Похожие презентации:
Extrasystole and blocks
1. Extrasystole
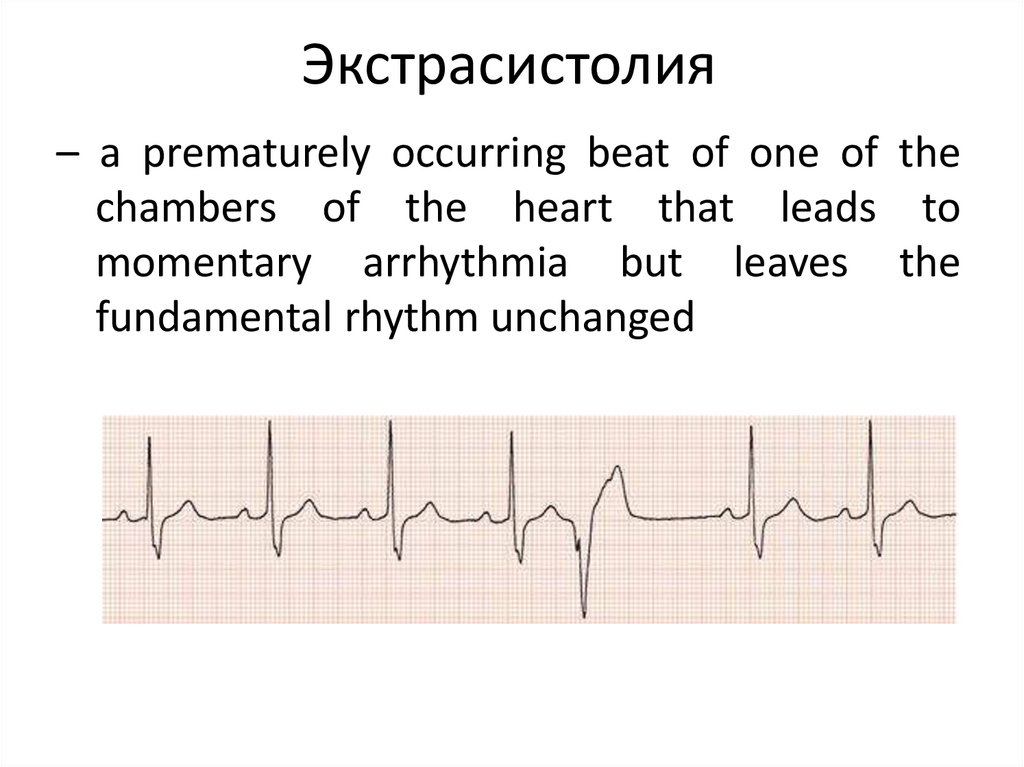
2. Экстрасистолия
– a prematurely occurring beat of one of thechambers of the heart that leads to
momentary arrhythmia but leaves the
fundamental rhythm unchanged
3.
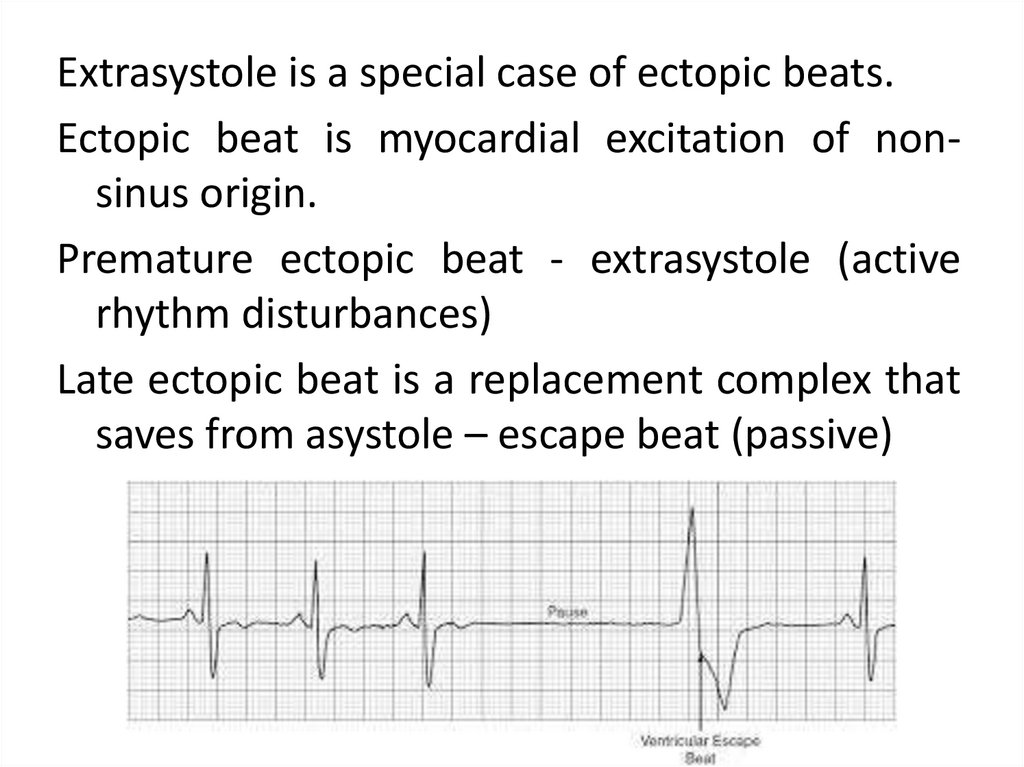
Extrasystole is a special case of ectopic beats.Ectopic beat is myocardial excitation of nonsinus origin.
Premature ectopic beat - extrasystole (active
rhythm disturbances)
