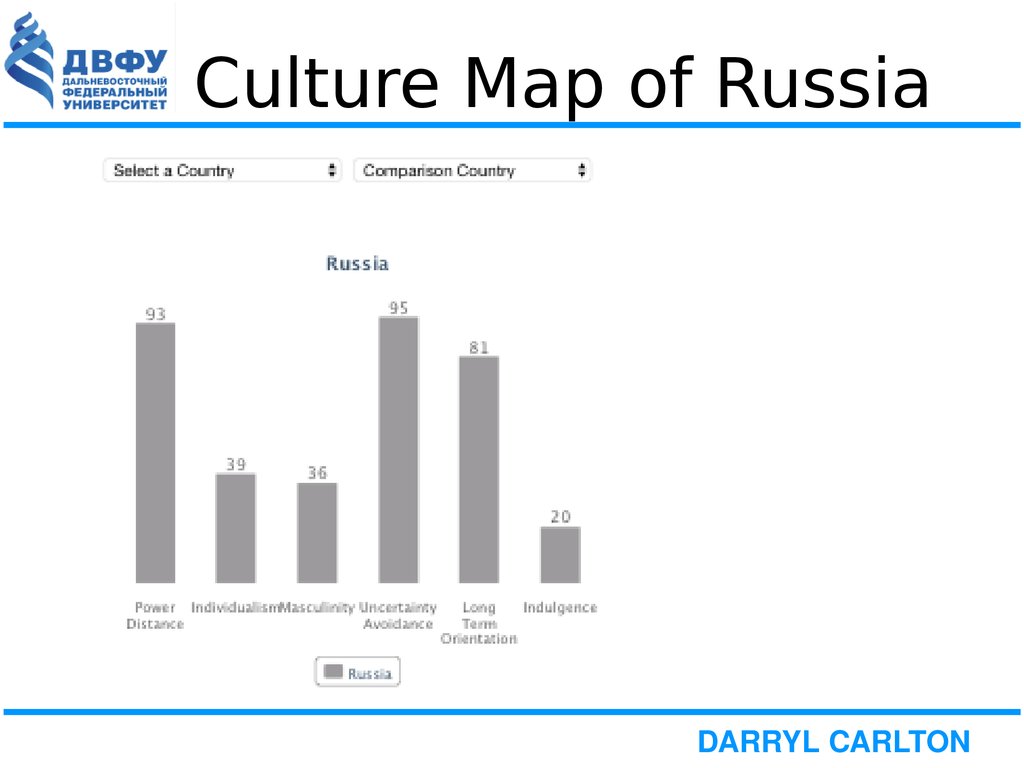
6. Culture Map of Russia
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДДDARRYL CARLTON
7. RUSSIA - Cultural Dimensions
Power DistanceRussia, scoring 93, is a nation where power holders are very distant in society. This is underlined by the fact that
the largest country in the world is extremely centralized: 2/3 of all foreign investments go into Moscow where
also 80% of all financial potential is concentrated. The huge discrepancy between the less and the more
powerful people leads to a great importance of status symbols. Behaviour has to reflect and represent the status
roles in all areas of business interactions: be it visits, negotiations or cooperation; the approach should be topdown and provide clear mandates for any task.
Individualism
If Russians plan to go out with their friends they would literally say “We with friends” instead of “I and my
friends”, if they talk about brothers and sisters it may well be cousins, so a lower score of 39 even finds its
manifestations in the language. Family, friends and the neighborhood are extremely important to get along with
everyday life’s challenges. Relationships are crucial in obtaining information, getting introduced or successful
negotiations. They need to be personal, authentic and trustful before one can focus on tasks and build on a
careful to the recipient, rather implicit communication style.
Masculinity
Russia’s relatively low score of 36 may surprise with regard to its preference for status symbols, but these are in
Russia related to the high Power Distance. At second glance one can see, that Russians at workplace as well as
when meeting a stranger rather understate their personal achievements, contributions or capacities. They talk
modestly about themselves and scientists, researchers or doctors are most often expected to live on a very
modest standard of living. Dominant behaviour might be accepted when it comes from the boss, but is not
appreciated among peers.
Uncertainty Avoidance
Scoring 95 Russians feel very much threatened by ambiguous situations, as well as they have established one of
the most complex bureaucracies in the world. Presentations are either not prepared, e.g. when negotiations are
being started and the focus is on the relationship building, or extremely detailed and well prepared. Also
detailed planning and briefing is very common. Russians prefer to have context and background information. As
long as Russians interact with people considered to be strangers they appear very formal and distant. At the
same time formality is used as a sign of respect.
