Похожие презентации:
Intestinal yersiniosis and Pseudotuberculosis
1.
Intestinal yersiniosis(Y.)
and
Pseudotuberculosis
(P.Т).
Identification – it is acute saprozoonotic of diseases
described by a affection of a small intestine and it of
lymphoid derivations and accompanying with various
toxico-allergic manifestations with a diffuse lesion of
many bodies and systems of an organism.
Historical reference:
1883 –L. Malasser and W. Vignal detected and described
properties a new of microorganism
1895 –C. Eberth detected of the same pathogen and
nodules of an inflammations similar on tubercular in
bodies perished animal and denominated disease
"pseudotuberculosis"
1899 – A. Pfeiffer allocated culture of P.T. in the pure state
2.
1953 - В.Массхофф and В.Кнапп detected of the pathogenP.Т. at a mesadenitis for man ( the first time )
1959 - in East of Russia there was a flashout of the disease
which had obtained the name FESF- « Far Eastern
scarlatinoform fever »
1965 - В.А. Знаменский and А.К. Вишняков isolated of the
pathogen FESF. from the patients. В.А. Знаменский
confirmed of an etiology FESF in experience
autoinfection as pseudotuberculosis
1939 - Д. Шлейфстен and M. Колеман detected of the new
pathogen Y. under the name Yersinia enterocolitica
Since 1944 – isolated pathogens Y. and PТ. are included in a
new genus “Yersinia"
3.
Etiology:The pathogen has 0.8 - 2 microns of length and 0.6 – 0.8
microns of width, gram-(-), facultative anaerobic,
nonspore-forming bacillus. They are nonmotile at 37dg.C,
but usually motile at 22 dg.C. ( have flagella).
When Y. is coccobacillary - it`s virulent and when Y. is
bacillary – it`s avirulent.
Grow on simple mediums, but they are better reproduced at
+4 - +8 dg.C.
Y. are steady against cycles freezing - defreezing
Y. are longly survived and are multiplied in ground .
They are sensitive to desiccation, UVL, to warming and
boiling (survive no more than 30 seconds) to all
disinfectant solutions in usual concentrations (survive no
more than 5 minutes.)
4. When Y. is coccobacillary - it`s virulent and when Y. is bacillary – it`s avirulent.
5.
They have O , Н ,V and W antigenes.On O antigene all pathogens are distributed on serotypes:
- 8 serotypes are revealed at PТ. - but for the people more
often cause diseases - 1st serotype ( 60 - 90%),
less often - 3rd serotype
and 2,nd 4 th, 5th serotypes are very seldom
- 50 serotypes are revealed at Y. – but for the people more
often cause diseases - 03- 08 - 09 serotypes
V and W - antigens of virulance ( located by exterior of
memdrane )
6.
Toxinoformation – the endotoxin become frees only atbacteria destraction.
The endotoxin Y. - has expressed enteropathogenic effect.
The endotoxin PТ.- has expressed invasion properties and
enteropathogenic effect have only some strains 1st and 3rd
serotypes.
