Похожие презентации:
Parodontosis (periodontal disease)
1. KARAGANDA STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY.
Report: Parodontosis.Made by: Belostockiy A.I.
Karagandy,2016.
2.
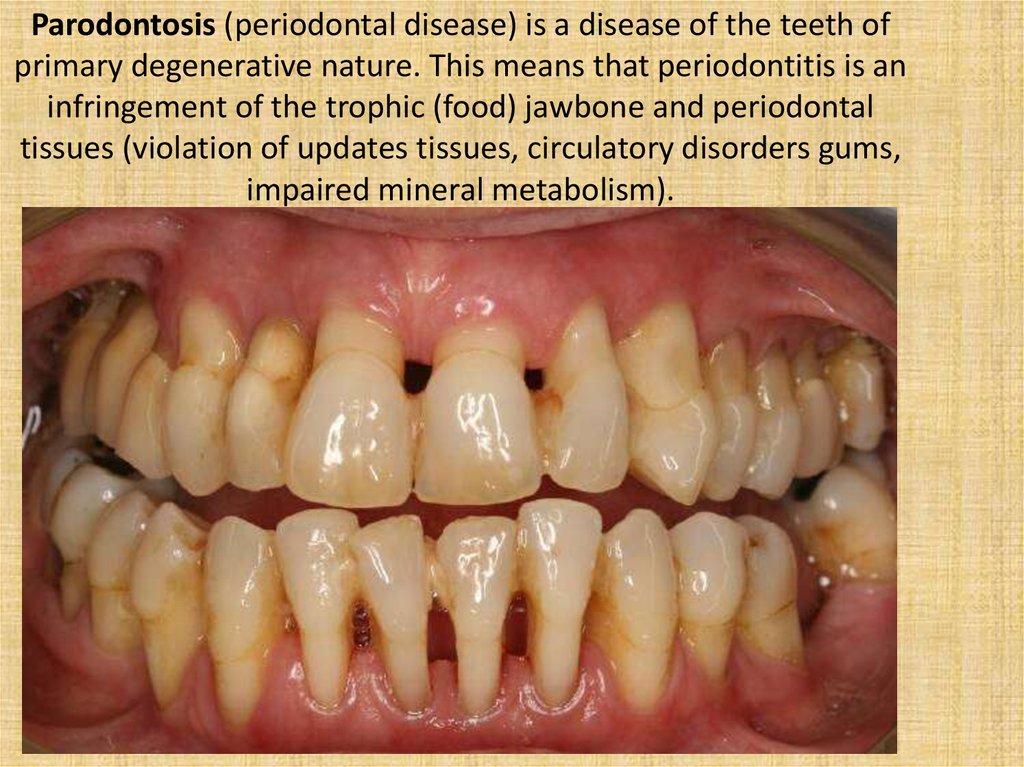
Parodontosis (periodontal disease) is a disease of the teeth ofprimary degenerative nature. This means that periodontitis is an
infringement of the trophic (food) jawbone and periodontal
tissues (violation of updates tissues, circulatory disorders gums,
impaired mineral metabolism).
3.
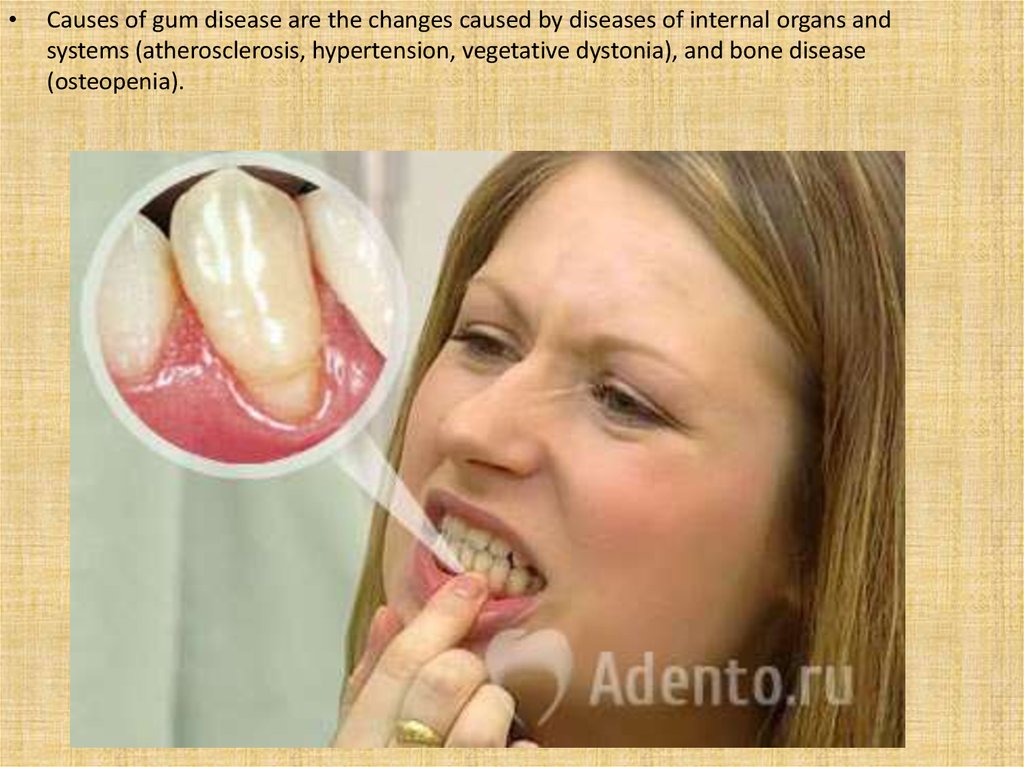
