Похожие презентации:
The role of social media in the process of political mobilisation
1.
The role of social mediain the process
of political mobilisation
Irina Alekseevna Gladchenko, PhD
international communication department
Shool of World Politics
Lomonosov Moscow State University
2.
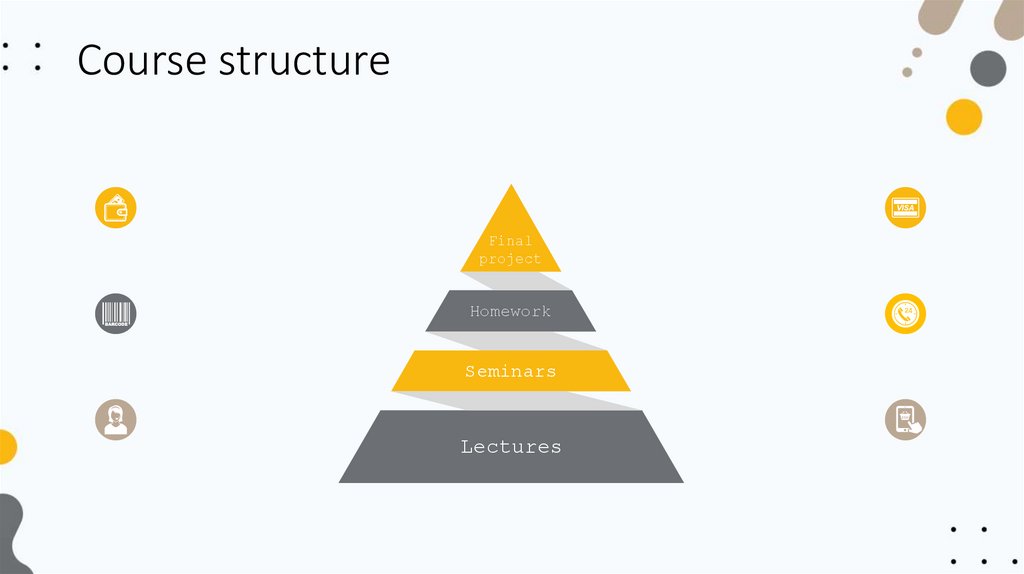
Course structureFinal
project
Homework
Seminars
Lectures
3.
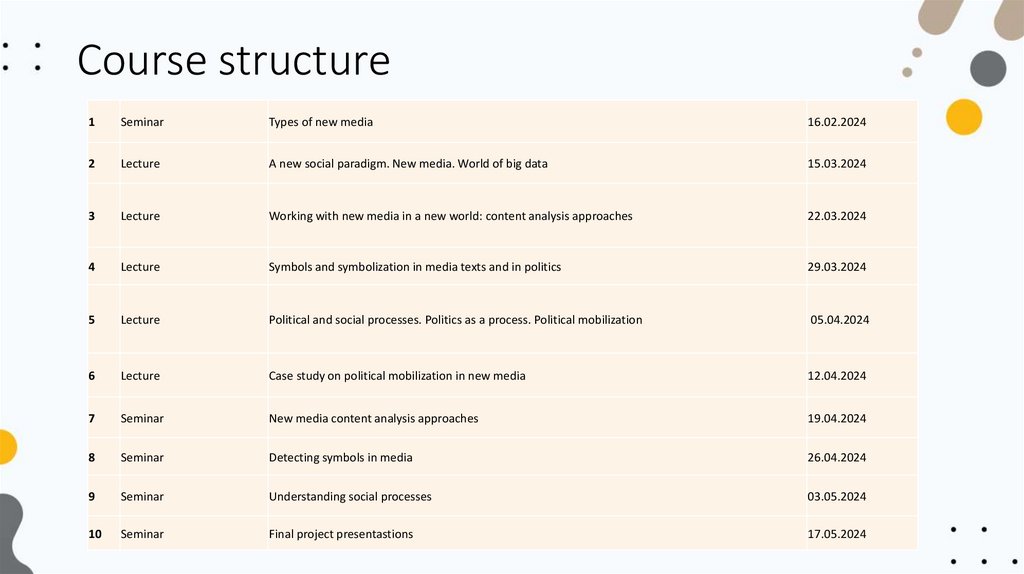
Course structure1
Seminar
Types of new media
16.02.2024
2
Lecture
A new social paradigm. New media. World of big data
15.03.2024
3
Lecture
Working with new media in a new world: content analysis approaches
22.03.2024
4
Lecture
Symbols and symbolization in media texts and in politics
29.03.2024
5
Lecture
Political and social processes. Politics as a process. Political mobilization
05.04.2024
6
Lecture
Case study on political mobilization in new media
12.04.2024
7
Seminar
New media content analysis approaches
19.04.2024
8
Seminar
Detecting symbols in media
26.04.2024
9
Seminar
Understanding social processes
03.05.2024
10
Seminar
Final project presentastions
17.05.2024
4.
