Похожие презентации:
Perception and illusions
1.
PresentationOn
perception.
PERCEPTION
and illusions
Fedorenko Anastasiia. PS-13
2.
WE DON’T SEE THINGS AS THEYARE,
WE SEE THINGS AS WE ARE
3.
4.
Brain process :(selecting, organizing, interpreting)
Factors of Perception:
Subjective (Fitness, Interest, Knowledge, Mental Capacity)
Objective (physical environment stimuli))
Social (Social value, Attitudes, Stereotype, Suggestion)
5.
Is based on:Figure
Ground
6.
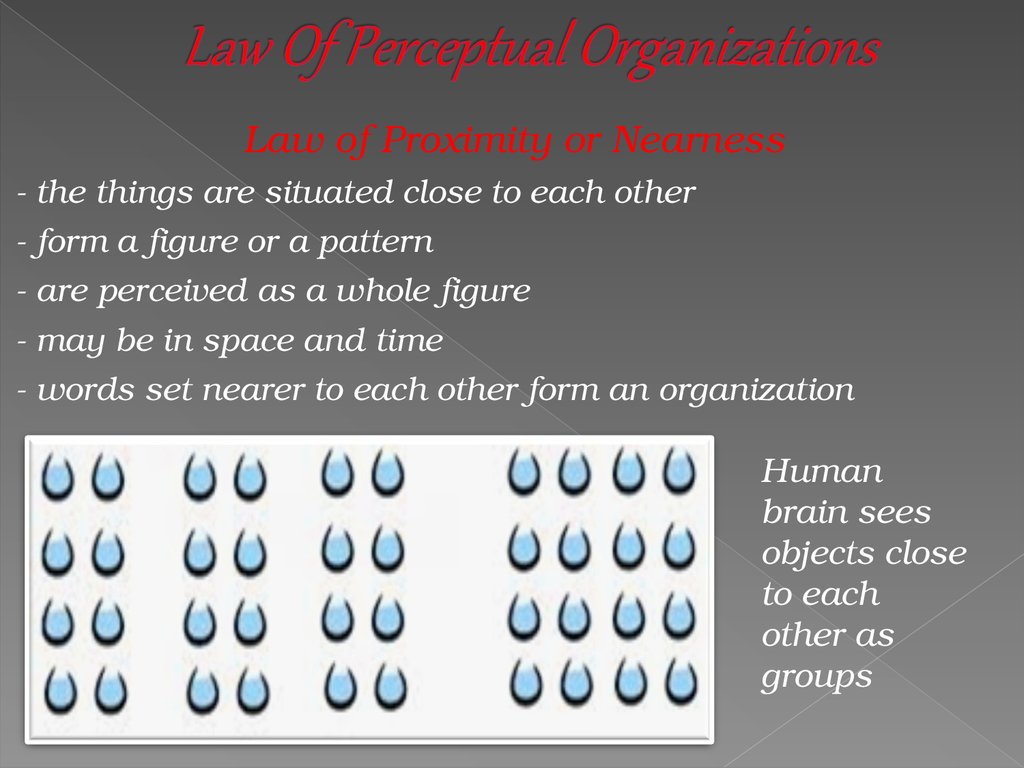
Law of Proximity or Nearness the things are situated close to each other
form a figure or a pattern
are perceived as a whole figure
may be in space and time
words set nearer to each other form an organization
Human
brain sees
objects close
to each
other as
groups
7.
Law of Similarity tendency to group similar elements
objects similar in shape are classified in a group
8.
Good ContinuationSymmetry
all the parts of a figure in
“one whole”
A symmetrical figure makes a
perceptual organization and
perceived sooner.
9.
ClosureCommon Direction
perceptual tendency to fill the
gaps or closure fills the gaps
to help us to perceive it as a
whole complete form
grouping in the perceptual
organization is classified in
two groups because of their
common direction
Inclusiveness
all the stimuli are include to
form a pattern.
10.