Causes of gum disease are the changes caused by diseases of internal organs and
systems (atherosclerosis, hypertension, vegetative dystonia), and bone disease
(osteopenia).
4.
Periodontal disease is uncommon (5-10% of cases). Periodontal disease does not
cause pain and other sensations, so patients usually do not seek medical attention.
5.
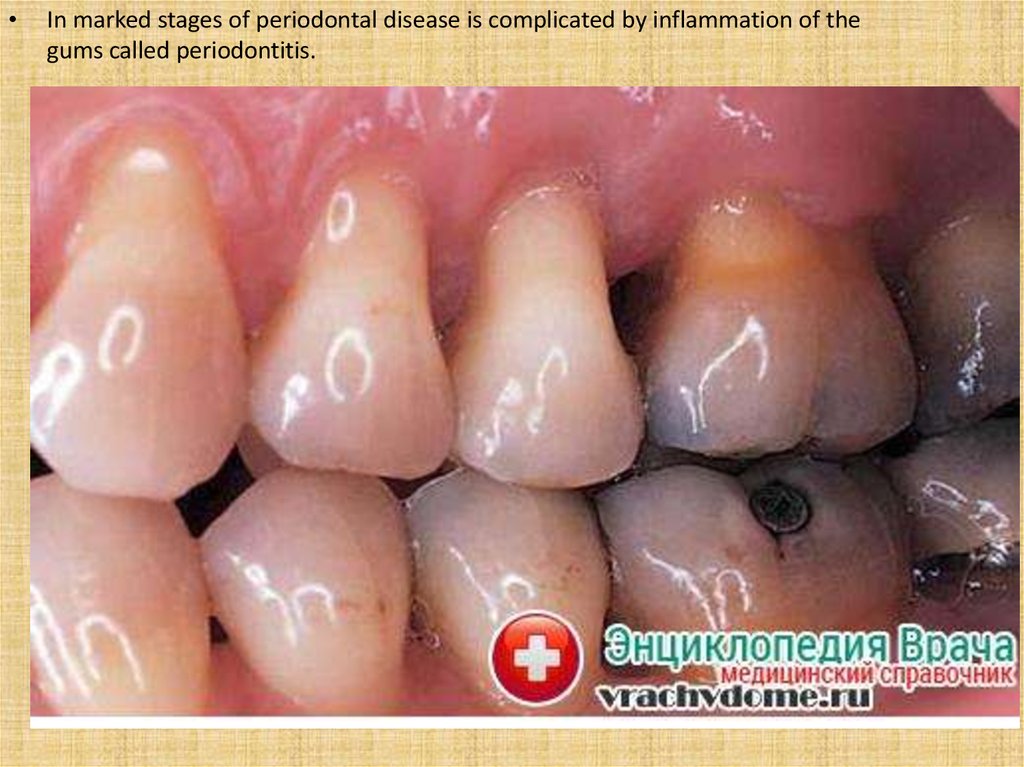
In marked stages of periodontal disease is complicated by inflammation of the
gums called periodontitis.
6.
• Clinical symptoms of periodontitis areinexpressive. Periodontal disease develops
slowly, a long time without showing
themselves.
