Похожие презентации:
What is fluorosis
1.
ФлюорозАвторы: Полков и Сиковой
2.
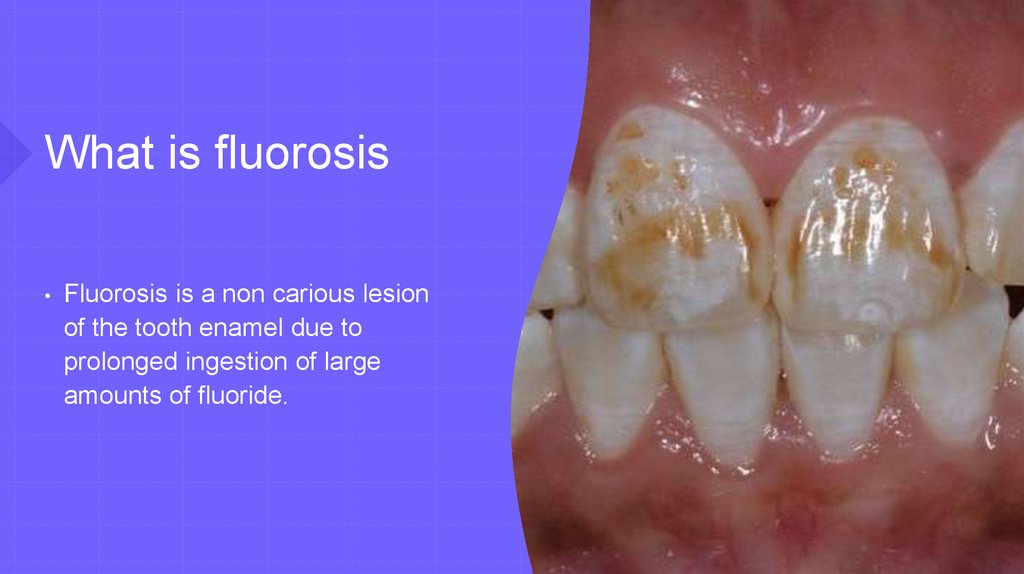
What is fluorosis• Fluorosis is a non carious lesion
of the tooth enamel due to
prolonged ingestion of large
amounts of fluoride.
3.
Сauses of occurrence• The disease is endemic in nature, it is
peculiar to a certain geographical area, in
this case, areas with a high content of
fluoride in drinking water suffer
4.
Fluoride is reasonThe recommended daily intake of
fluoride is 0.05-0.07 mg/kg. It
enters the body not only with
water, but also with other sources
like animal products: mutton, liver,
egg yolks, pork fat, marine fish
species;
vegetable products: cabbage,
beetroot, wheat;
tea, coffee;
5.
Types of fluorosis• Dental fluorosis can be generalized (affect
all teeth on the upper and lower jaw) and
localized (affect individual teeth, more
often these are the anterior central
incisors and the first molars of the upper
jaw)
6.
The dashed form ofFluorosis
• Stripes resembling strokes are visible in
the surface layer of the enamel. They are
especially noticeable when drying the
surface of the teeth. In this form, the upper
central and lateral incisors on the
vestibular surface (from the cheeks or lips)
are more often affected. Less often,
defects appear on the incisors of the lower
jaw.
7.
Spotted form offluorosis
• Small roundish spots are visible on the
areas of the teeth. They have a smooth
and shiny surface, the color of the spots in
the center is more intense, and at the
edges it disappears and merges with the
general background of the enamel. There
are no stripes in this form. The spots can
merge with each other.
8.
Chalky-speckled shapethe paint loses its luster, depressions in the
form of yellow-brown specks with a diameter
of 1-1.5 mm are visible on the surface, the
bottom and walls are rough. The process
often covers all groups of teeth. There are
chipped enamel, areas of erasability with the
exposure of pigmented dentin.
9.
