Похожие презентации:
The role of accounting in business. (Chapter 12)
1. Introduction to Business
2. The Role Of Accounting In Business
Chapter 12The Role Of
Accounting In
Business
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
2
3. Chapter Objectives
Define accounting and identify its uses
Understand the three basic financial statements
Apply breakeven analysis
Understand cash-basis vs. accrual
Evaluate a company’s performance
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
3
4. Stakeholders
“…parties who are interested in the activities of thebusiness because they’re affected by them…”
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
4
5. Accounting
“…measuring and summarizing business activities,interpreting financial statements, and
communicating the results to management and
other decision makers.”
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
5
6. Fields of Accounting
• Management Accounting – provides informationto decision makers inside the organization to help
operate the business
• Financial Accounting – furnishes information to
individuals and groups inside/outside the
organization to assess the firm’s financial
performance
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
6
7. Management Accounting
Provides information and analysis to decisionmakers inside the organization to help them
operate them operate the
business
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
7
8. Financial Accounting
• Prepare Statements• Income Statement
• Balance Sheet
• Statement of Cash Flow
• Using Generally Accepted
Accounting Principles
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
8
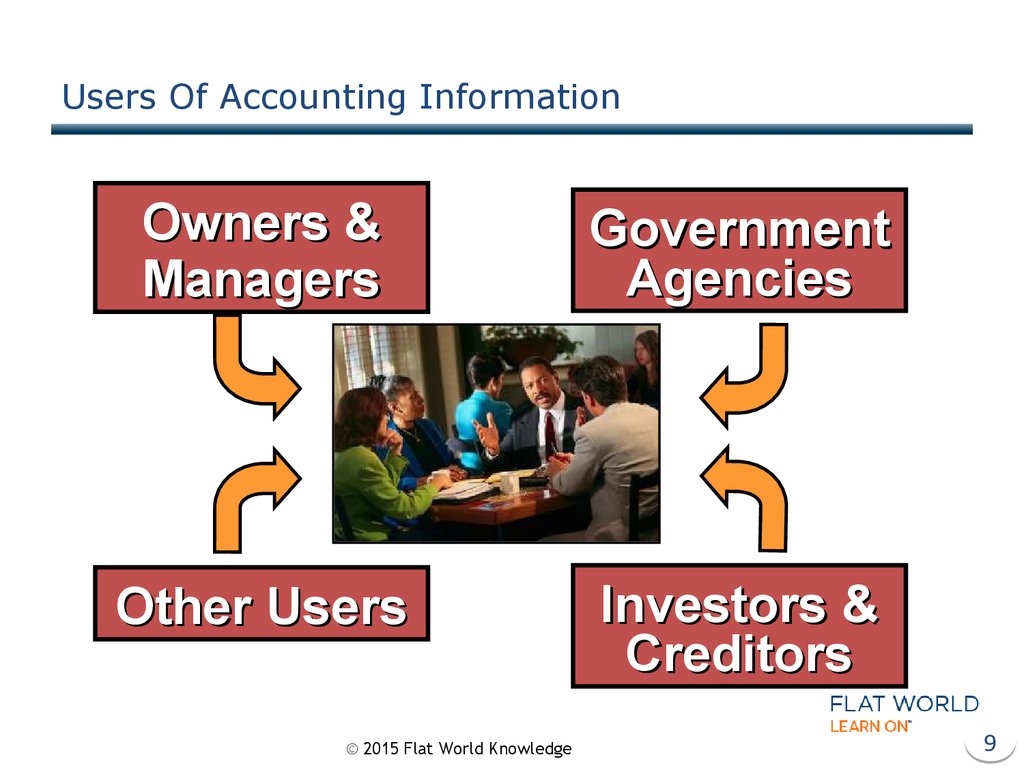
9. Users Of Accounting Information
Owners &Managers
Government
Agencies
Other Users
Investors &
Creditors
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
9
