Похожие презентации:
Модальные глаголы
1.
• Модальные глаголы являются одним из средстввыражения модальности в английском языке. Эти
глаголы обозначают не конкретные действия, а
выражают лишь отношение говорящего к действию.
С помощью модальных глаголов говорящий
показывает, что он считает то или иное действие
возможным, невозможным, вероятным,
необходимым, желательным и т.д. Поэтому
модальные глаголы не употребляются
самостоятельно, а только в сочетании с
инфинитивом смыслового глагола.
К модальным глаголам относятся can, could,
may, might, must, should, ought to, need и т.д.
2.
• Модальные глаголы отличаются от других глаголов не только своимзначением, но и системой грамматических форм. Модальные глаголы
являются недостаточными, дефектными глаголами (Defective Verbs). У них
отсутствует рад грамматических форм, которые имеют другие глаголы:
• 1.Модальные глаголы употребляются без частицы to: can, must (но не to can,
to must ).
• 2.Инфинитив смыслового глагола, следующий за модальным глаголом,
употребляется без частицы to.
You mustn’t phone now. It’s late.
I can translate this article.
3. В 3-ем лице единственного числа настоящего времени модальные глаголы
не имеют
окончания -s.
The doctor can see you now.
He should be more careful when driving a car.
• 4.Вопросительная и отрицательная формы предложений с модальными
глаголами образуются без вспомогательных глаголов. В вопросе модальный
глагол ставится перед подлежащим.
He cannot do it. You may not take it. He must not go there.
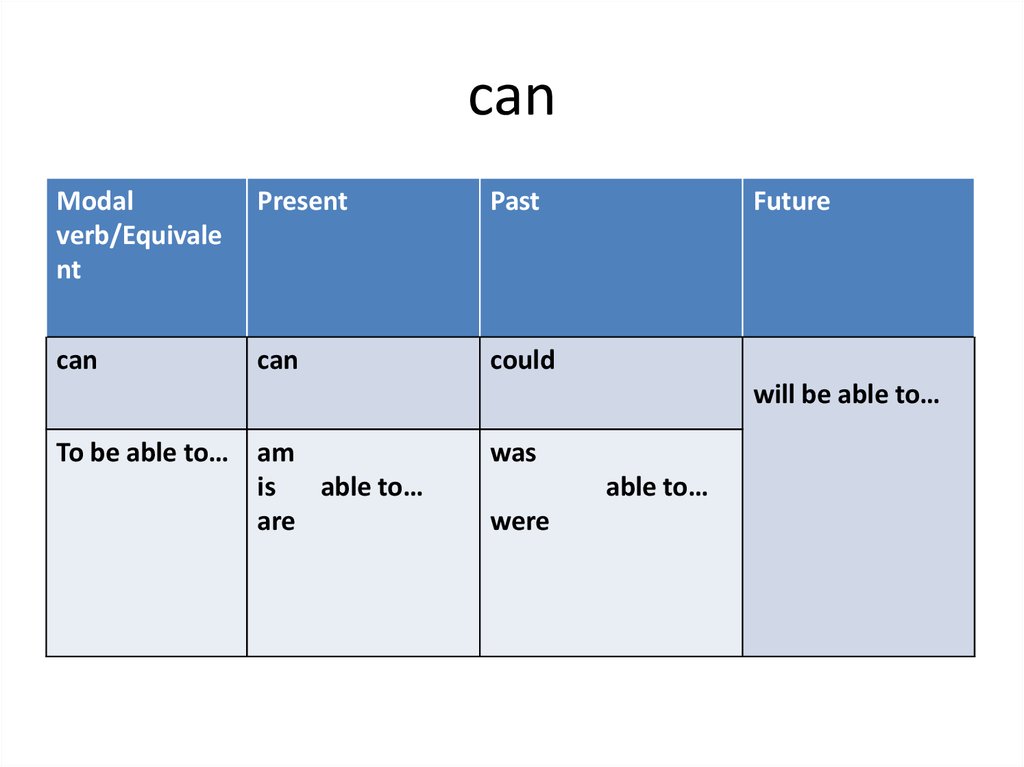
3. can
COULD / BE ABLE TO4. can
Modalverb/Equivale
nt
Present
Past
can
can
could
Future
will be able to…
To be able to… am
is
able to…
are
was
able to…
were
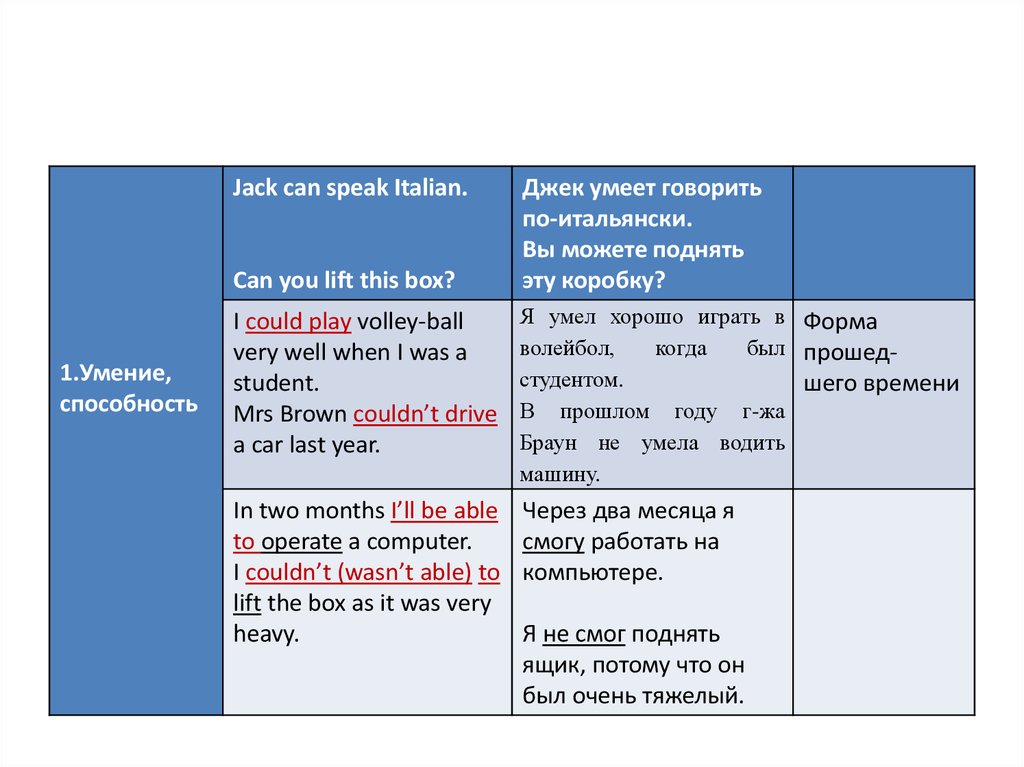
5.
