Похожие презентации:
Physiology lab
1. Physiology lab
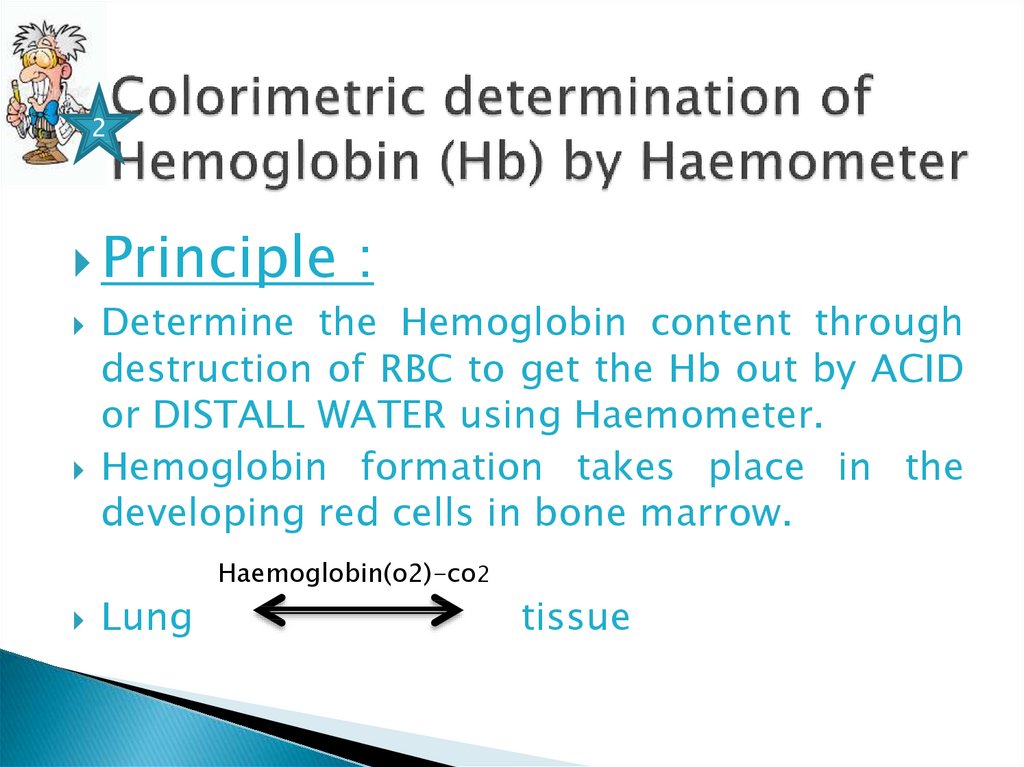
2. Colorimetric determination of Hemoglobin (Hb) by Haemometer
2Principle
:
Determine the Hemoglobin content through
destruction of RBC to get the Hb out by ACID
or DISTALL WATER using Haemometer.
Hemoglobin formation takes place in the
developing red cells in bone marrow.
Haemoglobin(o2)-co2
Lung
tissue