10. Understanding Financial Statements
• Income Statement – What sales and expensesare and whether a profit is made
Balance Sheet – Indicates assets and liabilities
and amount invested in company
Statement of Cash Flows – Shows how much cash
flows in and out
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
10
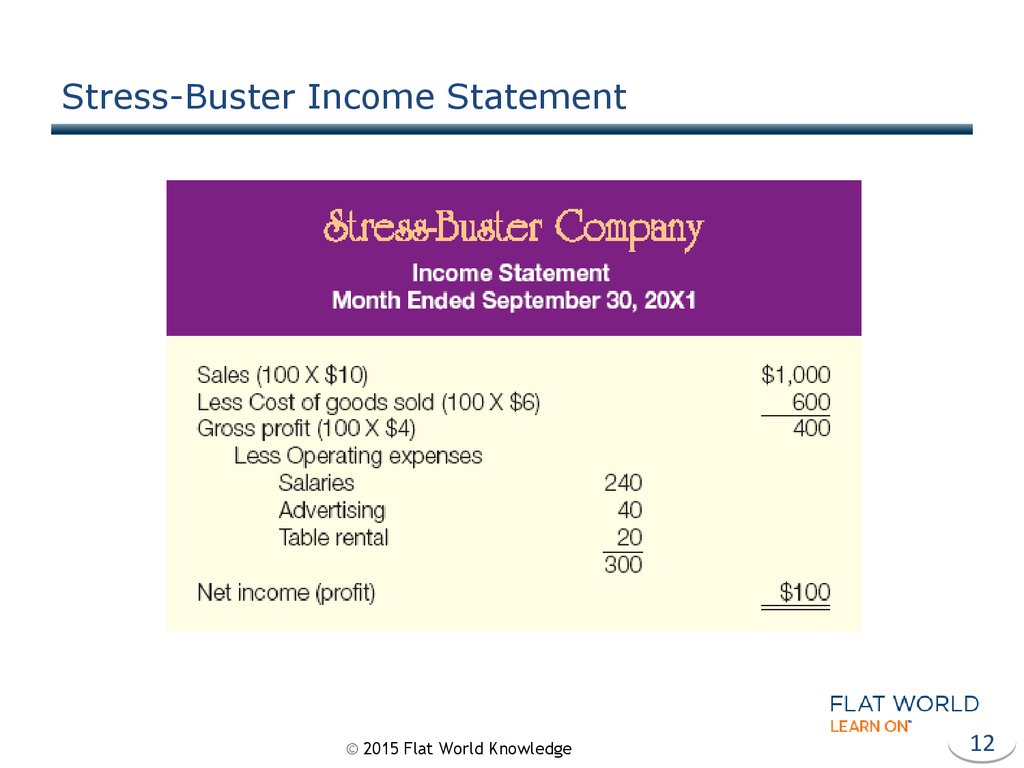
11. Income Statement
Revenues (or Sales)
Cost of Goods Sold
Gross Profit
Operating Expenses
Net Income (or Loss)
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
11
12. Stress-Buster Income Statement
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge12
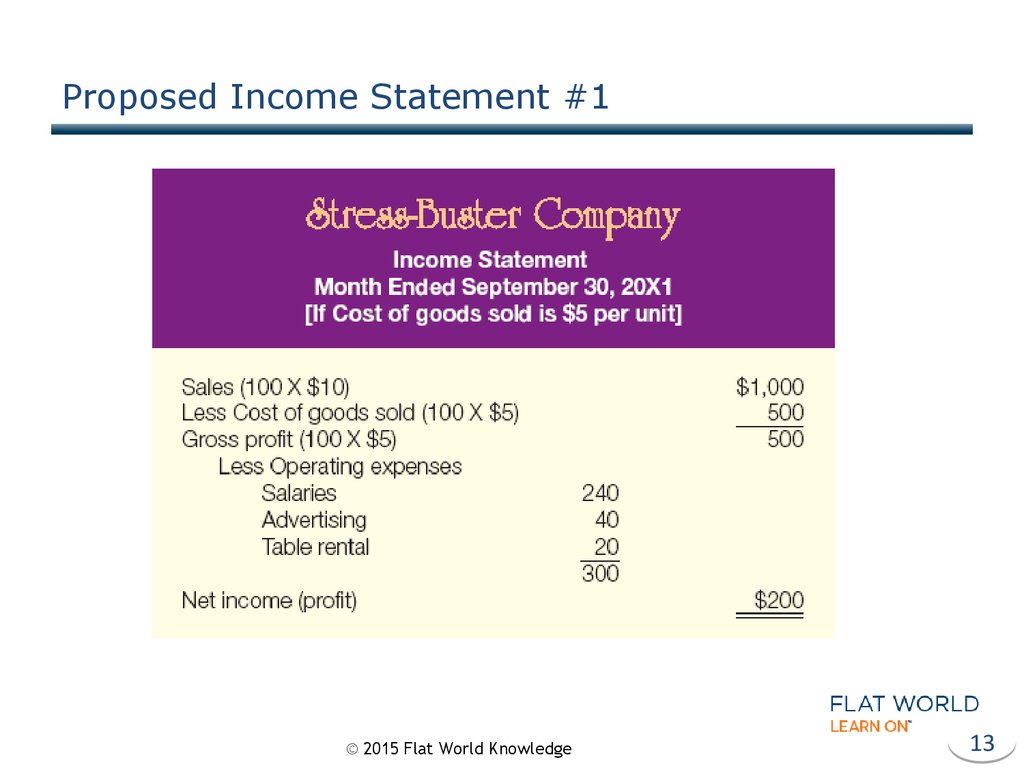
13. Proposed Income Statement #1
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge13
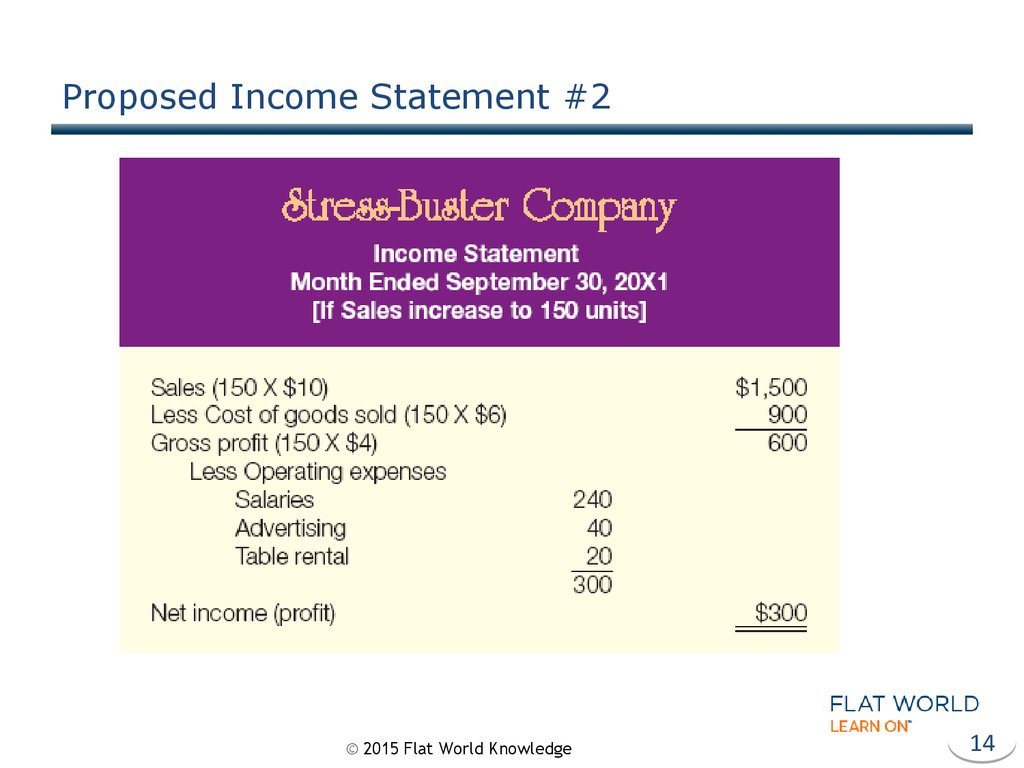
14. Proposed Income Statement #2
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge14
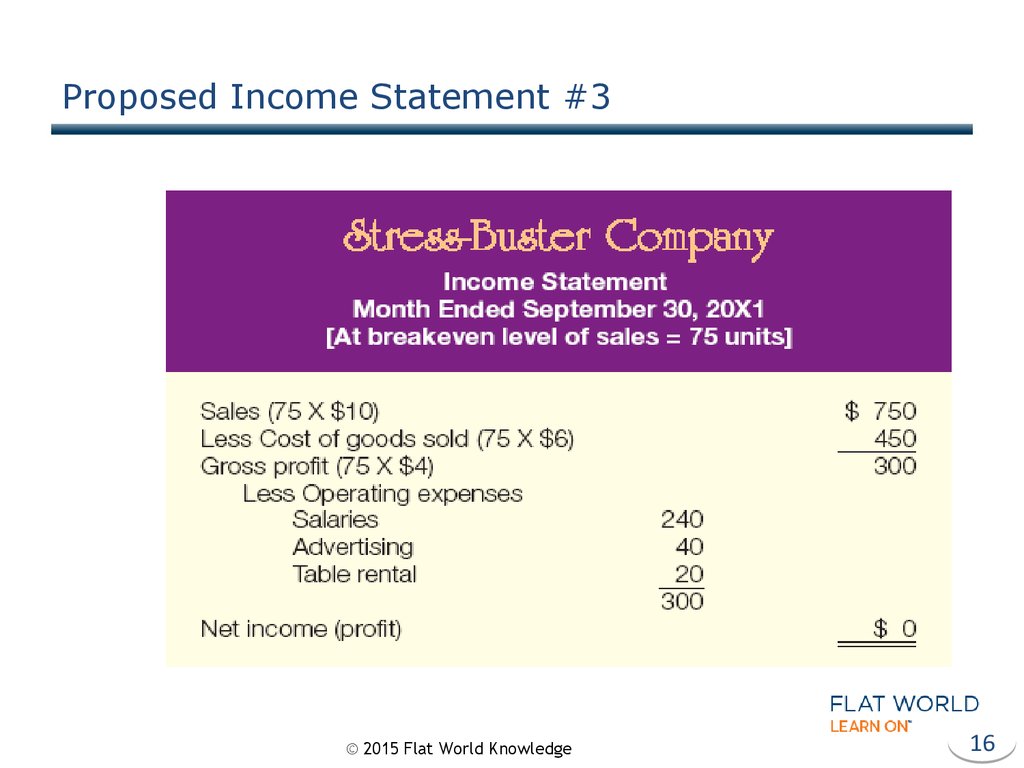
15. Breakeven Analysis