Types of new mediaTelegram
ChatGPT
Midjourney
VKontakte
Messenger
Messenger
Open AI
Open AI
SNS – social network site
5.
Mobilisation is....• The process of influencing somebory to induce an action required by
the initiator of the process;
• a process of reaction to provocation.
6.
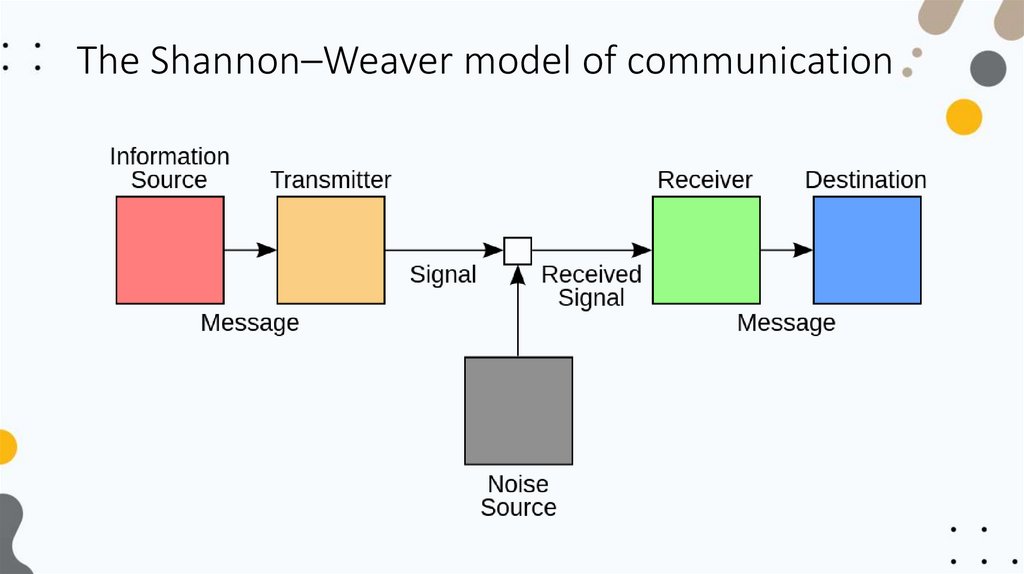
The Shannon–Weaver model of communication7.
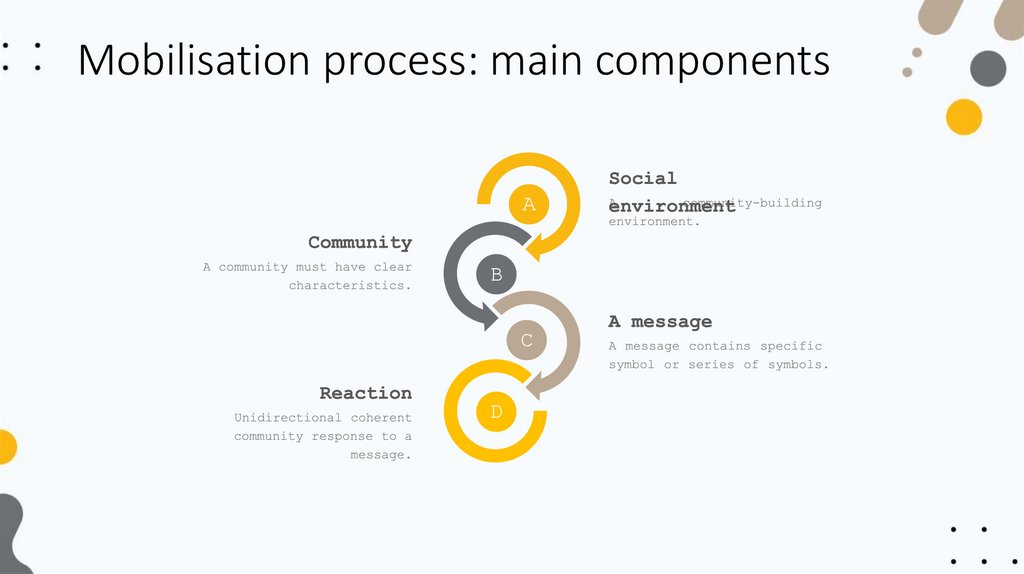
Mobilisation process: main componentsA
B
C
D
8.