Jack can speak Italian.Can you lift this box?
1.Умение,
способность
Джек умеет говорить
по-итальянски.
Вы можете поднять
эту коробку?
I could play volley-ball
very well when I was a
student.
Mrs Brown couldn’t drive
a car last year.
Я умел хорошо играть в Форма
волейбол,
когда
был прошедстудентом.
шего времени
В прошлом году г-жа
Браун не умела водить
машину.
In two months I’ll be able
to operate a computer.
I couldn’t (wasn’t able) to
lift the box as it was very
heavy.
Через два месяца я
смогу работать на
компьютере.
Я не смог поднять
ящик, потому что он
был очень тяжелый.
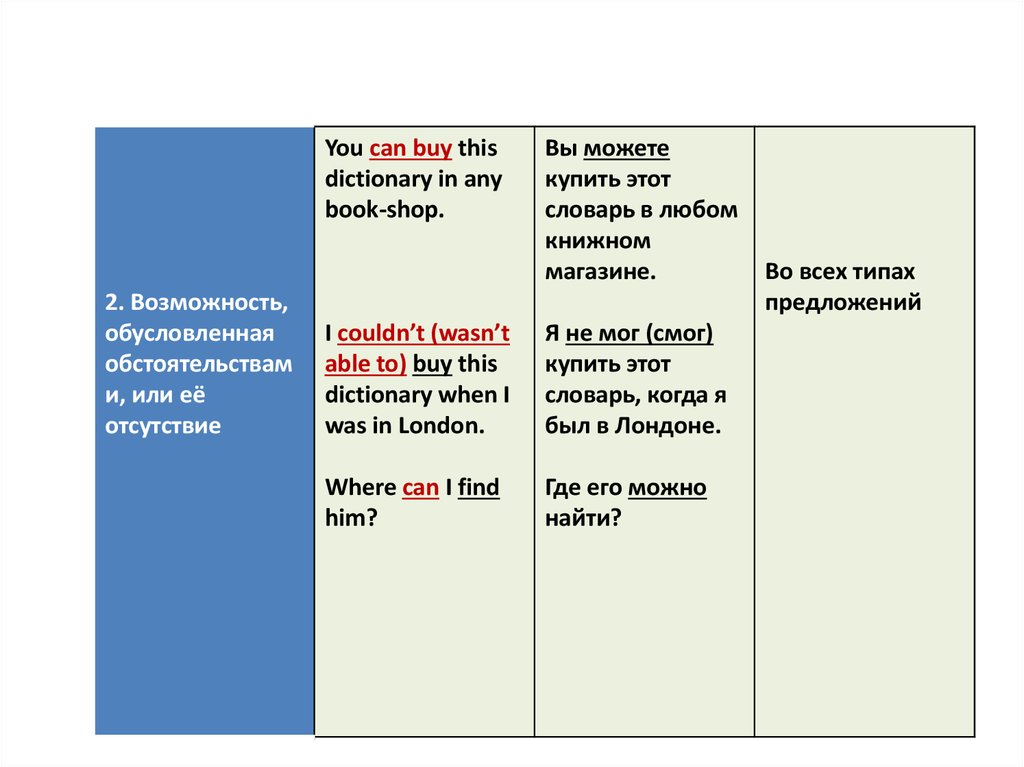
6.
You can buy thisdictionary in any
book-shop.
2. Возможность,
обусловленная
обстоятельствам
и, или её
отсутствие
Вы можете
купить этот
словарь в любом
книжном
магазине.
I couldn’t (wasn’t
able to) buy this
dictionary when I
was in London.
Я не мог (смог)
купить этот
словарь, когда я
был в Лондоне.
Where can I find
him?
Где его можно
найти?
Во всех типах
предложений
7.
3. а) Просьба;Can you go
(неофициальная shopping, Jack?
)
Could you do me
a favour?
Ты можешь
сходить за
покупками,
Джек?
Не могли бы вы
сделать мне
одолжение?
б) обращение за
разрешением;
Can I take your
umbrella today?
Можно мне
сегодня взять твой
зонтик?
с) разрешение
(неофициальное)
You can take my
mower.
Можешь взять
мою
газонокосилку.
Более вежливая форма
8.
4.You can’t use
Запрещение my dictionary
(неофициаль today.
ное)
You can’t
smoke here.
Я не могу
дать тебе
сегодня свой
словарь.
Здесь нельзя
курить.
9.
5. Сомнение,удивление,
недоверие
Can it be true?
Can he be working
now?
Could he have lost
his passport?
It can’t be true.
He can’t be
working now.
He couldn’t have
lost his passport.
Неужели это
правда?
Неужели он
сейчас работает?
В вопр. и отриц.
предложениях с различными формами инфинитива.
Неужели он
потерял свой
паспорт?
Не может быть,
что это правда.
Не может быть,
что он сейчас
работает.
Не может быть,
что он потерял
свой паспорт.
Форма could
усиливает
степень сомнения, удивления, недоверия.
