Похожие презентации:
Cognitive perspectives on language, culture and mind second language acquisition
1.
2.
“Learning a second language is like moving to a newtown—it takes time to establish connections and turn
acquaintances into friends.” (Chen, Y. p10.)
Cognitive Perspective. Cognition and cognitive
processes.
Cognition is part of mental process, the behavior and
ability through which we perceive and acquire
knowledge. It involves such mental activities as emotion,
motivation, and power. Knowing a word is one thing, but
mapping words on to concepts is another, which is
termed as categorization.
3.
Krashen's theories of language acquisition•Acquisition/Learning hypothesis
•Monitor hypothesis
•Natural order hypothesis
•Input hypothesis
•Affective filter hypothesis
4.
Acquisition / Learning - learning isexplicit instruction or consciously studying a
language
An acquisition - subconsciously absorbing
language as you use it for a variety of
purposes
5.
look at what historical background of language learning led up toKrashen's theories from
the 17th to the 19th century language learning was really
focused on grammar translation and this was based on the
learning that was coming out of translating Greek andLatin
in the 20th century focus became audio lingual method
for teaching audio lingual was very focused on memorization of
dialogues and of a particular vocabulary ,it was not very
intuitive and it was coming from BF Skinner's concept that
learners learn by repetition and Krashen moved this concept
forward
6.
For 1970s by saying really we don't learn by repetition thatcreates a prescribed and inauthentic method of learning a
language.
He thought that language was meant for communication which it
is and that therefore we learn it more in the same way that we
learn our first language as we think forward
Krash's theories are important but they are not the only ones now
and we look into the 2000s and we see last from last term the
National reading panel and their concepts of how we learn also
an article by Susan du TRO and many others as well where
they believe that we weave concrete instruction .
7.
The explicit language instruction is needed to learnacademic language, with simple everyday language
perhaps we can acquire it without any instruction but
academic language in particular needs to have specific
instruction .
Krashen believes that
Acquisition is the main player in fluency and when we
have a monitor or an internal editor that is trying to
correct our language learning we will actually not speak as
well or communicate as clearly. That learning functions as
that monitor that says ‘’Oh that doesn't sound right “.
There are some problems with this using a monitor and as
he states there are three necessary conditions for it
8.
1. Time2. Focus on form
3. Know the rule
9.
Time using - a monitor requires time we have to be ableto stop and think about the rule, in our head and then
apply it, which of course is going to stop the flow of
communication
Also you need to focus on form so you're focusing
instead on the communication you're focusing on ‘’How
did I say that” and of course you need to know the rules
and those rules need to be embedded in your mind but
often it lows us down as we stop to think about the rule
and it causes us to break the communication process.
10.
Grammar structures are acquired insomewhat of a predictable order.
1.
2.
Second language learners learn in an order
different from first language learners .
Learning adults and children show a pretty
similar order of what they learn and rules are
easiest to state
11.
The natural order hypothesis . Krashen believes that grammarstructures are acquired in somewhat of a predictable order but it's
not something that can be exactly figured out and therefore you
can't determine what to teach in grammar .There's no sequence
that's useful you need to ,just acquire it as it comes up in natural
communication .He believes that second language learners learn
in an order different from first language learners . Second
language learning adults and children show a pretty similar order
of what they learn and rules are easiest to state not necessarily are
the first acquired. For example the learning and teaching of the
article ‘a’ ‘the’ not difficult to teach to someone but it's often
difficult for students to learn it and be able to actually use it .
12.
Comprehensible input that is a message thatstudents can understand is a must.
1 Input must be slightly above the students
current level that is I + plus1.
2 Students learn at different rates and at
different levels
13.
The input hypothesis he believes that comprehensible input that is amessage that students can understand is a must. You can't have acquisition
without comprehensible input here's the ideas behind this. Input must be
slightly above the students current level that is I plus1 input plus 1. There
is a problem with this, in that he cannot define what is I plus1. How do
you figure out what is just above a language learners ability. And then that
students learn at different rates and at different levels. I think we all
understand that that must be true because we have students all across the
board in the classroom which means that we have to have differentiated
instruction to be able to meet everybody's needs. In order to make
comprehensible input we need to think about different ways that can be
done . We can use pictures, gestures, recycling the vocabulary in more and
more units repetition these are just a few ideas of how to make
comprehensible input.
14.
Conditions that are necessary foracquiring a language:
1. Motivation
2. Self-confidence
3. Low anxiety
15.
The Affective filter hypothesis. There are certain conditions thatare necessary for acquiring a language as emotional human
beings. We have all kinds of investment or lack of investment in
learning something new, so we need to consider the motivation.
Our students motivated to learn a language what is it they want
to do with the language that's going to affect their affective
filter self-confidence. Everyone has their own personality and
some people have more confidence than others, and certainly
we impact their confidence as well this will have an effect on
their effective filter. Their emotions about learning and finally
the low anxiety is an important piece to the teacher.
16.