Late ectopic beat is a replacement complex that
saves from asystole – escape beat (passive)
4.
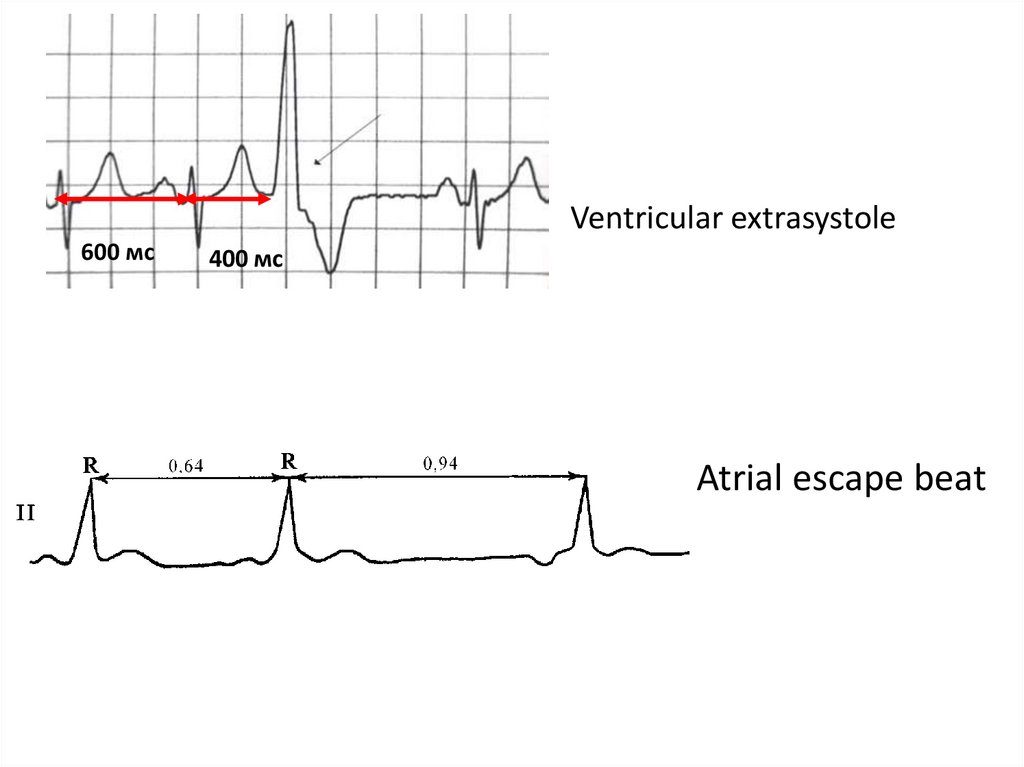
Ventricular extrasystole600 мс
400 мс
Atrial escape beat
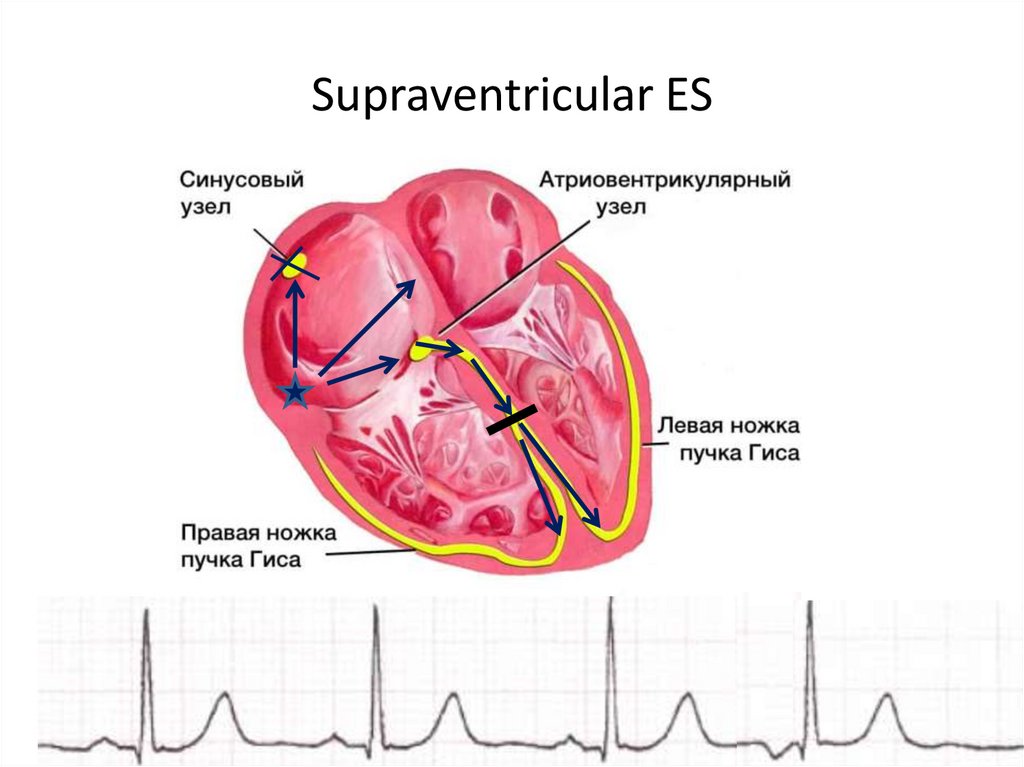
5. Supraventricular ES
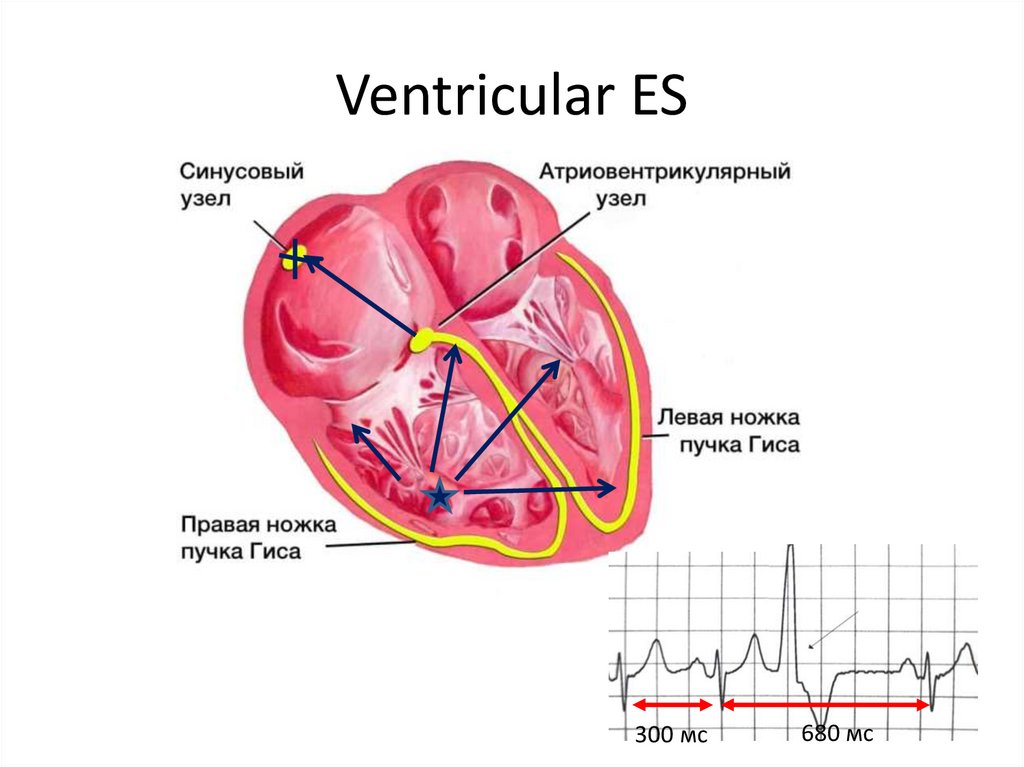
6. Ventricular ES
300 мс680 мс
7.
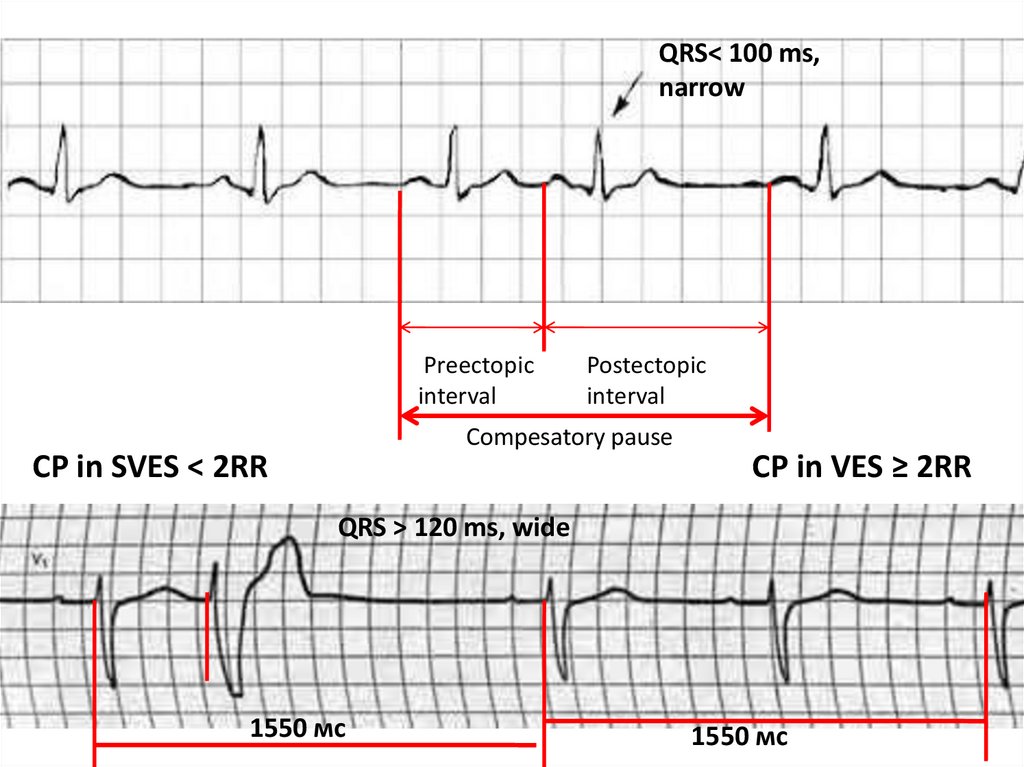
QRS< 100 ms,narrow
Preectopic
interval
Postectopic
interval
Compesatory pause
CP in SVES < 2RR
CP in VES ≥ 2RR
QRS > 120 ms, wide
