Похожие презентации:
Communicative normative phonetics
1.
COMMUNICATIVENORMATIVE PHONETICS
English Faculty of Junior Courses,
Department of English Phonetics
Done by Kh.Avilova
2.
Why to focus on phonetics?English has become the major language for communication between speakers
with different native languages, like yourself and your fellow learners. The
world-wide use of English has placed particular demands on speaking English. We
would like to welcome you all to the course!
What do you think is important in English pronunciation in a global
world?
What English pronunciation features do you find difficult?
What are your needs regarding English pronunciation?
What is your expectations from this course?
3.
Course: Communicative NormativePhonetics
Type of the course:
Course code:
Year:
Semester:
Form of the degree programme:
Optional
КОМF30715
1
1
Full-time students
Form of classes and number of hours per
150
semester:
60
Practical lessons
90
Self-study
Number of ECTS credits:
5
Form of assessment:
Course completion assessment (test+live
assessment of pronunciation)
Course language:
English
4.
Course objective (CO)CO2
By the end of the course Students will:
Be able to pronounce language units appropriately in communication
Be able to recognize and deal with phonetic peculiarities of language
units
CO3
Be able to understand the link between segmental and supra segmental
units
CO4
Be able to notice the characteristic features of English syllable
structures
CO1
CO5
Be able to notice the characteristic features of English stress structures
CO7
Be able to notice the characteristic features of English intonation
Be able to understand the importance of appropriate pronunciation in
communication
CO8
Be able to use phonetics reference books independently
CO6
5.
Learning outcomes (LO):In terms of knowledge students should have developed
Their ability to pronounce language units
effectively and accurately using appropriate
phonetic norms
Increased awareness of the relationship
between phonetic units
Autonomous learning strategies in the area
of phonetics
6.
Course contentPractical
lessons (60
hours)
Self-study
(90 hours)
Assessment
( whole course
150 hours)
7.
Brief course content of the subject1
• Varieties of English pronunciation
• Accents and dialects
2
• Letters and sounds. Consonant and vowel sounds; reading
rules of consonants and vowels
3
• Syllables; types of syllables
• Stress; types of stress and their role
4
• Intonation and its types
• Analysis of words and sentences
8.
Methods of AssessmentFormative & Summative
Formative assessment- to weigh
students’ skills via exercises and tasks,
with tutor feedback as appropriate and
to monitor student’s learning to
provide ongoing feedback that can be
used by instructors to improve their
teaching and by students to improve
their learning.
Summative assessment- to evaluate
student’s learning and academic
achievement at the end of a term, year
or semester by comparing it against
national education standards or
university benchmark.
Formative (on-going assessment)
Summative (course end assessment)
9.
In order to earn credits students mustcomplete at least 70% of the following tasks
successfully.
Formative assessment
№
Assessment type
1
Tests
2
Audio recording at the beginning of the course
3
4
5
6
Transcription assignments
Dictation
Phonetic analysis
Audio recording at the end of the course
Summative assessment
1
2
Grade
10%
10%
Total:
10%
10%
10%
10%
60%
Total:
20%
20%
40%
Mid-term exam
Final exam
10.
Grading scaleEuropean Credit
Transfer System
Uzbekistan system
(%)
«A»
90 — 100
«B»
«C»
70 — 89,9
«3» (satisfactory)
«D»
«E»
60 — 69,9
«2» (unsatisfactory)
«F»
0 — 59,9
Recommended
Uzbekistan system
«5» (excellent)
«4» (good)
11.
Formative assessment includes: (each tasktype is evaluated out of 10%)
1.Tests: Matching; gap filling; multiple choice
2.Audio recording at the beginning of the course
3. Transcription assignments
4. Dictations
5. Phonetic analysis
6. Audio recording at the end of the course
12.
Tests – 10%:Gap fill tasks;
Matching tasks;
Multiple choice tasks.
For assessing students’ self-study
on Moodle, at the end of several
lessons they are given different
types of tasks mentioned above.
They are marked automatically by
completing the test.
13.
Audio recording at the beginning of thecourse – 10%.
Students are supposed to record their voice on a concrete topic or questions
paying attention to own pronunciation and upload it on the platform.
Additionally, they are asked to listen to others’ recordings and make a peer
review indicating mistakes made by their partner.
14.
Transcription assignments – 10%.In this type of tasks learners should transcribe words in the given list or
sentences. At the end of the course they will be given texts to transcribe or
ready transcriptions to turn them into texts.
The film shows an
executive
of
an
American call centre
who goes to India to
teach prospective staff
“proper” English. In
the end, he falls in
love there (naturally)
and ends up speaking
English with a beautiful
Indian English accent
himself!
15.
Dictations– 10%.Dictation tasks require students to listen to some audios and fill in the table
with the words/sentences/texts they have heard.
16.
