Похожие презентации:
IDIC-Identifying Customers
1. IDIC-Identifying Customers
Course:Professor name
2. Preview
Why identify customers?
Customer identification in reality
“Identify” activities
Customer identification in the B2B space
Customer identification in the B2C space
Data collection
Integrating data to identify customers
Smart markets
Smart market strategy
3. Why Identify Customers?
• To build a relationship, we need to know who ourcustomers are:
– Which customers do we want
– Recognize them when coming into contact with them
• Types of relationships:
– Aggregate
– Individual
4. Customer Identification in Reality
• Industries’ overview– Long distance phone companies
– Retail banks
– Consumer packaged goods companies
– Insurance companies
– Computer hardware companies
– Carmakers
• Two-step method
– How much information do the companies already have
– Enabling customers to identify themselves
5. “Identify” Activities
• Define: what information do we need?• Collect: what mechanism to collect?
• Link: How is the customers’ information linked to the
transaction?
• Recognize: What are the different channels?
• Store: How to store and maintain information?
• Update
• Analyze
• Make available
• Secure
6. Customer Identification in B2B
• Challenge– Who is on the other side of the relationship?
– Who are end-users?
• Identifying end user
– Product consuming replenishable supplies
– Product complicated to use
– Product that needs periodic maintenance
• Identifying “relationships with relationships”
– Incentive for revealing the identities of the players
• Relationship adheres to the company, not the individuals
7. Customer Identification in B2C
• Challenge: Millions of customers• New technology makes it possible
– Power to record
– Power to find
– Power to compare
• Internet: A real one-to-one opportunity
– Amazon
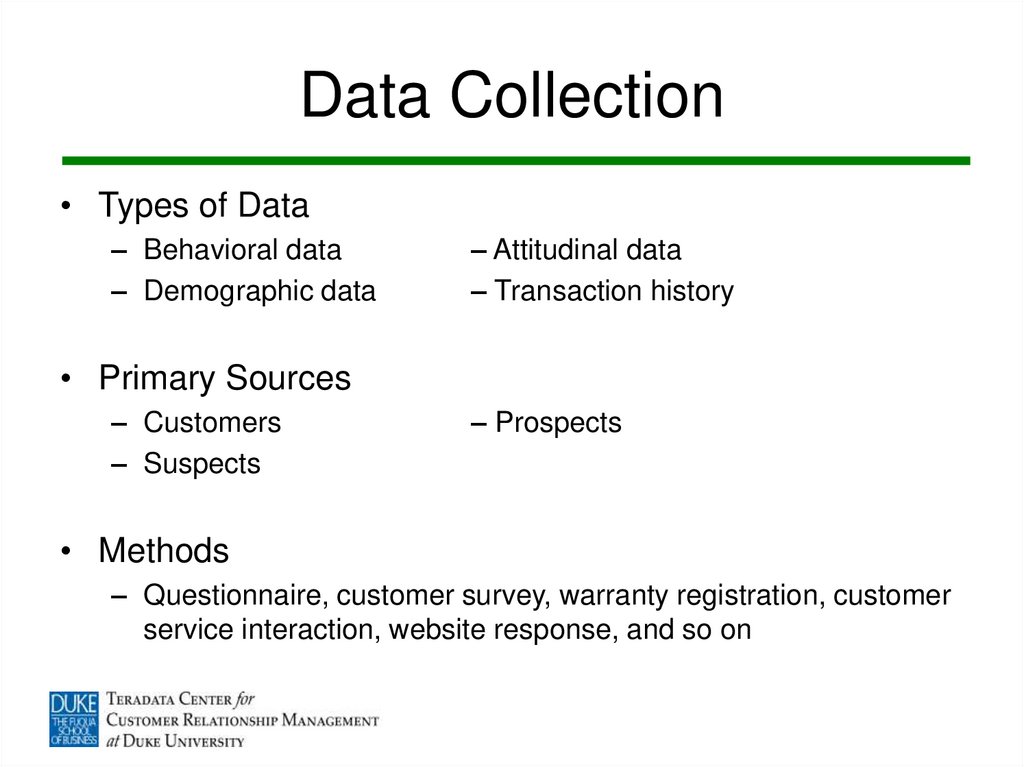
8. Data Collection
• Types of Data– Behavioral data
– Demographic data
– Attitudinal data
– Transaction history
• Primary Sources
– Customers
– Suspects
– Prospects
• Methods
– Questionnaire, customer survey, warranty registration, customer
service interaction, website response, and so on
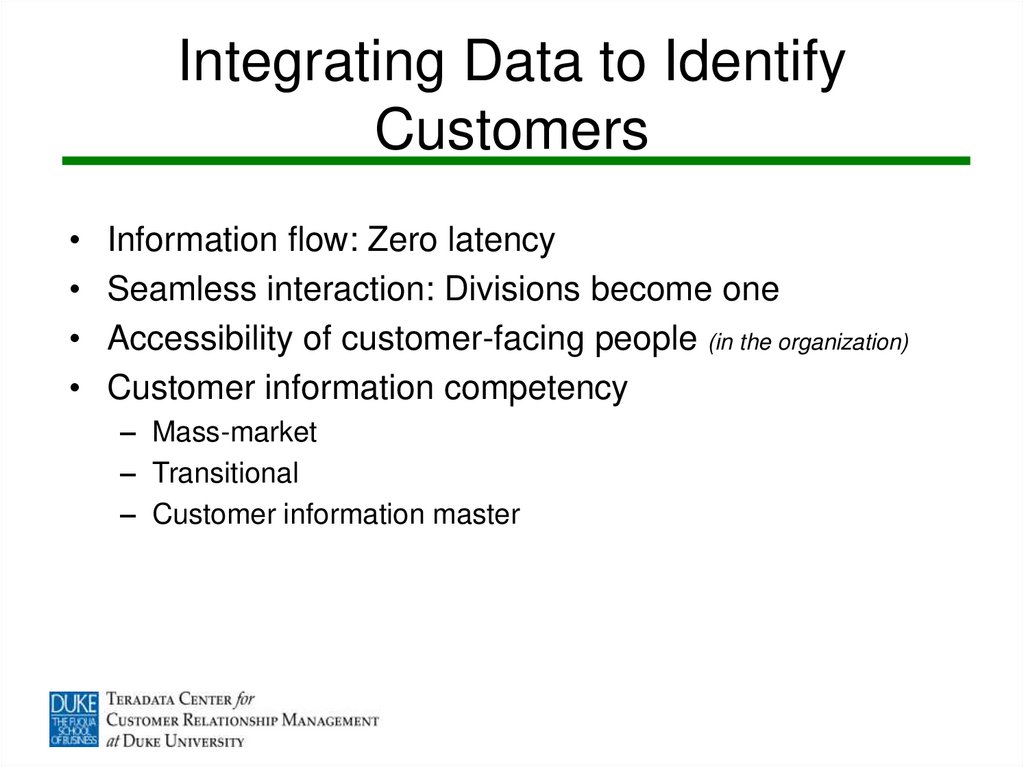
9. Integrating Data to Identify Customers
Information flow: Zero latency
Seamless interaction: Divisions become one
Accessibility of customer-facing people (in the organization)
