Похожие презентации:
Selection and Placement of Sales Personnel
1. TEACHING WEEK 7
Sales Management2. Objectives
After finishing this lecture student will be able to answer following questions -:Selection and Placement of Sales Personnel
Job Analysis, Proficiency Tests, Non-Structured Interview
Analysis of salesperson’s role
Choice of basic selling styles
Activities involved in Sales Force Management
Ten traits and abilities of top salespeople
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
2
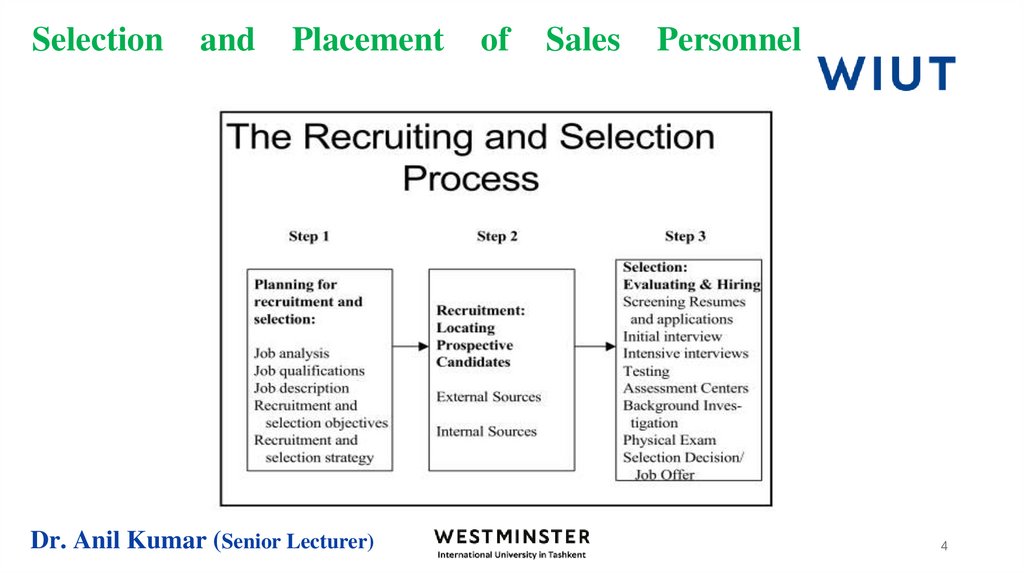
3. Selection and Placement of Sales Personnel
The selection process involves choosing the candidates who best meetthe qualifications and have the greatest aptitude for the job. There are
numerous tools, techniques, and procedures that can be used in the
selection process. Companies typically use initial screening interviews,
application forms, in-depth interviews, reference checks, physical
examinations, and tests as selection tools.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
3
4. Selection and Placement of Sales Personnel
Selectionand
Placement
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
of
Sales
Personnel
4
5. Selection and Placement of Sales Personnel
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)5
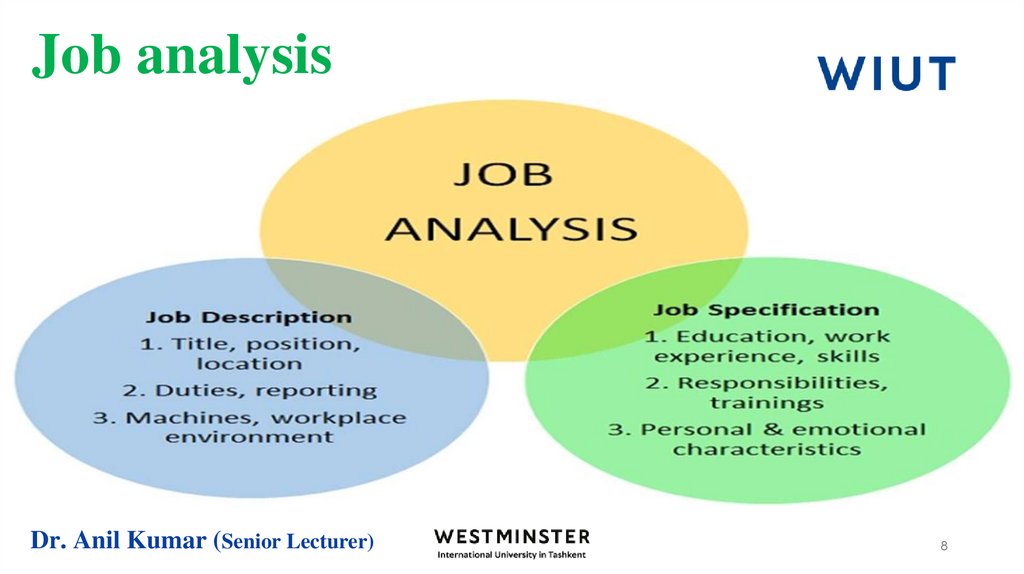
6. Job analysis
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)6
7. Job analysis
Job analysis is the process of studying a job to determine which activities andresponsibilities it includes, its relative importance to other jobs, the qualifications