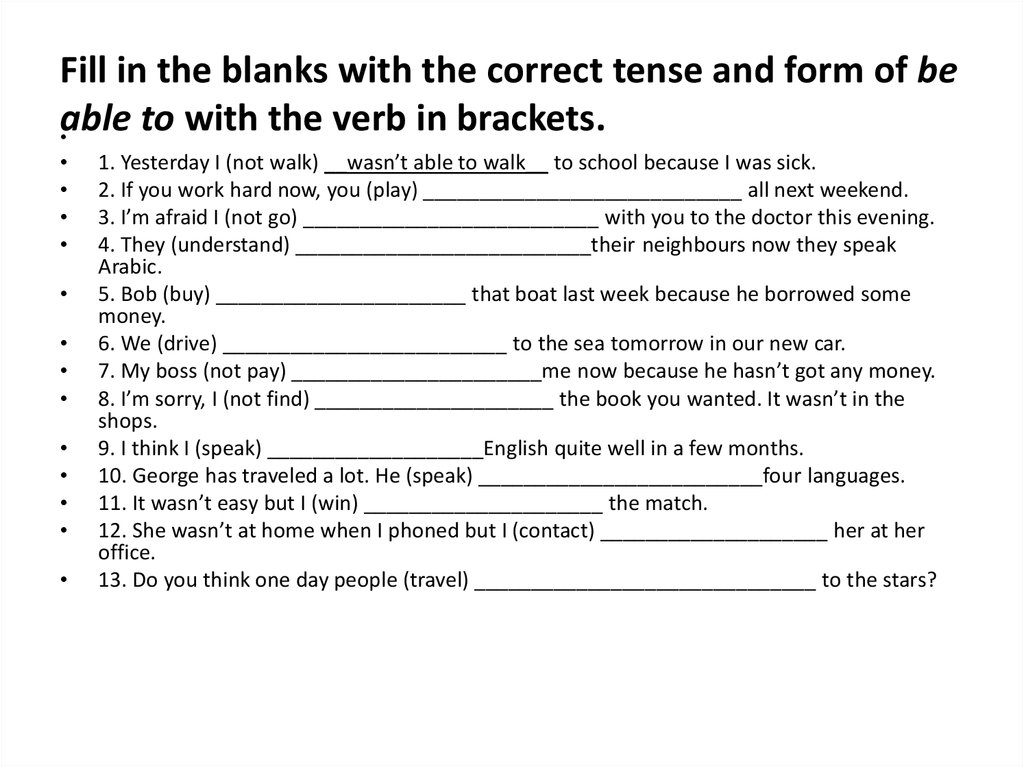
10. Fill in the blanks with the correct tense and form of be able to with the verb in brackets.
1. Yesterday I (not walk) __wasn’t able to walk__ to school because I was sick.
2. If you work hard now, you (play) ____________________________ all next weekend.
3. I’m afraid I (not go) __________________________ with you to the doctor this evening.
4. They (understand) __________________________their neighbours now they speak
Arabic.
5. Bob (buy) ______________________ that boat last week because he borrowed some
money.
6. We (drive) _________________________ to the sea tomorrow in our new car.
7. My boss (not pay) ______________________me now because he hasn’t got any money.
8. I’m sorry, I (not find) _____________________ the book you wanted. It wasn’t in the
shops.
9. I think I (speak) ___________________English quite well in a few months.
10. George has traveled a lot. He (speak) _________________________four languages.
11. It wasn’t easy but I (win) _____________________ the match.
12. She wasn’t at home when I phoned but I (contact) ____________________ her at her
office.
13. Do you think one day people (travel) ______________________________ to the stars?
11. CAN – to express doubt or strong astonishment Can he know Chinese so well? Неужели он так хорошо знает китайский язык?
Can/could he have forgottenНеужели он забыл попрощаться?
to say good-bye?
He can’t study at University.
Не может быть, что он учится в университете.
He can’t (couldn’t) have lost his passport. Не может быть, чтобы он потерял паспорт.
Translate into English
1. Не может быть, чтобы он опоздал.
2. Он не мог прочитать эту книгу так быстро; она трудна для него.
3. Не мог он этого сказать.
4. Неужели было так холодно?
5. Не может быть, чтобы он потерял эти документы.
6. Неужели они проиграли?
7. Не может быть, чтобы он был дома сейчас.
8. Неужели это маленькая Лизи? Как она выросла.
