Похожие презентации:
Covid-19 and Labour Law in China
1. Covid-19 and Labour Law in China
Wenwen Ding2.
Introduction of Chinese Labour LawThe Coronavirus Outbreak in China and Government Responses
Labor Laws Following COVID-19 Outbreak
An Emerging Employment Model—Employee Sharing
3. I. Introduction of Chinese Labour Law
• Laws: Labour Law, Labour Contract Law, Trade Union Law, Law on Mediation andArbitration of Labour Disputes, Social Security Law, Employment Promotion Law,
Law on the Prevention & Control of Occupational Diseases, etc.
• Interpretations of the Supreme People’s Court on Issues Relating to Labour;
• Administrative regulations and rules issued by the State Coucil;
• Administrative rules formulated by labour administrative departments;
• Local administrative rules formulated local governments and local labour
administrative departments.
4.
Introduction of Chinese Labour LawThe Coronavirus Outbreak in China and Government Responses
Labor Laws Following COVID-19 Outbreak
An Emerging Employment Model—Employee Sharing
5. II. The Coronavirus Outbreak in China and Governmental Responses
• Coronavirus outbreak timeline• Government’s measures to contain the virus
• Impact of Covid-19 Containment on the Economy
6. Coronavirus outbreak timeline
First CaseFirst death
Peak
Zero Cases
Dec.8.2019
Jan.9.2020
Feb.14.2020
Mar.19.2020
7. Economic Impact
The official unemployment rate 6.2%.Actual number might reach 20% (7080 million workers)
8.
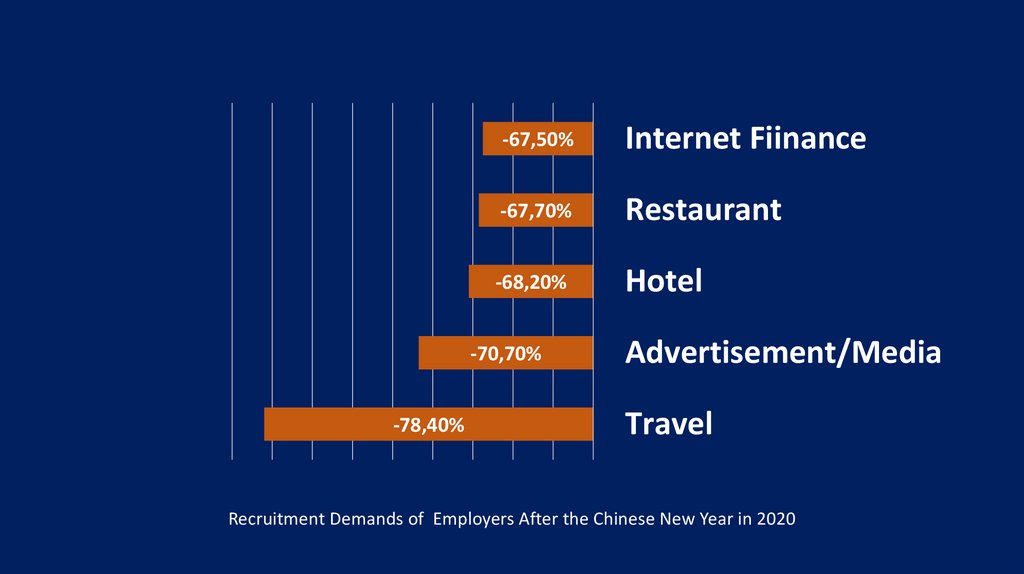
-67,50%Internet Fiinance
-67,70%
Restaurant
-68,20%
Hotel
-70,70%
-78,40%
Advertisement/Media
Travel
Recruitment Demands of Employers After the Chinese New Year in 2020
9.
Introduction of Chinese Labour LawThe Coronavirus Outbreak in China and Government Responses
Labor Laws Following COVID-19 Outbreak
An Emerging Employment Model—Employee Sharing
10. III. Labor Laws Following COVID-19 Outbreak
DismissalsWage Payments
Unemployment Insurance
Occupational Injury Insurance
Policies to Reduce burdens on Employers
11. Dismissals
• Dismissal Rules in Labour Contract Law(2008)• Employee Misconduct
• Lack of Capacity
• Economic, Technical, or Operational Needs of the Employer
• New rules:
• Department of Human Resources and Social Security, Notice on Properly
Handling Labor Relations during the Prevention and Control of Pneumonia
Epidemic of New Coronavirus Infection, March 20, 2020.