1550 мс
1550 мс
8.
9.
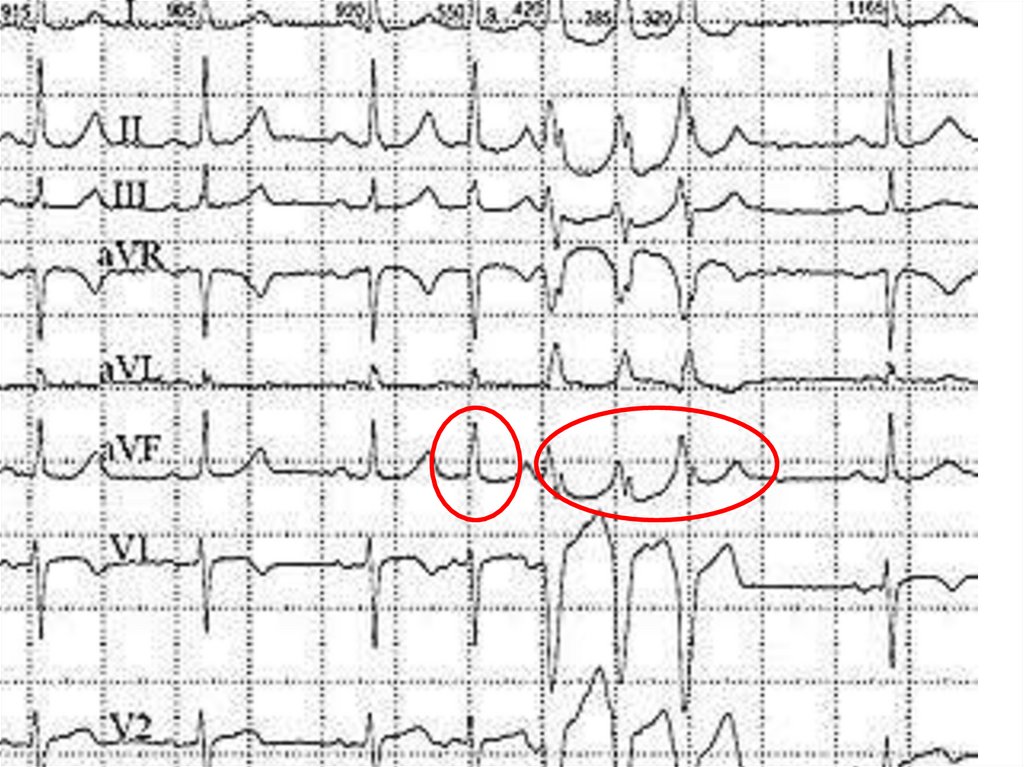
10. Ventricular ES
Classification (reference criteria):•The form
•A source
•Time of appearance
•Amount
•Allorhythmy
•Prognostic value (clinical)
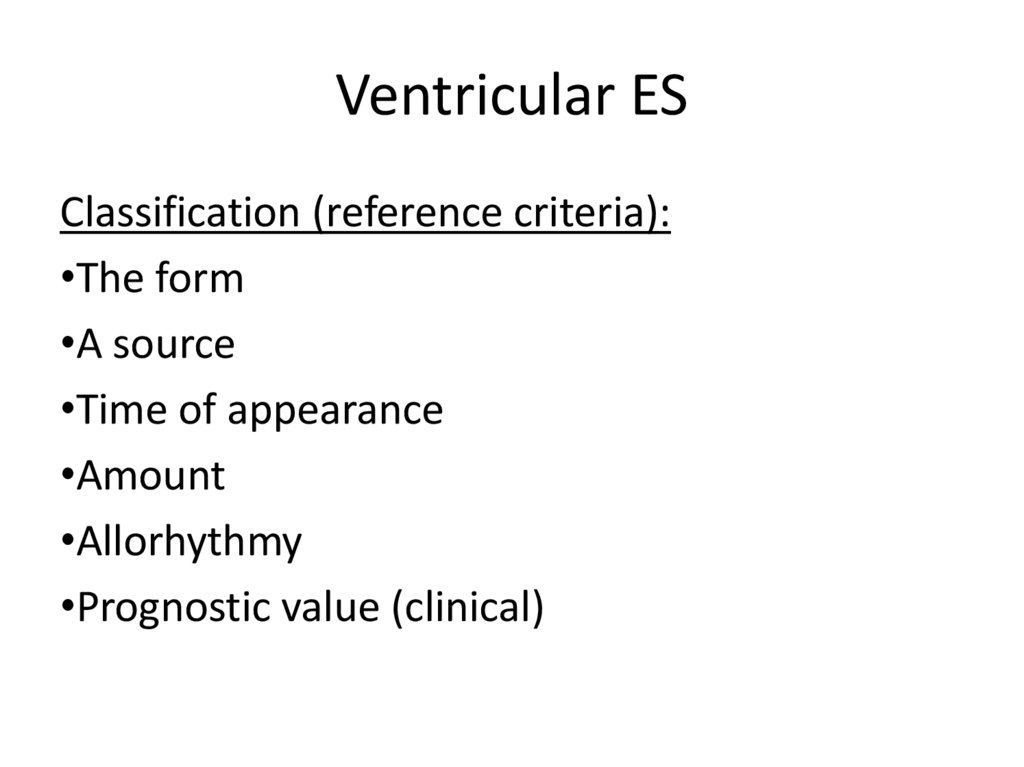
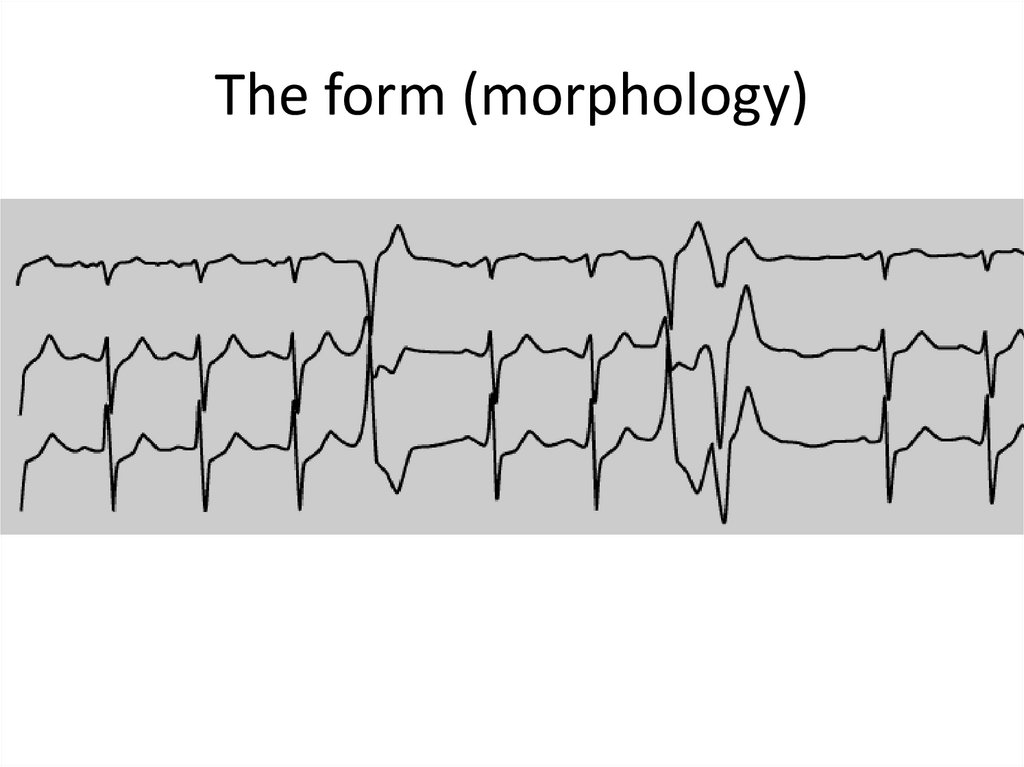
11. The form (morphology)
12.
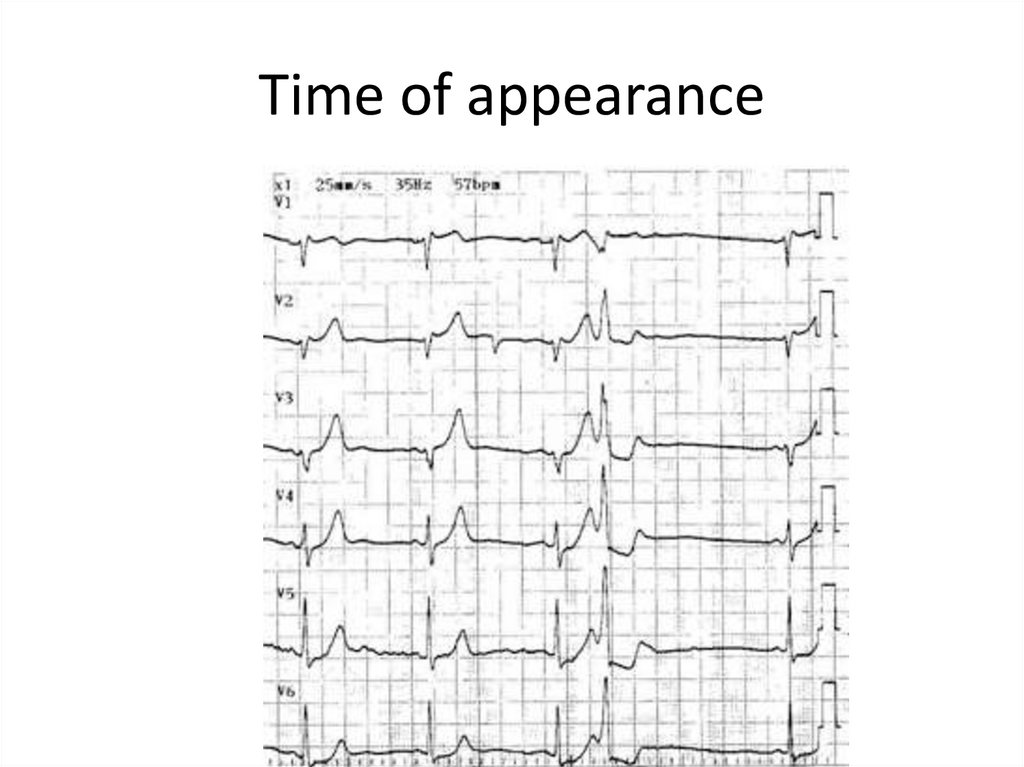
13. Time of appearance
14.
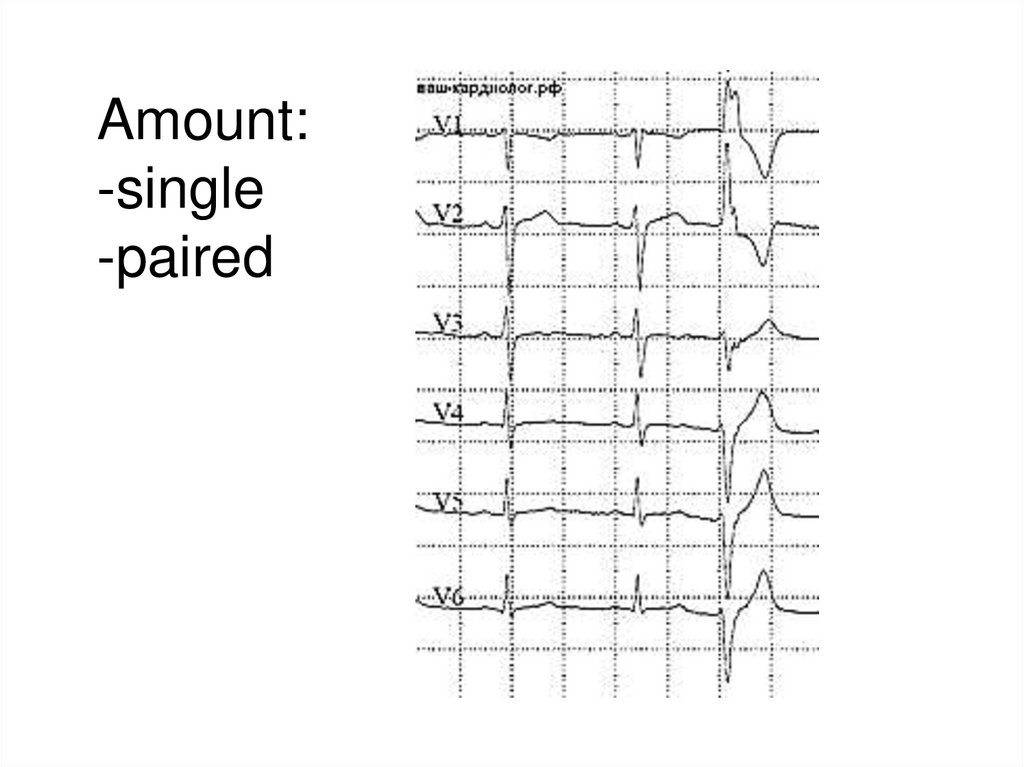
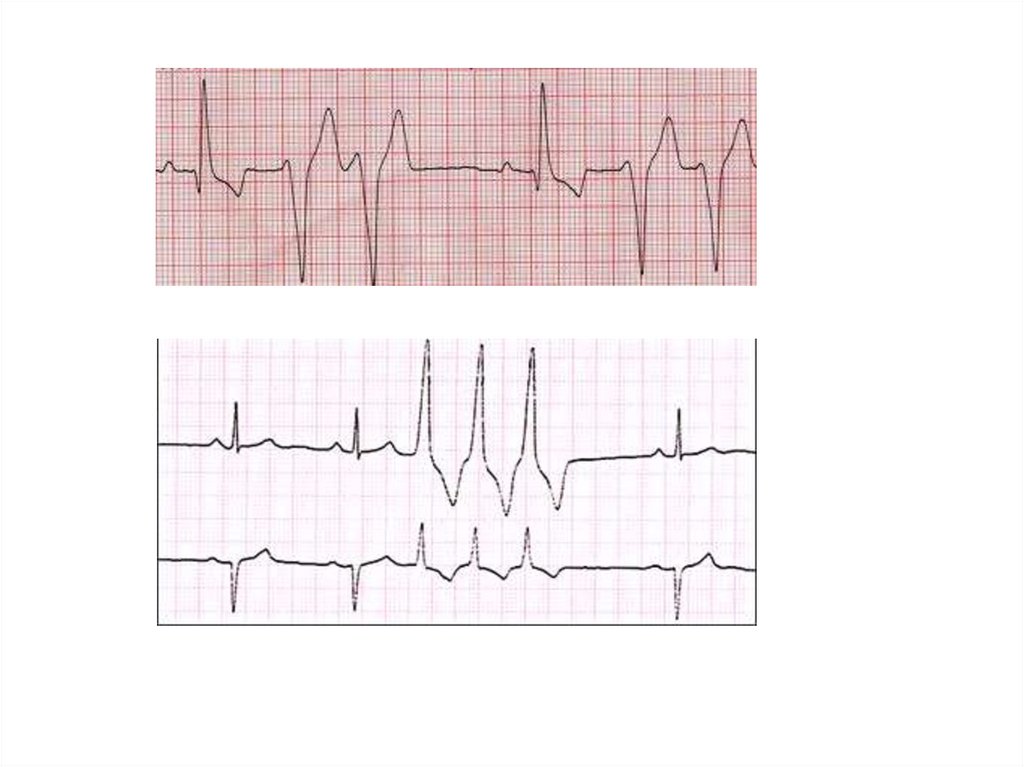
Amount:-single
-paired
15.