3. Tools
HaemometerHCL
Capillary tube
Dropper
1
Two
standard
tube
2
one
Graduated
tube
4. Steps
12
3
HCL
(O.1)
Add drops
till match
standard
tube
3Brownish
color
appear
HCL
(O.1)
5
drops
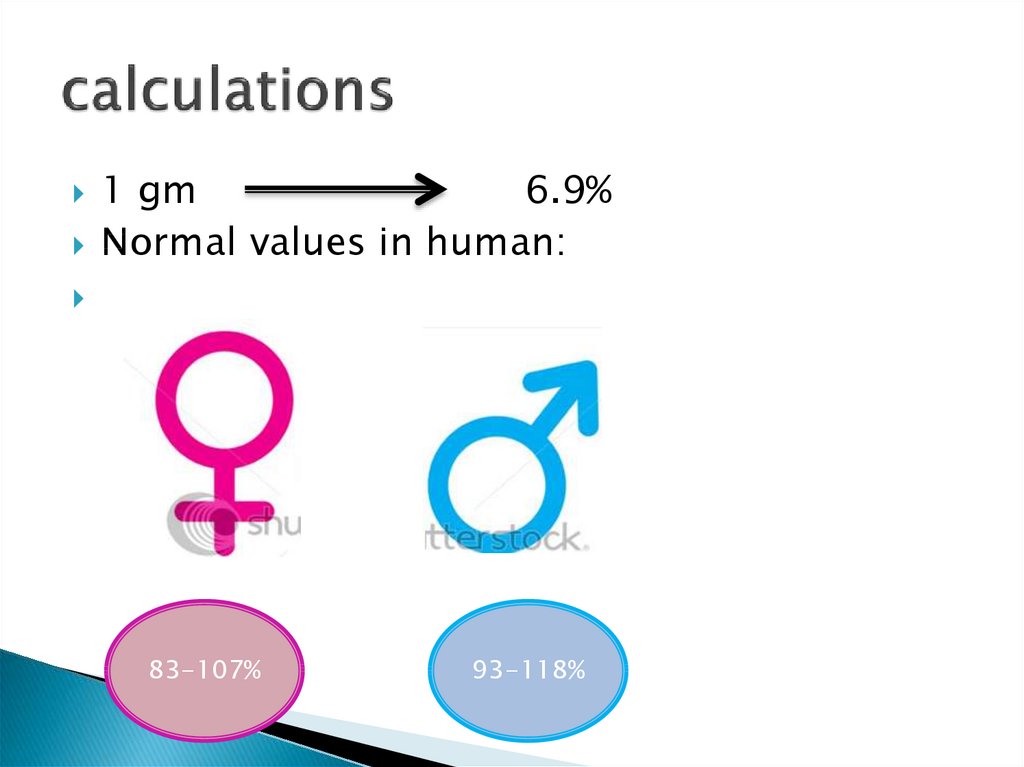
5. calculations
1 gm6.9%
Normal values in human:
83-107%
93-118%
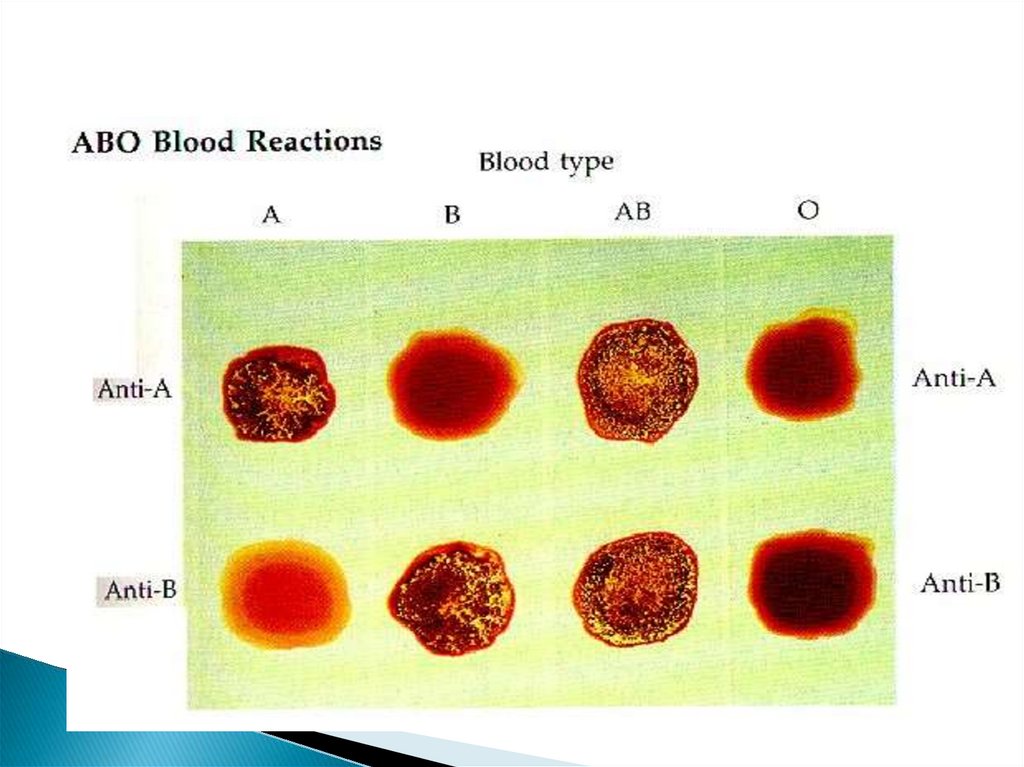
6. Blood groups
ForeignRBC may clump
together in the form of large