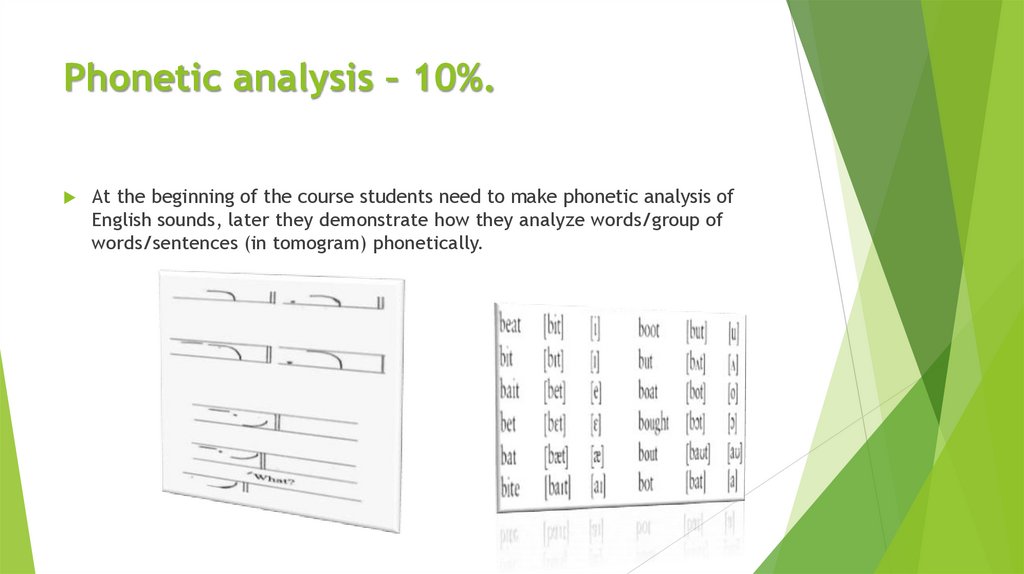
Phonetic analysis – 10%.At the beginning of the course students need to make phonetic analysis of
English sounds, later they demonstrate how they analyze words/group of
words/sentences (in tomogram) phonetically.
17.
Audio recording at the end of the course –10%.
This time teachers ask learners to record their voice of the same material
given at the beginning of the course again in order to see the progress they
have made. Instead of peer review students should write reflection showing
whether all taught materials and practice have helped to develop their
pronunciation or not. At the end teachers give feedback evaluating students’
progress in pronunciation.
18.
Summative assessment consists of:Mid-term exam – 20%.
The first part of this assessment is oral where students should recite any 3 vowel
sounds out of 20 asked by the teacher for what they get half of mark-10%. Another
half of mark-10% is given to 30 tests completion where teachers check students’
comprehension of taught materials.
Final exam – 20%.
At the end of the course learners pass final in two stages again:
Oral (recite rhymes or tongue twisters given beforehand paying big attention to
pronunciation and read dialogues/jokes/short texts dramatically which is
evaluated in terms of both pronunciation and intonation online). Each stage is
given 5% overall 10%.
Written (50 online tests on checking students’ comprehension of the whole
course) – 10%.
19.
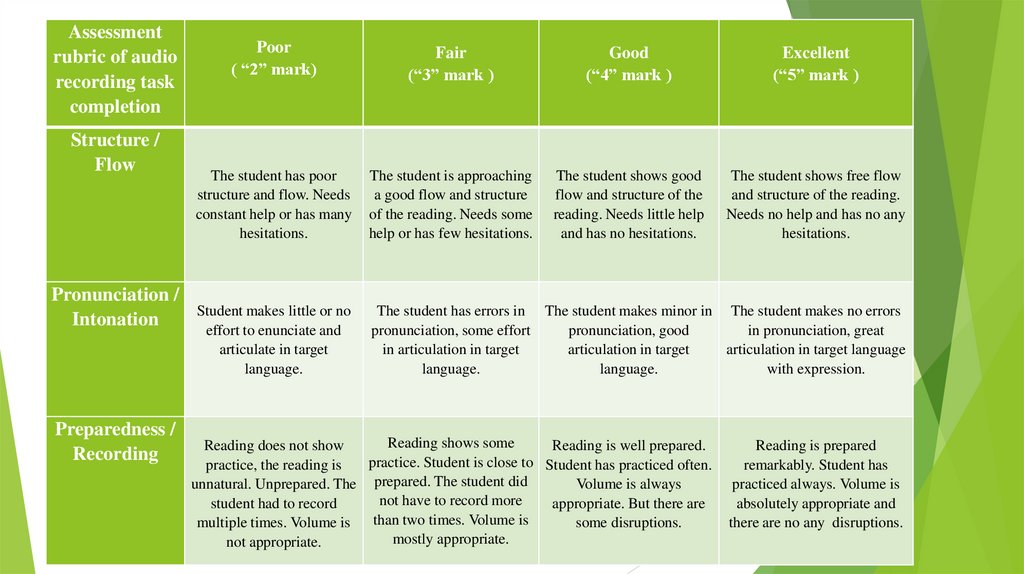
Assessmentrubric of audio
recording task
completion
Structure /
Flow
Pronunciation /
Intonation
Preparedness /
Recording
Poor
( “2” mark)
Fair
(“3” mark )
Good
(“4” mark )
Excellent
(“5” mark )
The student has poor
structure and flow. Needs
constant help or has many
hesitations.