16.
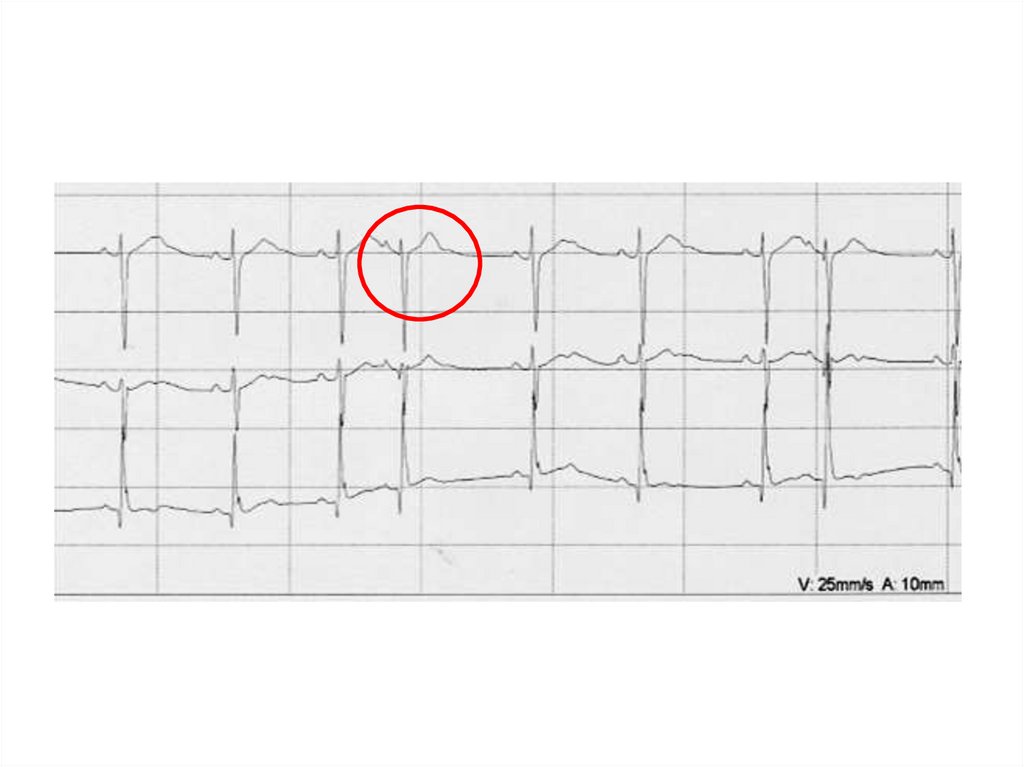
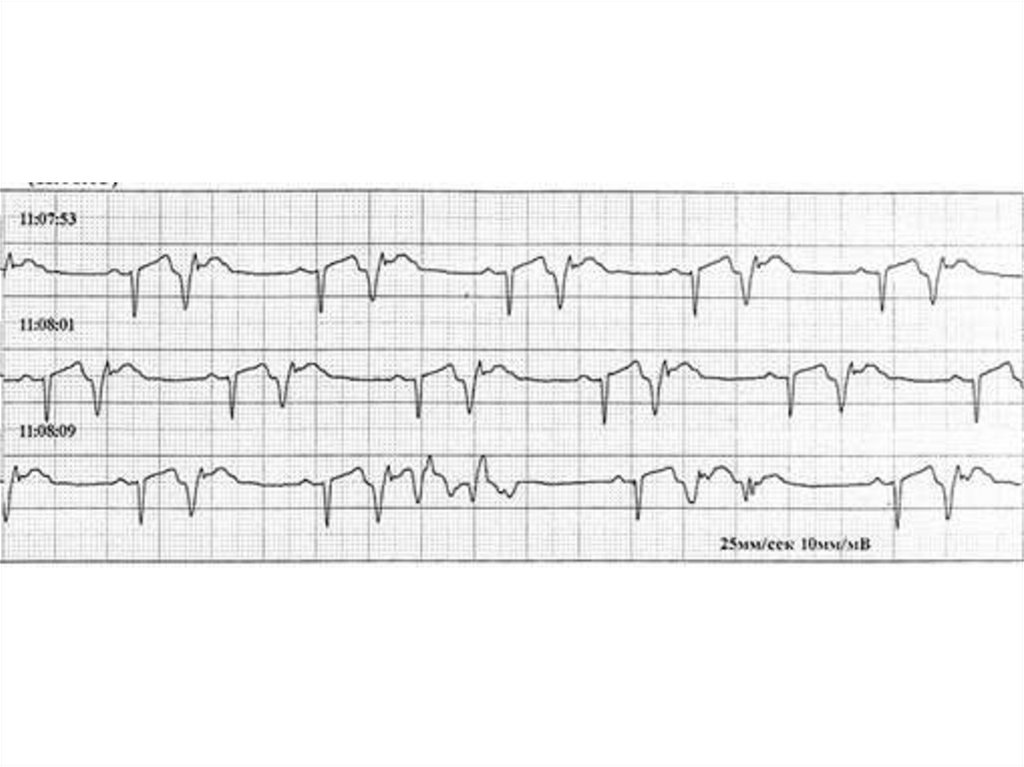
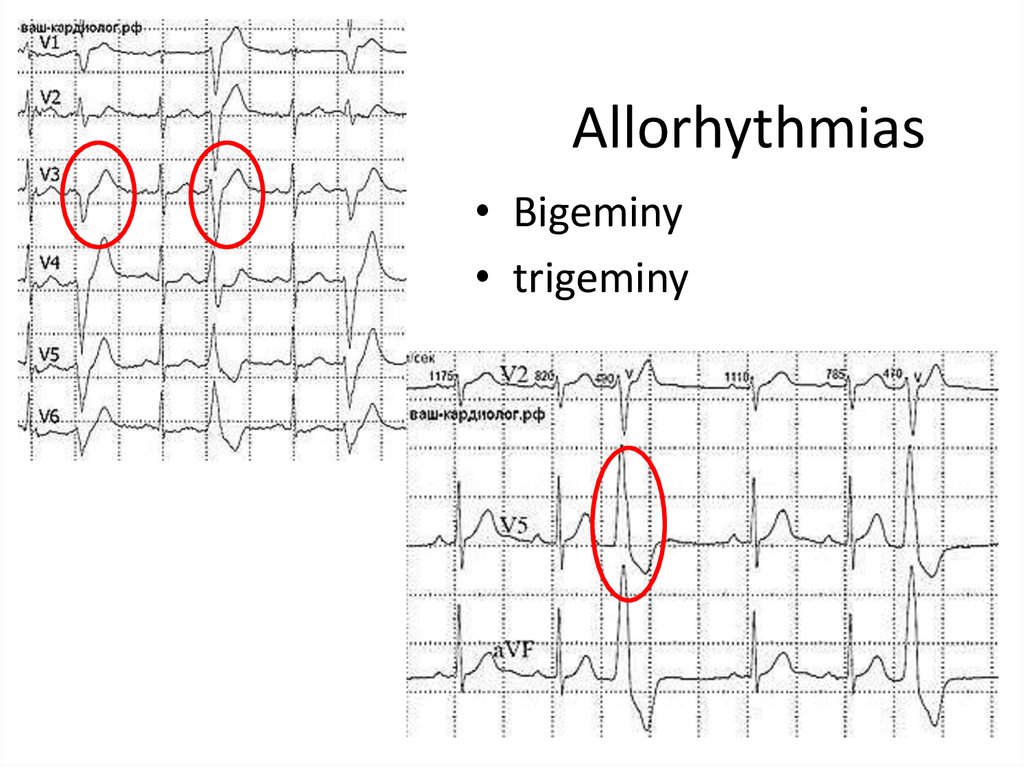
17. Allorhythmias
• Bigeminy• trigeminy
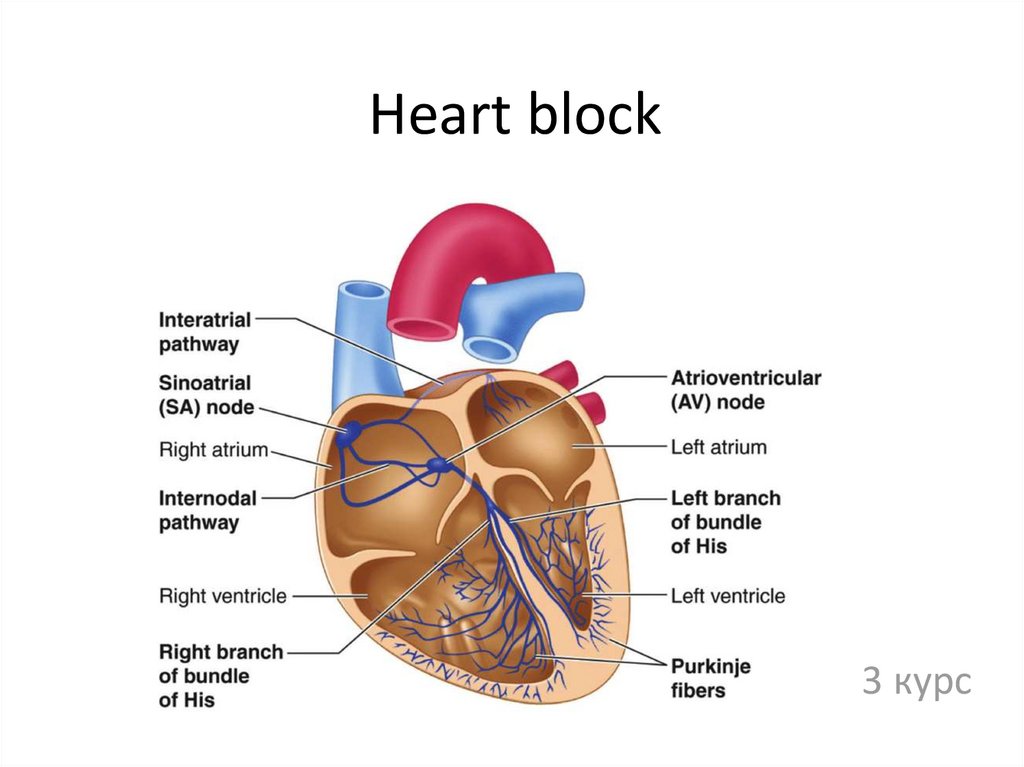
18. Heart block
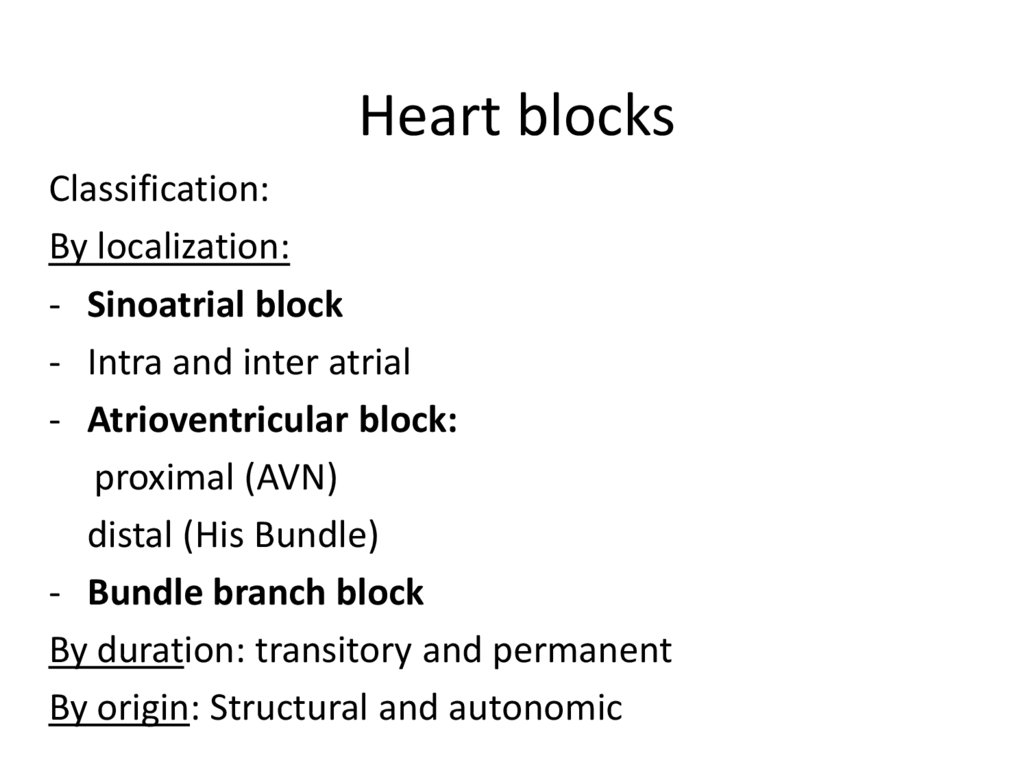
3 курс19. Heart blocks