aggregates agglutination.
That agglutinated RBC are
haemolysed releasing a large
amount of Hb into plasma .
7.
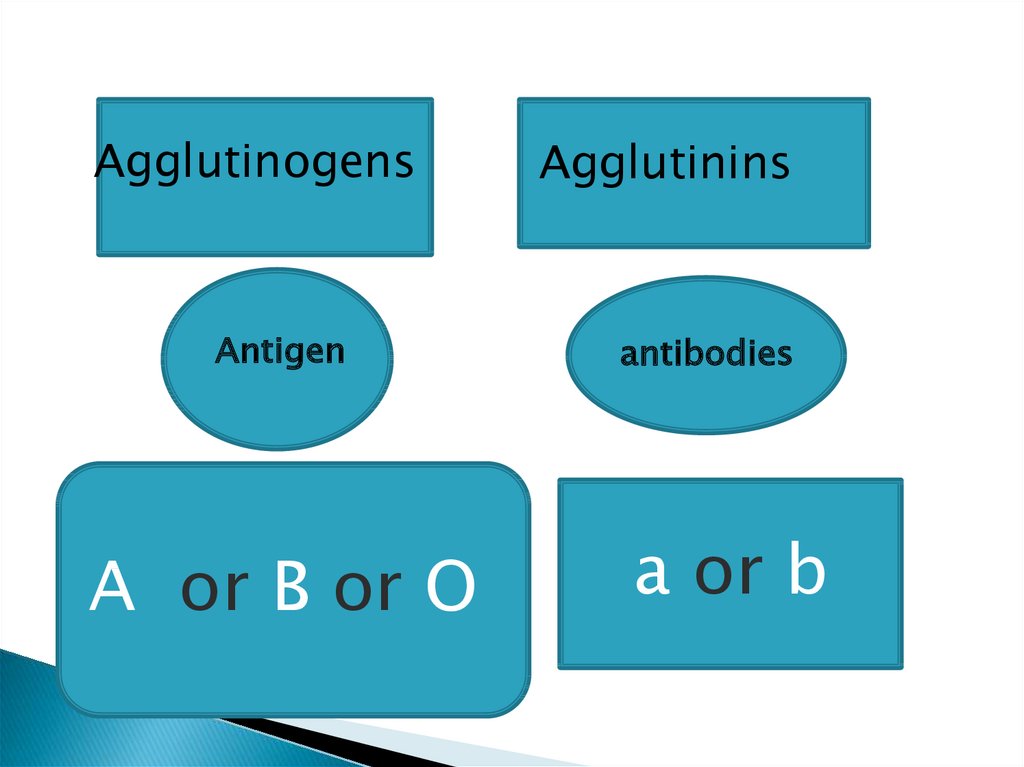
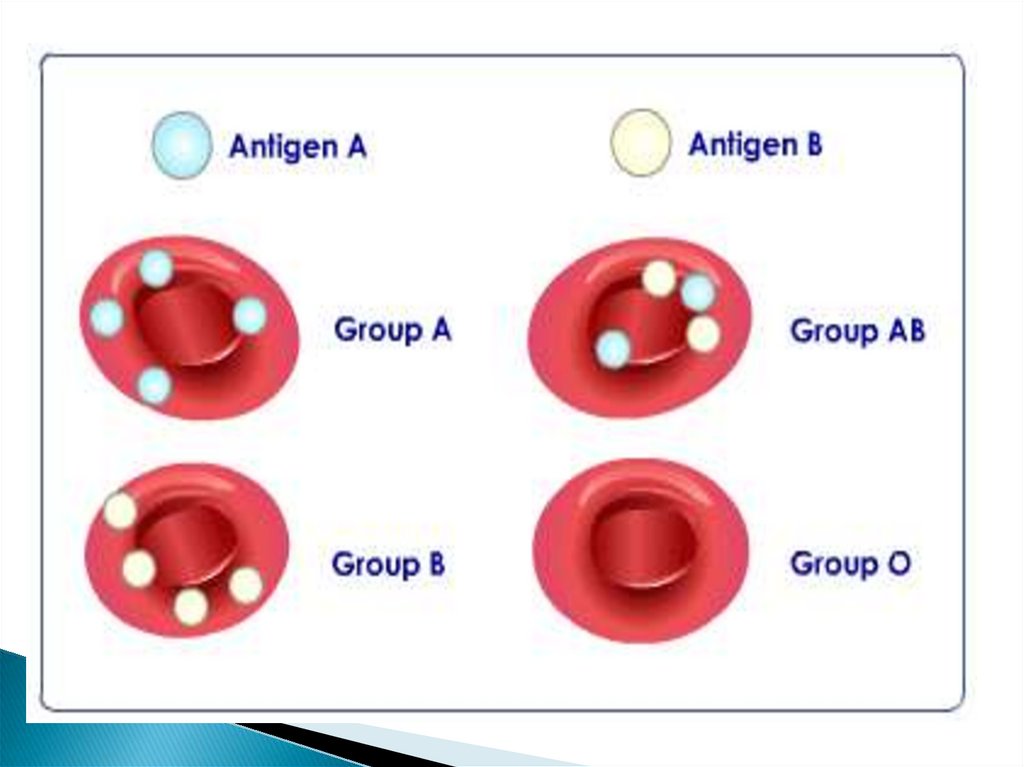
AgglutinogensAntigen
A or B or O
Agglutinins
antibodies
a or b
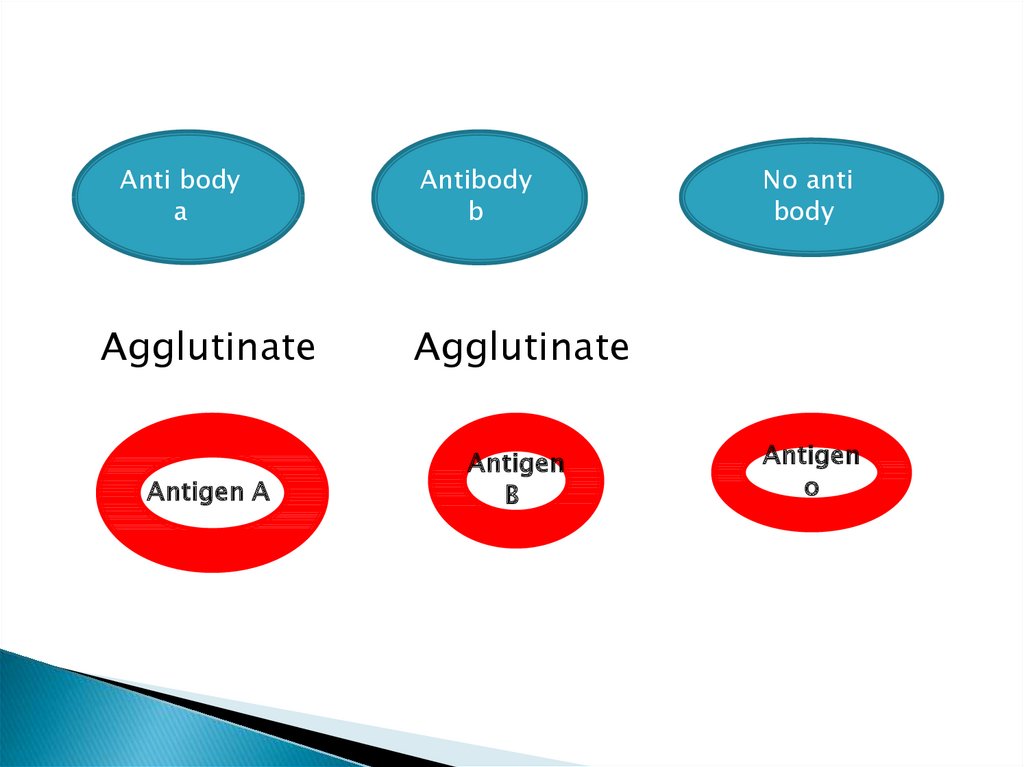
8.
Anti bodya
Antibody
b
Agglutinate
Agglutinate
Antigen A
Antigen
B
No anti
body
Antigen
o
9.