The student is approaching
a good flow and structure
of the reading. Needs some
help or has few hesitations.
The student shows good
flow and structure of the
reading. Needs little help
and has no hesitations.
The student shows free flow
and structure of the reading.
Needs no help and has no any
hesitations.
Student makes little or no
effort to enunciate and
articulate in target
language.
The student has errors in The student makes minor in The student makes no errors
pronunciation, some effort
pronunciation, good
in pronunciation, great
in articulation in target
articulation in target
articulation in target language
language.
language.
with expression.
Reading shows some
Reading does not show
Reading is well prepared.
practice. Student is close to Student has practiced often.
practice, the reading is
unnatural. Unprepared. The prepared. The student did
Volume is always
not have to record more
student had to record
appropriate. But there are
than
two
times.
Volume
is
multiple times. Volume is
some disruptions.
mostly appropriate.
not appropriate.
Reading is prepared
remarkably. Student has
practiced always. Volume is
absolutely appropriate and
there are no any disruptions.
20.
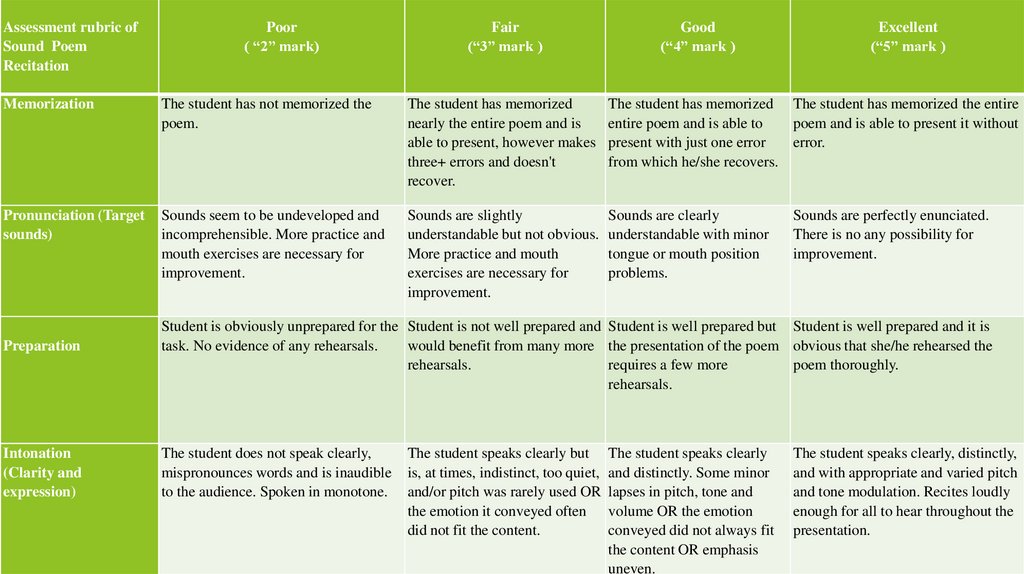
Assessment rubric ofSound Poem
Recitation
Poor
( “2” mark)
Fair
(“3” mark )
Good
(“4” mark )
Excellent
(“5” mark )
Memorization
The student has not memorized the
poem.
The student has memorized
nearly the entire poem and is
able to present, however makes
three+ errors and doesn't
recover.
The student has memorized The student has memorized the entire
entire poem and is able to
poem and is able to present it without
present with just one error
error.
from which he/she recovers.
Pronunciation (Target
sounds)
Sounds seem to be undeveloped and
incomprehensible. More practice and
mouth exercises are necessary for
improvement.
Sounds are slightly
understandable but not obvious.
More practice and mouth
exercises are necessary for
improvement.
Sounds are clearly
understandable with minor
tongue or mouth position
problems.
Preparation
Intonation
(Clarity and
expression)
Sounds are perfectly enunciated.
There is no any possibility for
improvement.
Student is obviously unprepared for the Student is not well prepared and Student is well prepared but Student is well prepared and it is
task. No evidence of any rehearsals.
would benefit from many more the presentation of the poem obvious that she/he rehearsed the
rehearsals.
requires a few more
poem thoroughly.
rehearsals.
The student does not speak clearly,
mispronounces words and is inaudible
to the audience. Spoken in monotone.
The student speaks clearly but
is, at times, indistinct, too quiet,
and/or pitch was rarely used OR
the emotion it conveyed often
did not fit the content.
The student speaks clearly
and distinctly. Some minor
lapses in pitch, tone and
volume OR the emotion
conveyed did not always fit
the content OR emphasis
uneven.
The student speaks clearly, distinctly,
and with appropriate and varied pitch
and tone modulation. Recites loudly
enough for all to hear throughout the
presentation.















 Английский язык
Английский язык








