Похожие презентации:
Data analysis. Data management. Анализ данных. Управление данными. Lection 6
1. DATA ANALYSIS. DATA MANAGEMENT Анализ данных. Управление данными
Lection 6DATA ANALYSIS.
DATA MANAGEMENT
АНАЛИЗ ДАННЫХ. УПРАВЛЕНИЕ
ДАННЫМИ
2. contents
CONTENTSData analysis bases.
Methods of collection, classification
and prediction.
Decision trees.
Processing of large volumes of data.
Methods and stages of Data mining.
Tasks of Data mining.
Visualization of data.
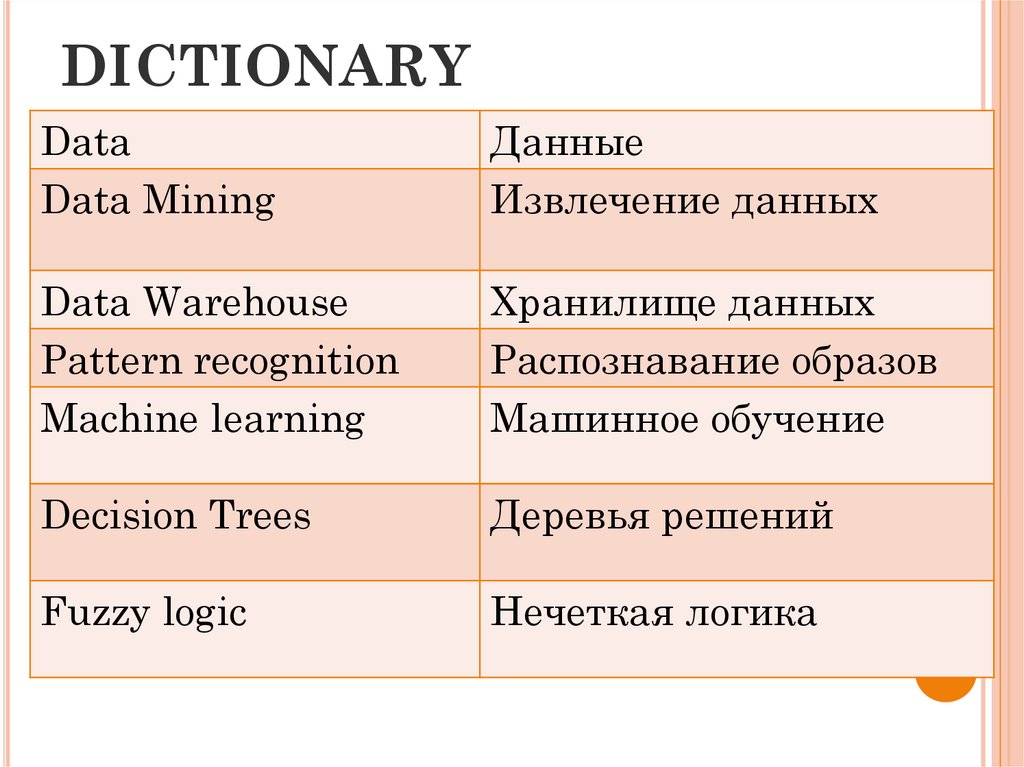
3. DICTIONARY
DataData Mining
Данные
Извлечение данных
Data Warehouse
Pattern recognition
Machine learning
Хранилище данных
Распознавание образов
Машинное обучение
Decision Trees
Деревья решений
Fuzzy logic
Нечеткая логика
4. DATA
theraw material provided by
data providers and used by
consumers
for
generating
information based on data
facts,
text, graphics, images,
sound, analog or digital video
segments
5. DATA MINING
DATA MININGmultidisciplinary
area,
arising and developing on the
basis of such Sciences as
applied statistics, pattern
recognition,
artificial
intelligence,
theory
of
databases, etc.
6. KNOWLEDGE DISCOVERY IN DATABASES (KDD)
KNOWLEDGE DISCOVERY INDATABASES (KDD)
DM, popularly referred to Knowledge
Discovery in Databases (KDD), is the
automated or convenient extraction
of patterns representing knowledge
implicitly stored or captured in large
databases which can contain millions
of rows related to Database subject,
Data
Warehouses,
Web,
other
massive information repositories or
data streams.