Classification:By localization:
- Sinoatrial block
- Intra and inter atrial
- Atrioventricular block:
proximal (AVN)
distal (His Bundle)
- Bundle branch block
By duration: transitory and permanent
By origin: Structural and autonomic
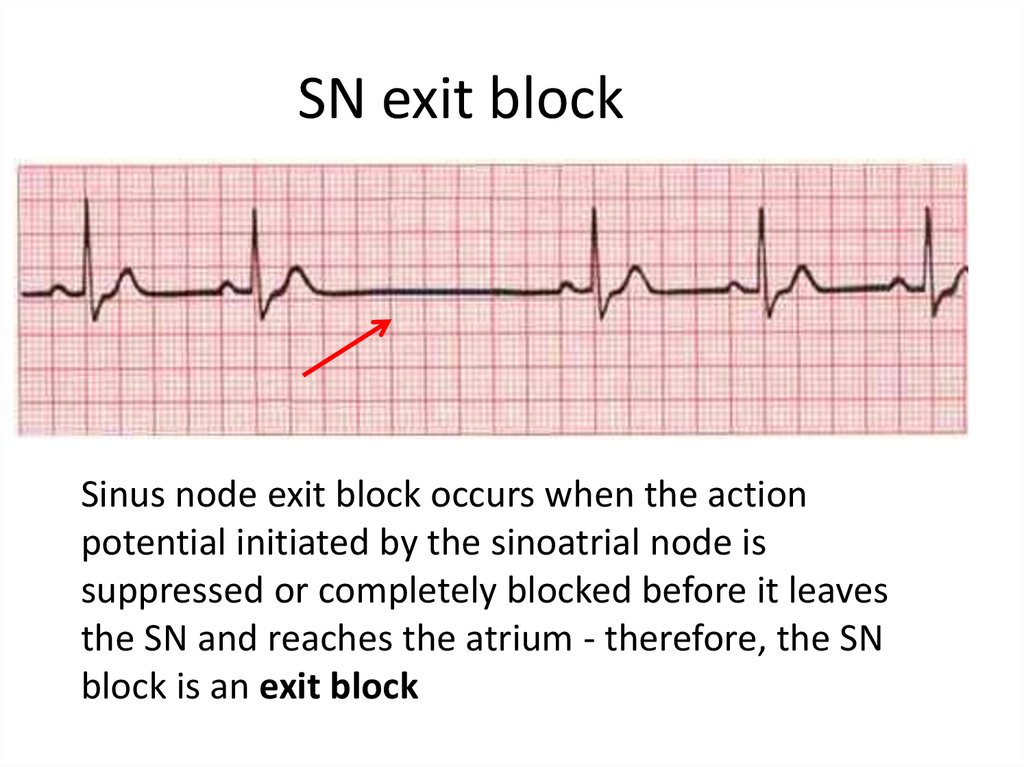
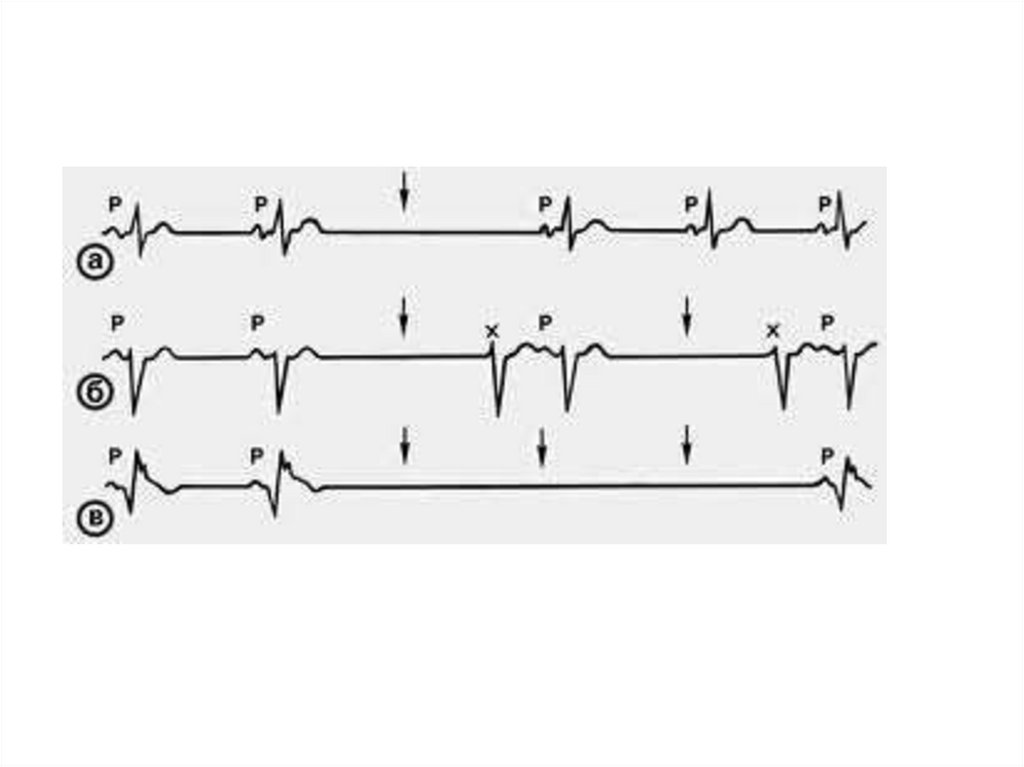
20.