“…To break even, total sales revenue must exactly equal allyour expenses…”
•Fixed Costs
•Variable Costs
•Contribution Margin
Per Unit
•Breakeven Point In Units
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
15
16. Proposed Income Statement #3
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge16
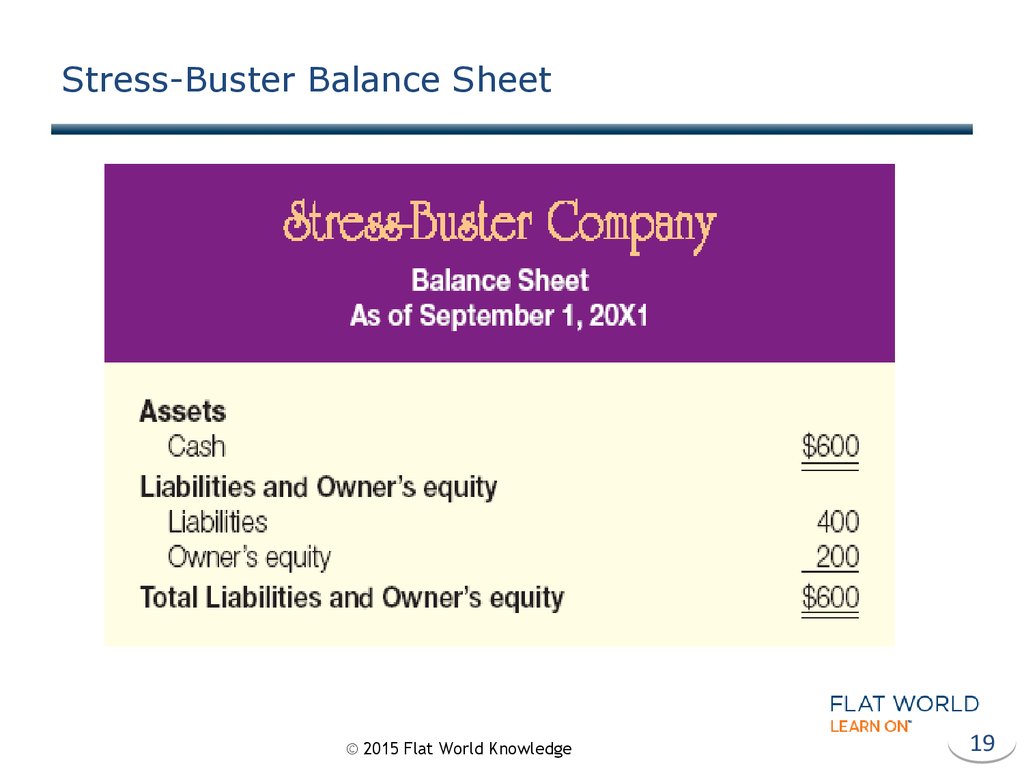
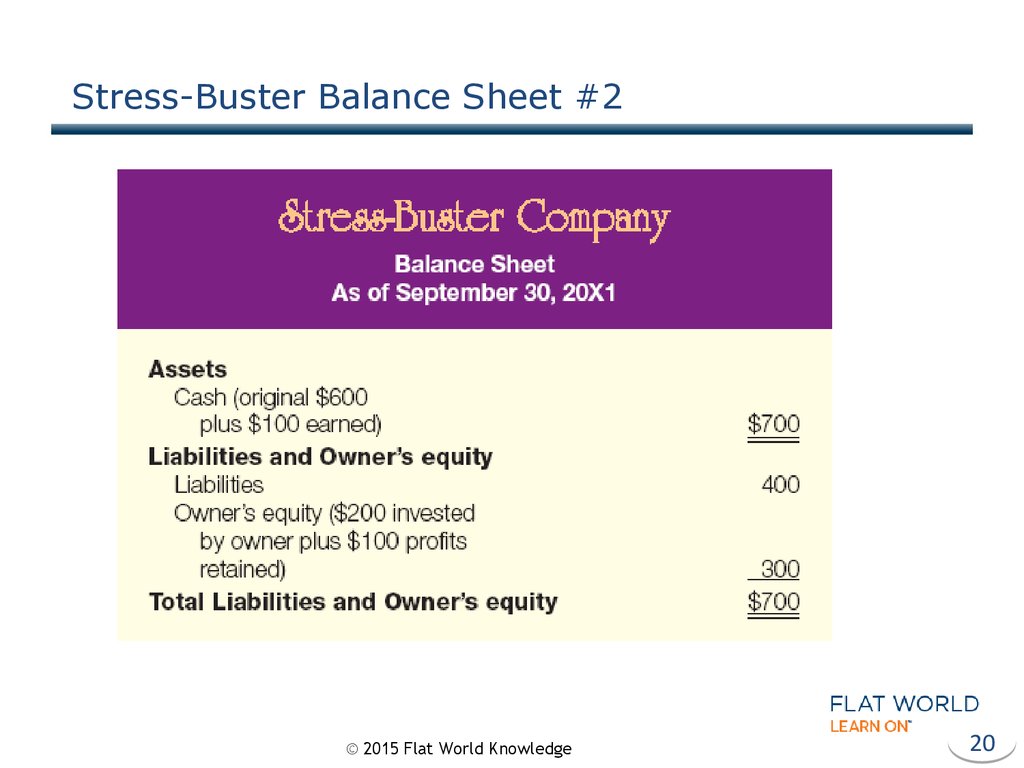
17. Balance Sheet
“…tells what you have (and where it came from) ata specific point in time…”
•Assets – Business resources
•Liabilities – Debts owed to outside
entities
•Owner’s Equity – Amount invested
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
17
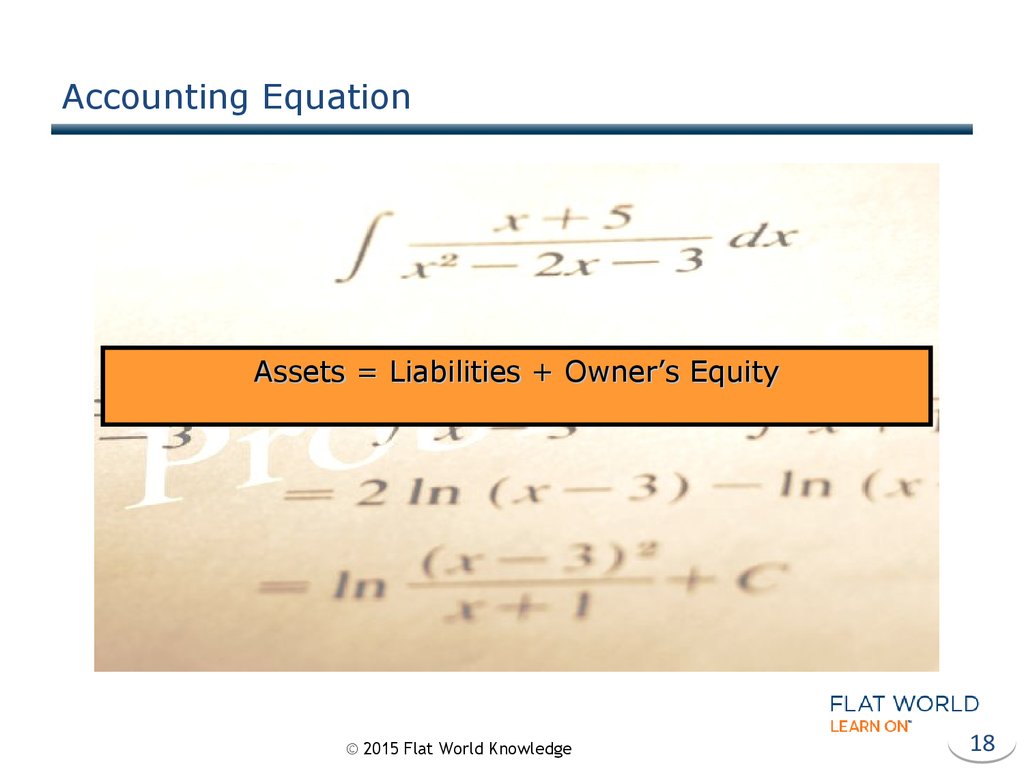
18. Accounting Equation
Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
18
19. Stress-Buster Balance Sheet
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge19
20. Stress-Buster Balance Sheet #2