7.
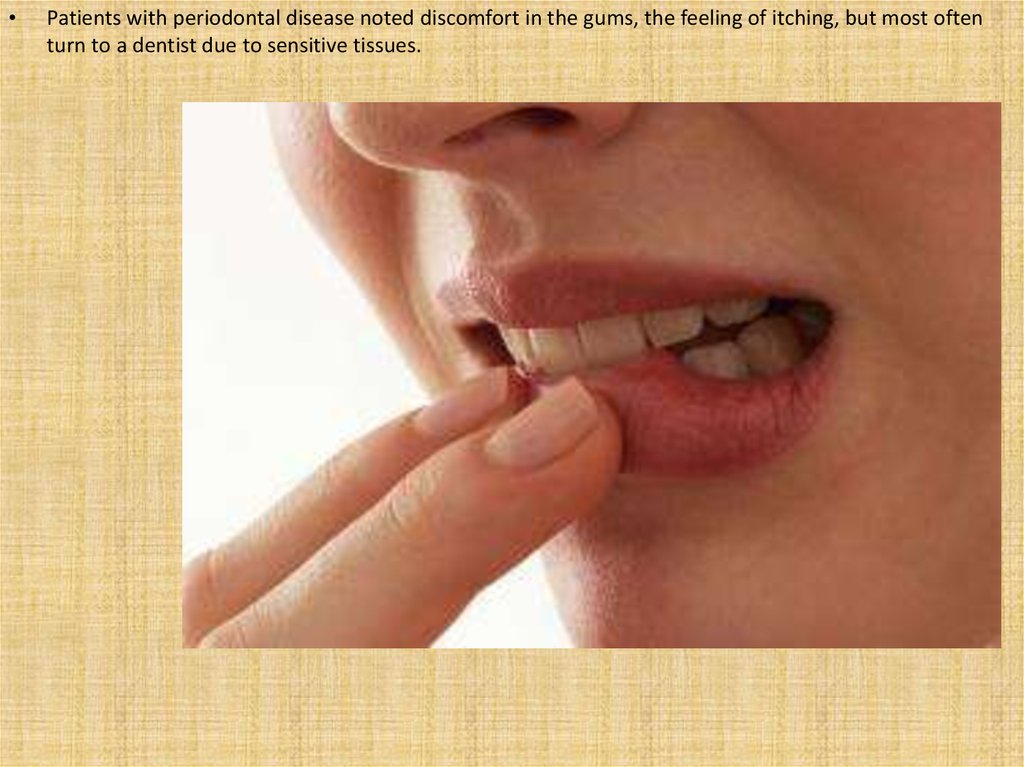
Patients with periodontal disease noted discomfort in the gums, the feeling of itching, but most often
turn to a dentist due to sensitive tissues.
8. Signs of periodontal disease
• pale staining of the gums, no signs of inflammation;• retraction of the gums to expose the neck of the tooth, and then
the tooth root, it looks like the “elongation” of the tooth;
• no bleeding gums;
• periodontal disease may be associated with lesions of non-carious
tooth tissue type – erosion of the enamel of wear of the tooth,
wedge-shaped defect;
• with periodontitis often present diseases of the cardiovascular
system, endocrine and metabolic disorders.
9.
• TreatmentThe treatment of parodontitis depends on the stage of
the disease:
• First the dentist carefully removes all causes for the
inflammation, e.g. removes plaques and tartar.
• The next step is to evenly distribute the load for the
whole set of teeth. This often requires slightly grinding
some teeth so that the masticatory surfaces fit well into
one another.
• Missing teeth have to be substituted because a
complete set of teeth is essential for an even load.
• If the disease has reached an advanced stage existing
gingival and infrabony pockets are removed. To
accomplish this various methods have been developed.
• Teeth that are already loose can be stabilized by fixed
or removable dental splints.
10.
• Task III. Complete the sentences:• Parodontosis (periodontal disease) is a disease … of
the teeth of primary degenerative nature.
• Causes of gum disease are … the changes caused by
diseases of internal organs and systems
(atherosclerosis, hypertension, vegetative
dystonia), and bone disease (osteopenia).
• Clinical symptoms of periodontitis are …
inexpressive.
• Patients with periodontal disease noted …
discomfort in the gums, the feeling of itching, but
most often turn to a dentist due to sensitive
tissues.











 Английский язык
Английский язык