Social environment• is the space constituted by all the elements created by the human
being, which surround the individuals and interact with them, such as
the infrastructure, the social relations and the cultural universe that
surrounds them.
• Historical aspect
• Cultural aspect (traditions, values, lifestyle, etc.)
• Technological aspect
• Location
• Economical and political conditions
9.
Modern society10.
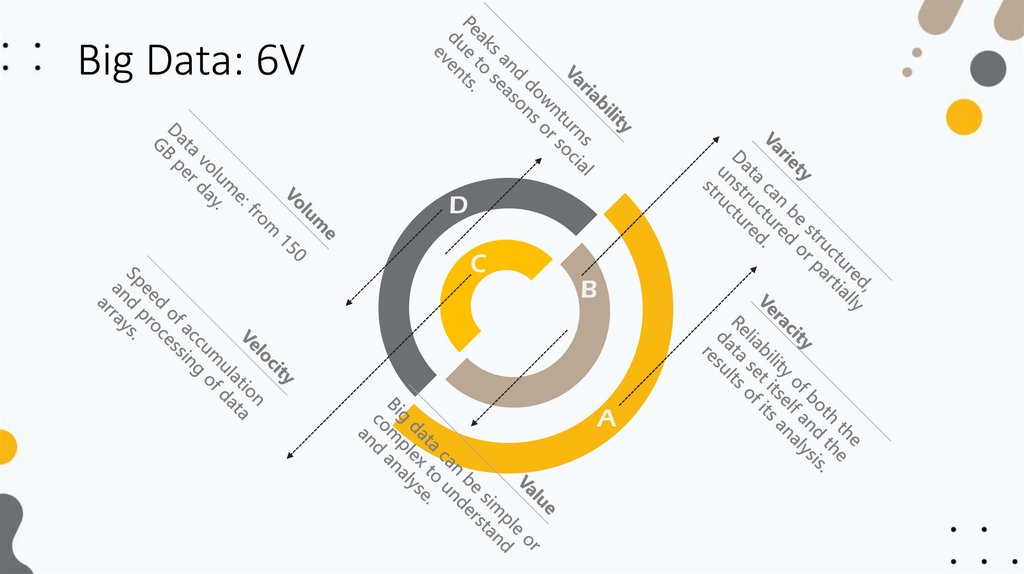
Big Data: 6VD
C
B
A
11.
The main sources of (big) data:• Internet of Things (IoT) and connected devices;
• social networks, blogs and media;
• company data: transactions, orders for goods and services, taxi and
carsharing trips, customer profiles;
• instrument readings: meteorological stations, air and water
composition meters, satellite data;
• city and state statistics: data on displacement, births and deaths;
• medical data: tests, illnesses, diagnostic scans.
12.
Society vs CommunityAn audience
A mob
A nation
A crowd
Masses
Electorate
A social network group
A network
13.