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge20
21. Accrual Accounting
“…accountant records a transaction when itoccurs…”
• Account Receivable
• Account Payable
• Inventory
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
21
22. Classified Balance Sheet
• Assets• Current—Convert to cash within a year
• Long-Term—Hold for more than a year
• Liabilities
• Current—Pay off within a year
• Long-Term—Not due for more than a year
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
22
23. College Shop Balance Sheet
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge23
24. College Shop Income Statement
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge24
25. End-of-Year Balance Sheet
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge25
26. Statement Of Cash Flows
“…tells…where cash came from and where it went.”Activities:
•Operating
•Investing
•Financing
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
26
27. Cash Flow Statement
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge27
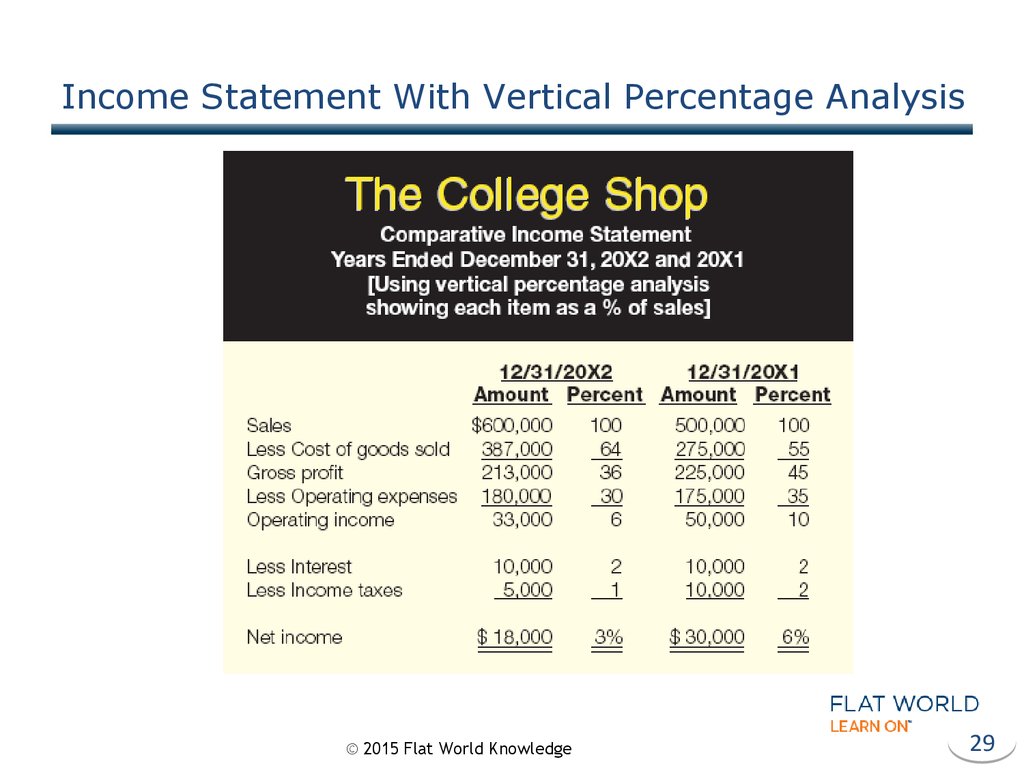
28. Comparative Income Statement
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge28
29. Income Statement With Vertical Percentage Analysis
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge29
30. Ratio Analysis
• Profit MarginHow much of each sales dollar is left after certain costs have
been covered
• Management Efficiency
measure a company's ability to use its assets and manage its
liabilities
• Management Effectiveness
How well the company is performing with the invested money
• Financial Condition
Assess firm’s financial strength
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
30
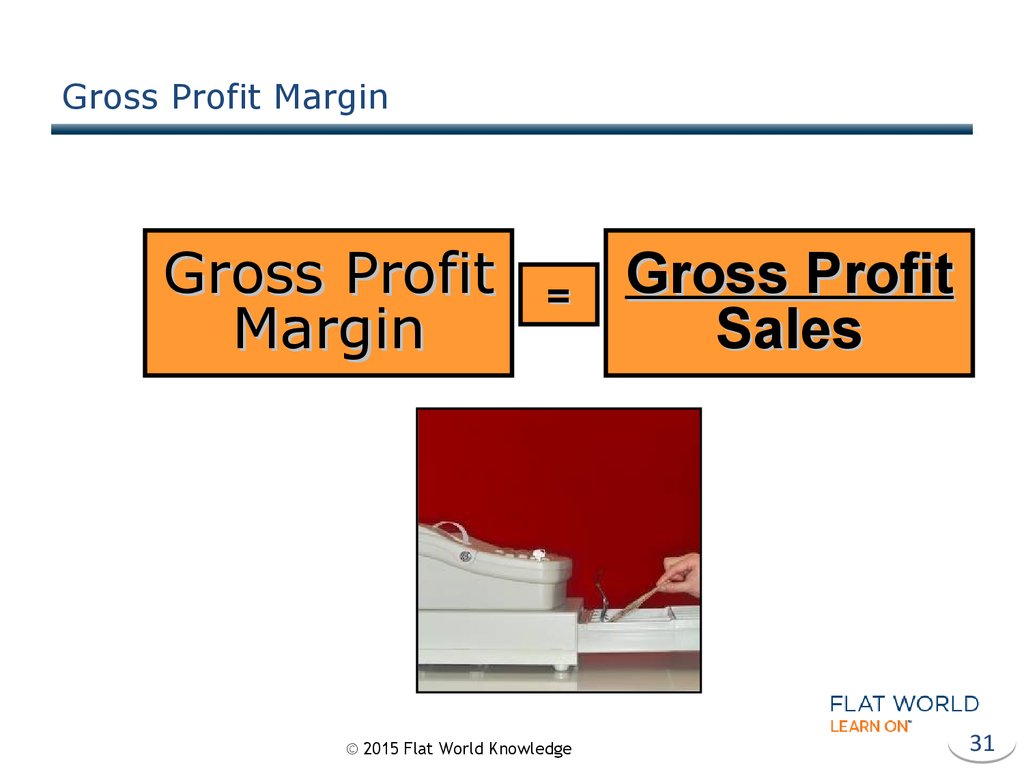
31. Gross Profit Margin
Gross ProfitMargin
=
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
Gross Profit
Sales
31
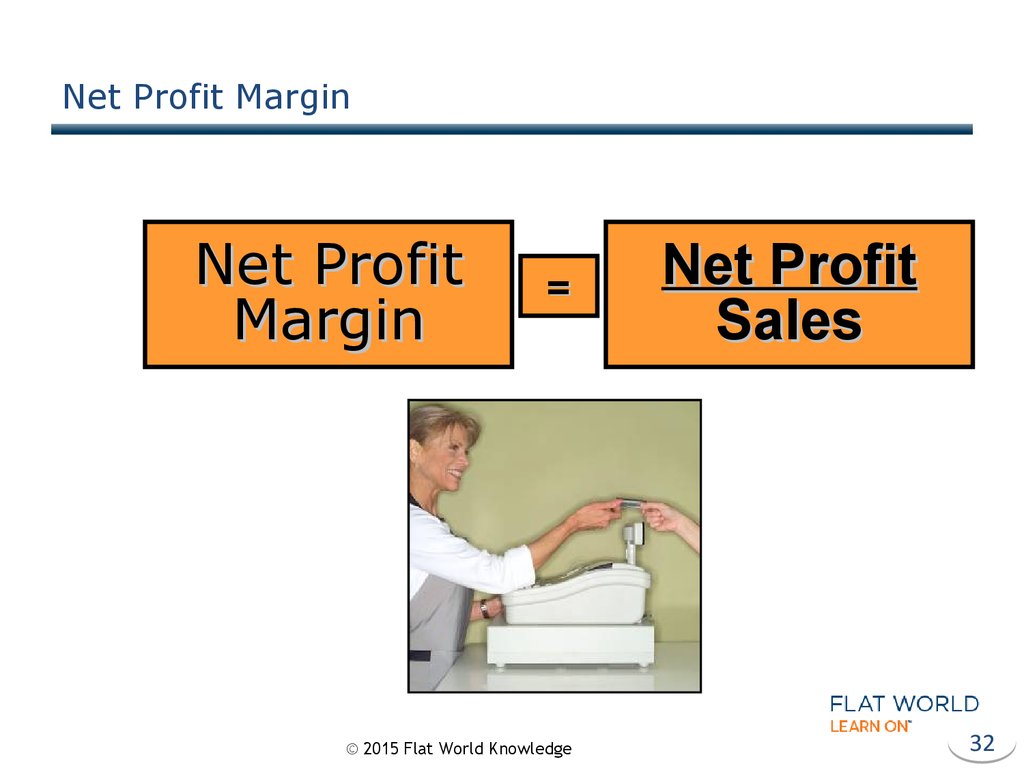