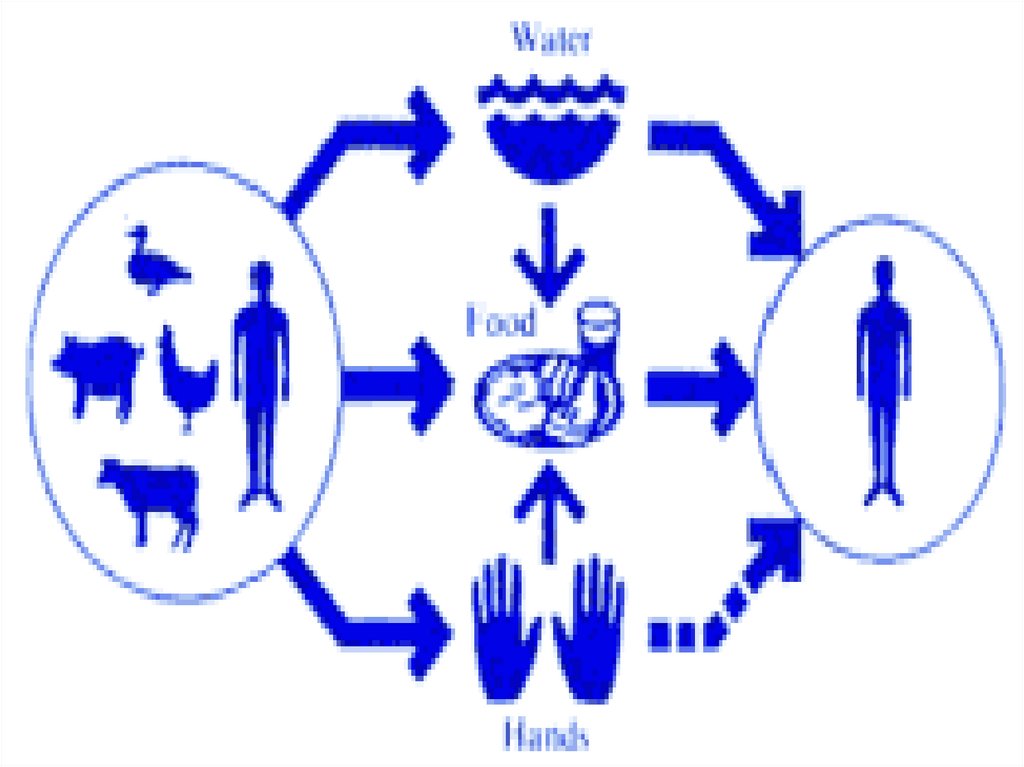
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Saprozoonosis. Many birds and animal are sick Y. and PТ.
Main source for the man – are variety domestic (dogs), and
wild ( rodents ) mammals which by own the excretions
infected food and water.
Auxiliary source - ground, water and molluscs
7.
The mechanism of infection - faecal-oralTransmission has usually traced to contact with
infected animals ( hands - to -mouth) or
contaminated food or water.
The factors of transmission:
- vegetable dishes (salads from fresh vegetables)
- milk (without boiling)
- water (open reservoirs)
- the contact mode of transmission – person-toperson is proved at only at intestinal yersiniosis!!!
8.
9.
Susceptibility general, but children are sick more oftenespecially in the closed collectives ( have common public
catering organization)
Peak of a case rate:
Y. – October- November ( become more frequent all IIT)
PТ. - March – May ( most activity of the rodents )
The sporadic and group cases rate are recorded
Pathogeny:
1.After infection through a mouth Y. advance on a small
intestine up to its terminal portion (place of primary
localization pathogens). In a lumen of a small intestine Y.,
apparently, intensively do not multiply ( confirmation - in
seedings of a feces they are found out only in 1- 3 % of
cases!
10.
2.Y. reach a terminal portion of a small intestine, pass
through an epithelium up to lamina propria and clump of
an lymphoid tissue (Peyer’s patches ), where occurs
them colony.
Here concentration Y. are in 1000 times more, than in other
portions of an intestine!
3. The macrophages capture Y. but killing them more often
is not completed.
With a current of a lymph Y. are brought in of lymphoid
derivation of an intestine and mesenteric lymph nodes,
causing in them an inflammation
11.
4. Diarrhea, which frequently develops at Y. has secretorycharacter, being by a consequence of activation of the
system «adenylcyclase – of cyclic 3,5 adenosinemonophosphates » of cellilar membrane of enterocytes with the
thermostable enterotoxin.
5. At Y the contents of prostaglandin Е (itself is capable to
cause a diarrhea) and prostaglandin F 2а (itself is cause
allergic reactions) increase in plasma.
6. More often at this stage the infectious process is
completed and by 5- 9 days the cellular immunity and by
12th - 15th to days humoral immunity are shaped.
12.
7. At an incompetence of immunity Y. will penetrate inblood- stream and are carried on all organism with a
toxico-allergic lesion of many bodies and systems.
The generalizations of the process are promoted by used of
iron preparations with the medical purpose (oppress a
phagocytosis).
The particular value has a serotype of the Y. e.g.:
- 03 serotype Y. - more often localized forms of disease
are shaped
- and 09 serotype Y. - generalized forms of disease are
shaped
13.
