Похожие презентации:
Introduction to Sales Personnel
1. TEACHING WEEK 6
Sales Management2. Objectives
After finishing this lecture student will be able to answer followingquestions -:
Introduction to Sales Personnel
What is Recruitment
Sources of Recruitment
Factors Affecting the Recruitment Policy of Sales Personnel
3 Ways to Design Sales Force
Centralisation vs Decentralization in Sales Organisation
Recruitment Process of Sales Personnel
Trait of a good sales personnel
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
2
3. Introduction to Sales Personnel
“A salesman is someone who sells goods that won’t come back to customers who will.” (Anonymous)
Importance of personal sales:
Direct link to the customer
Most customers see the sales person as the company
Designing the sales force internationally is one of the most important functions of the marketing department
Today’s salesperson is usually a highly-trained professional
Sales professionals take a customer-oriented approach employing truthful, non-manipulative tactics in order to satisfy the
long-term needs of both the customer and the selling firm
Today’s professional salespeople are problem solvers who seek to develop long-term relationships with customers
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
3
4. Introduction to Sales Personnel
Today’s salesperson is usually a highly-trained professional
Sales professionals take a customer-oriented approach employing truthful, nonmanipulative tactics in order to satisfy the long-term needs of both the
customer and the selling firm
Today’s professional salespeople are problem solvers who seek to develop
long-term relationships with customers
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
4
5. Missionary Sales and Sales Professional
Selling in which the salesperson's role is to inform an individual withthe power to influence others to buy a product, rather than to make a
direct sale to that person; a missionary salesperson is also known as a
Detailer.
E.g. - Sales representative may provide a doctor with clinical
information about a particular drug in hopes that the
doctor will prescribe it for his/her patients.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
5
6. Missionary Sales and Sales Professional
A missionary salesperson is often referred to a detailer. Missionarysales are common in technical, pharmaceuticals, text books, life
insurance and other financial products.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
6
7. What is Recruitment
“Recruitment is a process to discover the source of manpower to meet therequirements of the staffing schedule and to employ effective measures for attracting
that manpower in adequate numbers to facilitate effective selection of an efficient
working force.
Recruiting involves identifying potential salespeople and attracting them to the
company
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
7
8.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)8
9. RECRUITING SOURCES
Recruiting the right person is an essential task for a sales manager. There are a variety of different sources fromwhich candidates can be found to recruit:
Internally from the staff;
Clients from other associates;
Individuals from competitor companies;
Individuals from non-competitor companies.
Classified Ads - Reaches wide audience (trade publications may narrow the reach)
Used if high turnover
Tend to over-produce under-qualified candidates
Present Employees
Familiar w/ company products & procedures
Established job histories
Sales as a promotion
Over-rely on previous experience
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
9
10.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)10
11. Types of Recruitment
Typesof
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
Recruitment
11
12. Internal recruitment
Internal recruitment is the process of filling job vacancieswithin a company by exclusively considering current
employees. It involves advertising positions internally and
leveraging existing talent from different teams and departments
to address skills gaps and promote career growth.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
12
13. Implementing a successful internal recruitment strategy
identifying a member of your organization to promote internal recruitment, ensuring thatthat whole organization understands the benefits of value of this approach
Encourage a culture where employees can confidently discuss their career aspirations and
skillsets with their line manager. Career pathing makes that process transparent and
achievable.
When considering internal candidates in a broader application process, ensure they are
treated the same as any prospective external candidates.
#1 barrier to successful internal recruitment was managers who were reluctant to release
talented team members to another department. This process is called talent hoarding.
Use technology to evaluate your internal talent pool. Dedicated succession planning
or career pathing software can help to streamline and expedite both processes.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
13
14. Factors Affecting the Recruitment Policy of Sales Personnel
Generally, following factors are involved in the recruitment policy:1. Number of recruits desired
2. Recruitment sources
3. Recruitment needs
4. Recruitment cost
5. Size of sales organisation
6. Rate of turnover
7. Forecasted sales volume
8. Government policies
9. Personnel policies of competing organisation
10. Organisational personnel policies.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
14
15. 3 Ways to Design Sales Force
• Expatriates• Local Nationals
• Third Country Nationals
Advantages/Disadvantages of all 3:
• 1. Expatriates (declining)
Advantages
Used most when products are highly technical or requires a lot of information in
order to sell
• Familiar with headquarters policies, procedures
• Opinions/Ideas are valued more by home office
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
15
16.
DisadvantagesHigh cost
Cultural and legal barriers
Difficult to recruit – many highly skilled will not re-locate overseas
Other type of Expatriates
Virtual Expatriates
Created by the internet and other advanced types of communications, where they
manage operations in other countries, but do not move to that country
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
16
17.