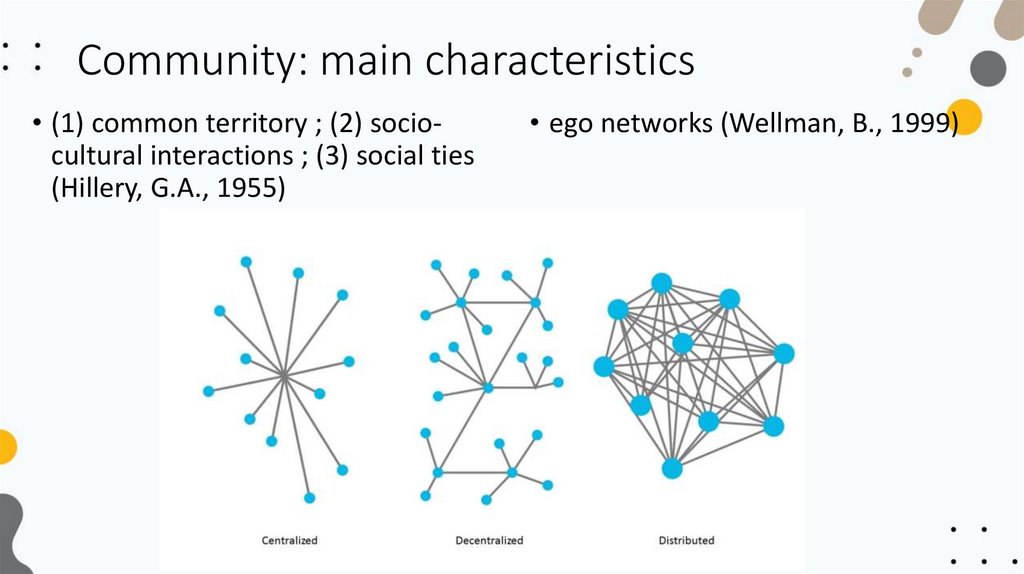
Community: main characteristics• (1) common territory ; (2) sociocultural interactions ; (3) social ties
(Hillery, G.A., 1955)
• ego networks (Wellman, B., 1999)
14.
Community in a virtual world• self-organization, cross-boundary, voluntary, self-governance
• decentralization, interactivity, horizontal coordination
• based on the management of available information
• uncertainty of spatial and temporal localization
• common goal
• undistinct borders
• weak ties
• unsustainability
15.
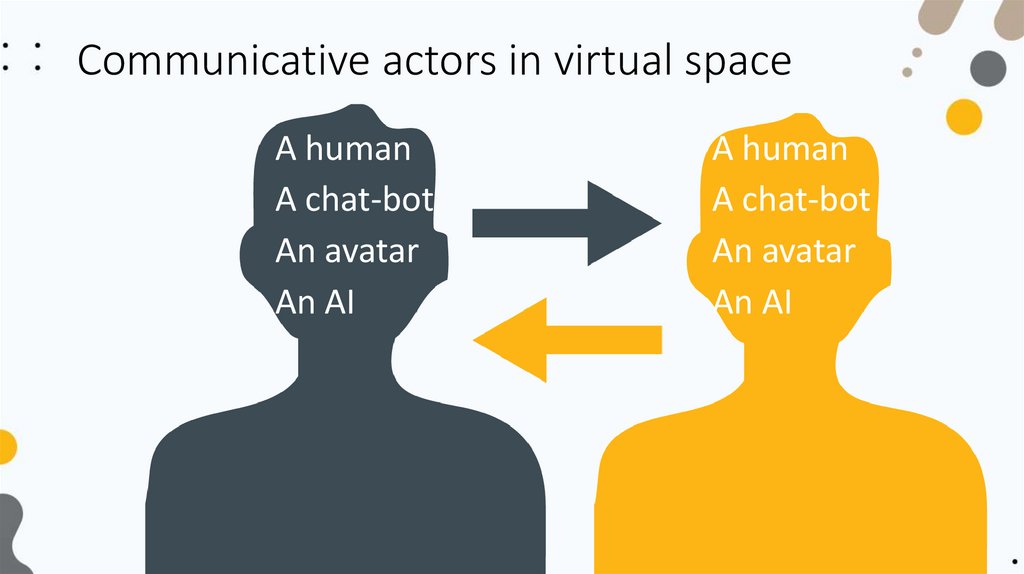
Communicative actors in virtual spaceA human
A chat-bot
An avatar
An AI
A human
A chat-bot
An avatar
An AI
16.
Time is short!• The mobilized state persists for a short period of time.
• Short-term communities:
• emerge at a certain point when there happens an informational
exposure,
• share a common goal,
• share a similar background,
• disintegrate as soon as the informational influence ceases.
17.
Social media content• Text
• Video
• Audio
• Pictures
• Pfotos
• Mems
• etc.
18.
Content distribution patterns• Administrative pattern:
1) mechanics of coercive
dissemination of information
2) peculiar to state structures
3) relies on the obligations that
employees have to fulfil within
the organisation
19.
Content distribution patterns• Market pattern:
1) market-based
2) requires a financial
investment
3) utilizes as many
dissemination channels as
possible
20.