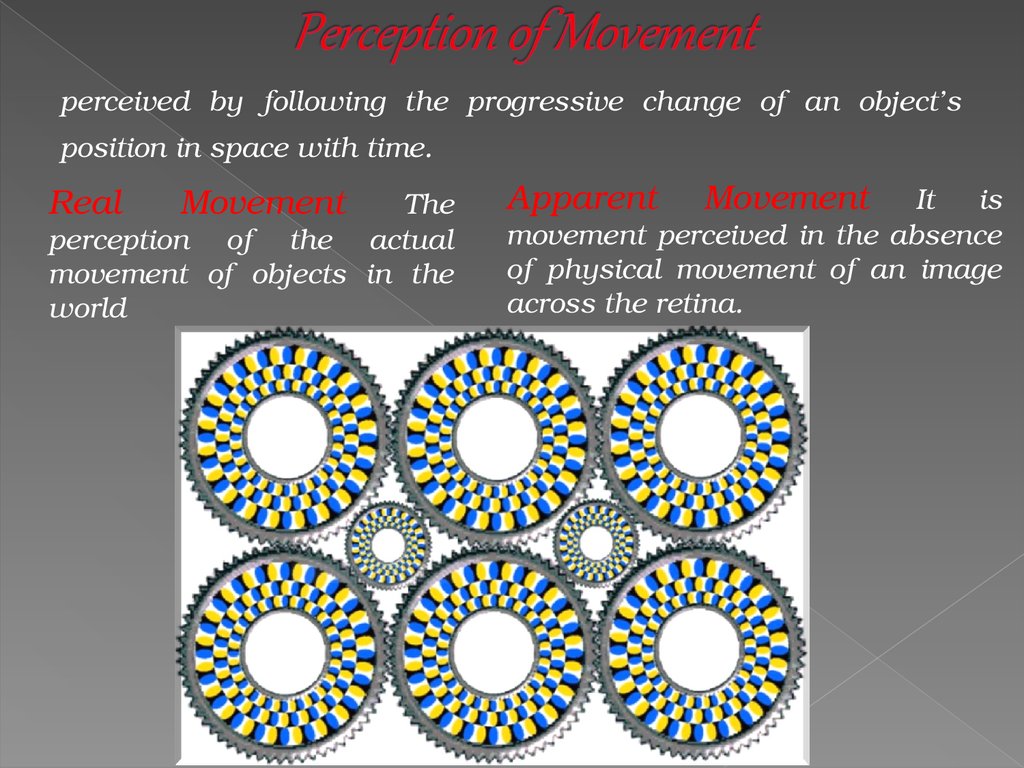
perceived by following the progressive change of an object’sposition in space with time.
Real
Movement
The
perception of the actual
movement of objects in the
world
Apparent
Movement
It is
movement perceived in the absence
of physical movement of an image
across the retina.
11.
“This ability helps to perceive threedimensional space and to accurately judge
distance”
12.
Size constancy is the tendency to perceiveobjects in a consistent manner despite the changing
sensations that are received by our senses.
13.
Shape Constancy When we know that the object is acertain shape, we tend to perceive it as the same shape,
regardless of the viewing angle.
14.
Color Constancy: Colors of objects tend to remainconstant in perception when we know their true color.
Visual objects also appear constant in their degree of
whiteness, grayness and blackness.
15.
Something that looks or seems different from whatit is something that is false or not real but that seems to
be true or real.
Causes of Illusion:
Physical causes
Habit & Familiarity.
Expectancy & Mental Set.
Momentary State of Mind or Mood.
Incomplete analysis of the collective impression.
Apperception.
Suggestion.
Arrangement of stimuli.
16.
The illusion Of motion.When a stationary stimulus is
perceive as moving, it is named as
illusion of motion or movement.
The Illusion Of forms.
Form perception is attained in relation
to the figure and ground according to
the law of perception Organization. As
the figure is smaller then the ground
according to perceptual.
The illusion of distance.
The illusion of distance occurs when
the parallel lines seem to bend in
different directions.
17.
It seem that the curving line behind thespiral have become the cause of this illusion. The
illusion is also known as the false spiral, or by its
original name, the twisted cord illusion.
18.
The parallel lines seem to bend to eachother instead of looking straight. The reason of
this Illusion is the smaller diagonal lines cutting
the parallel line.
19.
If two parallel line are dissected by anotherstraight line separately, a large straight line seem
cutting the parallel line instead of two partial line.
20.
A near object is near usually perceivedlarger and farther object is perceived smaller
but in the moon illusion, moon is perceived
larger on horizon where the earth and sky seem
to meet.



















 Психология
Психология Английский язык
Английский язык