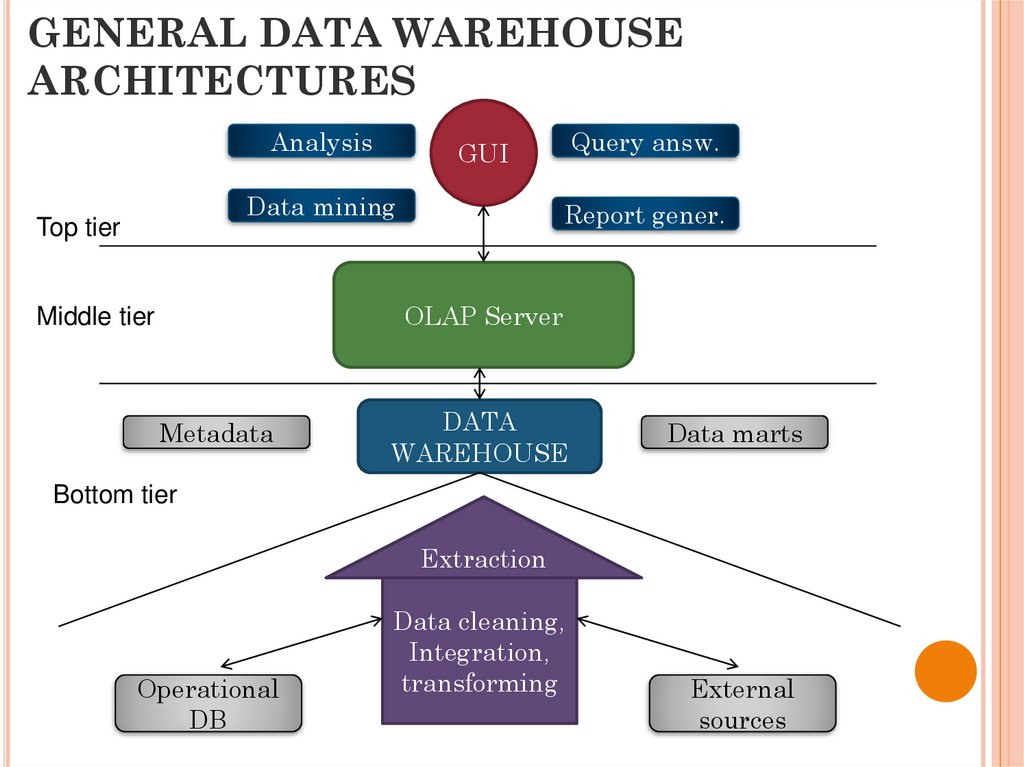
7. GENERAL DATA WAREHOUSE ARCHITECTURES
AnalysisData mining
Top tier
Query answ.
GUI
Report gener.
OLAP Server
Middle tier
Metadata
DATA
WAREHOUSE
Data marts
Bottom tier
Extraction
Operational
DB
Data cleaning,
Integration,
transforming
External
sources
8. DATA MINING MODELS AND TASKS
Data miningPredictive
models
Descriptive
models
Prediction
Classification
Clustering
Summarizati
on
Time Series
Analysis
Regression
Association
rules
Sequences
discovery
9. PREDICTIVE MODEL
PREDICTIVE MODELenables to predict the
values of data by using
known results from
different sets of sample
data
10. PREDICTIVE MODEL
PREDICTIVE MODELClassification
enables
to
classify data from a large data
bank into predefined set of
classes.
Regression is one of statistical
techniques which enable to
forecast future data values based
on the present and past data
values.
11. PREDICTIVE MODEL
PREDICTIVE MODELTime series analysis is a part
of Temporal mining which
enables to predict future values
for the current set o f values
which are time dependent.
12. descriptive model
DESCRIPTIVE MODELEssence of a descriptive
models is determination
of the pattern and
relationships in a
sample data.
13. descriptive model
DESCRIPTIVE MODELClustering is a data processing
in some sense opposite to
classifications which enables you
to create new groups and classes
based on the study of patterns
and relationship between values
of data in a data bank.