Long Term Orientation
With a very high score of 81, Russia is definitely a country with a pragmatic mindset. In societies with a
pragmatic orientation, people believe that truth depends very much on situation, context and time. They show
an ability to adapt traditions easily to changed conditions, a strong propensity to save and invest. thriftiness and
perseverance in achieving results.
Indulgence
The Restrained nature of Russian culture is easily visible through its very low score of 20 on this dimension.
Societies with a low score in this dimension have a tendency to cynicism and pessimism. Also, in contrast to
Indulgent societies, Restrained societies do not put much emphasis on leisure time and control the gratification
of their desires. People with this orientation have the perception that their actions are Restrained by social
norms and feel that indulging themselves is somewhat wrong.
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДД
DARRYL CARLTON
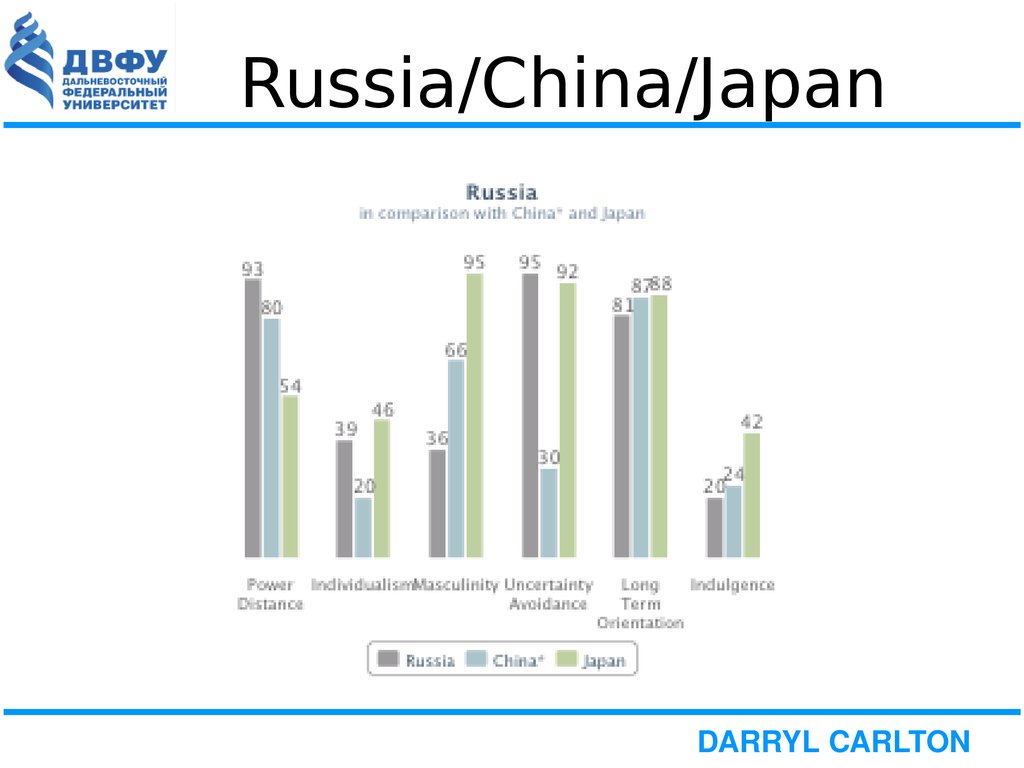
8. Russia/China/Japan
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДДDARRYL CARLTON
9. The Chinese Cultures
each of thesecountries is essentially
a “chinese culture”
But even when we
might expect them to
be the same, there are
cultural differences
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДД
DARRYL CARLTON
10. South-East Asia
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДД
power is centralised and
workers rely on their
bosses and rules that they
can follow
family is the centre of
Singapore culture, “we”
replaces “I”
being modest and humble
is seen as very important
Singapore is a “fine”
country … you will get
fined for anything
very strong rule following
Government
in their personal
transactions uncertainty is
accepted
DARRYL CARLTON
11. India, a traditional ally of Russia
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДД
India is hierarchical,
strong top-down culture
strong visual
representation of power
and success
nothing is certain in
India, tolerance for the
unexpected is high,
quality is not expected
“nothing is impossible
in India, if one can
adjust”
rules are meant to be
broken
DARRYL CARLTON
12. Why is Cultural Awareness Important?
Why is Cultural Awareness
Important?
in the1980’s the Australian Wheat Board was trying to sell flour and other
grains to the Japanese
The Japanese consumed very little flour, everything was based on rice. It was a
big market!
the Australian’s were very clever, they did lots of market research.