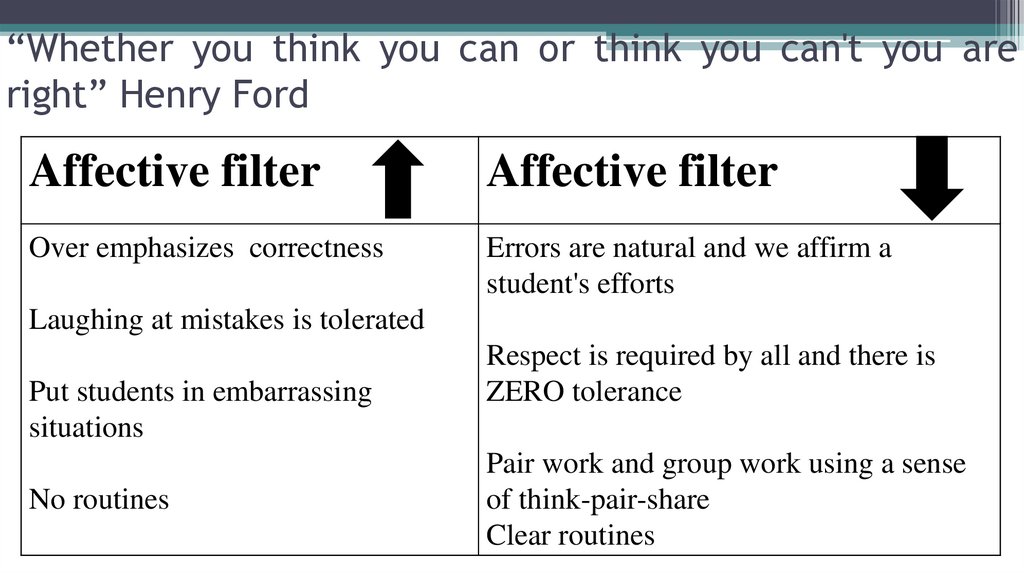
“Whether you think you can or think you can't you areright” Henry Ford
Affective filter
Affective filter
Over emphasizes correctness
Errors are natural and we affirm a
student's efforts
Laughing at mistakes is tolerated
Put students in embarrassing
situations
No routines
Respect is required by all and there is
ZERO tolerance
Pair work and group work using a sense
of think-pair-share
Clear routines
17.
The teacher needs to be the one who's creating a low anxietyclassroom where there is not sense that they are going to be
bullied or have any sense of fear - hi the filter prevents input from
being used for acquisition . So let's take a look at what can help
create an effective classroom with a low effective filter here's a
quote from Henry Ford – ‘’Whether you think you can or think
you can't you are right ‘'.’ So a high effective filter which is
something we do not want in a classroom this comes when the
teacher over emphasizes correctness when the teacher is saying
that's not right and is always redirecting students to do
something correctly that creates anxiety and raises the affective
filter. If there's laughing at mistakes is tolerated ,if the teacher lets
that go on then students will not feel comfortable being able to
speak or use the language .
18.
So a high effective filter which is something wedo not want in a classroom this comes when the
teacher over emphasizes correctness when the
teacher is saying that's not right and is always
redirecting students to do something correctly
that creates anxiety and raises the affective filter.
If there's laughing at mistakes is tolerated ,if the
teacher lets that go on then students will not feel
comfortable being able to speak or use the
language .
19.
They do have and that will create a higher effective filter . If theteacher puts students in embarrassing situations ,if they force
them to answer then a student is going to often clam up and
not want to speak at all. Another important thing that we
maybe don't think as related to the effective filter is having no
routines . Routines help students feel safe they know what to
expect and what to do and it can raise the affective filter if
there are no routines .
Now let's look at the positive side how do we lower the
effective filter in a classroom when errors are natural and we
affirm a student's efforts we can help lower their effective filter
instead of saying –’’That's not right ‘’ when we say –’’Oh you
made a really good effort.’’
20.
Let's look at what we might do to fix that we can lower thateffective filter when respect is required by all and there is ZERO
tolerance of disrespect and a very important piece in any
classroom it's true for all of the students not just for our second
language learners. Another way to lower the effective filter is
using pair work and group work using a sense of think-pairshare
Then as a second language learner I have an opportunity to learn
from my group or my partner and to help me understand if I
really get the concept before I'm having to speak in front of the
whole class. And then setting very clear routines so that students
have that sense of comfort in the classroom. So Stephen Krashen
said on second language acquisition we acquire a language in
one way and only one way when we get comprehensible input
in a low anxiety environment.
21.
Stephen Krashen said on secondlanguage
“We acquire a language in one
way and only one way when we
get comprehensible input in a low
anxiety environment”
22.
• Let's take a look now in a nutshell at his theories and his ideasSo comprehensible input is where we begin with
comprehensible input. That is a real piece of the teacher, what
have you done in your lesson to help students be able to
understand, if your lesson is made up just of words you're like a
talking head and they're not going to understand you need to
give pictures maybe even a pantomime or a little video different
ways for students to be able to understand what you're saying
and doing. Then we need to think about the Affective filter - what
have I done to help create a comfortable classroom am i giving
students an opportunity to share with each other to learn from
each other or am i raising that effective filter, have I created a
barrier between learning ,because students feel afraid or
nervous- have I created a sense of safety so that students won't
feel that they are bullied or embarrassed or ridiculed .
23.
I need to think about these pieces of the effective filter if I've done a good jobof comprehensible input ,if I have lowered the effective filter then
information can get into the LAD or language acquisition device as
Chomsky said this means that I have acquired the knowledge and this is
where we want to have students be that they have actually learned or
acquired has become a part of them.
Up here we have learned knowledge this is things that we actually teach and
this is what helps function using our monitor .So when we think about
something we're going to say or write then our learned knowledge is using
our monitor to check ourselves is it correct.
Did I do it right and finally we get the output something to think about is how
much is it just acquired and how much do we actually need to teach that is
learned knowledge these are pieces to think about for yourself and to
consider into the future as you become the teacher in the classroom.






















 Английский язык
Английский язык