14. descriptive model
DESCRIPTIVE MODELSummarization is a technique
which enables to summarize a
large chunk of data contained in
a Web page or a document. Thus,
summarization is also known as
characterization or
generalization.
15. descriptive model
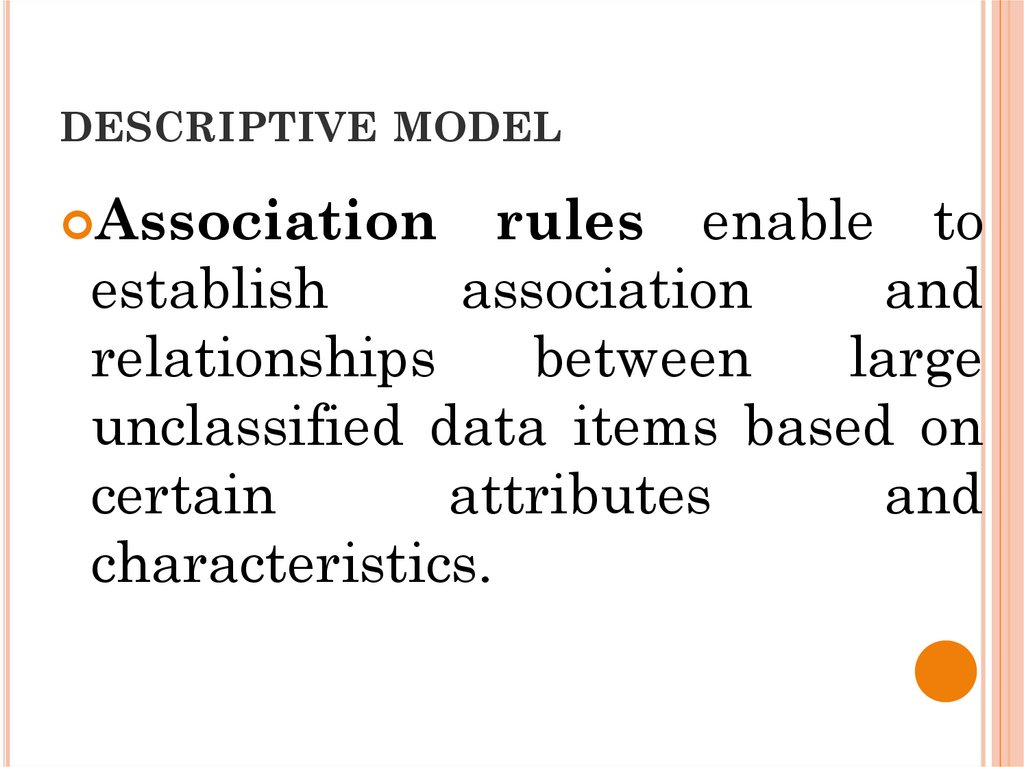
DESCRIPTIVE MODELAssociation
rules enable to
establish
association
and
relationships
between
large
unclassified data items based on
certain
attributes
and
characteristics.
