Похожие презентации:
Introduction to petroleum development. Field development planning
1.
Petroleumdevelopment method
Chapter One
Introduction To Petroleum Development And
Field Development Planning
By
Eng: Sadam.H
2.
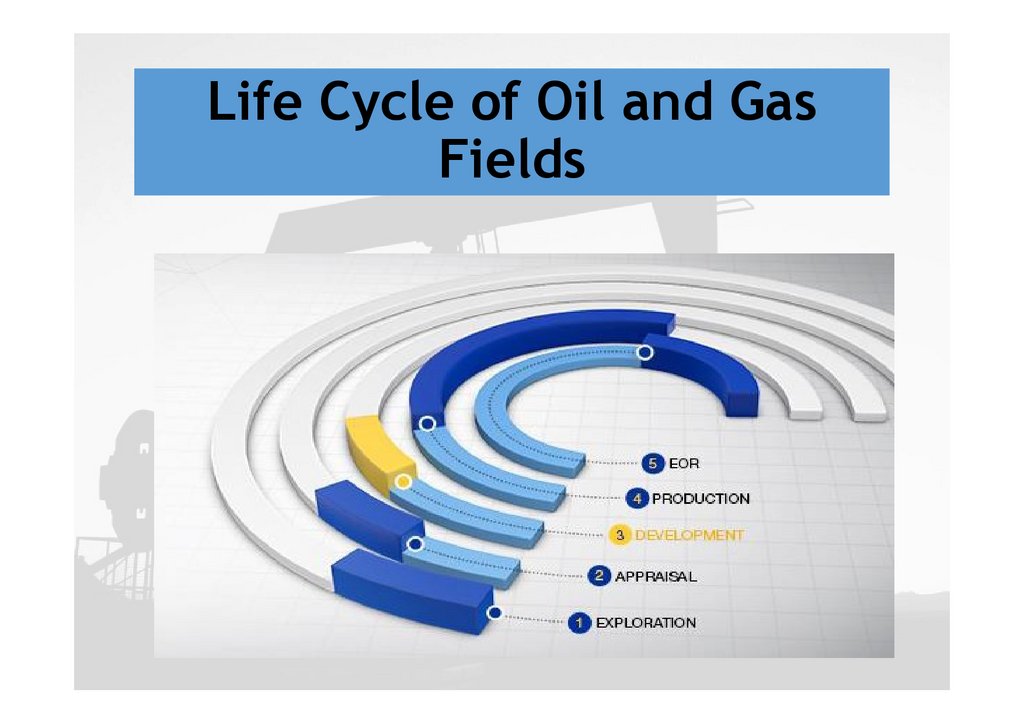
Life Cycle of Oil and GasFields
3.
Cont….4.
Appraisal Stage of Life CycleIt is closely intertwined with the exploration
and
its objective is to obtain information about
the reservoir in order to make a decision
whether or not to proceed with
development of the field
The value of this information must always
exceed its cost which is usually that of
acquiring additional seismic data as well as
the drilling of appraisal wells
5.
Cont..In this stage the key characteristics of the reservoir
are identified and ranked according to their impact
on the type of development under consideration
Some of the disciplines involved in appraisal stage
are :
reservoir simulation engineer
Seismic interpreter
6.
Development StageWell development occurs after exploration has
located an economically recoverable field, and
involves the construction of one or more wells from
the beginning (called spudding) to either:
Abandonment if no hydrocarbons are found, or
To well completion if hydrocarbons are found in
sufficient quantities
The development stage takes place after
successfully completing the appraisal period and
before the beginning of the field production
7.
Cont..The initial phase of field development planning
could involve the assessment of more than one
development option. Four components of
development plan can be used to describe each
option:
Reservoir: number location, type of well;
assessment of oil recovery mechanism; assessment
of production over the development stage
Wells : the design of wells to meet production
requirement
8.
Cont..Facilities : process facilities, infrastructure,
terminal/export facility
Operating and maintenance strategy: manning
level, daily production level ,support requirement,
for example , helicopter, supply vessels
It can be categorized in to initial phase and later
phase
9.
Cont..The initial phase of the development stage
involves field development planning that includes
the assessment of more than one development
option
The later phase targeted at developing facilities
and infrastructures as well as operation and
Maintenance
These are the phases that involve the Multidiscipline technical positions
10.