9. Неужели он твой брат?
10. Неужели вы не помните, что я вернул вам эту книгу?
10. Не может быть, чтобы эта команда выиграла матч.
11. Не может быть, чтобы она провалилась на экзамене.
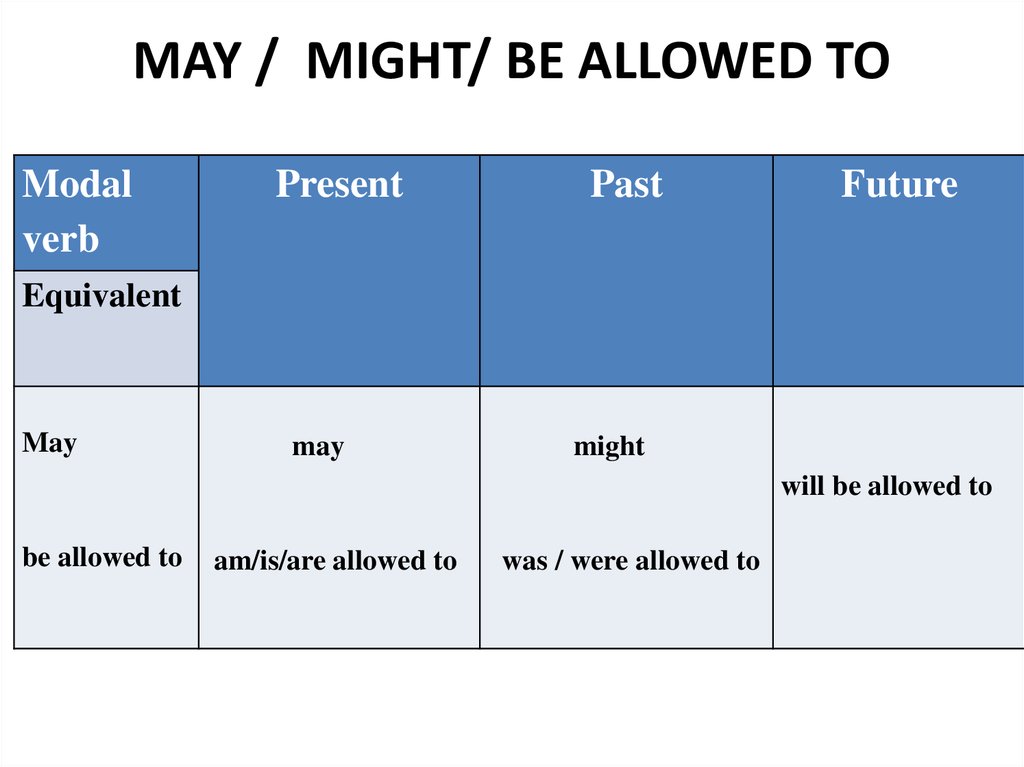
12. May
MIGHT/ BE ALLOWED TO13. MAY / MIGHT/ BE ALLOWED TO
Modalverb
Present
Past
Future
Equivalent
May
may
might
will be allowed to
be allowed to
am/is/are allowed to
was / were allowed to
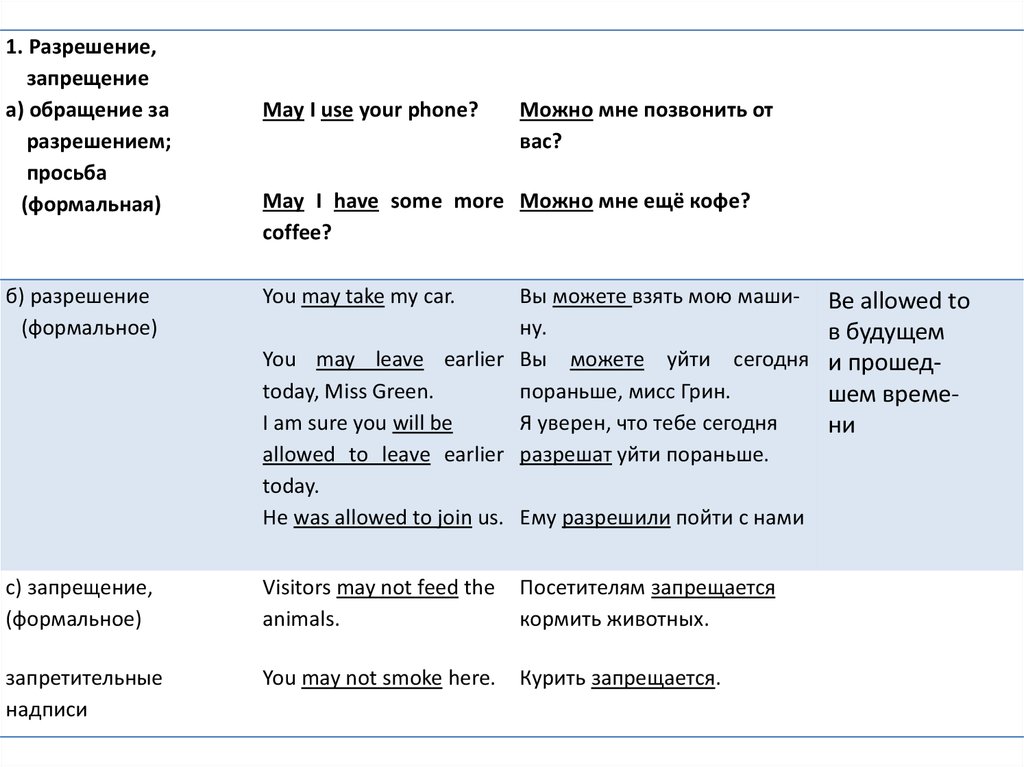
14.
1. Разрешение,запрещение
а) обращение за
разрешением;
просьба
(формальная)
May I use your phone?
Можно мне позвонить от
вас?
May I have some more Можно мне ещё кофе?
coffee?
б) разрешение
(формальное)
You may take my car.
Вы можете взять мою машину.
You may leave earlier Вы можете уйти сегодня
today, Miss Green.
пораньше, мисс Грин.
I am sure you will be
Я уверен, что тебе сегодня
allowed to leave earlier разрешат уйти пораньше.
today.
He was allowed to join us. Ему разрешили пойти с нами
с) запрещение,
(формальное)
Visitors may not feed the
animals.
Посетителям запрещается
кормить животных.
запретительные
надписи
You may not smoke here.
Курить запрещается.
Be allowed to
в будущем
и прошедшем времени
15.
2. Конкретнаявозможность
We may go to Italy this Мы можем поехать
summer.
(возможно поедем) в Италию
этим летом.
Jane may not like these Джейн могут не понравиться
flowers.
эти цветы.
3. Предположение с оттенком
неуверенности,
сомнения
He may be in the
library now.
He may not know
anything about it.
He may be working
now.
He may have forgotten
to post the letter.
They might have
wanted to tell you
something important.
Возможно, он сейчас в библиотеке.
Может быть, он ничего не
знает об этом.
Возможно, он сейчас работает.
Может быть, (возможно),
он забыл отправить письмо.
Возможно, они хотели сказать тебе что-то важное.
В утверд. и
отрицат.
предложениях со
всеми
формами инфинитива
mightменее
вероятно,
чем may
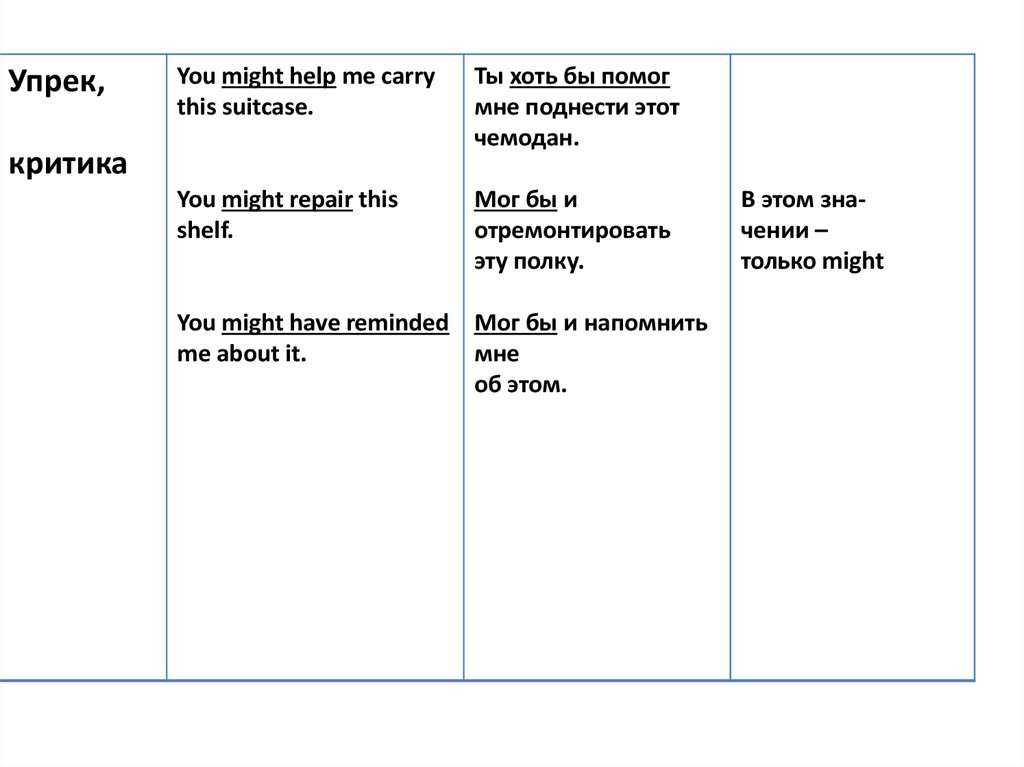
16.