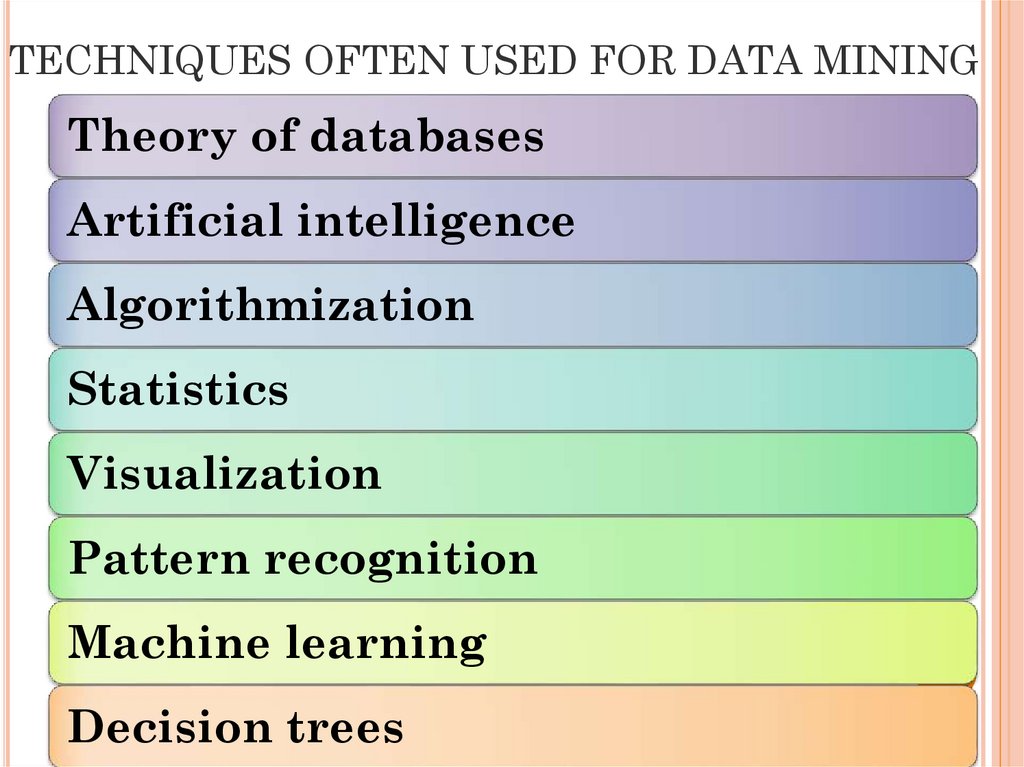
16. TECHNIQUES OFTEN USED FOR DATA MINING
Theory of databasesArtificial intelligence
Algorithmization
Statistics
Visualization
Pattern recognition
Machine learning
Decision trees
17. DATA MINING APPLICATIONS
BusinessElectronic (and traditional) commerce
Computer security
Banking and financial processing
Bioinformatics, Medicine, Health care
News and entertainment data
18. PROCESS MODELS OF DATA MINING
5ACRISP-DM
SEMMA
SIX-SIGMA
CLASSIFICATION
DECISION TREE
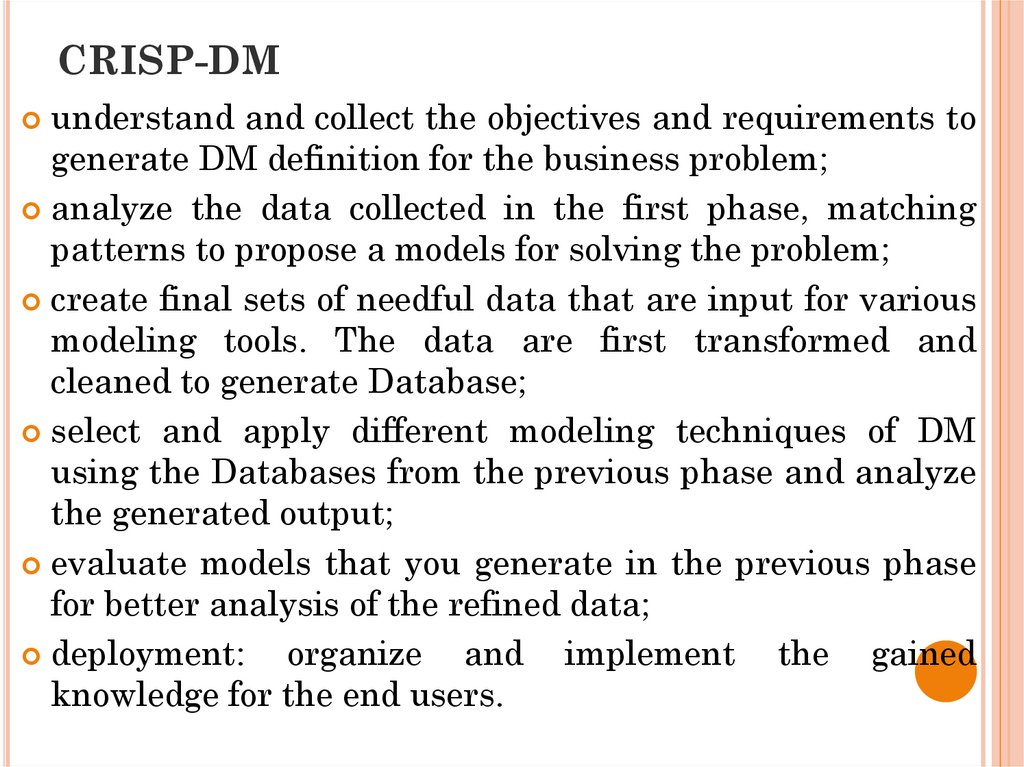
19. CRISP-DM
understand and collect the objectives and requirements togenerate DM definition for the business problem;
analyze the data collected in the first phase, matching
patterns to propose a models for solving the problem;
create final sets of needful data that are input for various
modeling tools. The data are first transformed and
cleaned to generate Database;
select and apply different modeling techniques of DM
using the Databases from the previous phase and analyze
the generated output;
evaluate models that you generate in the previous phase
for better analysis of the refined data;
deployment:
organize and implement the gained
knowledge for the end users.