Cont..Some of the technical disciplines within the later
phase of the development stage includes:
Multi-discipline Maintenance Engineer Performs:
Maintenance analysis of platform equipment and
Systems, analysis of maintenance work content and
Development of work order documentation
Subsea Engineers:
Involves in any structural engineering taking place
beneath the surface of the sea. They design, build and
install mechanical systems used under the ocean, such
as underwater pipelines and pumps, subsea wellheads
and offshore drilling rigs
11.
Cont..Operation ManagerDirect supervision of operation, repair maintenance
With diverse product lines as Tubular, liner hangers,
Artificial lift, completions Fishing, drilling tools and
wire line
12.
Cont..Common procedures in field appraisal and
Development :
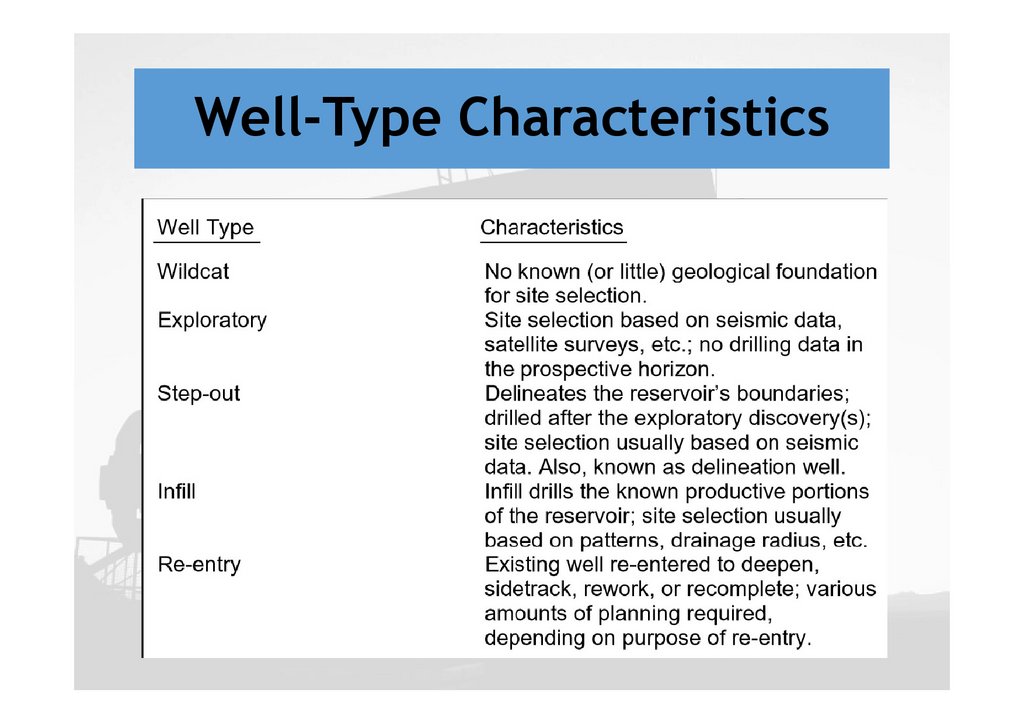
Step-out drilling
Well-Spacing
Infill drilling
Step-out drilling
A well drilled at a later time over remote, undeveloped
portions of a partially developed continuous reservoir
rock
It helps to identify the size and shape of the field for
calculating its future economic value
13.
Cont..Well-Spacing
The optimum number of wells needed to be drilled
to deplete a reservoir over a reasonable period of
time
Infill Drilling
Adding new wells in an existing field within the
original well patterns to accelerate recovery or to
test recovery method
It is an addition of wells that decrease average well
spacing
14.
Cont..This practice both accelerates expected recovery
and increases estimated ultimate recovery in
heterogeneous by improving the continuity b/n
injectors and producers.
As well spacing is decreased, the shifting well
patterns alter the formation fluid flow paths and
increase sweep to areas where greater
hydrocarbon saturations exist
15.
Well-Type Characteristics16.
Field development planningField Development Plans (FDPs)- provide the
necessary support for field optimization, and
include all activities and processes required to
optimally develop a field.
In general, development activities and processes
involves:
environmental impact, geophysics, geology,
reservoir and production engineering,
infrastructure, well design and construction,
completion design, surface facilities, economics and
risk assessment
17.
Cont..The activities and people involved in the development
stage are:
–Define a precise Field Development Plan (FDP) –
geologists, geophysicists and reservoir engineers
–Decide the best production/injection well placement
and design – drilling engineers, reservoir engineers,
geologists
–Select the optimal production facilities required to
properly process hydrocarbons before their treatmen –
production engineers, reservoir engineers, facilities
engineers
–choose the transport options and route to export oil
and gas – logistics engineers
18.
