Похожие презентации:
Child diseases. Pneumonia in infants
1.
Prepared by:Checked by:
Siyazova ZH.E 229GMF
Mukhametzhanova ZH.A
2.
Plan:Introduction.
The main part:
Causes.
Viral and Bacterial Pneumonia.
Symptoms.
Diagnosis.
Solutions.
Treatment.
Prevention.
Conclusion.
Literature.
3.
Introduction.If baby suffering from recurrent
fever, cough or has difficulty in
breathing? If yes, then do get the baby
examined by a pediatrician
immediately, as these might be the
symptoms of pneumonia. This article
elucidates a few more symptoms,
causes and relative treatments for the
same.
4.
The main part.Causes.
Babies develop this disease when they have respiratory syncytial
virus infection or if they are infected with Group B Streptococcus,
which might be passed on to the baby from the mother during a
vaginal birth.
The reasons for bacterial pneumonia include Streptococcus
pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus and Chlamydia pneumoniae.
5.
Viral pneumonia is caused due to parainfluenza virus, the flu virusand adenovirus.
Anything that affects the baby's bronchial tubes may also result in
this disease. If the mother suffers from this disease, it can be
transmitted to the infant while breastfeeding or when coughing and
sneezing. Hence, it is very important to maintain proper hygiene.
6.
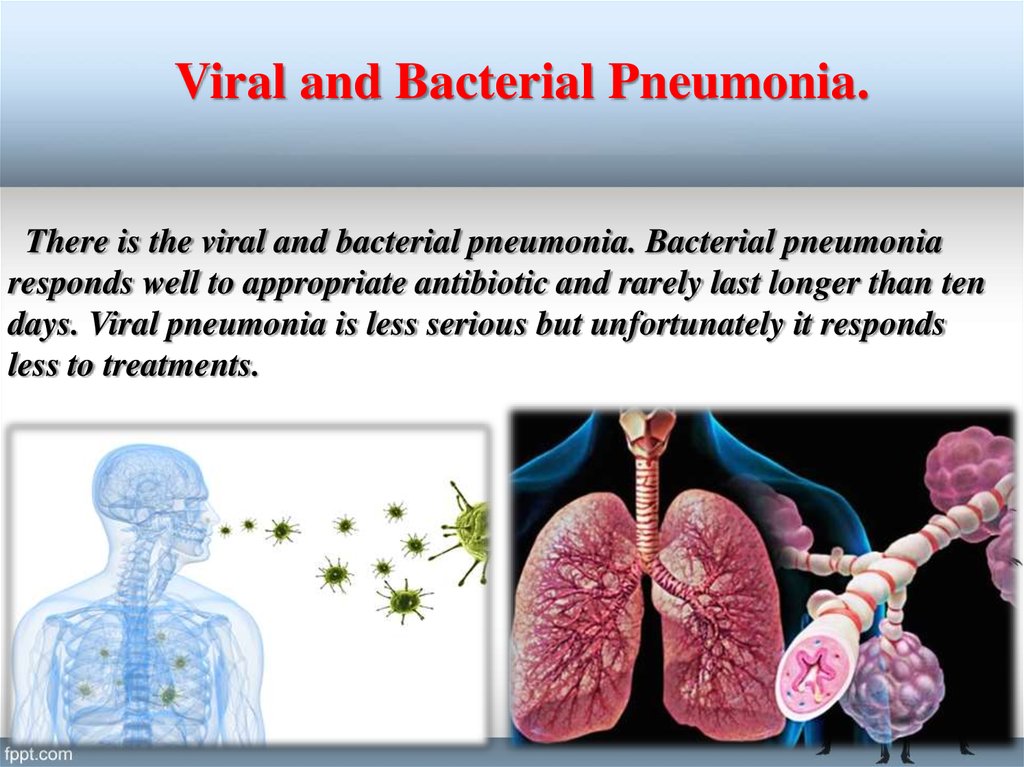
Viral and Bacterial Pneumonia.There is the viral and bacterial pneumonia. Bacterial pneumonia
responds well to appropriate antibiotic and rarely last longer than ten
days. Viral pneumonia is less serious but unfortunately it responds
less to treatments.
7.
Symptoms.The symptoms may vary and are identical to flu indications. Some of
the common signs are:
Relentless fever or cough;
Diarrhea;
Weakness;
Breathing difficulty;
Fever and severe chills;
8.