SN exit blockSinus node exit block occurs when the action
potential initiated by the sinoatrial node is
suppressed or completely blocked before it leaves
the SN and reaches the atrium - therefore, the SN
block is an exit block
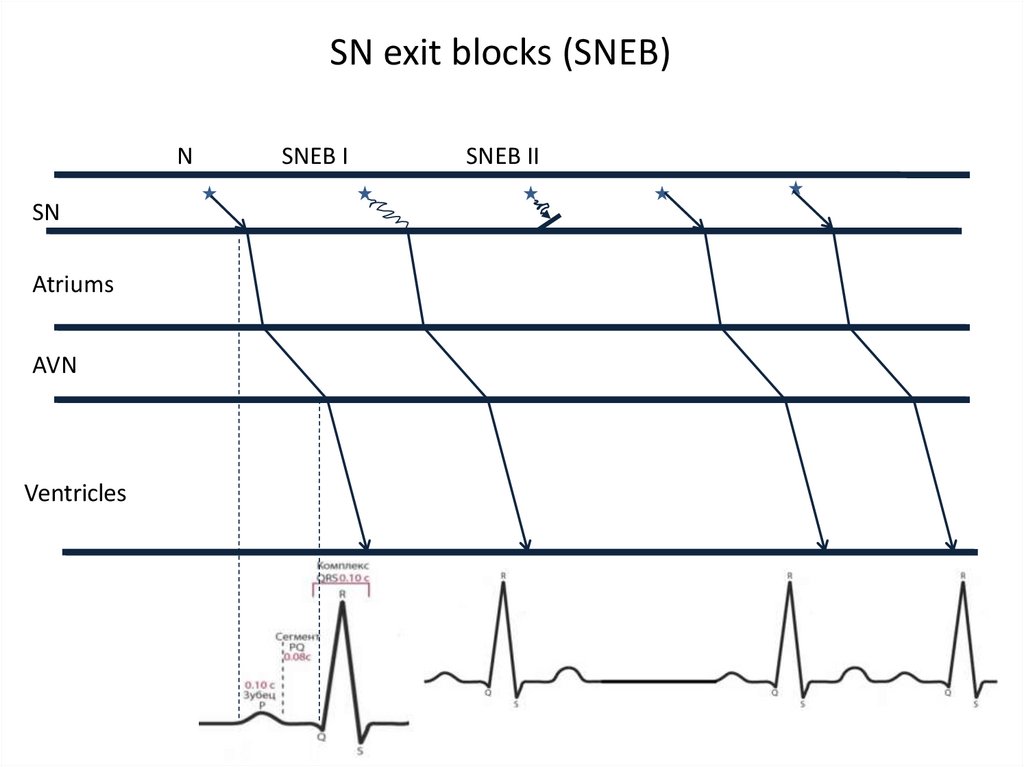
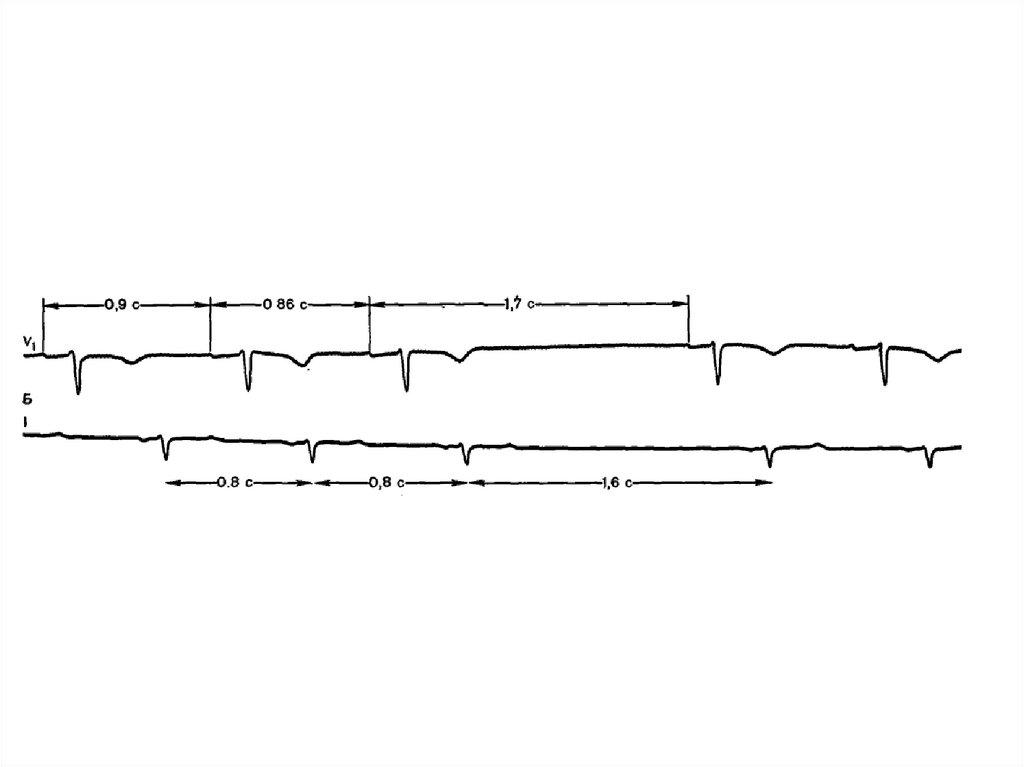
21.
SN exit blocks (SNEB)N
SN
Atriums
AVN
Ventricles
SNEB I
SNEB II
22.
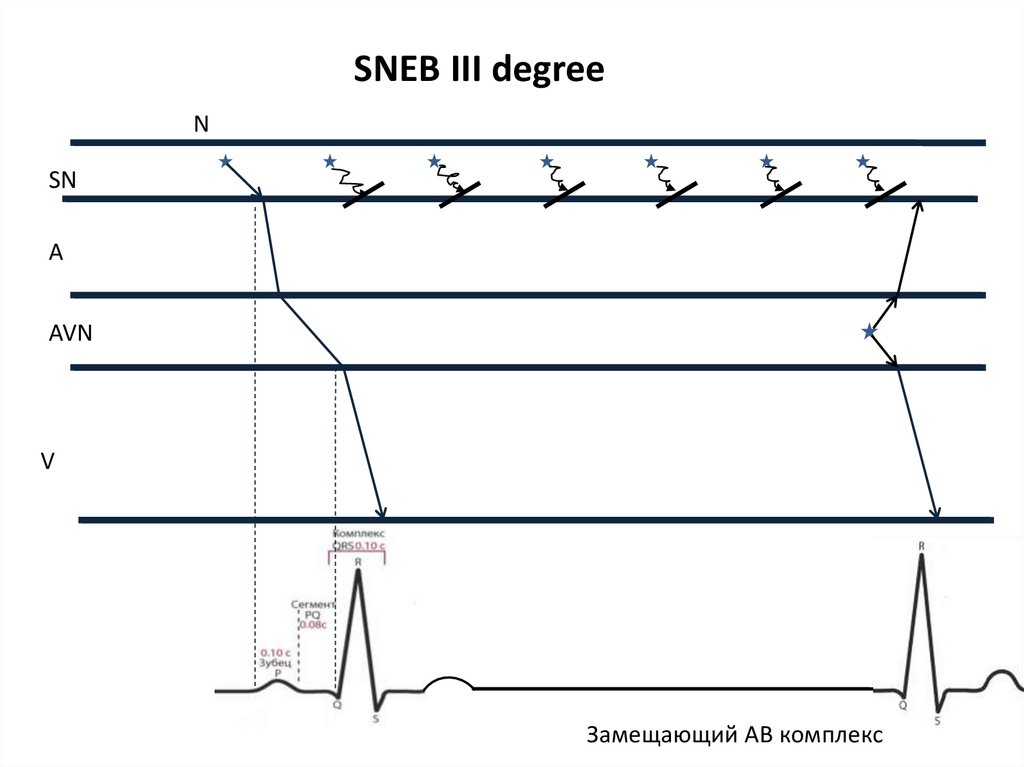
SNEB III degreeN
SN
A
AVN
V
Замещающий АВ комплекс
23.
24.
25.
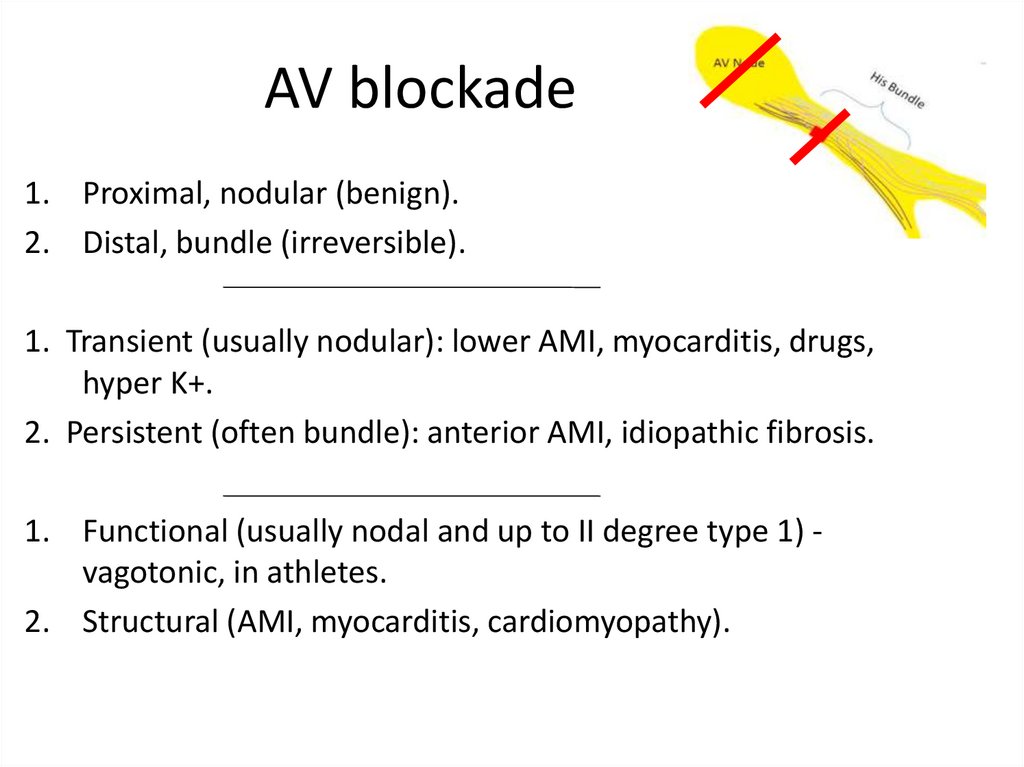
26. AV blockade
1. Proximal, nodular (benign).2. Distal, bundle (irreversible).
1. Transient (usually nodular): lower AMI, myocarditis, drugs,
hyper K+.