20. STATISTICS METHODS OF DATA MINING
Descriptive analysisLinkage analysis
Multivariate statistical analysis
Time series analysis
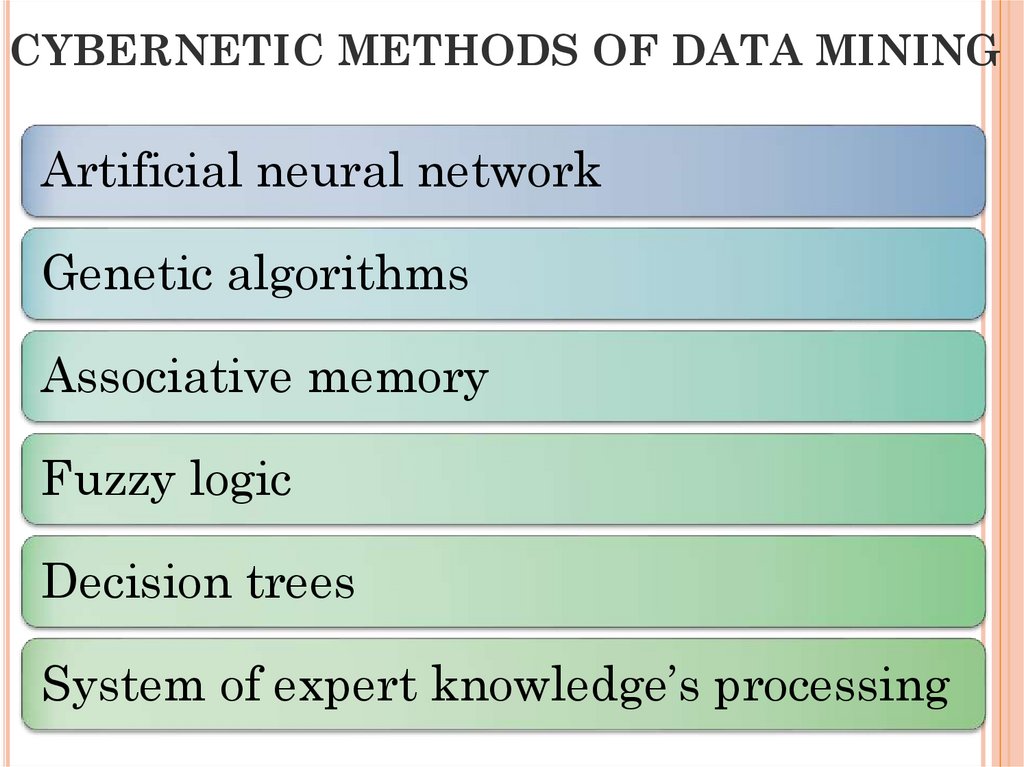
21. CYBERNETIC METHODS OF DATA MINING
Artificial neural networkGenetic algorithms
Associative memory
Fuzzy logic
Decision trees
System of expert knowledge’s processing
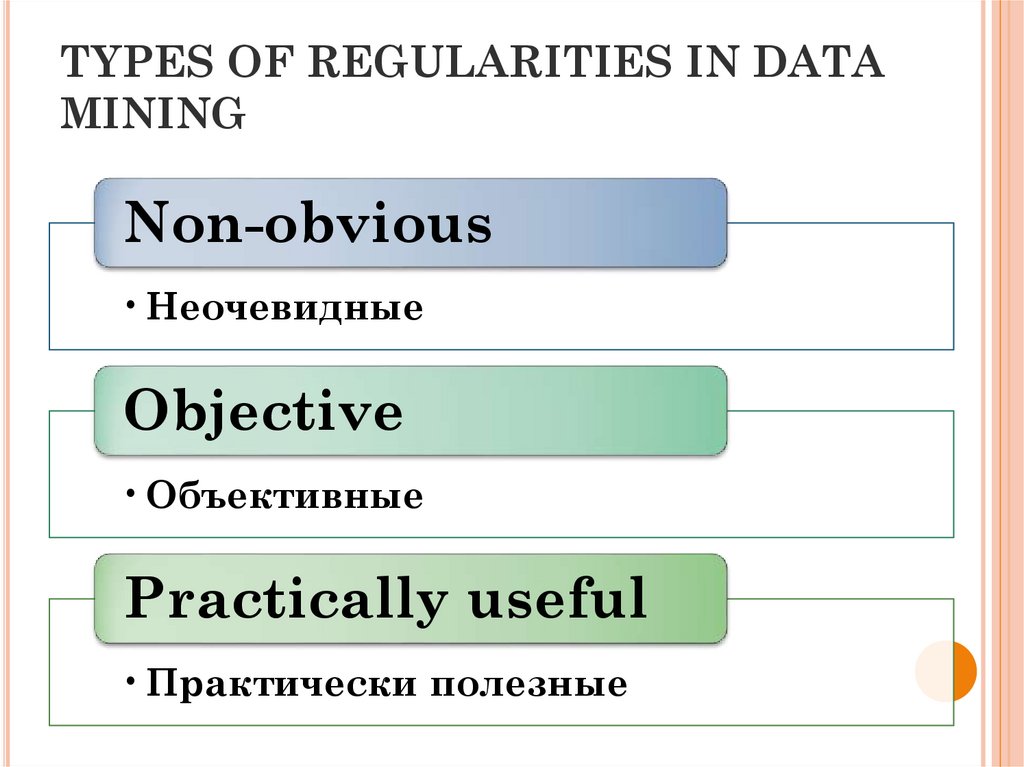
22. TYPES OF REGULARITIES IN DATA MINING
Non-obvious•Неочевидные
Objective
•Объективные
Practically useful
•Практически полезные
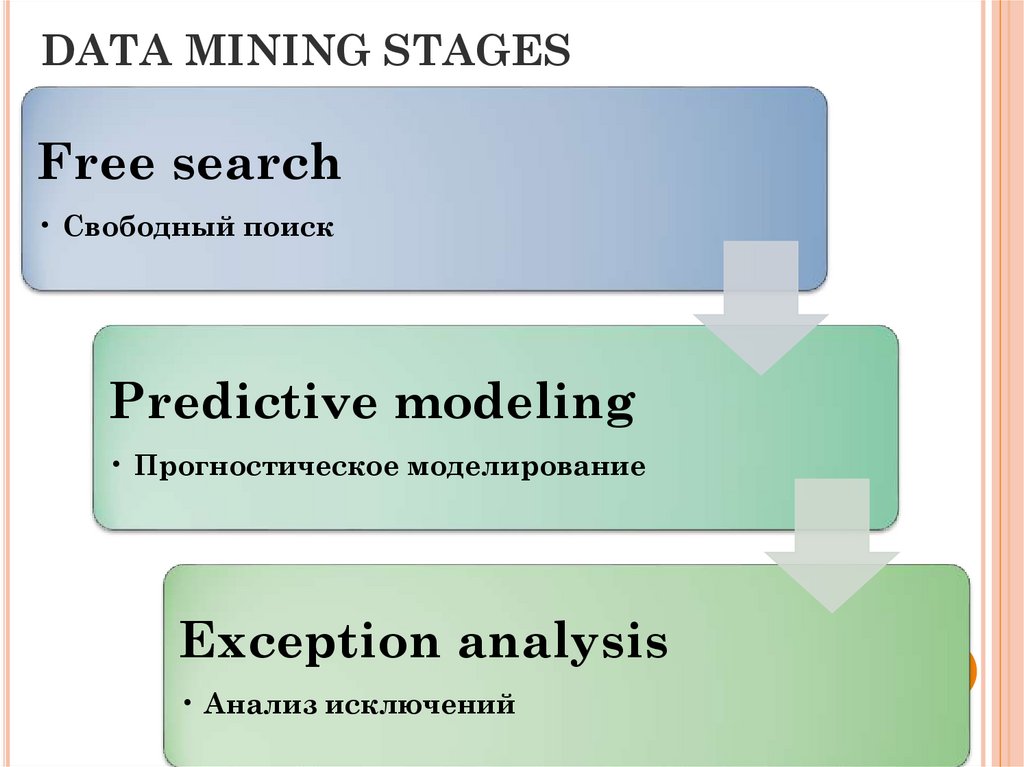
23. DATA MINING STAGES