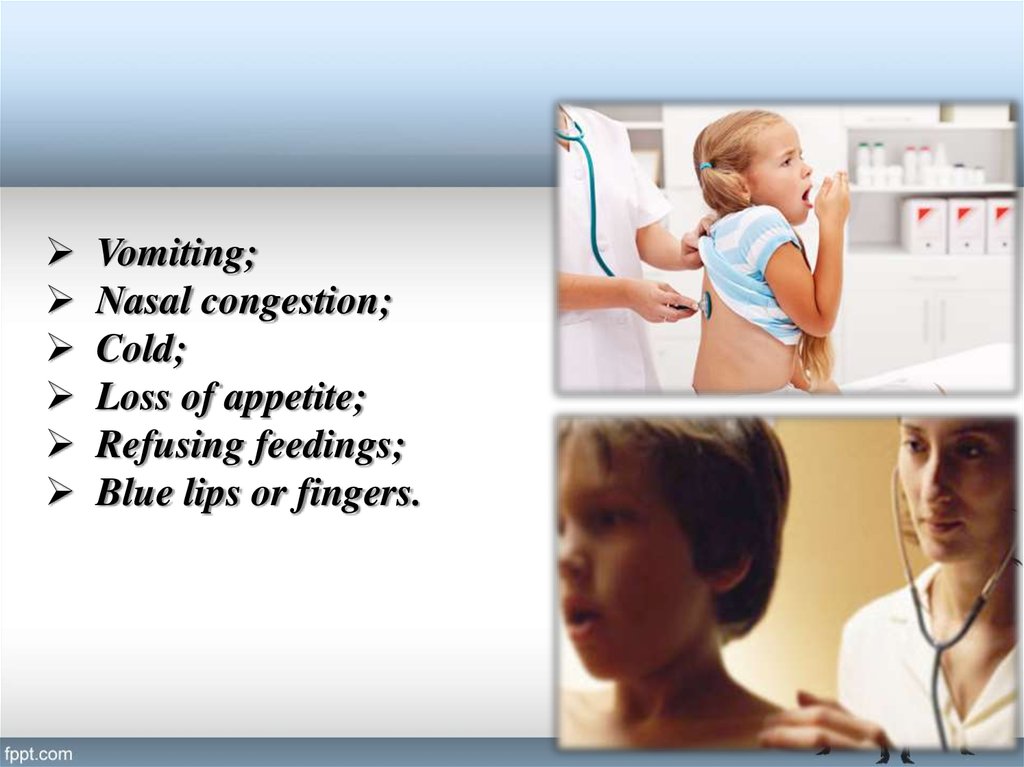
Vomiting;Nasal congestion;
Cold;
Loss of appetite;
Refusing feedings;
Blue lips or fingers.
9.
Diagnosis.The diagnosis is done depending on the type of pneumonia the infant
has. After noticing any of the above-mentioned symptoms in your
baby, make sure you immediately inform the pediatrician. He might
advise a full chest X-ray of the lungs, blood test, sputum test in
extreme cases, physical examination or identify the condition by
listening to the breathing sounds using a stethoscope.
10.
Solutions.The child must be taken to hospital immediately. This is
note the kind of disease that you may try the wait–and-see
if the child will feel better situation.
11.
Treatment.This lower respiratory tract respiratory disease needs a lot of care
and bed rest. The baby should be frequently fed with liquids to
prevent dehydration.
Antibiotics are prescribed in case of bacterial pneumonia but not
for the viral one, which is treated with ample rest and fluids.
12.
If the baby is facing difficulty while breathing, the doctor gives abronchodilator, a drug which relaxes and dilates the bronchial
passageways and improves the passages of air into the lungs.
In infants aged two months or younger or in severe cases,
hospitalization is recommended.
Apart from the baby, even the breastfeeding mother should follow a
healthy diet that is rich in vitamins A, C and E. This helps the baby
recover faster and build a stronger immune system.
13.
Prevention.o Key prevention measures include adequate nutrition and required
vaccinations.
o For protection against bacterial pneumonia, the baby should be
administered with pneumococcal vaccine. Pneumonia can be
prevented with the vaccines that are given for the prevention of
pertussis, measles and Haemophilus influenzae.
14.
o Reducing indoor pollution, not exposing the infants to smoking byothers and washing your hands before touching or going anywhere
close to the infant are a few other preventive measures.
o Avoid bringing out your baby in public if he/she is suffering from
even mild cold.
15.
Conclusion.Pneumonia kills countless children every year making it a very
dreaded disease to mothers. It is such as dangerous disease as it
affects the lungs and our lives depend on the continuous
functioning of the lungs. The lungs, unlike other body parts, can
not take a rest as they must function continuously. If the lungs can
not cope with the disease, then death is inevitable.














 Английский язык
Английский язык