necessary for performance of the job and the conditions under which the work is
performed.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
7
8. Job analysis
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)8
9. Job description
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)9
10. What is a job description?
A job description is a written explanation that outlines the essential responsibilities and
requirements for a vacant position. Job descriptions should be thorough, clear, and concise
and include:
A brief introduction to the company and its mission.
An overview of the job responsibilities.
The necessary skills, competence levels, knowledge, and qualifications relevant candidates
should have.
Testing that the company may require.
Working conditions and location. It should also cover whether the role is office-based,
remote, or hybrid.
Environmental factors or strenuous components of the job.
The type of employment—full-time, part-time, or independent contractor.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
10
11. Job descriptions vs. job responsibilities
Job descriptions and job responsibilities are both vital to the recruitment process.
A job description is an employer document that describes an open role at the company. It’s
often included in job ads to give prospective candidates a clear idea of a role’s scope and
what skills and experience are required to succeed in it. It also typically includes a summary
of the position, job title, and information about the company culture and benefits.
On the other hand, job responsibilities are what a company outlines as the specific tasks and
duties people in each role are accountable for. These can change over time as a role evolves
with the company and changes in business needs.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
11
12. Job specification
A job specification lists out the qualifications,experience, training, skills, emotional attributes,
mental capabilities of an individual to perform the
job. A job description measures the tasks and
responsibilities attached to the job.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
12
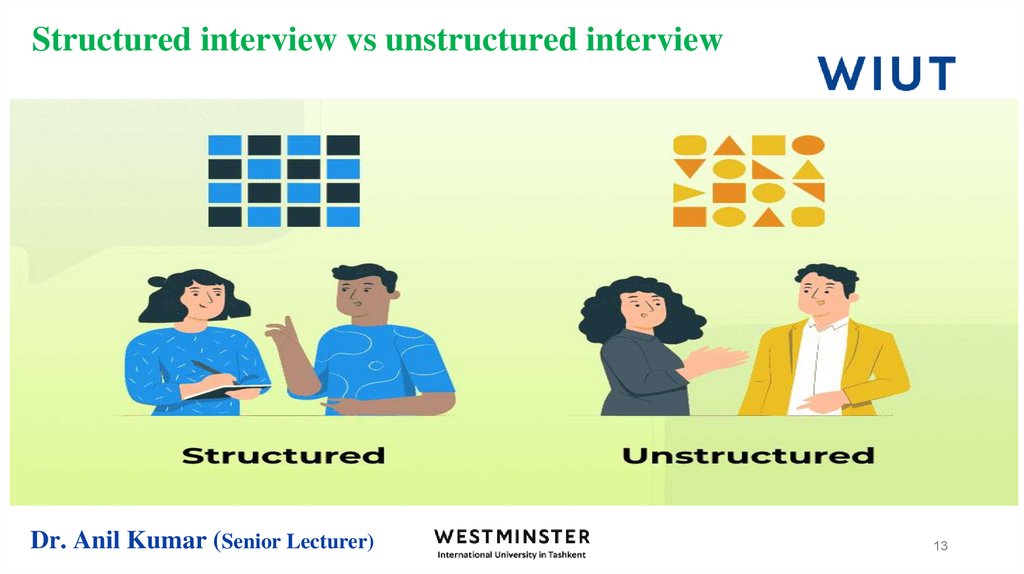
13. Structured interview vs unstructured interview
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)13
14. Structured interview vs unstructured interview
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)14
15. Proficiency Tests
Achievement Tests (Proficiency Tests): Achievementtests seek to determine how much the individual knows
about a subject. They determine the admission feasibility
of the candidate and measure what he is capable of
doing.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
15
16.