Упрек,You might help me carry
this suitcase.
Ты хоть бы помог
мне поднести этот
чемодан.
You might repair this
shelf.
Мог бы и
отремонтировать
эту полку.
критика
You might have reminded Мог бы и напомнить
me about it.
мне
об этом.
В этом значении –
только might
17. Write five possibilities and say why you want to do them.
Example: I may go to Egypt because I want to see the pyramids.
1
___________________________________________________________________________
2
___________________________________________________________________________
3
___________________________________________________________________________
4
___________________________________________________________________________
5
___________________________________________________________________________
18. Think about next weekend. Say what you might or might not do if …
1 …it’s raining
4 …it’s sunny
2 …it’s snowing 5 …you have work to do
3 …it’s cold
6 …you feel tired
Example: I might stay at home and watch TV.
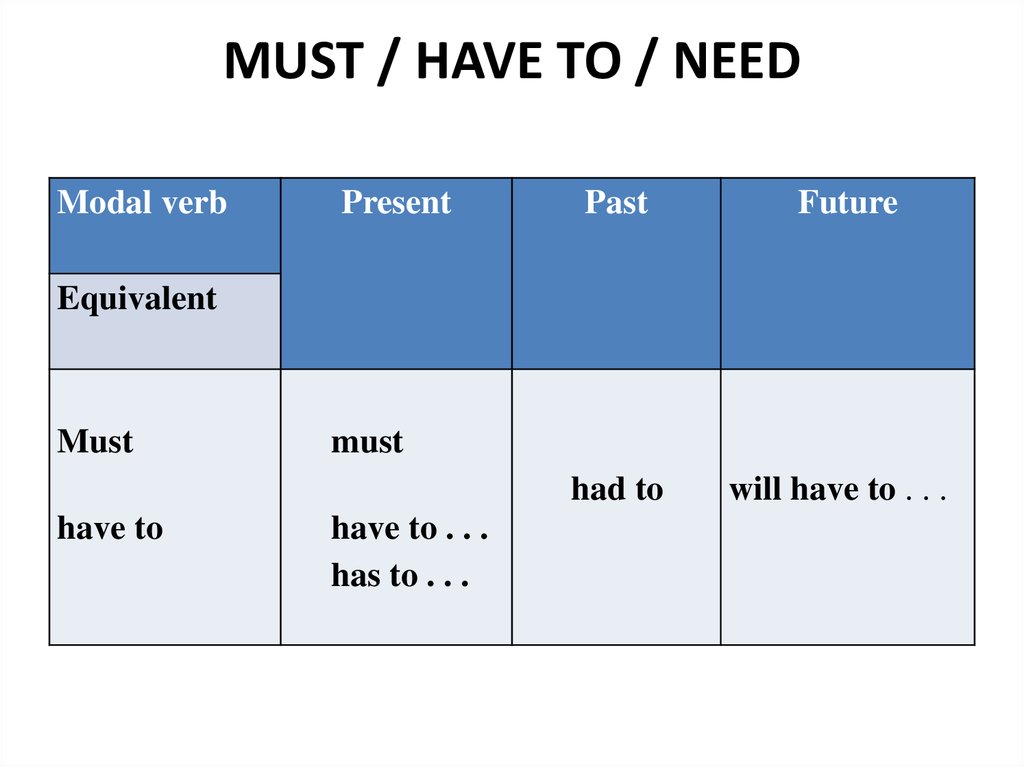
19. MUST
HAVE TO / NEED20. MUST / HAVE TO / NEED
Modal verbPresent
Past
Future
had to
will have to . . .
Equivalent
Must
have to
must
have to . . .
has to . . .
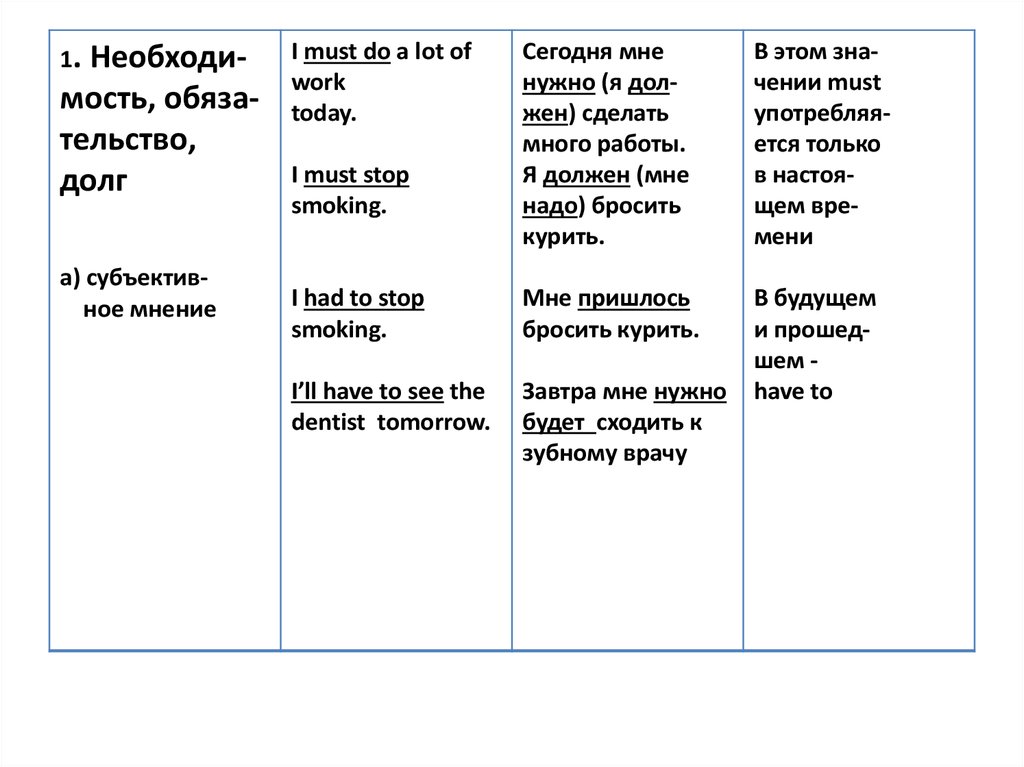
21.
1. Необходи-мость, обязательство,
долг
а) субъективное мнение
I must do a lot of
work
today.