Customer information competency
– Mass-market
– Transitional
– Customer information master
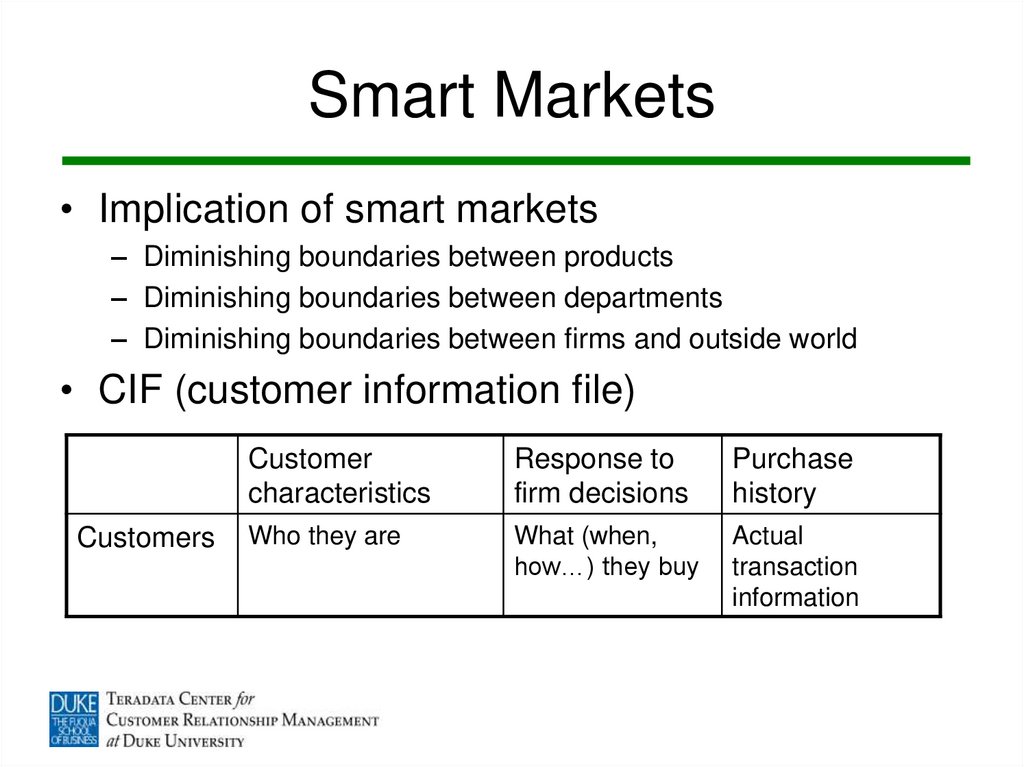
10. Smart Markets
• Implication of smart markets– Diminishing boundaries between products
– Diminishing boundaries between departments
– Diminishing boundaries between firms and outside world
• CIF (customer information file)
Customers
Customer
characteristics
Response to
firm decisions
Purchase
history
Who they are
What (when,
how…) they buy
Actual
transaction
information
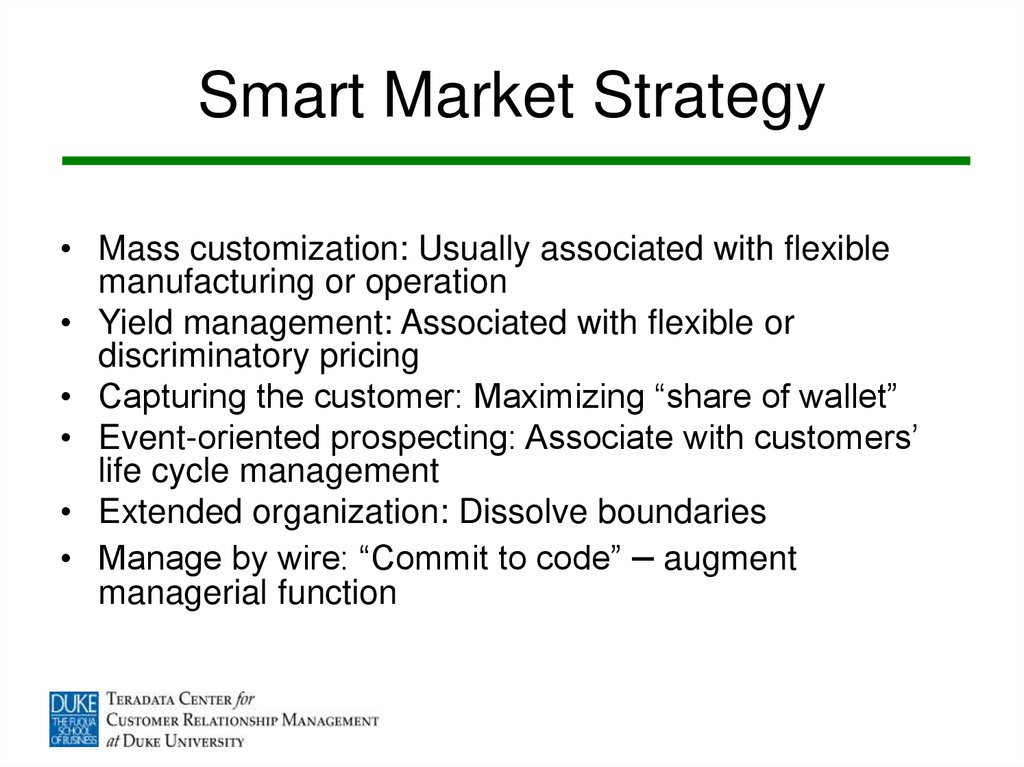
11. Smart Market Strategy
• Mass customization: Usually associated with flexiblemanufacturing or operation
• Yield management: Associated with flexible or
discriminatory pricing
• Capturing the customer: Maximizing “share of wallet”
• Event-oriented prospecting: Associate with customers’
life cycle management
• Extended organization: Dissolve boundaries
• Manage by wire: “Commit to code” – augment
managerial function
12. Smart Market Key Indicators
• Profitability per customer• Share of customer
• Customer satisfaction
Challenge: Implementation of these new
indicators into the organization’s system and
culture








 Английский язык
Английский язык