Erosive formIn this form, areas where enamel is absent appear
on pigmented areas of tooth enamel. These are
the so-called erosions. They vary in color, shape
and depth. The edges and bottom of these defects
are rough, yellow or yellow-brown in color. The
enamel loses its luster, becomes brittle and easily
chips off. In this form, the abrasion of enamel and
dentin is pronounced. There is pain when exposed
to temperature stimuli on the surface of the teeth
10.
Destructive formIt refers to a severe form of fluorosis, found in
regions with high fluoride content in drinking
water. There is an increase in the fragility of the
enamel, erasability. The enamel is chipped off, so
the tooth acquires an atypical shape. Not only the
enamel is affected, but also the dentin, capturing
various areas of the teeth. Sensitivity to temperature
stimuli is increased.
11.
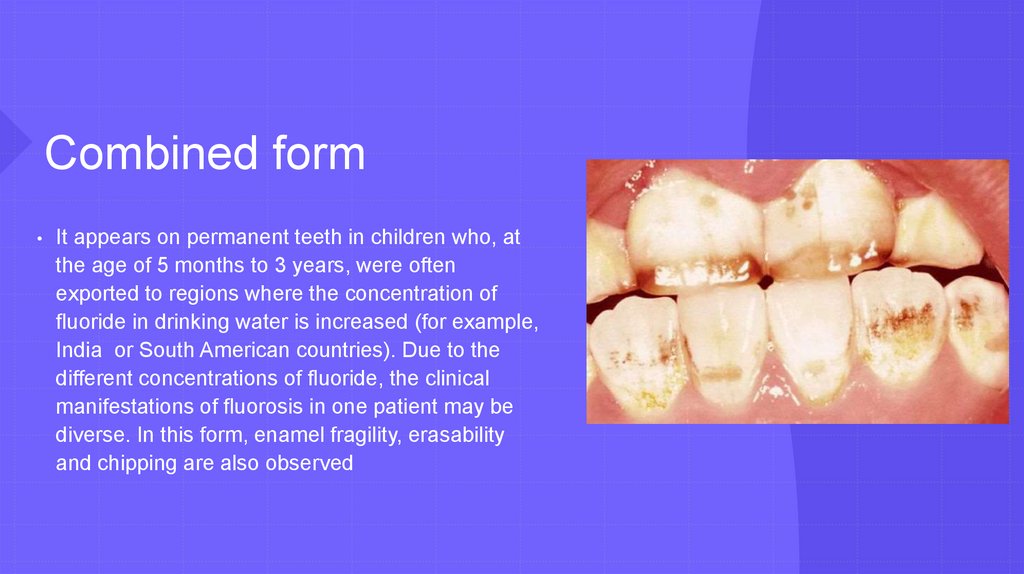
Combined formIt appears on permanent teeth in children who, at
the age of 5 months to 3 years, were often
exported to regions where the concentration of
fluoride in drinking water is increased (for example,
India or South American countries). Due to the
different concentrations of fluoride, the clinical
manifestations of fluorosis in one patient may be
diverse. In this form, enamel fragility, erasability
and chipping are also observed
12.
Treatment of fluorosisAt the first stage of fluorosis, bleaching is
prescribed followed by a course of
remineralization. The course of treatment
consists of 10 to 20 procedures, including the
application of applications containing calcium
and phosphorus. If necessary, electrophoresis
or ultraphonophoresis is performed. In some
cases, the course of treatment is supplemented
with taking medications.
13.
Treatment of fluorosisIn the case of moderate to severe damage to
the dental tissue, natural restoration of the
enamel is impossible. Restoration of the
normal appearance of teeth is carried out
with the help of composite materials, crowns,
veneers. The use of sealing materials is
impractical — the seal will fall out due to the
fragility of the areas affected by erosion.
14.
Prevention of fluorosis• Drinking water without
fluoride
• To live in areas with clean air
• A balanced diet












 Английский язык
Английский язык