DATA MINING STAGESFree search
• Cвободный поиск
Predictive modeling
• Прогностическое моделирование
Exception analysis
• Анализ исключений
24. TECHNOLOGICAL METHODS OF DATA MINING
Saving data•Сохранение данных
Templates distillation
•Дистилляция шаблонов
25. DECISION TREES
a way of representing therules in a hierarchical and
sequential
structure,
where
each
object
corresponds to a single
node that provides the
solution
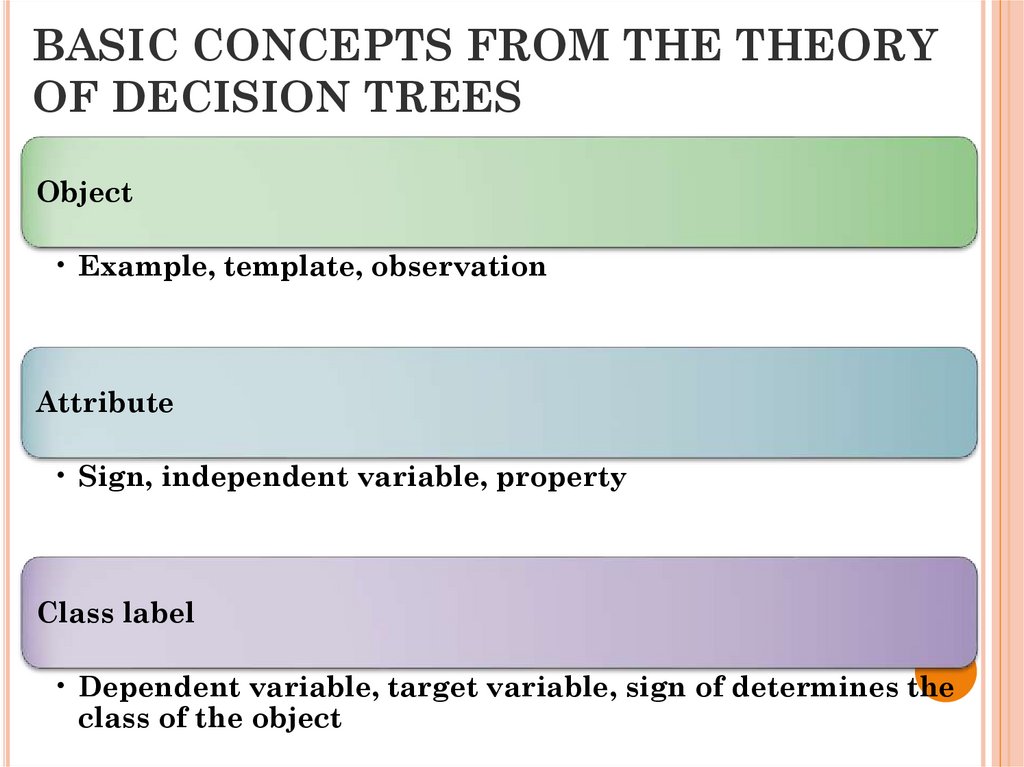
26. BASIC CONCEPTS FROM THE THEORY OF DECISION TREES
Object• Example, template, observation