Сегодня мне
нужно (я должен) сделать
много работы.
Я должен (мне
надо) бросить
курить.
В этом значении must
употребляяется только
в настоящем времени
I had to stop
smoking.
Мне пришлось
бросить курить.
I’ll have to see the
dentist tomorrow.
Завтра мне нужно
будет сходить к
зубному врачу
В будущем
и прошедшем have to
I must stop
smoking.
22.
b) Объективновызванная
необходимость
нужда
Mr. Brown has to work
hard to keep his
garden in good
condition.
Г-ну Брауну
приходится
много работать,
чтобы
поддерживать сад
в хорошем
состоянии.
Jack had to get up very Джеку
early because he lived приходилось рано
a long way from the
вставать, потому
university.
что он жил
далеко от
университета.
I’ll have to stay at
home
because my son has
fallen ill.
Мне придется (я
должна)
остаться дома,
потому что
у меня заболел
сын.
Sue doesn’t have to
Сью не нужно
get up early
завтра рано
tomorrow. It’s her day- вставать. У нее
off.
выходной
В этом значении употребляется
have to во
всех типах
предложений в
настоящем,
прошедшем
и будущем
времен
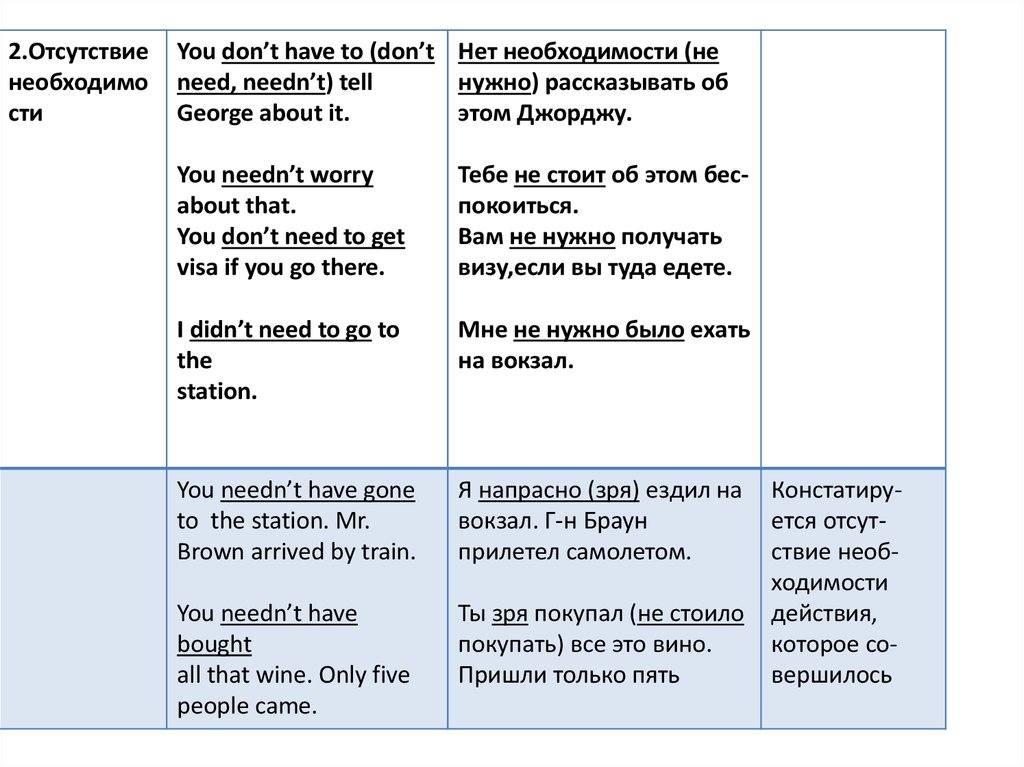
23.
2.Отсутствиенеобходимо
сти
You don’t have to (don’t Нет необходимости (не
need, needn’t) tell
нужно) рассказывать об
George about it.
этом Джорджу.
You needn’t worry
about that.
You don’t need to get
visa if you go there.
Тебе не стоит об этом беспокоиться.
Вам не нужно получать
визу,если вы туда едете.
I didn’t need to go to
the
station.
Мне не нужно было ехать
на вокзал.
You needn’t have gone
to the station. Mr.
Brown arrived by train.
Я напрасно (зря) ездил на
вокзал. Г-н Браун
прилетел самолетом.
You needn’t have
bought
all that wine. Only five
people came.
Ты зря покупал (не стоило
покупать) все это вино.
Пришли только пять
Констатируется отсутствие необходимости
действия,
которое совершилось
24.
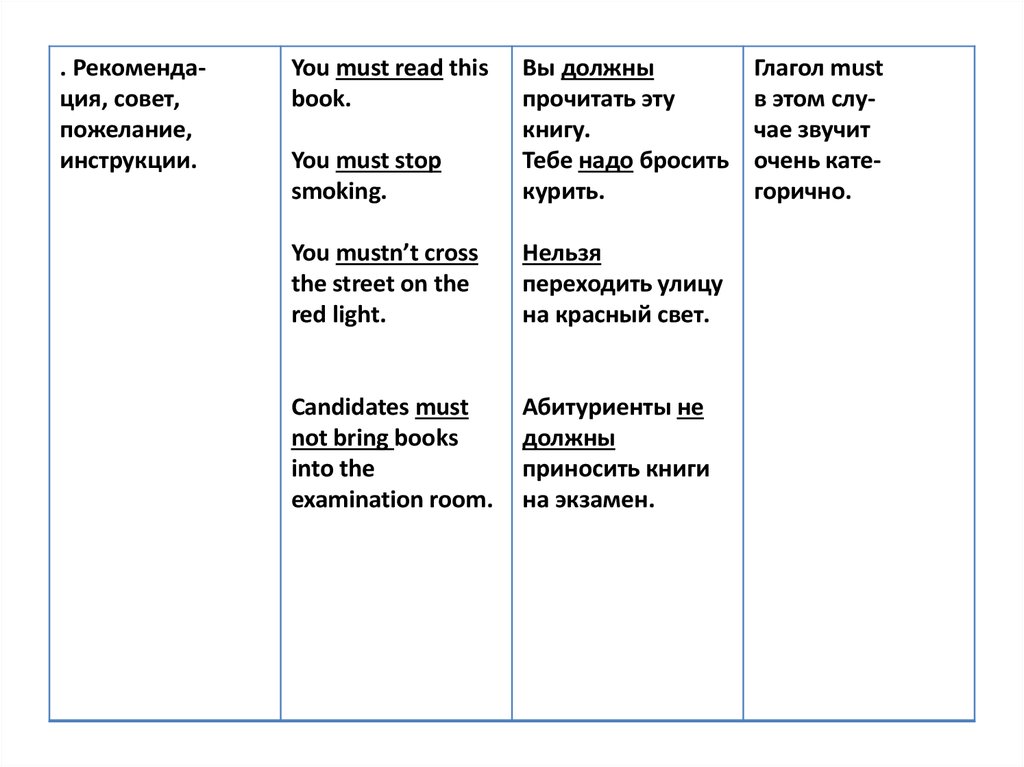
. Рекомендация, совет,пожелание,
инструкции.