Cont…FDP- is a primary work after getting a discovery in
a given field
Require multidisciplinary integration and
agreements with reasonable justifications
So needs a strong team work & performance, a
communal written report and an oral presentation
to management
19.
Cont..Objectives:
a) To define key tasks, scope of work, input data,
method and deliverables of each area/ discipline
b) To assign specific task to each team members
c) To keep the team focused on the key tasks
d) To ensure the timeliness of the project
20.
Cont..A field development plan establishes the
following:
The number of wells to be drilled to reach
production objectives,
The recovery techniques to be used to extract the
fluids within the reservoir,
The type and cost of installations, such as
platforms, depending on the marine environment
(tides, storms, waves, winds, corrosion, …),
21.
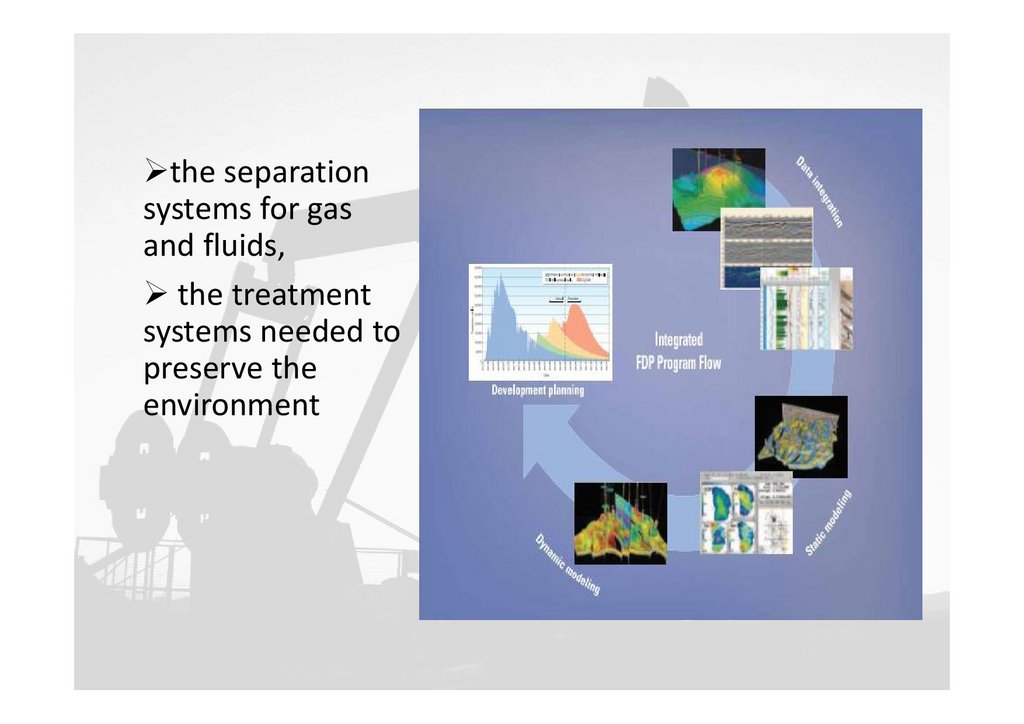
the separationsystems for gas
and fluids,
the treatment
systems needed to
preserve the
environment
22.