2. Persistent (often bundle): anterior AMI, idiopathic fibrosis.
1. Functional (usually nodal and up to II degree type 1) vagotonic, in athletes.
2. Structural (AMI, myocarditis, cardiomyopathy).
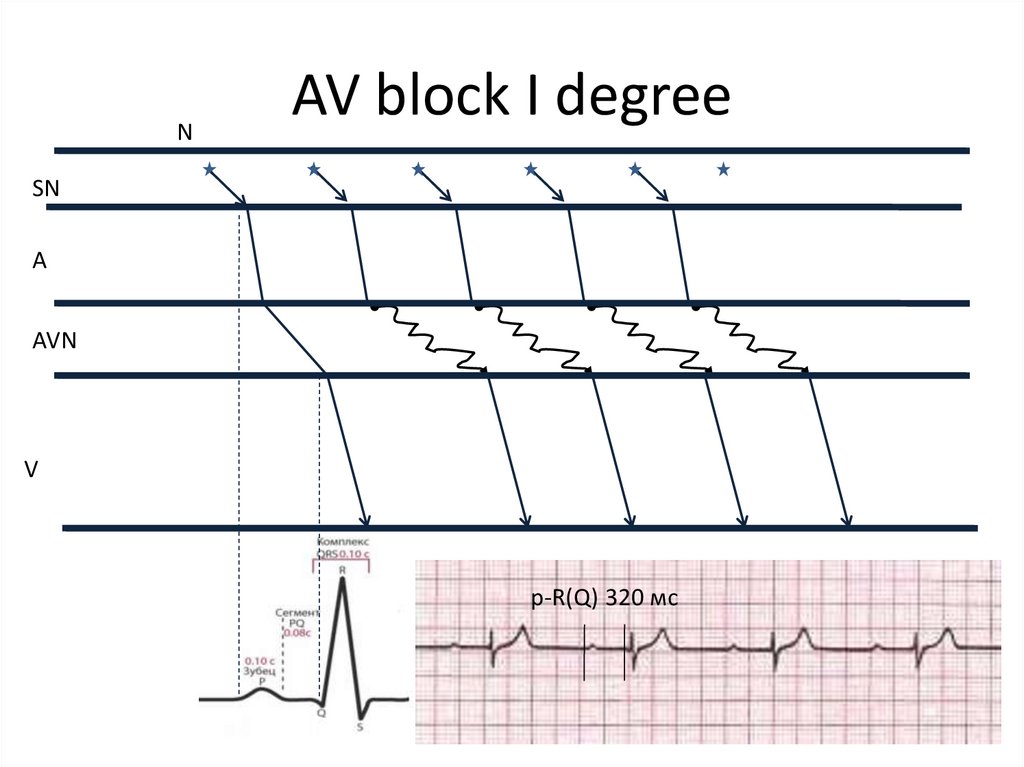
27. AV block I degree
NAV block I degree
SN
A
AVN
V
p-R(Q) 320 мс
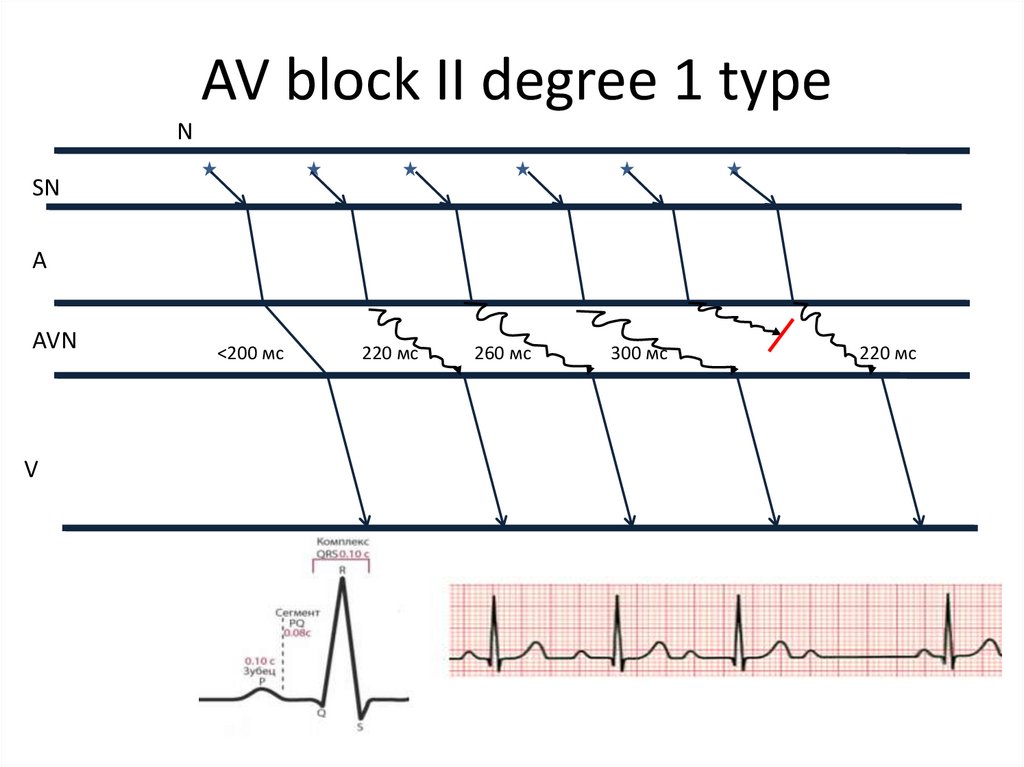
28. AV block II degree 1 type
NSN
A
AVN
V
<200 мс
220 мс
260 мс
300 мс
220 мс
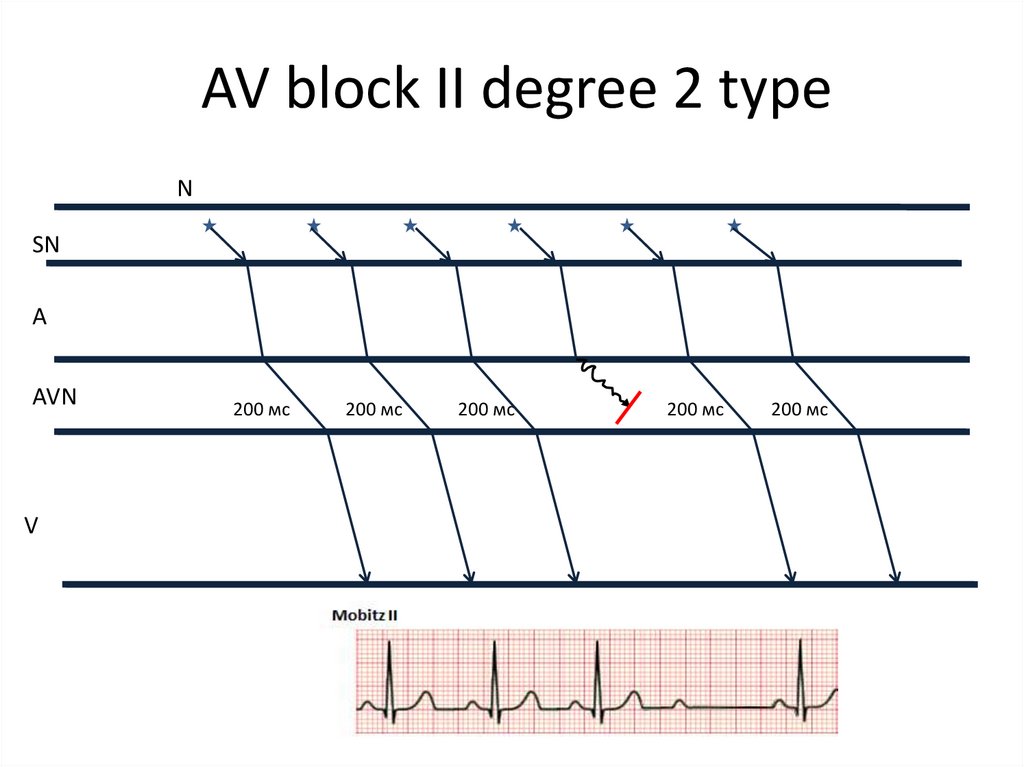
29.
AV block II degree 2 typeN
SN
A
AVN
V
200 мс
200 мс
200 мс
200 мс
200 мс
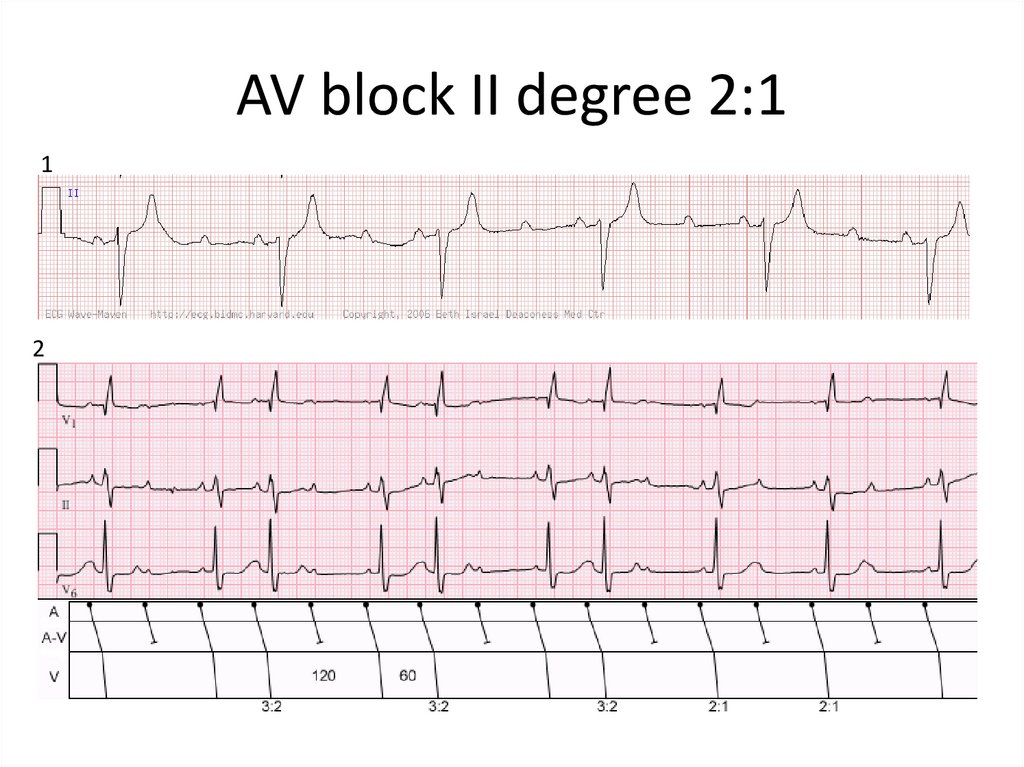
30. AV block II degree 2:1
12
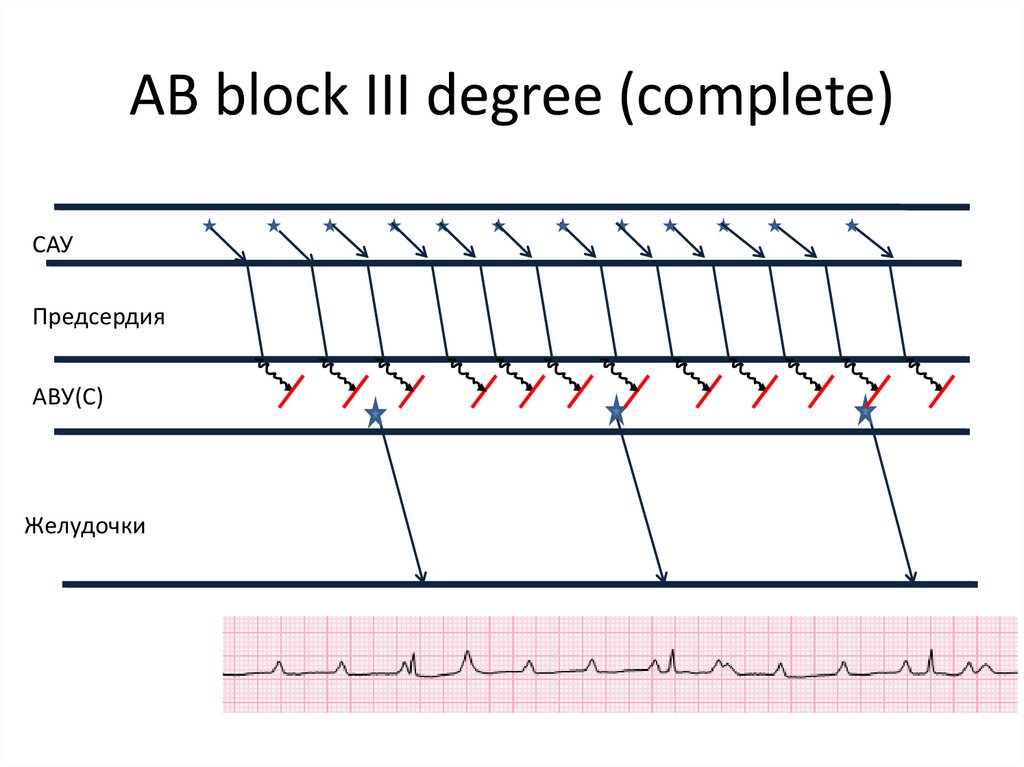
31. AB block III degree (complete)
САУПредсердия
АВУ(C)
Желудочки
32.