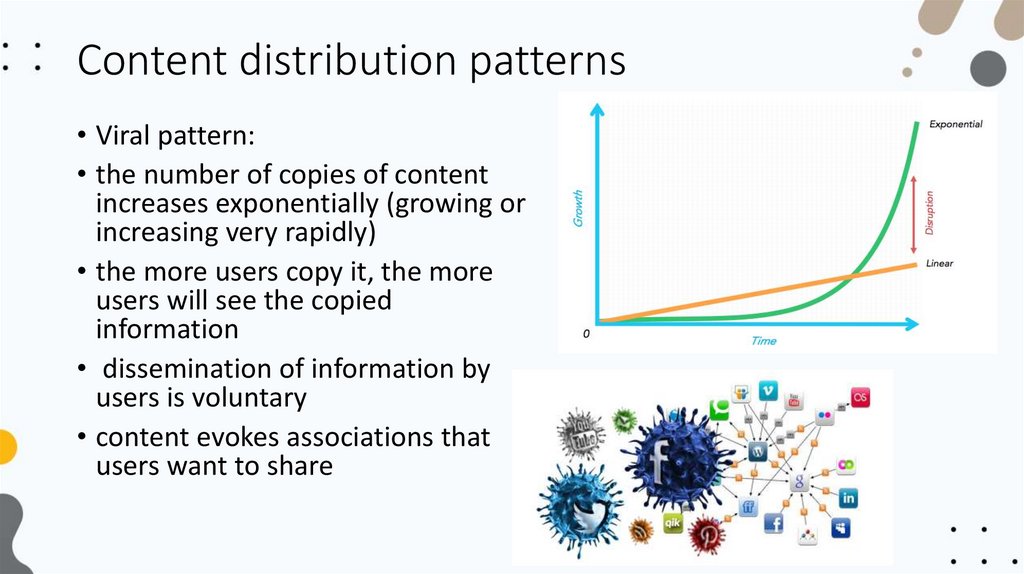
Content distribution patterns• Viral pattern:
• the number of copies of content
increases exponentially (growing or
increasing very rapidly)
• the more users copy it, the more
users will see the copied
information
• dissemination of information by
users is voluntary
• content evokes associations that
users want to share












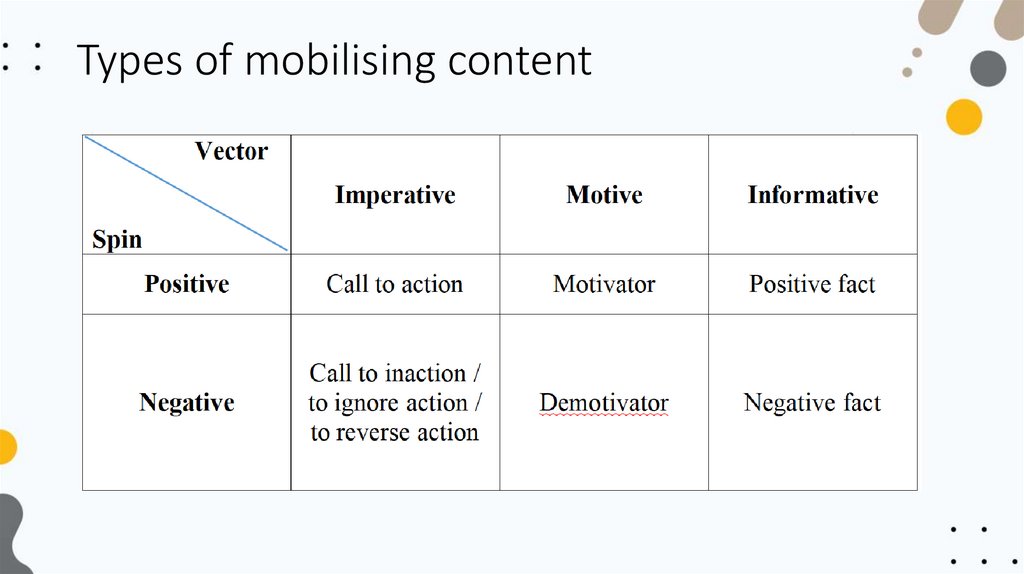
 Английский язык
Английский язык