they figured out that Japanese kitchens are small, and they do not have an
oven to bake cakes … but every kitchen had a rice cooker
so, they invented a cake formula for making cakes in a rice cooker
they went to shopping centres and demonstrated the technique and let the
japanese house wife sample the cakes cooked this way
everyone loved the rice cooker cakes …. but no-one purchased the flour or
cake mix
the “problem” was that the japanese house wife was worried that cooking
cakes in her rice cooker would change the taste of the rice when she next
made rice, and having good tasting rice was really important to the japanese
house
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДД
DARRYL CARLTON
13. Igor Ansoff
Born in Vladivostok, in December of 1918ДДДДДД ДДДДДДД
DARRYL CARLTON
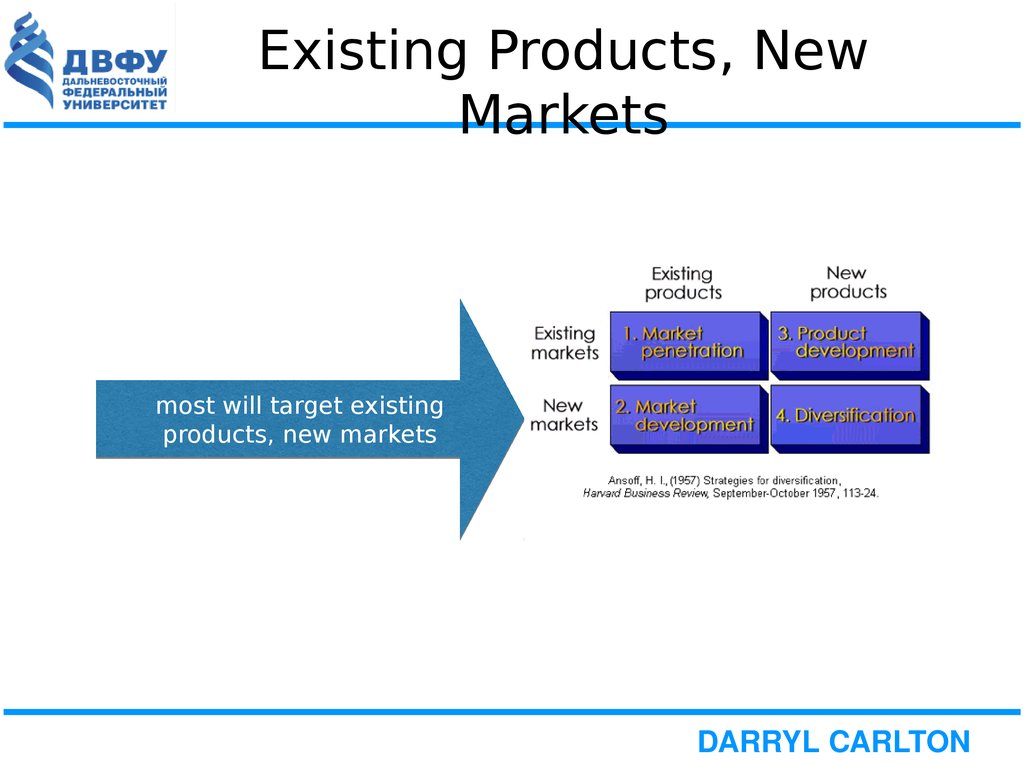
14. Existing Products, New Markets
most will target existingproducts, new markets
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДД
DARRYL CARLTON
15. Why is Culture Important
Cultural Awareness goes beyond how you personally interact with
individuals from other countries
Cultural Awareness impacts how you;
Package your product or service offering
Promote your product or service offering
Price your product or service offering
What you perceive as a gap in the market, may not be a gap for
the country you are targetting, there could be good reasons why
they do not have companies offering what you have …
But of course it might just be that you have a superior product
or service and all you need to be successful is to figure out how
to approach a new market
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДД
DARRYL CARLTON
16. Cultural Mistakes
Coca-Cola
in India coke had to change its marketing message when it was
discovered that water was drunk at most meals and soft drinks
were typically reserved for guests and special occassions (Malhotra,
Agarwal, and Peterson, 1996)
In Japan “Diet Coke” was renamed “coke light” after they realised
that the term “diet” carried an embarrassing meaning (Cateora, International
Marketing 14th ed, 2009)
UPS
in Spain the brown trucks had to be repainted because they
resembled the vehicles used as funeral hearses (Cateora, International Marketing
14th ed, 2009)
In Germany, the drivers uniforms had to be changed because the
“brown short” had not been worn since 1945 and reminded the
community of Nazi Germany (Cateora, International Marketing 14th ed, 2009)
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДД
DARRYL CARLTON
17. Australian Beer in Vietnam
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДД
Fosters tried to replicate the
consumer experience of “The
Australian styled beer” in
Vietnam and failed – in the initial
stages, the slogan caught the
attention of the Vietnamese
customers. The brand expression
was that of the home country,
Australia but soon it caught the
unpleasant eyes of the host
country for the reason that the
Vietnamese people thought that
they were giving into another
foreign brand and were losing
their identity
DARRYL CARLTON
18. Walmart fails to translate success
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДДin South Korea, the company did not understand the local
preferences for buying small packages at local stores, and
the preferences among shoppers changed, according to
The New York Times. Similar problems resulted in Walmart
shutting down its operations in Germany, where groceries
were sold for lower prices at local stores.