Local Nationals
• Advantages
• Most knowledgeable about culture, legal environments, business
structure, distribution networks
• Disadvantages
Home office does not see as the “experts” in the field
• Seen as not being familiar with home office procedures, policies
• Not the experts on the products
Difficult to recruit most skilled and knowledgeable
• Recruiting the best may mean taking away from another company or competitor – this goes
against some cultural believes where “loyalty” is important
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
17
18.
Third-Country NationalsAdvantages
If recruited within same area most are familiar with culture, language, how to conduct
business
Disadvantages
Host country does not see individual as one of their own
Many of the same disadvantages to a smaller scale with the expatriate.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
18
19. Centralization vs Decentralization in Sales Organisation
In centralised system, recruitment, training, compensation and evaluationare all managed from the central head quarter while in decentralised
system the field sales managers take up most of these functions.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
19
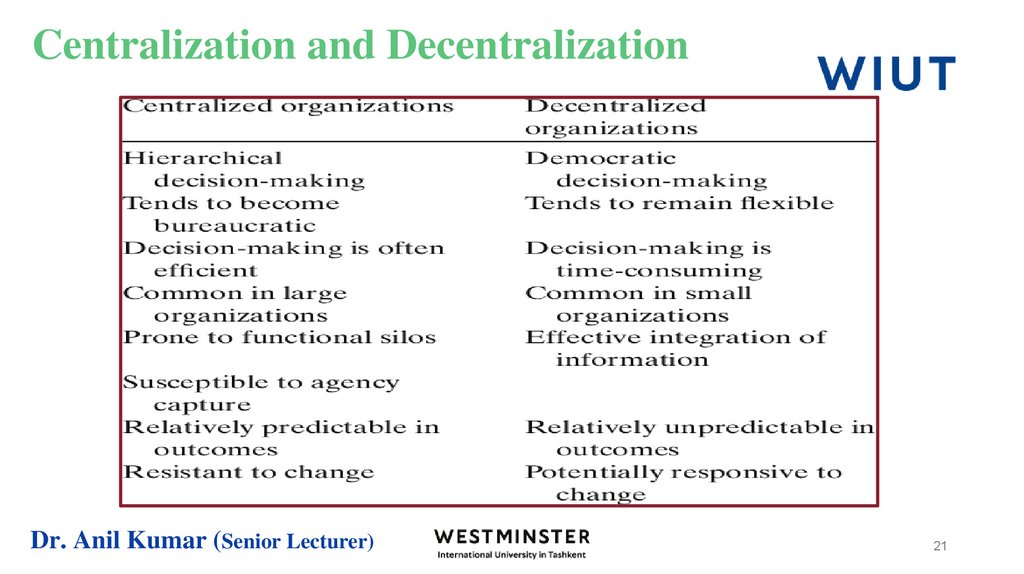
20. Centralization and Decentralization