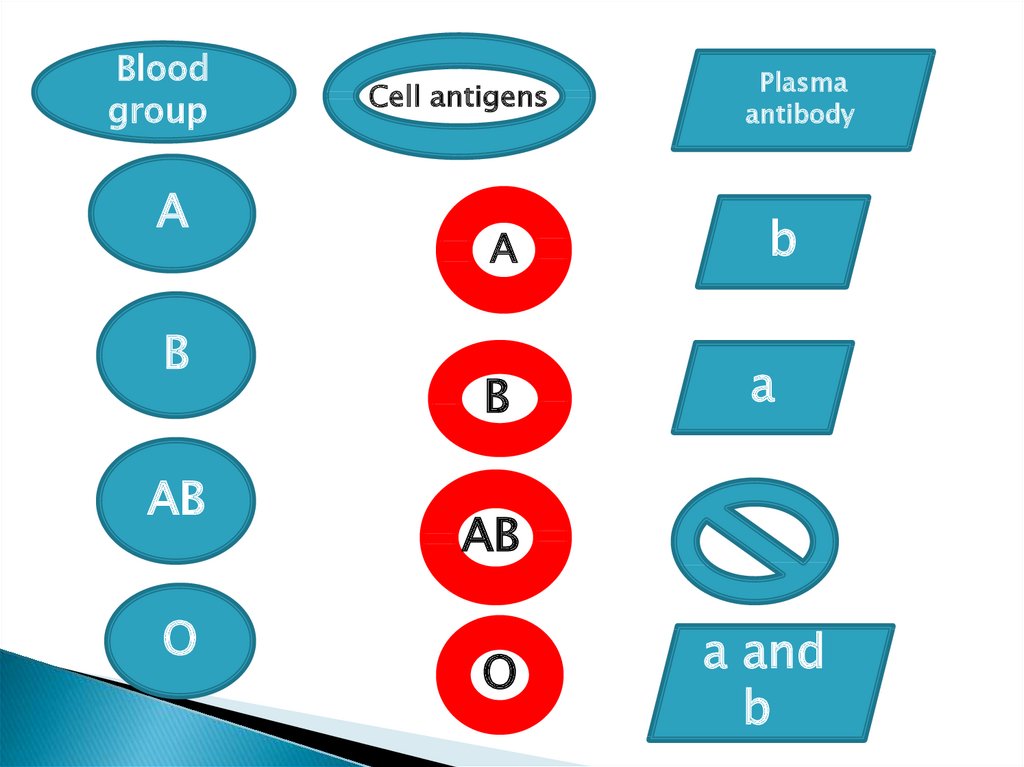
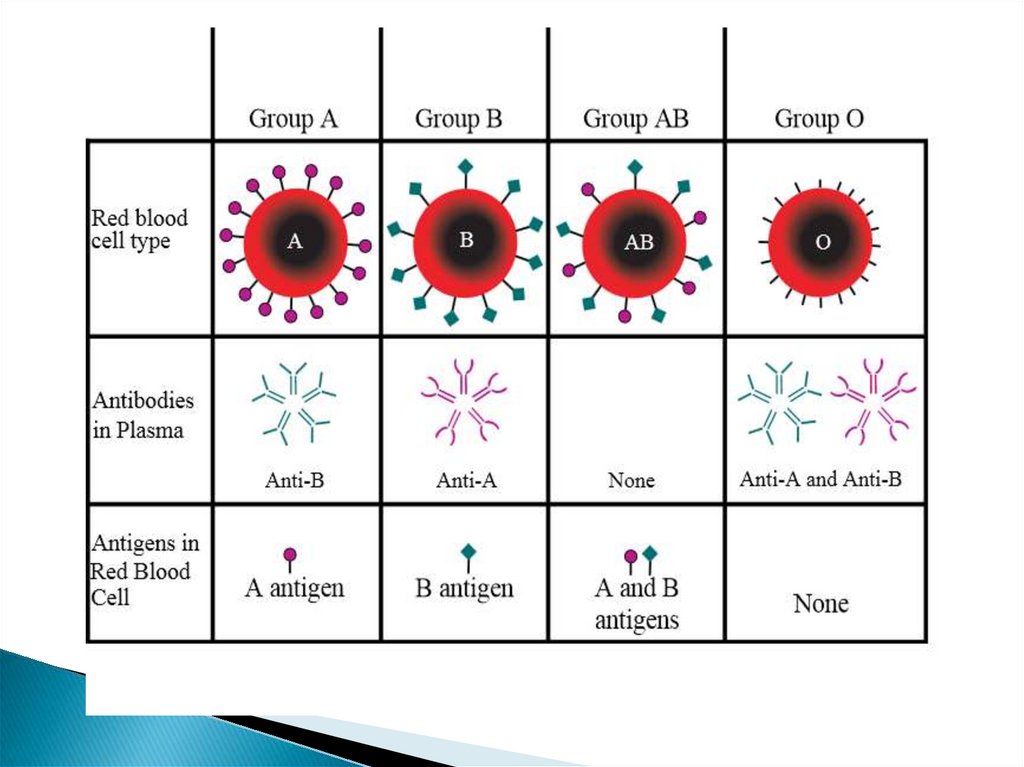
If the RBC have antigen A the correspondingplasma must have antibody b and not a
If the RBC have antigen B, the corresponding
plasma must have antibody a and not
RBC with both A and B antigen are present in
plasma which has no antibody at all
Also, RBC contain antigen O accompany
plasma has both antibodies a and b
10.
Bloodgroup
A
B
AB
O
Cell antigens
A
B
Plasma
antibody
b
a
AB
O
a and
b
11.
12.
