Похожие презентации:
Language and linguistics
1. Language and Linguistics
Kazakh University of International Relations and WorldLanguages named after Abylai Khan
Teacher Training Department
Discipline: English for Specific Purposes
Language and Linguistics
2.
Contents:I. Language and Linguistics
1.1.Language and its definition;
1.2. Linguistics and its definition;
1.3.Branches of Linguistics;
1.4.
3.
the most importantmeans of human
communication
prompt
actions
(appellative
function)
convey and exchange
information (informative
function)
Language
commit oneself to do
something (obligatory
function)
open, hold and
end social
contact (contact
function
convey and exchange
artistic/ aesthetic
creations (poetic
function)
4.
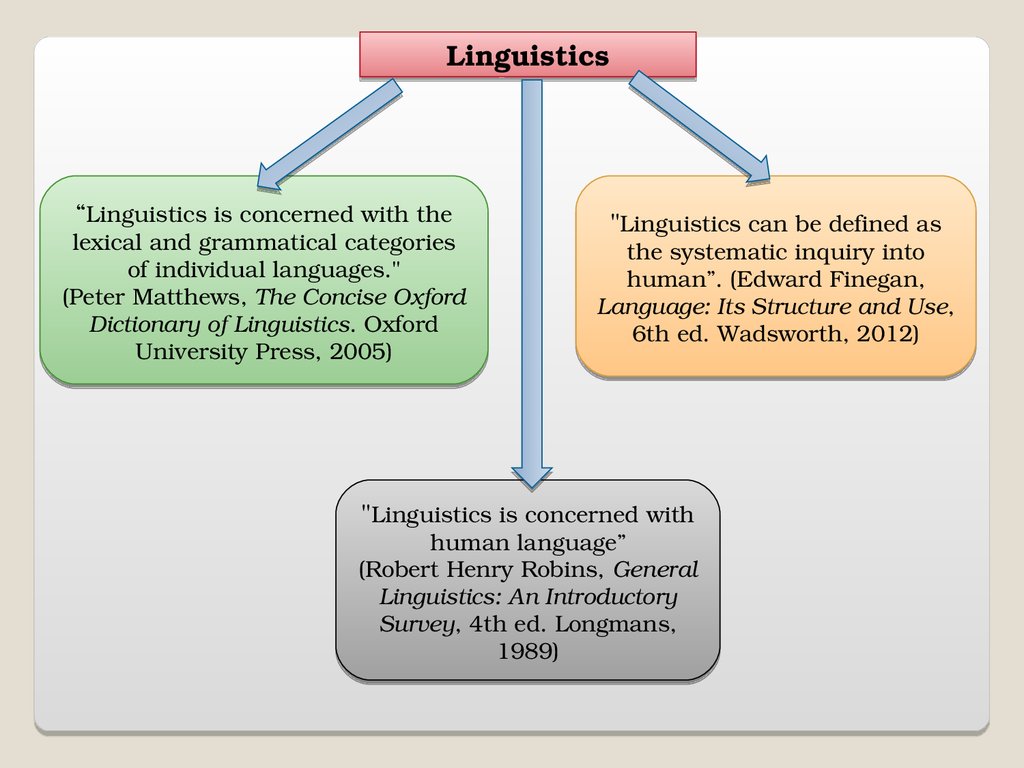
Linguistics“Linguistics is concerned with the
lexical and grammatical categories
of individual languages."
(Peter Matthews, The Concise Oxford
Dictionary of Linguistics. Oxford
University Press, 2005)
"Linguistics can be defined as
the systematic inquiry into
human”. (Edward Finegan,
Language: Its Structure and Use,
6th ed. Wadsworth, 2012)
"Linguistics is concerned with
human language”
(Robert Henry Robins, General
Linguistics: An Introductory
Survey, 4th ed. Longmans,
1989)
5.
Branches ofLinguistics
Phonetics
Definition
concerns the acoustic waveform itself, the
systematic disruptions of air molecules that
occur whenever someone utters the expression.
Phonology
concerns the sound system consonants,
vowels, and syllables.
Morphology
concerns the words and meaningful subwords
constructed out of the phonological.
Syntax
concerns the arrangement of those
morphological elements into phrases and
sentences.
Semantics
concerns the ways in which sounds and
meanings are related.




 Английский язык
Английский язык Лингвистика
Лингвистика