• Dismissal Restrictions on workers who cannot provide work because they
• are coronavirus patients;
• are suspected coronavirus patients;
• or have close contact with coronavirus patients.
• Extension of Expired Labor Contract under mandatory quarantine
12. III. Labor Laws Following COVID-19 Outbreak
DismissalsWage Payments
Unemployment Insurance
Occupational Injury Insurance
Policies to Reduce burdens on Employers
13. Wage Payments
• Public holiday extension (Jan. 31 – Feb. 2)• Notice on Extension of Spring Festival Holidays,
General Office of the State Council, January 27, 2020
• Jan. 24- Jan. 30 Chinese New Year Holiday
• Jan. 31 – Feb. 2 Extended Period
• Nature of the extension period
• Public holidays?
• Business shutdowns?
• Law on the Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases (2005), article
42.
• Rest days
14. Wage Payments
• Delayed work resumption period (Feb.3- Feb.10)• Law on the Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases
(2005), article 42
• Nature of this period
• Rest days: Shanghai government
• Normal work days: Jiangsu province
15. Wage Payments
• Quarantine Period• Law on the Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases (2005),
article 42
• Workers should be paid during the quarantine period.
• New rules to protect workers who are affected by the coronavirus
• Notice on the issues related to medical workers contracting coronavirus
due to the performance of their duties, Ministry of Human Resources and
Social Security, Department of Finance and National Health Commission,
Jan. 23, 2020.
• Employers should continue to pay workers who
• are coronavirus patients;
• are suspected coronavirus patients;
• or have close contact with coronavirus patients.
16. III. Labor Laws Following COVID-19 Outbreak
DismissalsWage Payments
Unemployment Insurance
Occupational Injury Insurance
Policies to Reduce burdens on Employers
17. Unemployment Insurance
• Opinions on Strengthening Employment Stabilization Measures inResponse to the Impact of the Coronavirus Epidemic, The General
Office of the State Council, March 20, 2020
• New Rules to Ensure Basic Living of Unemployed Workers
• Extending the Time Limit for Claiming Unemployment Insurance
• Measures for Application for and Payment of Unemployment Insurance (Department of
Human Resources and Social Security, 2018), article 6.
• Simplifying the Application Process
• Covering More Workers and for a Longer Period of Time
• Problems with these Measures
18. III. Labor Laws Following COVID-19 Outbreak
DismissalsWage Payments
Unemployment Insurance
Occupational Injury Insurance
Policies to Reduce burdens on Employers
19. Occupational Injury Insurance
• Social Insurance Law (2008), article 36; Regulation on OccupationalInjury Insurance(2010), articles 14 and 15.
• Get injured during work time, in the workplace, and because of work;
• or suffer from an occupational disease.
• Can Workers Contract Coronavirus in the Workplace Get Coverage?
• The Case of Medical Workers
• Notice on the issues related to medical workers contracting coronavirus due
to the performance of their duties,, Ministry of Human Resources and Social
Security, Department of Finance and National Health Commission, Jan. 23,
2020.
20. III. Labor Laws Following COVID-19 Outbreak
DismissalsWage Payments
Unemployment Insurance
Occupational Injury Insurance
Policies to Reduce burdens on Employers
21. Measures to Reduce Burdens on Employers
• Reduction of Social Insurance Contribution• Since 2019, reducing social insurance contribution rate
• New Policy:
• Opinions on Strengthening Employment Stabilization Measures in
Response to the Impact of the Coronavirus Epidemic, The General
Office of the State Council, March 20, 2020
• Exempting employers from paying pension, unemployment, and
occupational injury contributions for a certain period of time.
• Medium, small, and micro-sized enterprises
• Large enterprises
22. Measures to Reduce Burdens on Employers
• Financial Assistance through UnemploymentInsurance
• Since 2019, Refund Employment Insurance Payments if No
or Few Firings
• New Policy for Medium, Small and Micro-Sized Enterprises
• Firing rate< 5.5%
• No Firing
23.
Introduction of Chinese Labour LawThe Coronavirus Outbreak in China and Government Responses
Labor Laws Following COVID-19 Outbreak
An Emerging Employment Model—Employee Sharing
24. IV. Employee Sharing
• What is employee sharing?• Typical Cases
• Advantages of the employee sharing model
• Labor law questions

























 Медицина
Медицина