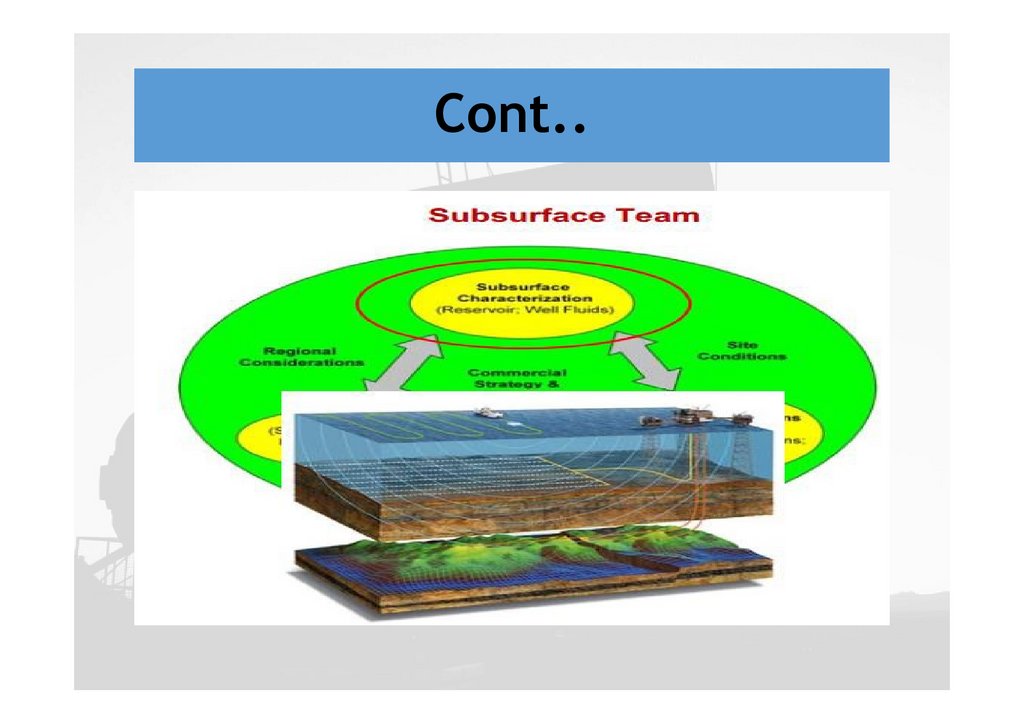
Cont..23.
Cont..24.
Cont..25.
Field development phasesThere is a standardized process of field
development and categorized in to 5 stages.
At each stage the management decides whether
the results gathered so far are promising enough to
continue the field development and justify entering
the next phase
26.
Cont..Stage1- IDENTIFY
This stages involves in identifying the presence of
potential development project based the wildcat
well/ exploration result
It is done by evaluating the well data and analysis
of the drill cores to make clear conclusion that oil
or gas has been found
27.
Cont..Stage2- Assess/ Assessment phase
This stage aims to highlight the technical and
commercial feasibility of the project
Works to find out as much as possible about the
reservoir and to minimize the uncertainties.
Measures that help to do so include other wells
(appraisal), but also dynamic reservoir models
28.
Cont..The reservoir engineers generate a 3D model of
the subsurface so that they can estimate how much
oil is hidden under the surface.
Then, with the help of computer calculations, they
can estimate the volume of oil or gas that can
actually be produced
29.
Cont..At this stage the engineers, plan the entire production
phase and address all sorts of practical questions,
such as:
How many wells must be drilled and where?
Can the oil be recovered to the surface in an on-shore
with a simple horse-head pump?
Is the oil so corrosive that the pipes need a special
coating?
How can the maximum production volume be
achieved- for example, by injecting water or gas into
the reservoir? And
When should this procedure begin?
30.
Cont..Stage 3- SELECT/ selection
The assessment phase has shown that there are many
possibilities for developing a crude oil or natural gas field
In this stage all development concepts are examined in
detail and
compares them with each other and then decides which
one to adopt
HSE plays a key role in this decision-making process like:
The safety precautions necessary for production
The impact on the environment are taken into account in
the concepts and represent major factors that influence
the decision.
31.
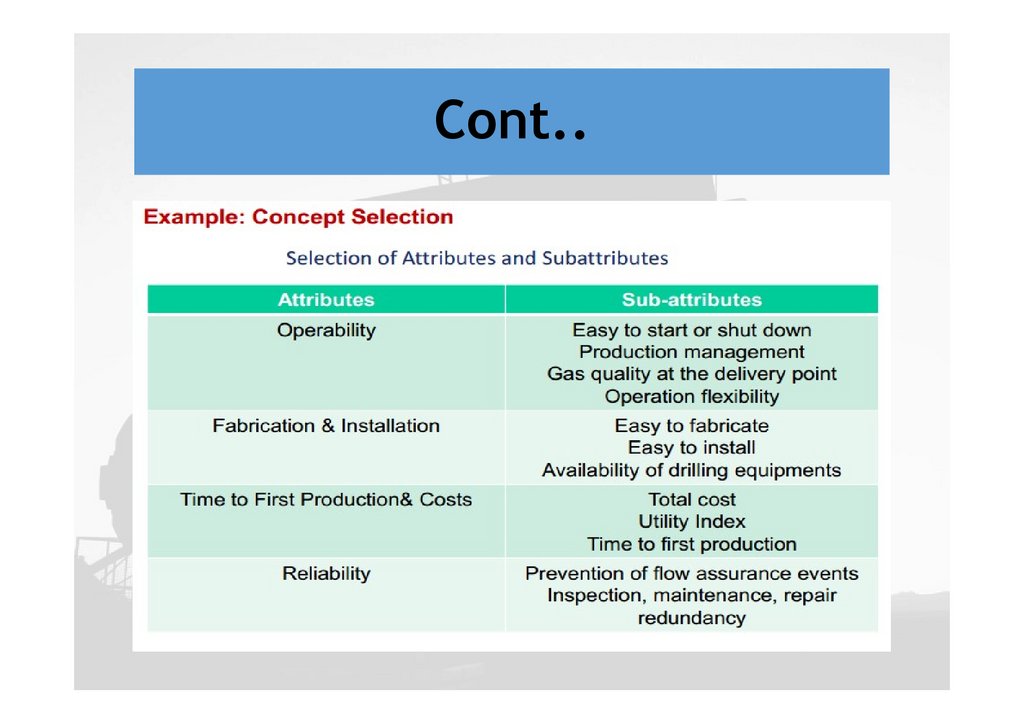
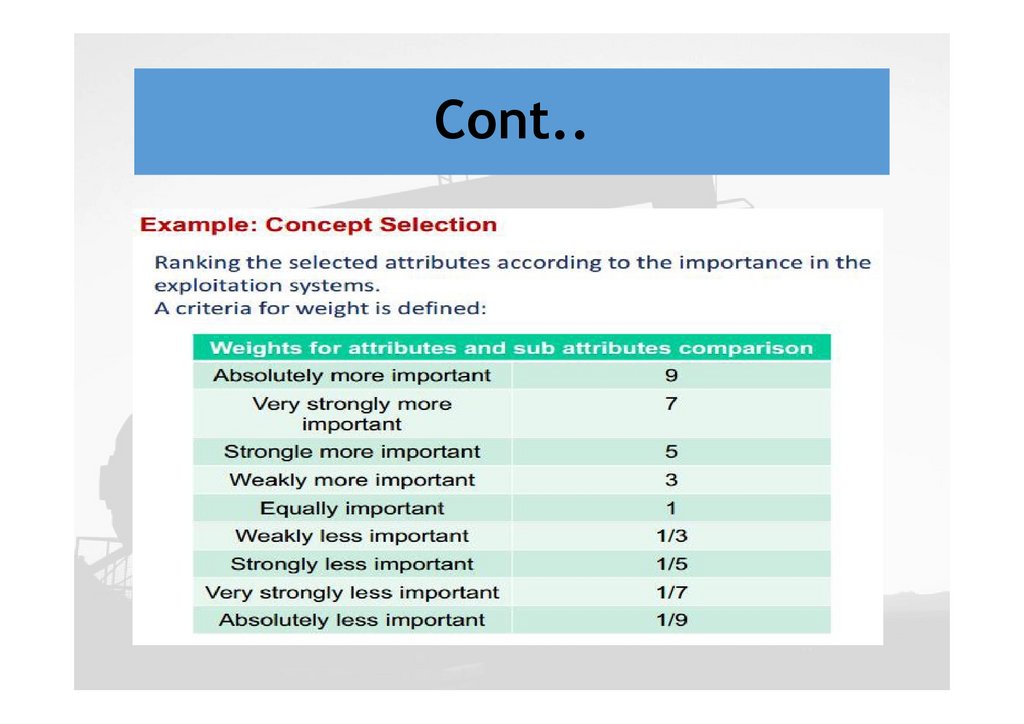
Cont..The project team evaluates all the development
options using criteria such as:
The production volume expected
The necessary investments
Operating costs
Economic feasibility
HSE and the time needed until completion
32.
Cont..Then the company management chooses the most
suitable concept based on these criteria and
Finally, Makes the decision to develop this concept
further
33.