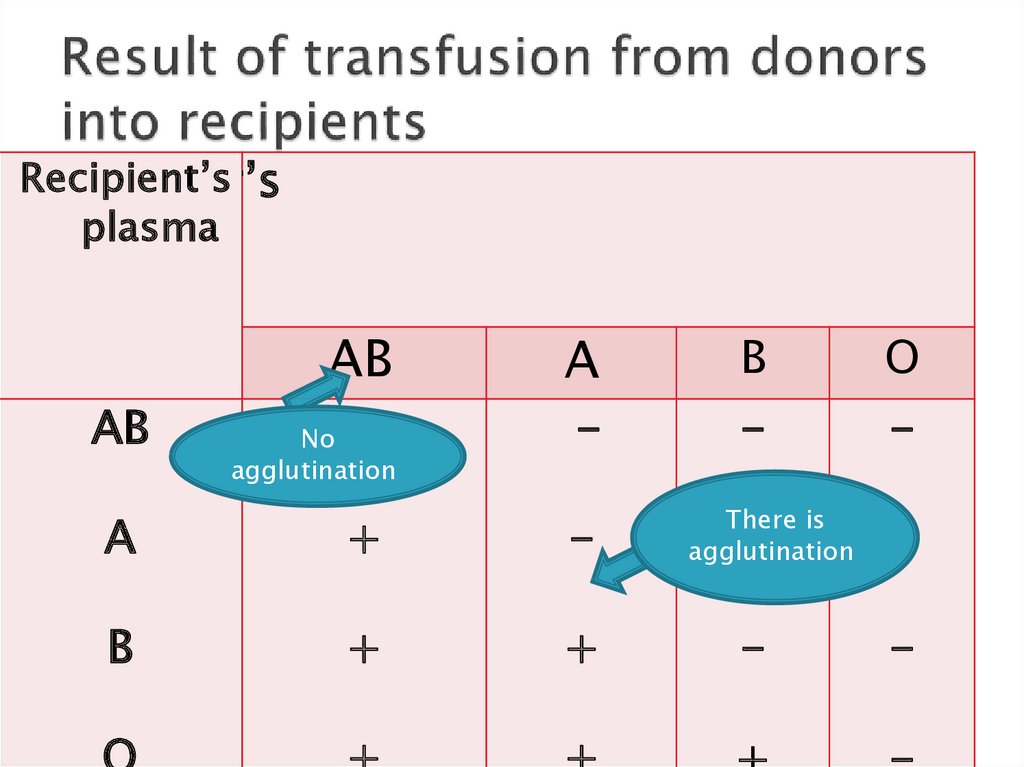
13. Result of transfusion from donors into recipients
Recipient’sDonor’s
plasma
RBC
AB
AB
A
B
O
-
-
-
-
No
agglutination
A
+
-
B
+
+
There is
agglutination
+
-
-
-
14.
15.
Group AB is called universal recipient , andgroup O is known as universal donor
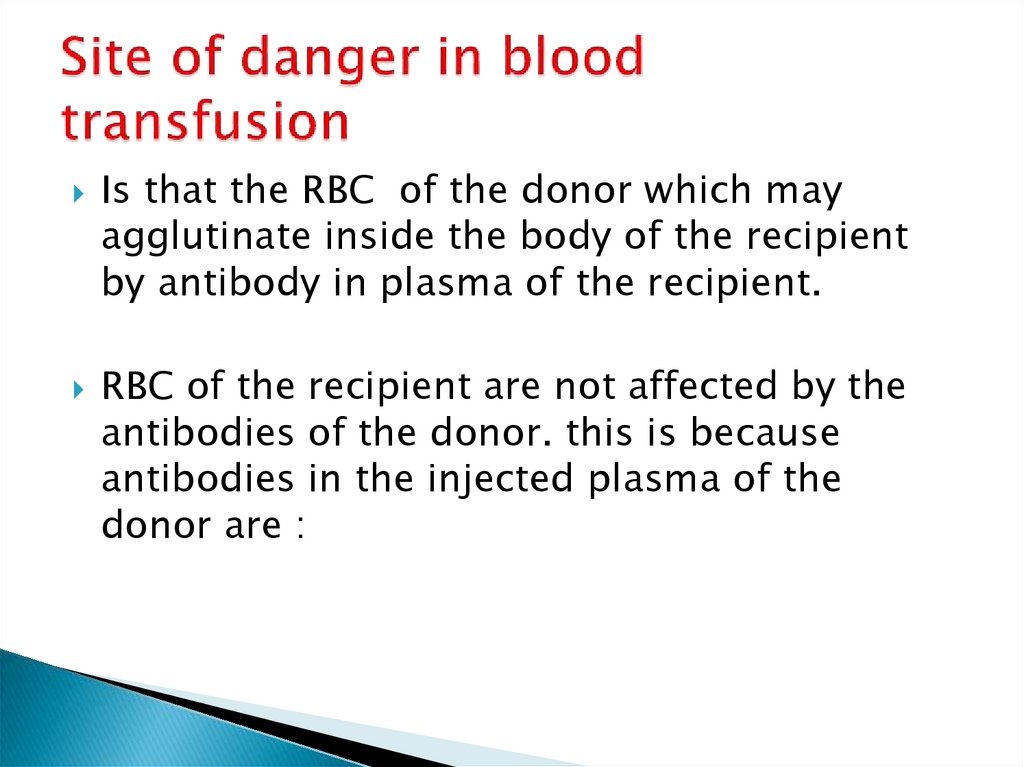
16. Site of danger in blood transfusion
Is that the RBC of the donor which mayagglutinate inside the body of the recipient
by antibody in plasma of the recipient.
RBC of the recipient are not affected by the
antibodies of the donor. this is because
antibodies in the injected plasma of the
donor are :
17.
1.2.