8. The long-lived finding in a blood and tissues Y. results invarious autoimmune processes, frequently with increase
of circulating immune complexes
9. The link between Y. and following diseases fixed:
- Reiter’s and Krohn’s Illnesses, reactive arthritises
- erythema nodosum, myocardites, uveites
Is suspected them participation at:
- set of symptoms Gougerot- Sjhogren’s
- thyroid disease, glomerulonephritis
- hemolytic anemia, haemolytico-uremic set of symptoms
- Schonlein’s, Bechterew’s, Behcet’s diseases etc.
14.
More probably all Y. is "caused" by these diaseases,enlarging autoantibodyformation!
9. The liberation of an organism from Y. occurs slowly, the
exacerbations and relapses are often, as the immunity is
shaped not so strong
PATHOMORPHOLOGY:
At autopsies or surgical operations find various changes:
- in a small intestine: catarrhal, ulcerative, hemorrhagic,
and necrotic enteritises
- in the lymphatic system: a mesadenitis, appendicitis
terminal ileitis etc.
- in bodies SMP: at PT. find out granulomas reminding
tubercular
15.
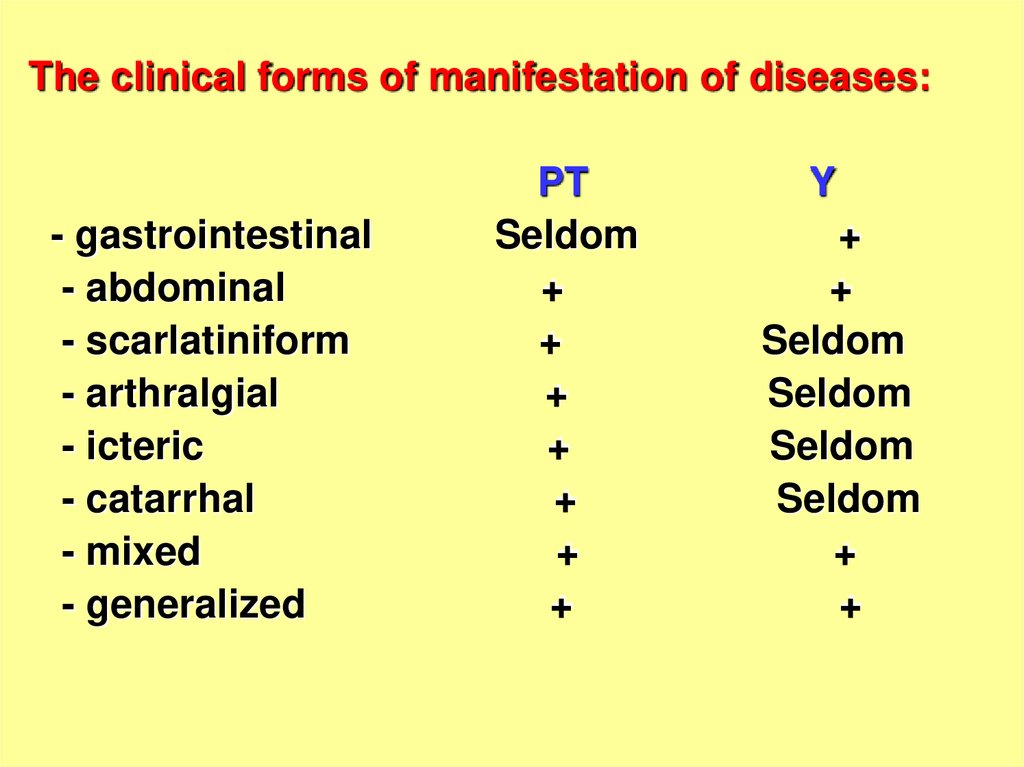
The clinical forms of manifestation of diseases:- gastrointestinal
- abdominal
- scarlatiniform
- arthralgial
- icteric
- catarrhal
- mixed
- generalized
PT
Seldom
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Y
+
+
Seldom
Seldom
Seldom
Seldom
+
+
16.
Clinicalal manifestations gastrointestinal form:For Y. and PT. is characteristic cyclic of current and
polymorphism of clinical manifestations!
INCUBATION:
At Y. (1- 6 days )
at PТ. (3 - 18 days )
Initial period: (1 - 5 days)
- the disease starts is acute, without a prodrome:
- fever up to 38 - 40 d.C
- nasal cold, tickling in throat or pharyngalgia at a
swallowing, cough
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, moderate pains in
mesogastrium
17.