32. Net Profit Margin
Net ProfitMargin
=
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
Net Profit
Sales
32
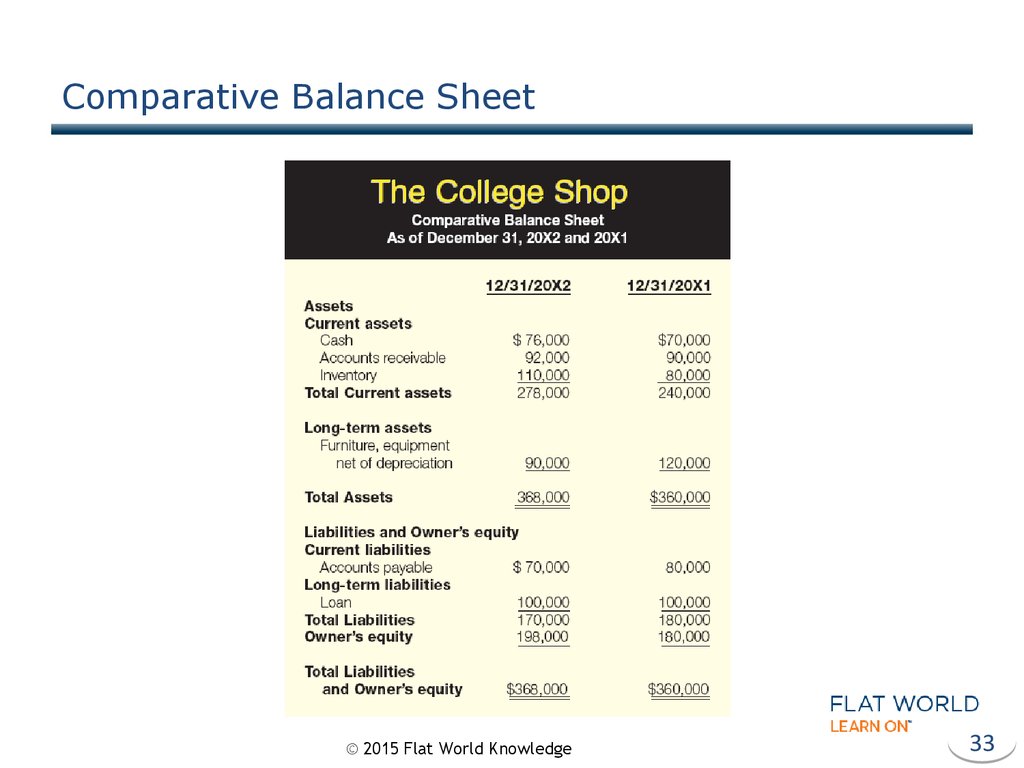
33. Comparative Balance Sheet
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge33
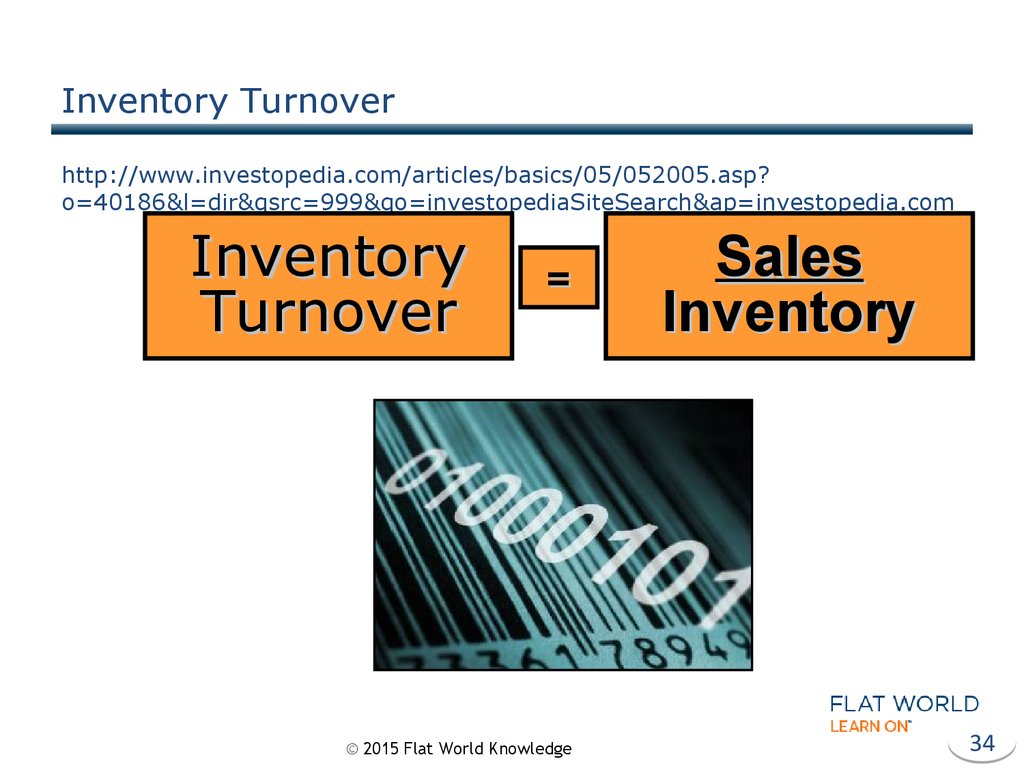
34. Inventory Turnover http://www.investopedia.com/articles/basics/05/052005.asp?o=40186&l=dir&qsrc=999&qo=investopediaSiteSearch&ap=investopedia.com
Inventory Turnoverhttp://www.investopedia.com/articles/basics/05/052005.asp?
o=40186&l=dir&qsrc=999&qo=investopediaSiteSearch&ap=investopedia.com
Inventory
Turnover
=
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
Sales
Inventory
34
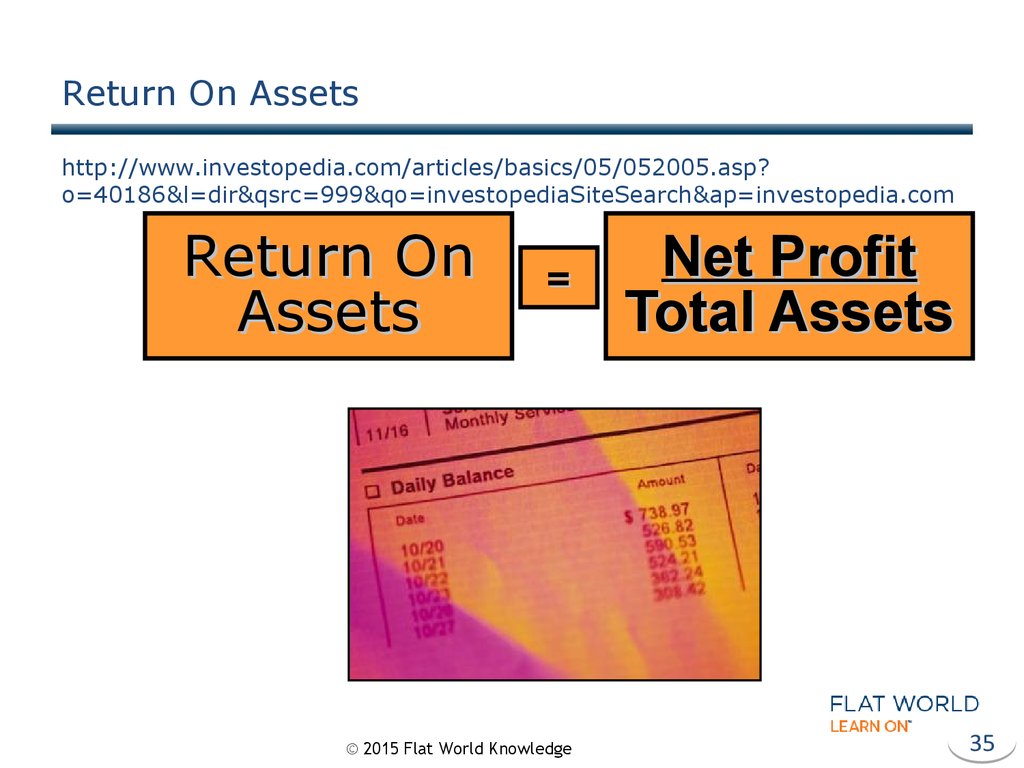
35. Return On Assets http://www.investopedia.com/articles/basics/05/052005.asp?o=40186&l=dir&qsrc=999&qo=investopediaSiteSearch&ap=investopedia.com
Return On Assetshttp://www.investopedia.com/articles/basics/05/052005.asp?