Attribute
• Sign, independent variable, property
Class label
• Dependent variable, target variable, sign of determines the
class of the object
27. BASIC CONCEPTS FROM THE THEORY OF DECISION TREES
Node• Internal tree node, check node
Sheet
• Final tree node, decision node
Test
• Condition in the node
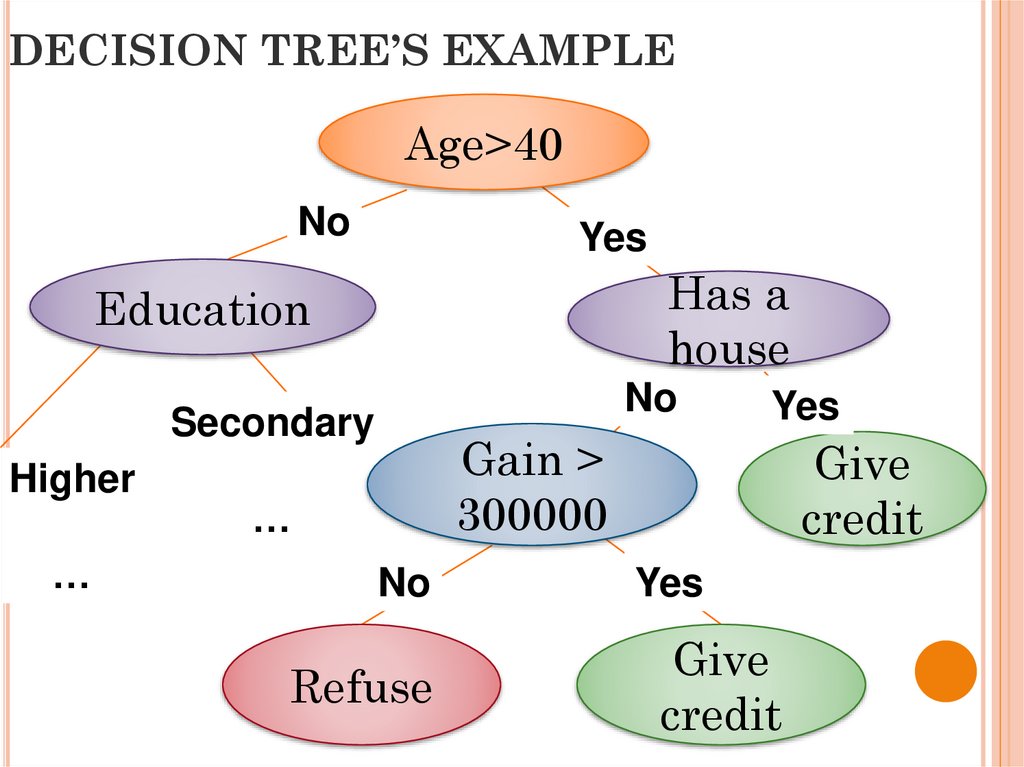
28. DECISION TREE’S EXAMPLE
Age>40No
Yes
Has a
house
Education
No
Secondary
Higher
…
Yes
Gain >
300000
…
No
Refuse
Give
credit
Yes
Give
credit
29. ALGORITHMS FOR DECISION TREES
CARTC4.5
30. BIG DATA
a set of approaches, tools andmethods for processing of
structured and unstructured
data of enormous volume and
significant variety to obtain
the perceived results
31. CHARACTERISTICS OF BIG DATA
Volume• Объем
Velocity
• Скорость прироста
Variety
• Многообразие
32. CONCLUSION
DataMining is a multidisciplinary
area, arising and developing on the
basis of such sciences as applied
statistics,
pattern
recognition,
artificial
intelligence,
theory
of
databases, etc.
3 stages of Data Mining
3 characteristics of big data (VVV)



















 Информатика
Информатика