- bring down or absence of appetite- weakness, malaise, headache and muscle pains,
insomnia,
OBJECTIVE:
- dry and hot skin, swollen the face, conjuctivitis, scleritis
- at PT. - a punctate eruption on hands, stops, neck
(as “gloves“, “socks", "hood") and acyanotic nasolabial
a triangule
- at Y. micropunctate or micromacular an eruption on
extremities or trunk.
HEIGHT of disease (5 - 7 DAYS):
- the fever and the intoxication amplifies
- the liver and lien is enlarged
18.
19.
- there is a punctate rash on a skin flexions of extremitiesand side part of a trunk, is especial in skin folds ( с-м Пастиа ),
(The skin of the face without an eruption )
- the arthralgias (through 7 - 14 days can be transformed
to a polyarthritis, around of them occurs macromacular an
eruption or nodal erythema
- the anorexia, nausea, vomiting (is sometimes saved),
diarrhea
- coated tongue - « white strawberry tongue », but to the 5th
to day refines - «red strawberry tongue »
20.
21.
- at a palpation of a abdomen- murmur both painfulness inmesogastrium and hypogastrium (on the right)
- CVS - tachycardia, moderate lowering BP, dull of cardiac
sounds
- on the part of urine - signs of a syndrome “toxic kidney”
- the brain - edema also can be serous a meningitis
- WBC -neutrophilic a leukocytosis 10-30 х 10 in 9th dg.\L
ESR - 20 - 55 mm / h, sometimes eosinophilia
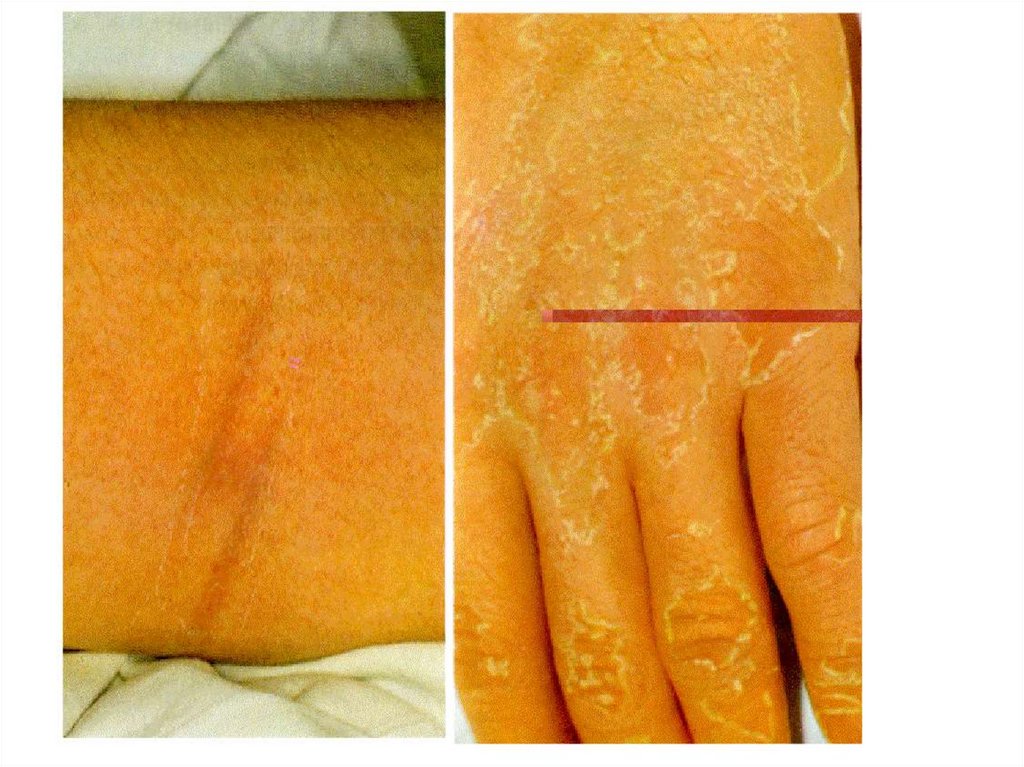
The period convalescence:- is accompanied by lowering
temperature and sluggish restoration of the function of the
struck bodies.