Diluted by the recipient plasma
Neutralized by the free water
soluble antigens present in the
recipient’s blood and tissue
fluids and which are produced by
the daily destruction of about 1%
of his RBC
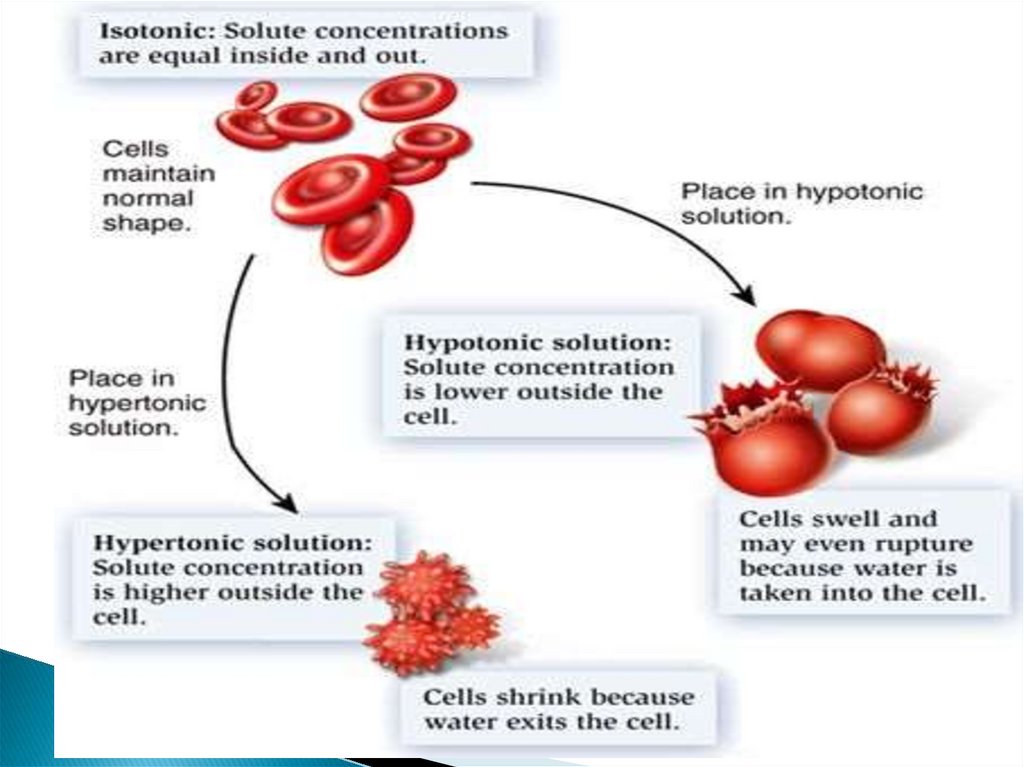
18. Osmotic behavior of blood
19. Osmosis
Lowconcentration
of water
Water
High
concentration
of water
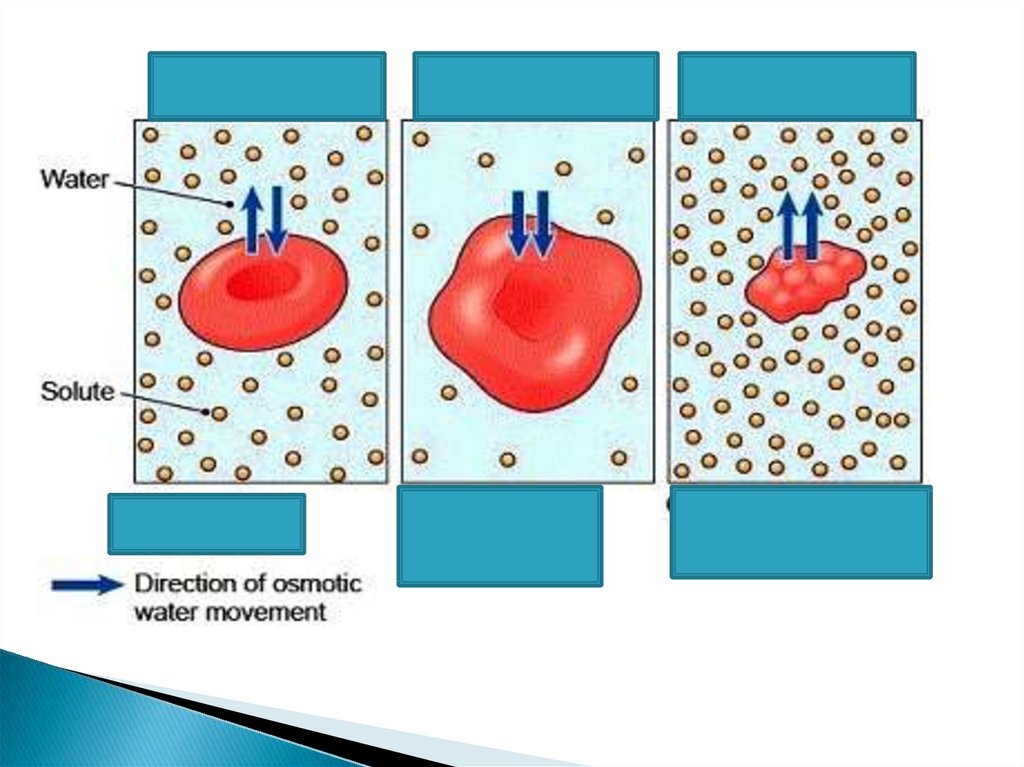
20.