33.
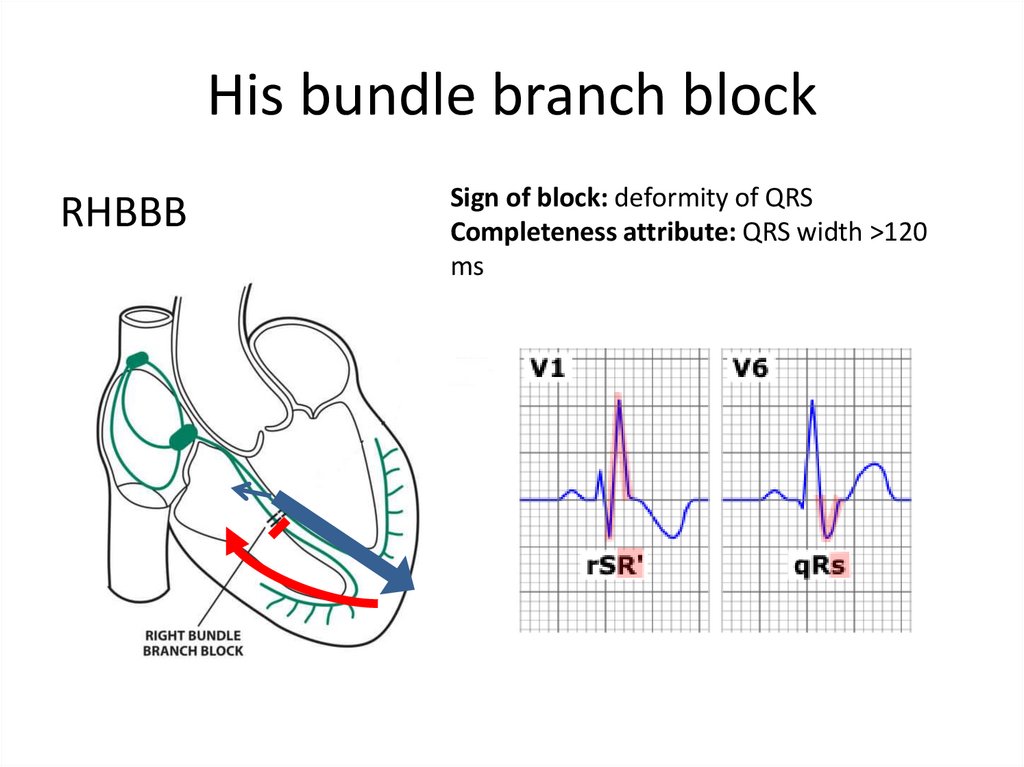
34. His bundle branch block
RHBBBSign of block: deformity of QRS
Completeness attribute: QRS width >120
ms
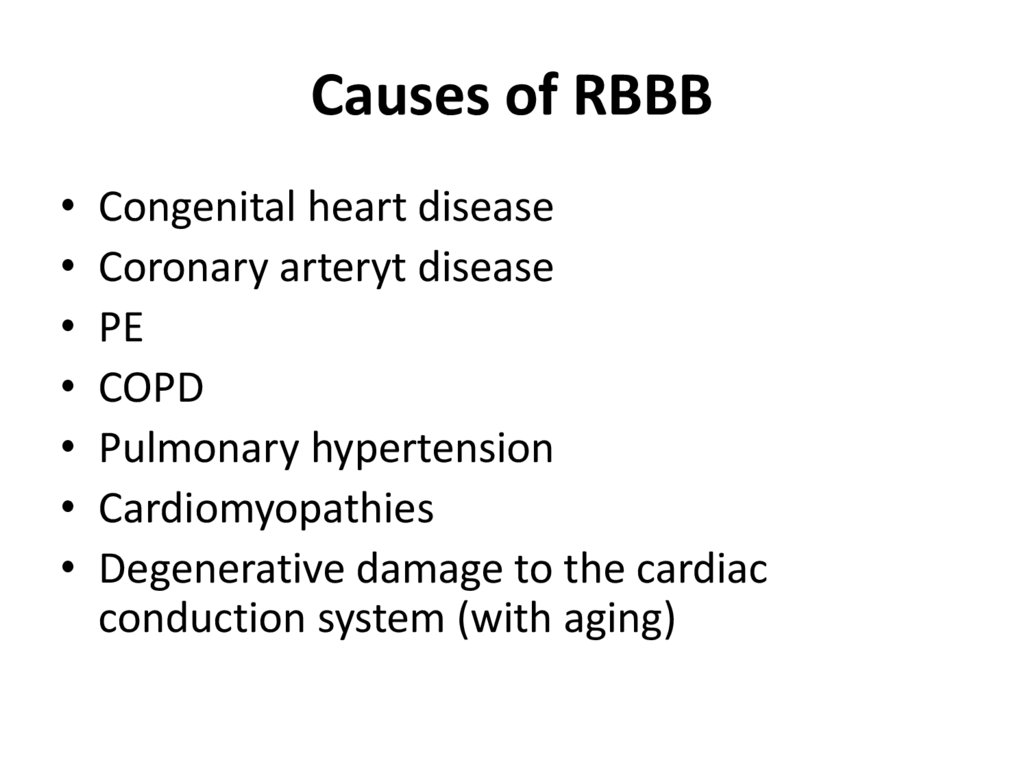
35. Causes of RBBB
Congenital heart disease
Coronary arteryt disease
PE
COPD
Pulmonary hypertension
Cardiomyopathies
Degenerative damage to the cardiac
conduction system (with aging)
36.
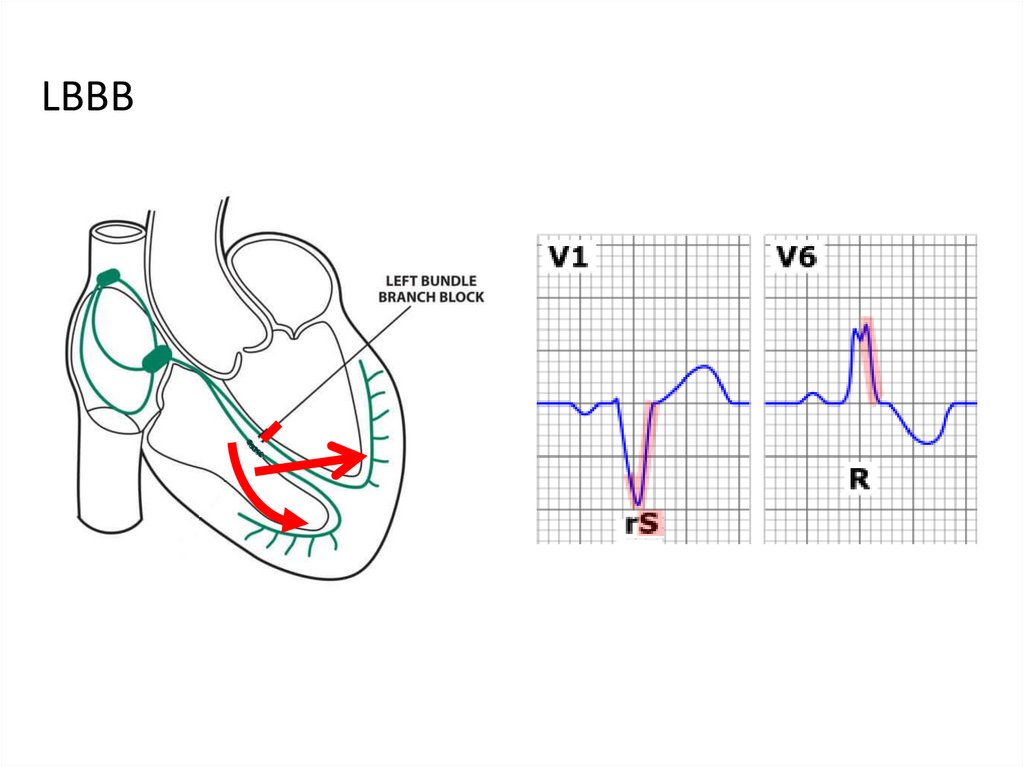
LBBB37. Causes of LBBB:
AH
CAD
LVH
Myocarditis
Valve defects
Cardiopathies
Degenerative damage to the conducting
system