Centralization and Decentralization are the two types of structures, thatcan be found in the organization, government, management and even in
purchasing.
Centralization of authority means the power of planning and decision
making are exclusively in the hands of top management.
Decentralization refers to the dissemination of powers by the top
management to the middle or low-level management. It is the
delegation of authority, at all the levels of management.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
20
21. Centralization and Decentralization
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)21
22. PROS AND CONS OF Centralisation vs Decentralization
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)22
23.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)23
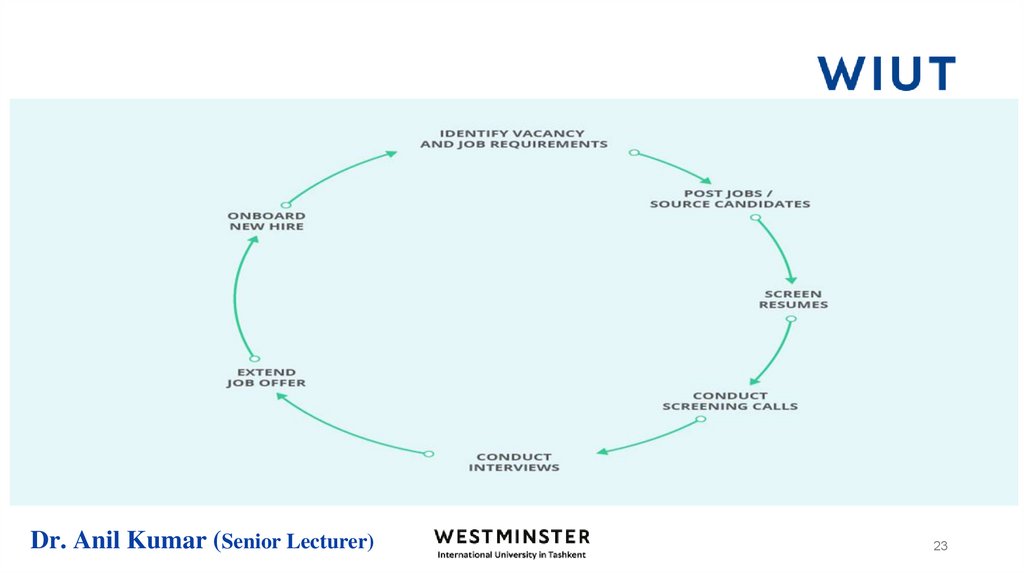
24. Recruitment Process of Sales Personnel
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)24
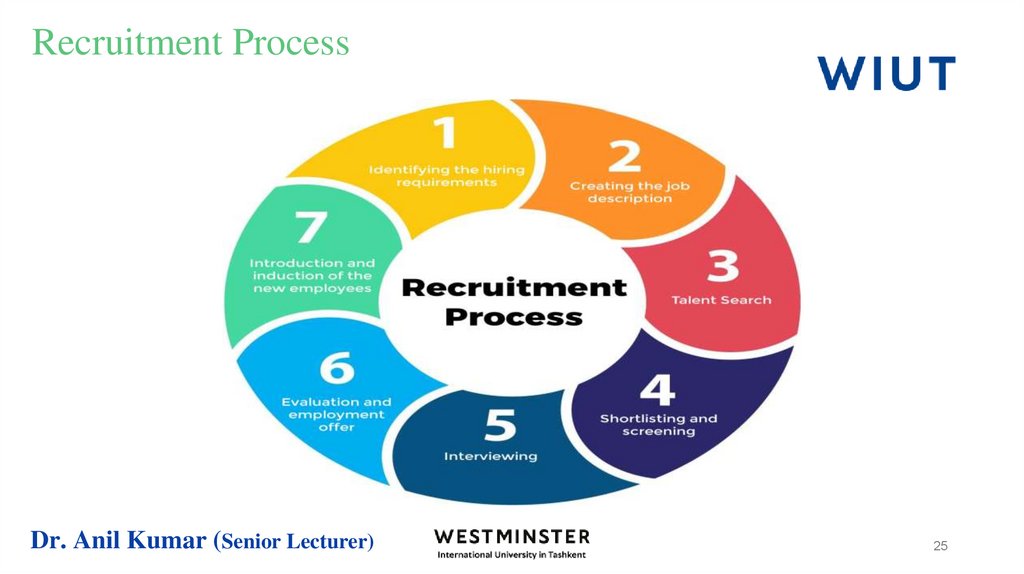
25. Recruitment Process
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)25
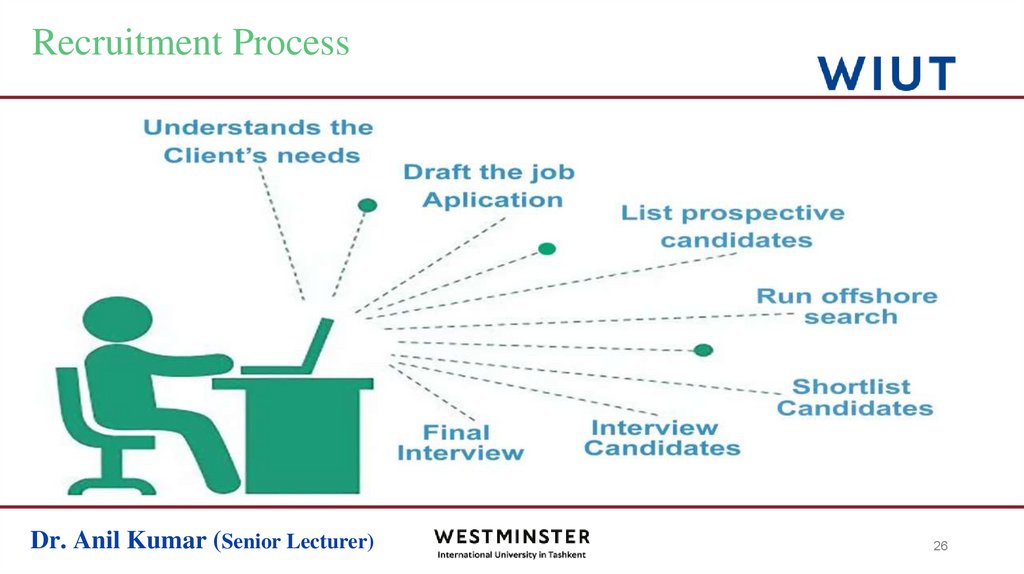
26. Recruitment Process
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)26
27. QUESTIONS
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)27























 Английский язык
Английский язык