You must read this
book.
You must stop
smoking.
Вы должны
прочитать эту
книгу.
Тебе надо бросить
курить.
You mustn’t cross
the street on the
red light.
Нельзя
переходить улицу
на красный свет.
Candidates must
not bring books
into the
examination room.
Абитуриенты не
должны
приносить книги
на экзамен.
Глагол must
в этом случае звучит
очень категорично.
25.
4. Нежеланиевыполнить
действие.
Must you go so
soon?
Must I finish this
work by
Friday?
5. Предположение, граничащее с уверенностью.
This house must be
very old.
Неужели вам
нужно так
скоро уходить?
Мне обязательно
нужно закончить эту работу
к пятнице?
Этот дом, должно
быть,очень старый.
Только в
вопросительных
предложениях.
Must в утв.
предложениях со всеBill must be
Билл, вероятно,
ми формаwatching television. смотрит телевизор. ми инфиRoger must have
Должно быть,
нитива
forgotten about his Роджер забыл
promise.
о своем обещании.
He must have gone Он, вероятно
to Rome.
(должно быть)
26. Complete the gaps in these sentences with a word or phrase from the box.
Complete the gaps in thesesentences with a word or
phrase from the box.
must
mustn’t (x2)
have to
don’t have to (x2)
had to
didn’t have to
1. You __________ smoke in the library.
2. It’s free to get in: you _______pay.
3. I missed my train and I _____ wait half an
hour for the next one.
4. It’s not a direct flight to New Zealand: you
______________ change planes at Bangkok.
5. There were only two people in front of me in
the queue so I ____________ wait long.
6. Don’t cry, Jessica – you ____________play
with John if you don’t want to.
7. Children ___________walk on the railway
line.
8. I ___________ remember to post this letter.
27. Fill in must, mustn’t, or needn’t as in the example.
28. Fill in must, mustn’t, or needn’t as in the example.
29.
MUST and MAY / MIGHT – to express
supposition
Не must be at home now.
Должно быть /вероятно, он сейчас
дома.
Combine the verb must with the proper
form of the infinitive in brackets.
1. She must (to be angry) with me. She
left without saying good-bye.
2. Mary must (to be ill), otherwise she
would have come.
3. It must (to be) a fearful shock to her. –
Indeed, it was.
4. The visitor was wearing an old style
greatcoat that must (to cost) a hundred
and fifty dollars.
5. The pianist is playing a piece that
hasn’t been announced. They must (to
change) the programme.
6. I’ll get your things out of the hotel. You
must not (to stay) here tonight.
7. He must (to take) a lot of photos when
he was on the island.
8. You haven’t eaten for hours. You must
(to be) hungry.
9. Mrs Cromwell took us round the yacht.
There was no doubt that it must (to cost)
her a lot of money.
10. “You must (to be) right,” I said.
He must have missed the train.
Должно быть /вероятно, он опоздал на
поезд.
He may be at his office now.
Может быть /возможно, он сейчас в
офисе.
He might be at his office now.
Может быть, он сейчас в офисе (хотя
едва ли).
He may /might have forgotten
everything.
Он, возможно, все забыл.
He may/might not have noticed you
Он, возможно, не заметил тебя в этой
толпе.
in that crowd.
30. SHOULD / OUGHT TO
31.
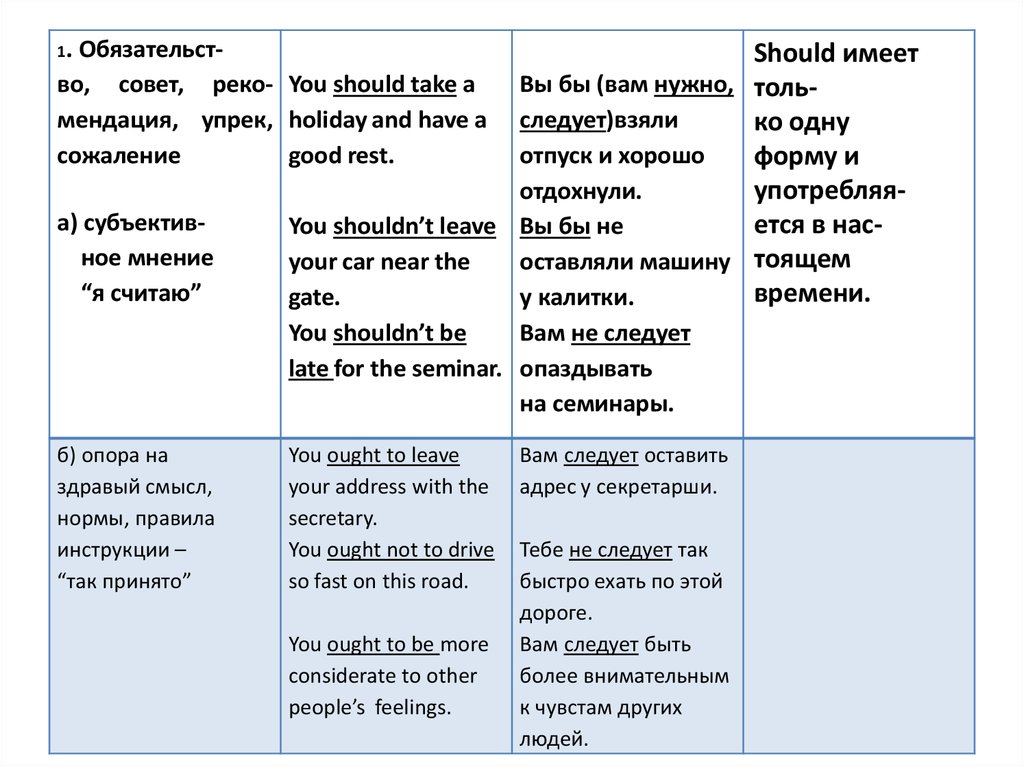
1.Обязательство, совет, реко- You should take a
мендация, упрек, holiday and have a
сожаление
good rest.