Walmart bought a share in the Seiyu Company, Japan and
attempted to implement its successful strategies in Seiyu
stores, such as the “Every Day Low Prices” campaign.
However, it was pointed out by BusinessWeek that this
does not have the same pitch in Japan as it does in the
United States because customers associate low prices with
cheap quality, making them wary about shopping there
DARRYL CARLTON
19. Guanxi - culture drives commerce
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДДThe online auctioning giant San Jose decided to enter the China
market in 2004 and bought a local company in china. They
changed to the eBay platform, and planned to sweep China in
short time frame. After all, they had dominated other countries’
markets. Why not China's?
Two years later, eBay shut down their portal, and the Chinese
auction space too was abandoned. Taobao, a local competitor
take over 95 percent of the china’s market share.
There was no mechanism for eBay to simulate guanxi.
According to a study conducted by researchers in the United
States and Hong Kong, this was a crucial error. While Taobao
allowed sellers and buyers to chat over IM, eBay did not. This
gave them a chance to establish a personal contact.
In China, business is not just business. It’s social. And they
quickly learn the power of social connections or "guanxi," when
you spend some time in China,. Guanxi drives business deals
and government contracts. It’s the invisible glue that ties
people together. This may seem like a trivial detail for a
powerful corporation. It’s not. It’s a mutual obligation and
connection that Chinese respect in personal relationships
DARRYL CARLTON
20. What Do The Chinese Want?
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДД
Internal Gratification vs. External
Gratification
• Russia, China and Malaysia all strive
for “external gratification”
• Western Countries; UK, Australia, USA
strive for “internal gratification”
Brands are VERY important when dealing
with China and South East Asia
Chinese consumers do not trust locally
made products
• in most markets you would translate
labels into the local language,
Australian business has been MORE
successful by leaving the labels in
English and promoting “made in
DARRYL CARLTON
Australia"
21. Negotiating with Asian Cultures
in Daoist philosophy the student is not allowed to debate
what is being taught - they sit quietly and either accept or
reject.
this acceptance or rejection is done quietly, internally
when Asian students sit quietly in a class, it is not because
they do not understand the language. It is the deeply
rooted Daoist culture of quietly accepting or rejecting
without debate
The Greek philosophy of debate is very different - to
achieve understanding we will ask questions, challenge
what was said, we will seek answers until we are confident
that we have all the information we need to make a
decision
In business this means that you cannot accept silence as
ДДДДДД
ДДДДДДД understanding or acceptance, you
DARRYL
CARLTON
either
must inquire
and
22. CONCLUSION
CULTURAL AWARENESS is far more than how individuals interact• to be a successful exporter or operator in another culture you
need to understand how that culture behaves with respect to your
product
• this is more than translation, this is subtle cultural cues
• the Ford Motor Company “Pinto” was a massive failure in South
America because in ‘slang’ the word “pinto” meant “tiny penis”
• this was not a direct translation into Spanish, it was a local
colloquium (a slang term), which you could only know by
understanding the local culture
• invest time to know the country and the people that you are
selling to
• do the features of your product, the features that make it
successful in Russia translate to the needs of the other country?
• does your marketing slogan work in another culture?
• the way that you compensate your sales teams or business
partners - does that work the same?
• culture needs to be considered from the perspective of “Whole
Product
ДДДДДД
ДДДДДДД Marketing”
DARRYL CARLTON
23. Doing Business in Asia-Pac
Doing Business in AsiaPac
Understanding Indonesian Business Culture
Measuring Communication Styles in the
Malaysian Workplace
http://www.expatfocus.com/expatriate-singapore-business-culture
Thailand - Business and Workplace Culture
http://wcaweb.org/measuring-communication-styles/
Singapore - Business and Workplace Culture
http://www.indosight.com/blog/understanding-indonesian-business-cu
lture/
http://www.expatfocus.com/expatriate-thailand-business-culture
https://www.thailandstarterkit.com/business/cross-cultural-managemen
t-thailand/
Understanding Vietnamese Business Culture
http://www.vietnam-culture.com/articles-116-17/Understanding-Vietna
mese-business-culture-and-etiquette.aspx
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДД
DARRYL CARLTON
24.
Thank YouДДДДДДД
ДДДДДД ДДДДДДД
DARRYL CARLTON




















 Бизнес
Бизнес