After 2 - 3 weeks for the majority of the patients have been a
desquamation of a skin of a trunk and extremities (palm
and sole)
22.
23.
The abdominal:- pain in the right half of abdomen
- moderate watery diarrhea up to 5 - 7 times per day with
slime, but without admixture of a blood. The duration of a
diarrhea is prolonged 2 - 3 weeks without treatment, but
sometimes can last by months!!!
The terminal ileitis (intoxication, fever in limits 38 - 39 dg.C
is less often taped, the colicy pains on the right in
hypogastric region during a defecation, are saved by
stationary values after it of the termination. X-ray
examination the site of contraction of a small intestine« a sign of a cord » is taped
Mesadenitis (acute beginning, nausea, vomiting, pain in
meso and hypogastrium, diarrhea 3 - 5 times per day,
moderate boring of a peritoneum, appearance of an
infiltrate on the right in hypogastrium, positive signs
Штейберга, Mc Fadden, Падалки
24.
Appendicular:Differs from clinic acute catarrhal of an appendicitis with
signs of an acute mesadenitis a little.
Frequently is accompanied by arthralgias, exanthema,
conjunctivitis, « by strawberry tongue ». Usually patients
are exposed to operating treatment after an advice of the
surgeon (clinic of an acute appendicitis + hyperleukocytosis).
Scarlеtform: More often at PT
Fever and intoxication, acyanotic a nasolabial triangle,
« strawberry tongue », punctate rash on a skin and its an
desquamation, absence of a diarrhea. Usually proceeds
without relapses!!!
25.
arthralgialThe main clinic signs this form are a damage of a
locomotory apparatus ( arthralgia and arthritises ) in a
combination to other manifestations Y. prevail
Icteric:
Appears by a reactive hepatitis with increase of a liver,
spleen by an icterus, rising ALT and AST in 5- 10 times
neutrophilic by a leukocytosis, negative markers VH.
catarrhal
The damage URT (rhinitis, pharyngitis, tracheitis, bronchitis
prevail. The exanthema meets seldom. More often
diagnosis as acute URTI
26.
Generalized:As a durably proceeding sepsis for the persons with
immunodeficiency with creation of multiple purulent
focuses of internal bodies.
A lethality in limits 50 % even for the patients treated by
antibiotics!!!
The forecast:
- favourable, except for the septic form.
- without antibiotics the illness stops in 1,5 months, but up
to 3 - 6 months can be prolonged
- relapses and exacerbations – 8 – 55%
- subacute and chronic course – 3 - 10%
27.
Complications:-myocarditis
-hepatitis
-cholecystitis
-pancreatitis
-appendicitis
-Intestinal obstruction
-Intestinal perforation
-peritonitis
-glomerulonephritis
-meningoencephalitis etc.
28.
Differential diagnosis:Scarlet fever
Acute intestinal diseases
Acute respiratory diseases
Rheumatic disease, polyarthritis,
Virus hepatitises
Adnexitis, appendicitis
Mononucleosis
Typhoids
Sepsis
Canicola fever ( leptospirosis )
Brucellosis
Chlamydiosis etc.
29.
Laboratory diagnosis:- Method of express - diagnosis - IFt
- Bacteriological method - inoculations of a blood, vomitive
masses, feces, operational and biopsied of a material on
phosphatno- buffered solution or medium Серова with the
subsequent cultivation at low temperature
(Frequency of detection Y. in a feces 1 - 3 %),
(Frequency of detection Y. in biopsied a material 33 %)
- Immunological method – HA test (1:200) and HAP test
(1:100) with usage of a method « of the pair serums »
- ELISA.
30.