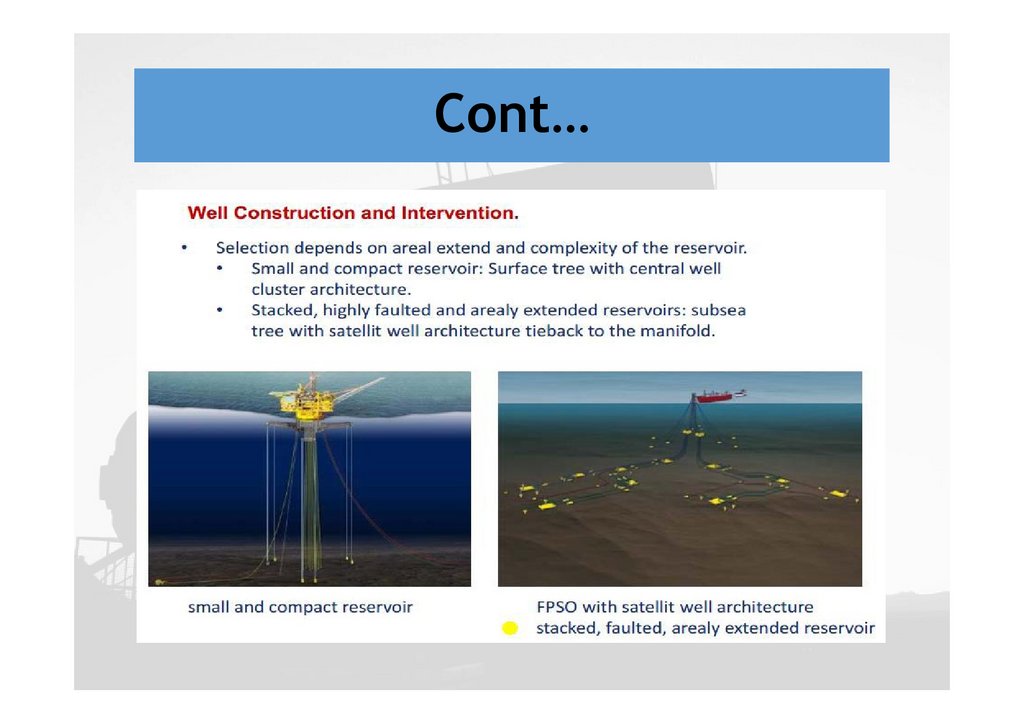
Cont…In general, there are many possibilities for
developing a crude oil or natural gas field. For
Instance,
You could select b/n stand-alone platform
A subsea tie back with an FPSO ( floating
production, storage and offloading ) or
A subsea tie back that is linked to already
existing host platforms
Eventually you will have to choose one
34.
Cont…35.
Cont..36.
Cont..37.
Cont..38.
Cont..39.
Cont..40.
Cont..41.
Cont..42.
Cont..43.