а) субъективное мнение
“я считаю”
Should имеет
Вы бы (вам нужно, тольследует)взяли
ко одну
отпуск и хорошо
форму и
отдохнули.
употребляяется в насYou shouldn’t leave Вы бы не
your car near the
оставляли машину тоящем
времени.
gate.
у калитки.
You shouldn’t be
Вам не следует
late for the seminar. опаздывать
на семинары.
б) опора на
здравый смысл,
нормы, правила
инструкции –
“так принято”
You ought to leave
your address with the
secretary.
You ought not to drive
so fast on this road.
You ought to be more
considerate to other
people’s feelings.
Вам следует оставить
адрес у секретарши.
Тебе не следует так
быстро ехать по этой
дороге.
Вам следует быть
более внимательным
к чувстам других
людей.
32.
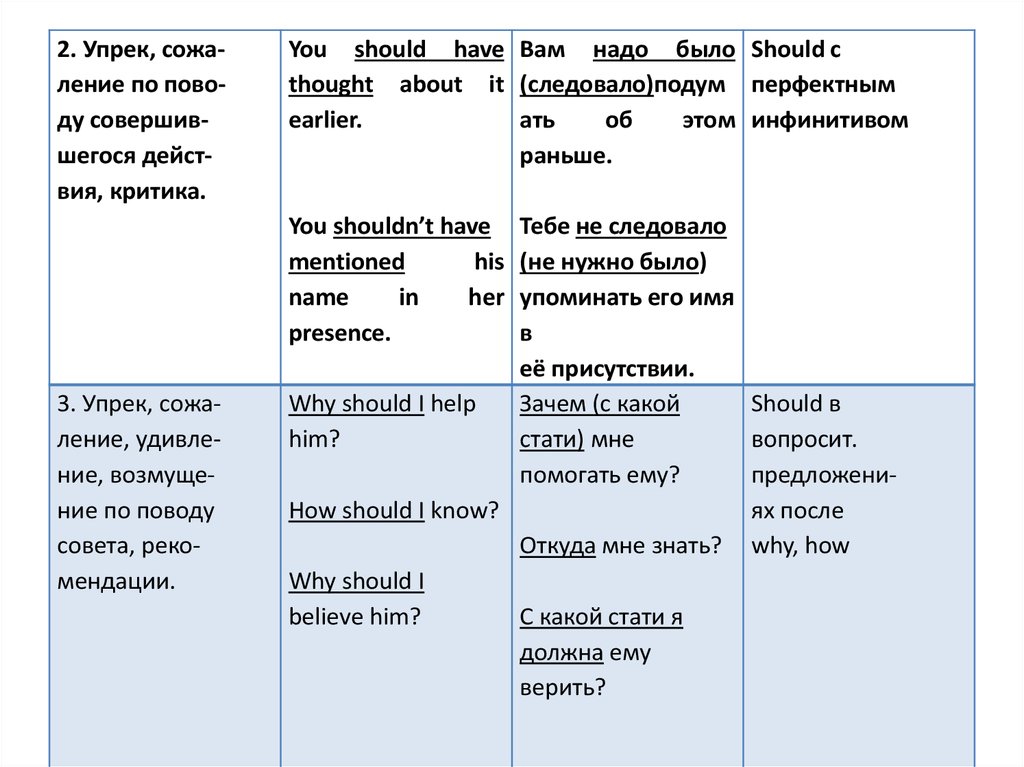
2. Упрек, сожаление по поводу совершившегося действия, критика.You should have Вам надо было Should с
thought about it (следовало)подум перфектным
earlier.
ать
об
этом инфинитивом
раньше.
You shouldn’t have
mentioned
his
name
in
her
presence.
3. Упрек, сожаление, удивление, возмущение по поводу
совета, рекомендации.
Тебе не следовало
(не нужно было)
упоминать его имя
в
её присутствии.
Why should I help
Зачем (с какой
Should в
him?
стати) мне
вопросит.
помогать ему?
предложениHow should I know?
ях после
Откуда мне знать? why, how
Why should I
believe him?
С какой стати я
должна ему
верить?
33. Problems Nick wants to be better at school. Trig wants to lose weight. Amanda wants to save money. What advice do you give
•ProblemsNick wants to be better at
school.
Trig wants to lose weight.
Amanda wants to save
money.
What advice do you give to
Nick, Trig and Amanda?
Write twelve sentences with
should or shouldn’t.
work harder in class
spend all your pocket money
drink Coke and fizzy drinks
eat bread and potatoes
eat salads and fruit
do little job for the neighbours
buy sweets and ice-cream
go babysitting
learn a little every day
spend so much on clothes
buy unnecessary things
do homework regularly
take more exercise
listen to the teacher
34. What advice would you give in the following situations? Use should.
1 Alan had a terrible quarrel with his wife at the weekend. It was his fault.
What do you think he should do? I think __he should apologise to his
wife.________
2 Lane watches videos every night. She never goes out with her friends.
What advice do you give? I think __________________________
3 David and Paula haven’t got much money. But they go out every night and
spend money. At the end of the month they can’t pay their gas and electricity bills.
What advice would you give?
I don’t think ___________________________________________________
4 Joseph is very intelligent, but he wants to leave school and get a job. His parents
think he
should go to university. What do you think?
I think ___________________________________________________
5 Maria told me some interesting news last night, but she said, “Please, don’t tell
anyone.” Now Claire has asked me about Maria’s news. What do you think I should
do?
I don’t think _____________________________________________________
35. Translate into English
• 1. When I was area manager, I could visit five customers a day.• 2. Only employees can buy products from the company shop.
• 3. This is a dander area. Employees may not enter this area without
protective clothing.
• 4. Next year we may launch a sales campaign in Japan.
• 5. May I make a comment at this point? – Yes, of course you may.
• 6. Many customers give to charity money that they might have
spent on themselves.
• 7. Changes in the quantity of money may or may not have an
influence on prices.
• 8. All the shareholders must receive an invitation to the meeting;
however, they needn’t attend.
• 9. These figures can’t be right. There must be a mistake
somewhere.
• 10. If you want my advice, you should find another supplier.





















 Английский язык
Английский язык