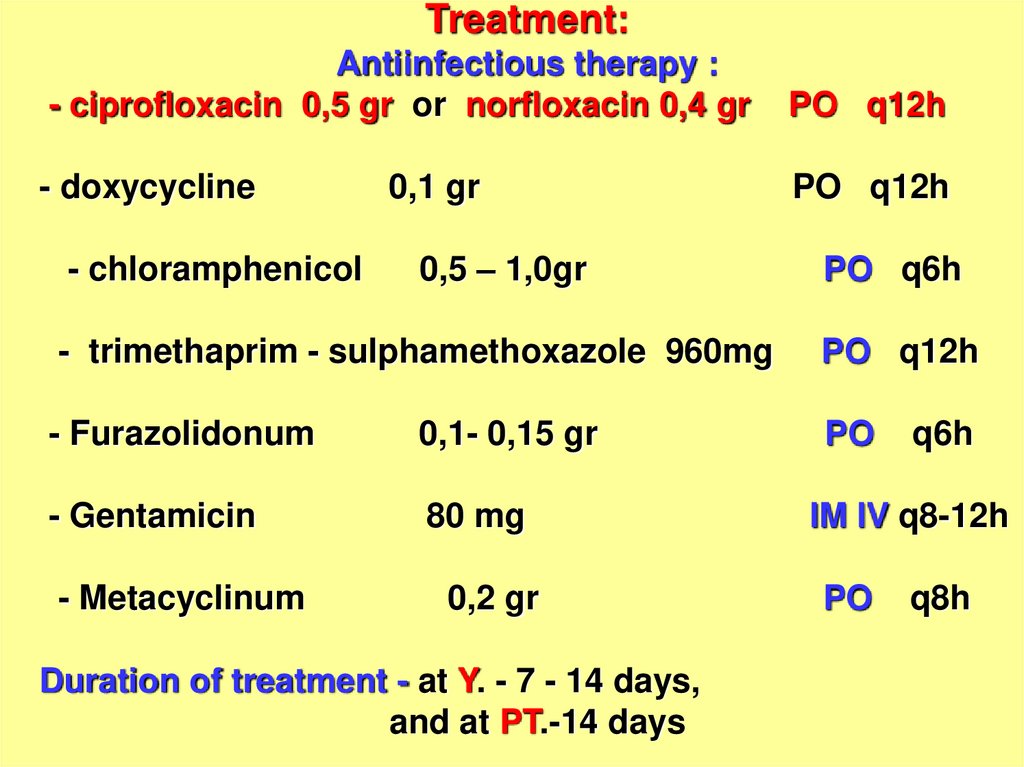
Treatment:Antiinfectious therapy :
- ciprofloxacin 0,5 gr or norfloxacin 0,4 gr
PO q12h
- doxycycline
PO q12h
- chloramphenicol
0,1 gr
0,5 – 1,0gr
PO q6h
- trimethaprim - sulphamethoxazole 960mg
PO q12h
- Furazolidonum
0,1- 0,15 gr
PO
- Gentamicin
80 mg
- Metacyclinum
0,2 gr
Duration of treatment - at Y. - 7 - 14 days,
and at PT.-14 days
q6h
IM IV q8-12h
PO
q8h
31.
- detoxication therapy- antihistamine drugs
- antiinflammatory therapy
- surgical treatment + antiinfectious drugs
- glucocorticoids ( at TIS, brain edema, rising in a blood
circulating immune of complexes)
Prophylaxis:
- Deratization and protection against of the rodents
vegetable stores
- Constant sanitary supervision of water supply, preparation
and storage of food
- Strict control at processing and storaging of foodstuffs
especially made of crude vegetables (salads)
32.
A 23 year- old male admited in the 6th municipal hospitalwith complaints : fever, malaise, nausea, vomiting, pain in
right hypogastric area, diarrhea 2 – 4 time per day.
Surgeon found of signs of an acute appendicitis and
neutrophilic hyperleucocytosis. Sick was opereted and
was removed catarrhal appendix. State of patient does not
improved- temperature , pain , diarrhea and
hyperleucocytosis are keeping. At repeated operation no
signs of purulent peritonitis but mesenteric lymphoid
nodes increased.
One node was removed for histologic and bacteriological
tests. Reveal agent Y. serological test (HA) detected
increase by antibody in titer 1:200. Doctor-infectionist
confirmed diagnosis of Y. Sick was treated by doxycycline
0.2 gr/day ( 14 days) Fever decrease at the 4th day and
diarrhea stoped at 5th day. Outcome of disease – complete
convalescence.



























 Медицина
Медицина