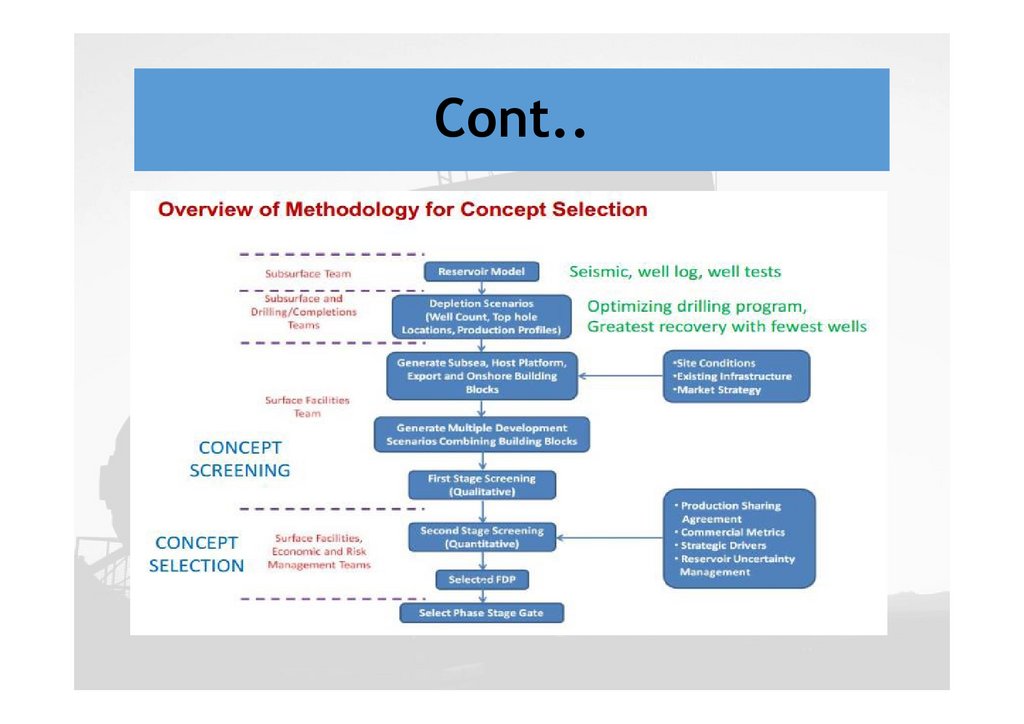
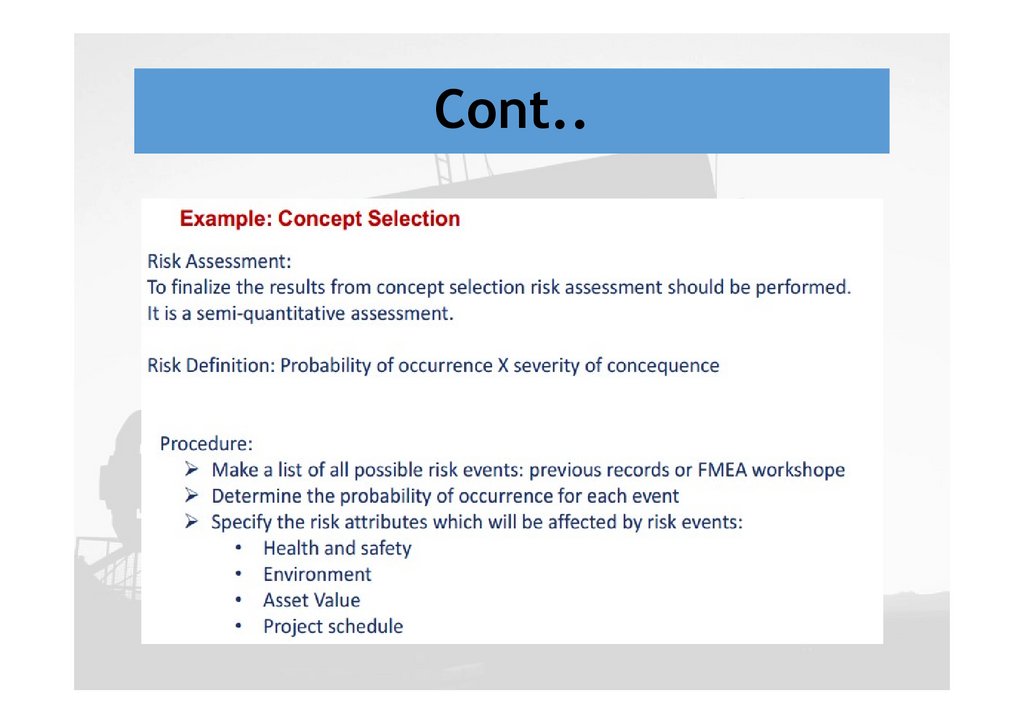
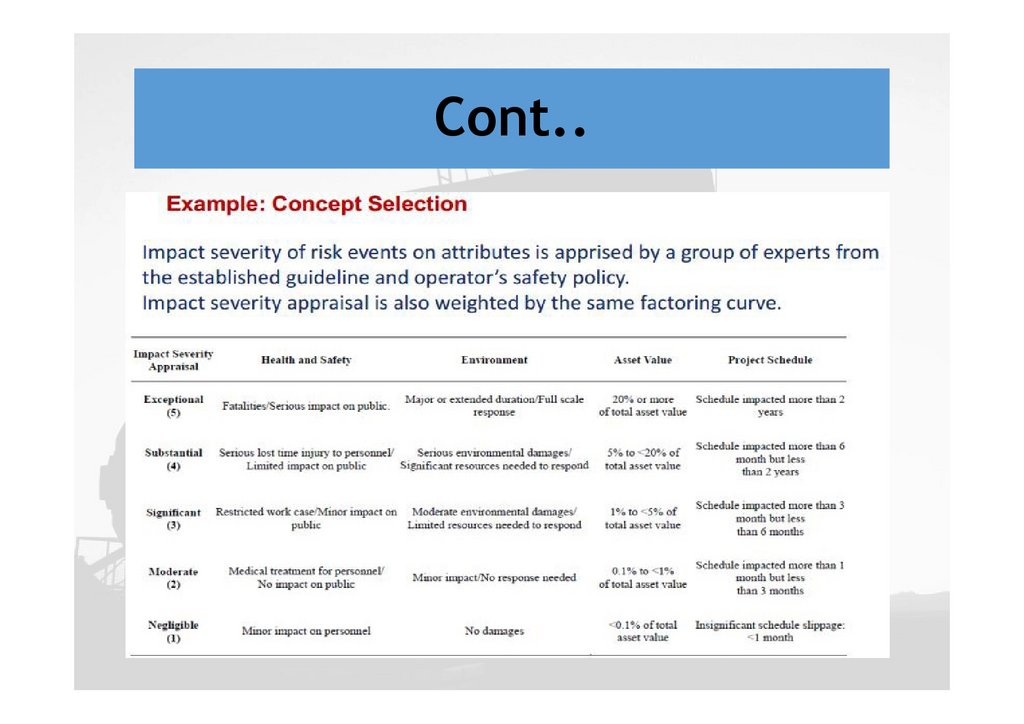
Cont..Conclusion on selection
Concept selection for field development is a
multidisciplinary task and needs contribution from:
Subsurface, drilling and completion, surface facility,
operation and maintenance, management and
commercial team
A structured methodology to generate, screen and
select the right development concept is required
44.