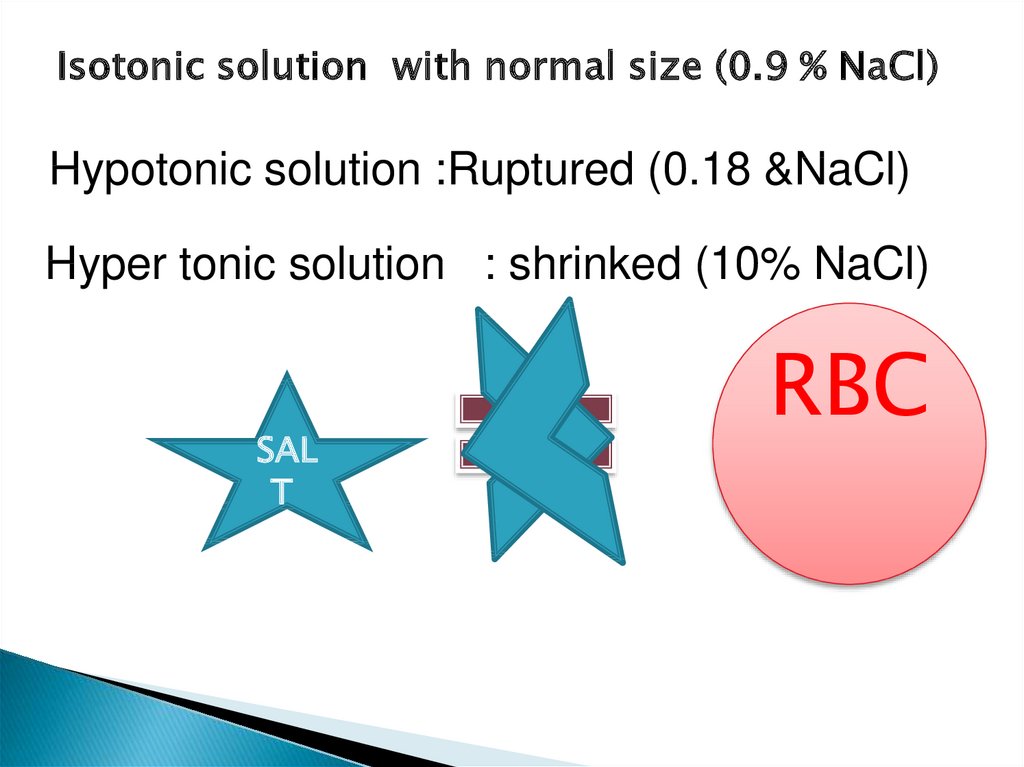
Isotonic solution with normal size (0.9 % NaCl)Hypotonic solution :Ruptured (0.18 &NaCl)
Hyper tonic solution : shrinked (10% NaCl)
SAL
T
RBC
RBC
RBC
Salt
21.
22. Tools:
A-3 test tubesB- slides
C-cover
D-dropper
23.
Mix , take drop2-add
ml of,
on a 10
slide
each solution
cover
it and
examine
24.
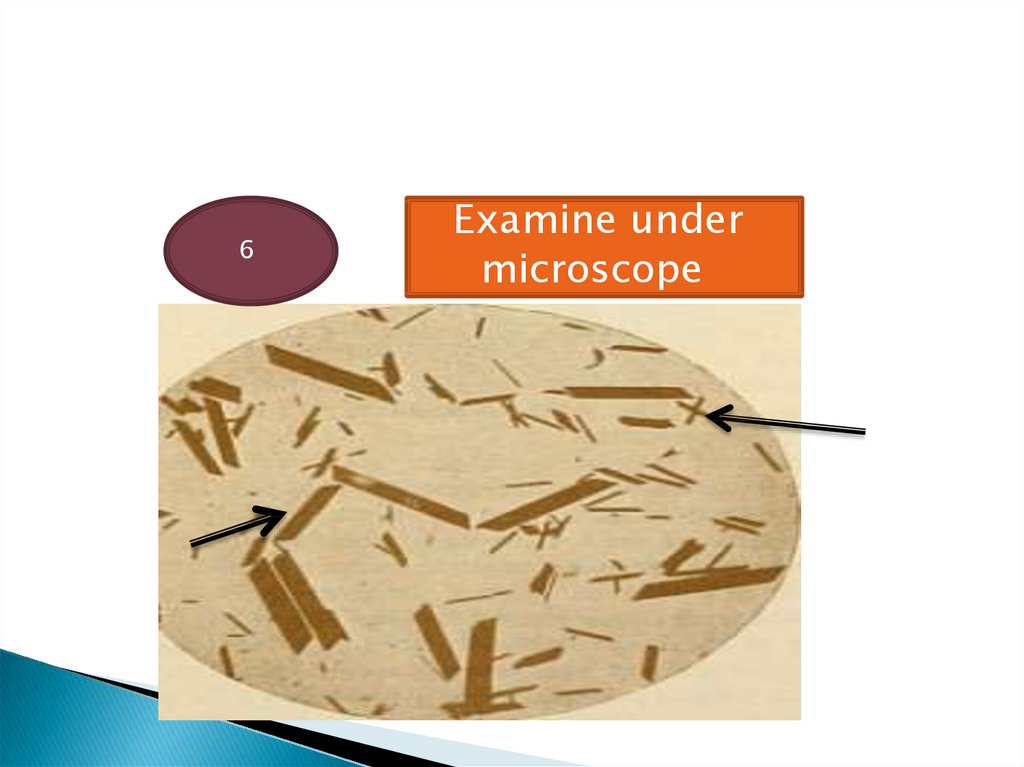
25. Haemin crystal
26.