Placement - An applicant who clears all the hurdles in theselection procedure is presumably offered a job. The main
problem after final selection of the candidate is to place the
worker on some suitable job. The act of offering the job to a
finally selected candidate is called 'Placement'.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
16
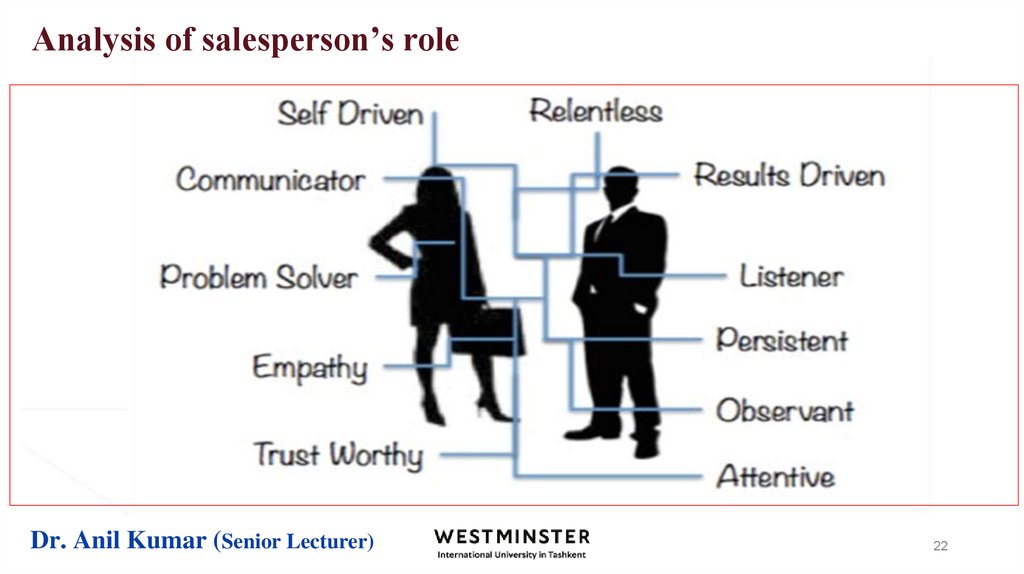
17. Analysis of salesperson’s role
Salespeople may be either active or passive forces in securing orders.The encyclopedia salesperson calling on households must often function as an
order getter
The driver-salesperson for a soft drink bottling company is primarily an order
taker.
In consumer goods marketing, the missionary salesperson’s major role is to assist
middlemen in making sales to their consumers.
In industrial-goods marketing, the sales engineer plays two major roles: advisor
to customers on technical product features and applications, and design
consultants to industrial users on installations or processes incorporating the
manufacturer’s products
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
17
18. Choice of basic selling styles
Choiceof
basic
selling
styles
Delivery sales person: The primary job of the delivery sales person is to deliver the product
e.g. soft drink, bread, milk etc. The selling responsibilities are secondary. Good service and
a pleasant personality may lead to more sales.
Missionary selling - These sales persons are not expected or permitted to solicit an order.
Their job is to build goodwill or to educate actual or potential user or provide services for
the customers, as in the case of Medical representatives, working for the pharmaceutical
company.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
18
19. Choice of basic selling styles
Outside order taker: The soap or spices sales person calling on retailer is an outside order
taker. They do little creative selling. In contract with store personnel these representatives
actually may be discouraged from doing any hard selling. That task is left to executives
higher in the hierarchy.
Inside order taker: The retail sales person standing behind a counter is an inside order
taker. The customer comes to the sales person with the intention to buy a product or service,
the sales person only serves him or her. The sales person may use suggestion selling but
ordinarily cannot do much more.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
19
20. Choice of basic selling styles
Commercial sales person: This field generally includes nontechnical sales tobusiness, industry, government and non-profit organization e.g. office equipment,
wholesale goods, building products, business services and others. Unlike the
previous two types, it is customary for the commercial sales person to make sales
on first or second call. The process stresses approach to right person (decision
maker), making a smooth presentation and closing the sales.
Technical sales personnel: The most distinctive characteristic of technical sales is
the product knowledge required by its sales person, unlike the consultative sales,
where sophistication in organization relationship and persuasive ability are sales
persons’ most valuable Most of the technical purchasing requires approval of
several people but only one or two people with technical knowledge influence
decision.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
20
21. Activities involved in Sales Force Management
Successful firms have procedures to aid in managing the salesforce:
• Norms for customer calls
• Norms for prospect calls
• Using sales time efficiently
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
21
22. Analysis of salesperson’s role
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)22
23. Ten traits and abilities of top salespeople
TraitEgo strength
Sense of urgency
Ego drive
Assertiveness
Willingness to take risks
Sociability
Abstract reasoning
Sense of skepticism
Creativity
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
Empathy
Related Ability
To handle rejection
To complete the sale
To persuade people
To be firm in negotiations
To be innovative
To build relationships
To sell ideas
To question, to be alert
To sell complex products and ideas
To understand customer needs
23
24.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)24




















 Английский язык
Английский язык