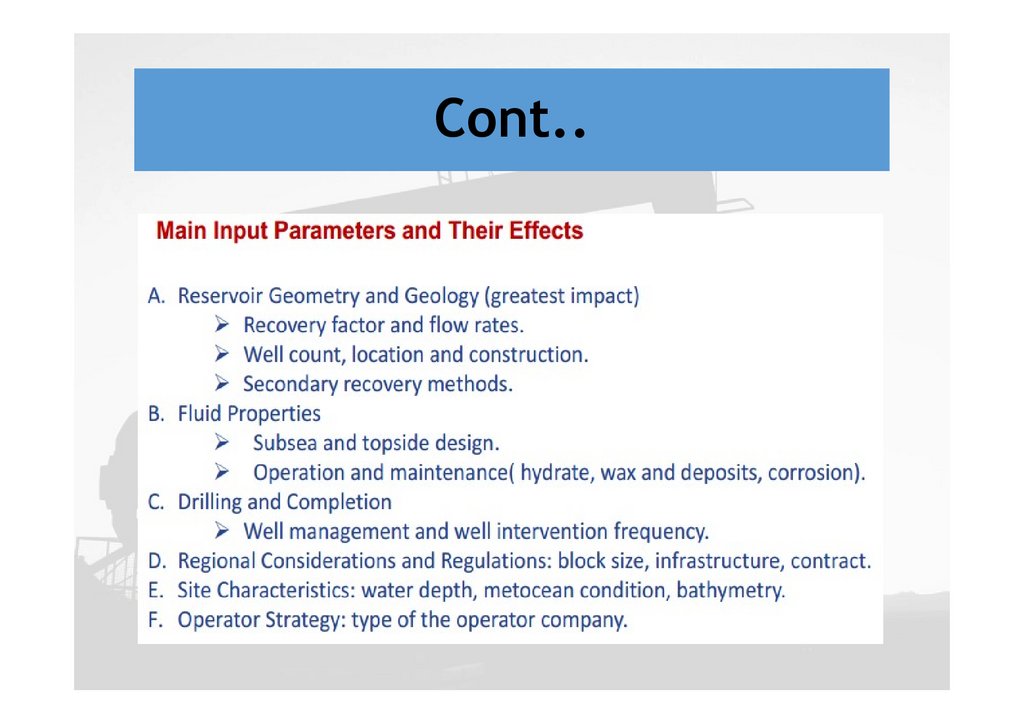
Cont..Concept selection is performed when the
uncertainty in the critical parameters which
determine the commercial success of the project is
high. Addressing subsurface data uncertainty in the
facility design phase is important.
Facility design is highly depends on subsurface data
Success of FDP highly depends on: Quality of
information, skills of subsurface team, technology
and reservoir modeling.
45.
Cont..Stage 4- Define
Once the field development concept has been
selected, the engineers take over the detailed field
development and
Prepare the so called Front End Engineering and
Design (FEED)
They now elaborate on the concept to include
every last detail
46.
Cont..In this stage, using simulations and construction
programs to help them:
They draw up precise plans for the production
wells that will recover the hydrocarbons
The production plants and the other infrastructure
requirements of the oil and gas produced
47.
Cont..Stage 5- EXECUTE
Finally at this stage the construction of the
platform begins
For onshore reservoirs these are built on-site
If the reservoir is under the seabed, the offshore
platform is built in a shipyard and the individual
parts transported to their final destination
48.
Cont..The field development ends with the ‘ first oil’’ or
‘first gas’’ –the start of commercial production
The new reservoir can now supply gas or oil
reliably for decades































 Промышленность
Промышленность