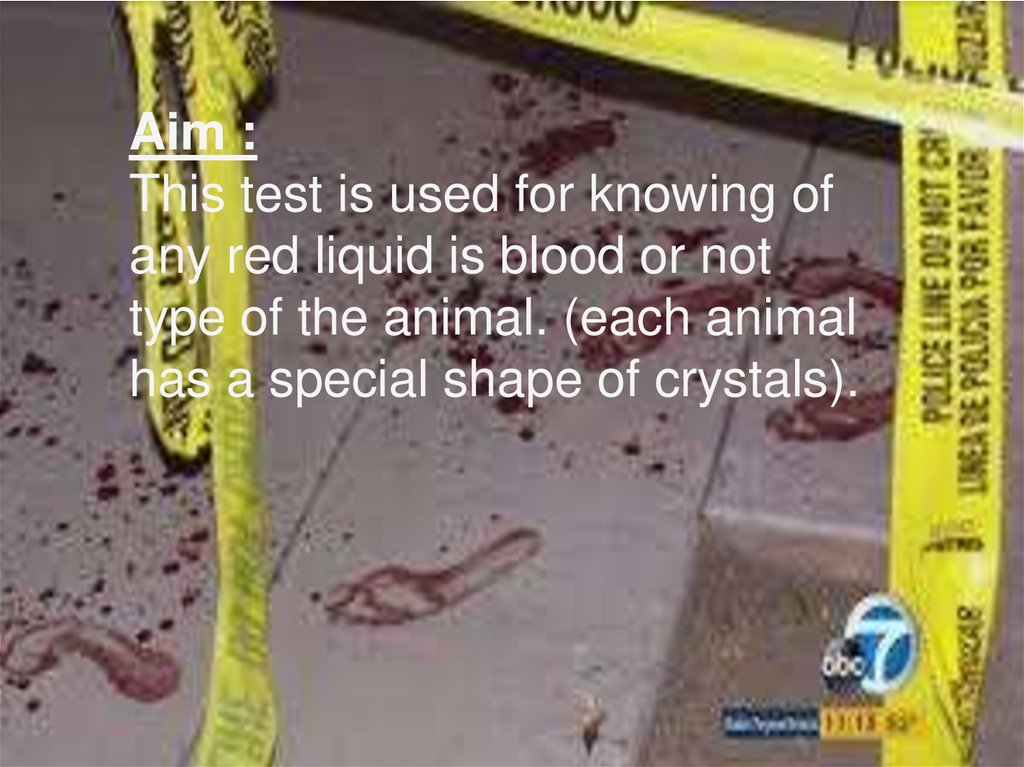
Aim :This test is used for knowing of
any red liquid is blood or not
type of the animal. (each animal
has a special shape of crystals).
27.
Principle :Blood is composed of haem and globine .
To determine the shape of haemin crystals we
must first get out the haem inside the RBCs
by a glacial acetic acid (decompose the RBC)
what produce the brownish color
NaCl
Na+ + Cl Hemoglobin + Cl
haem –chloride
(crystal )
28. Procedure
12
3
mix
29.
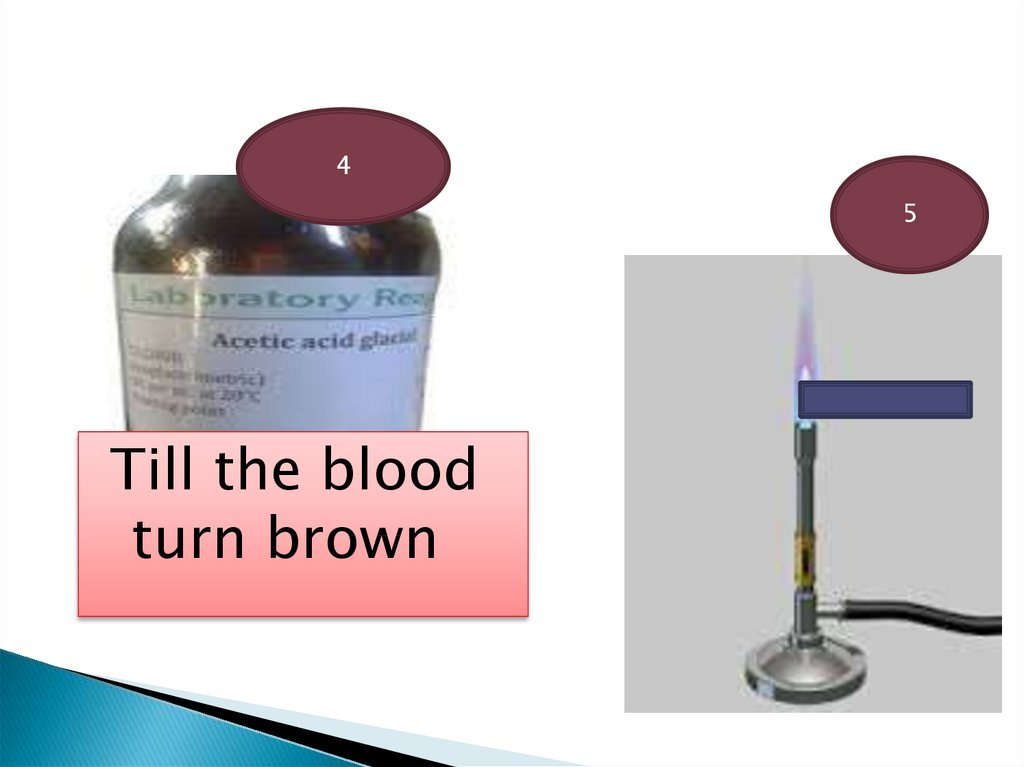
45
Till the blood
turn brown
30.
6Examine under
microscope
31. We can also find different type of crystal
Do you knowwhat is that
????
Salt
crysta
l
32. QUIZ
12

















 Химия
Химия