o=40186&l=dir&qsrc=999&qo=investopediaSiteSearch&ap=investopedia.com
Return On
Assets
=
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
Net Profit
Total Assets
35
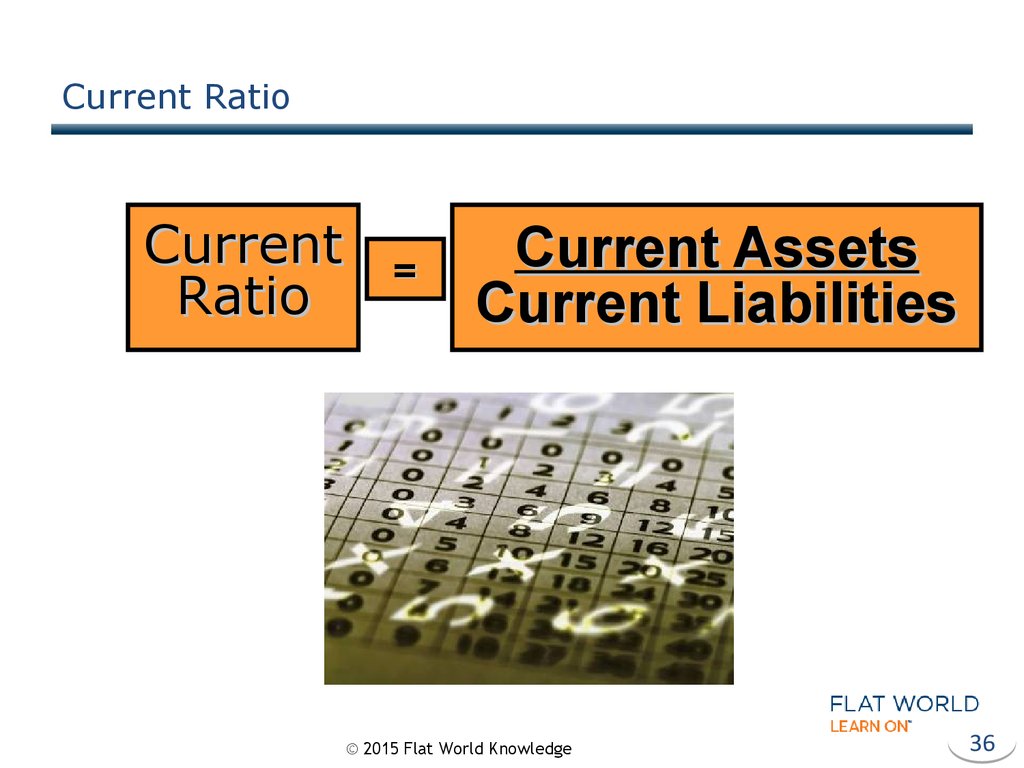
36. Current Ratio
CurrentRatio
=
Current Assets
Current Liabilities
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
36
37. Debt-To-Equity
Total Debtto Equity
=
Total Liabilities
Total Equity
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
37
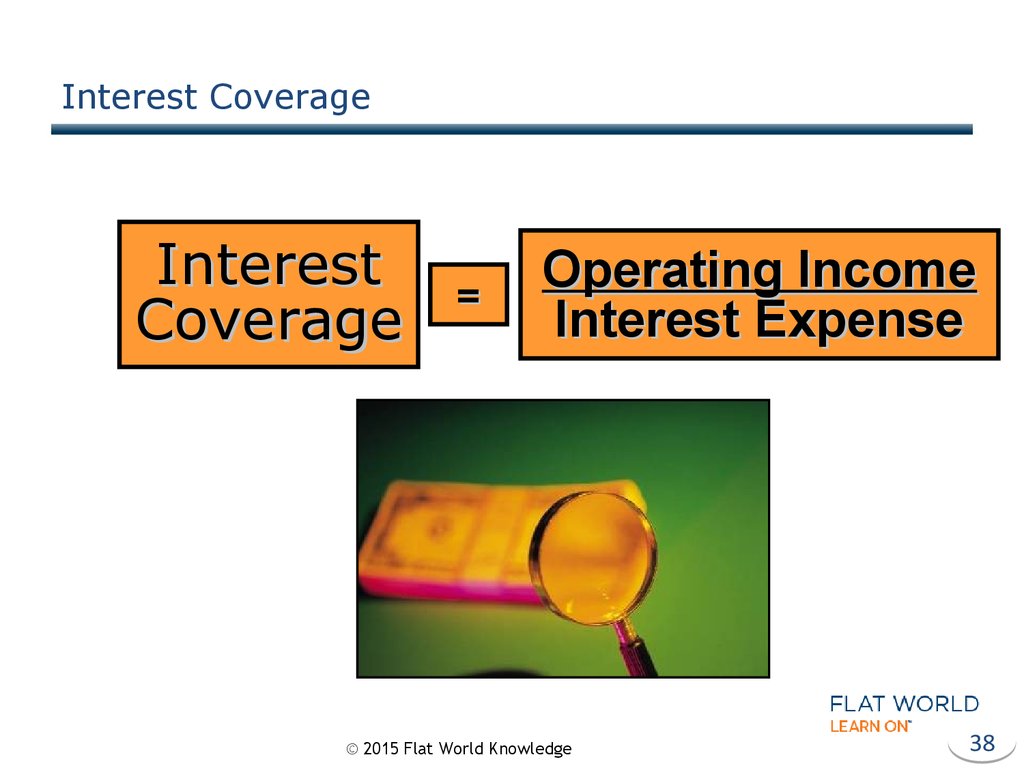
38. Interest Coverage
InterestCoverage
=
Operating Income
Interest Expense
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
38
39. In class activity: What Are Our Ratios Trying to Tell Us?
The accountant for your company just ran into theoffice and told you that your gross profit margin
increased while your net profit margin decreased.
She also reported that while our debt-to-equity
ratio increased, our interest coverage ratio
decreased.
She was puzzled by the apparent inconsistencies.
Help her out by providing possible explanations for
the behavior of these ratios.
© 2015 Flat World Knowledge
39























 Менеджмент
Менеджмент








