Похожие презентации:
Cognitive behavioural therapy
1.
CognitiveBehavioural
Therapy
Cindy and Katya
2.
Evolution of Behaviour TherapyPavlov
Watson
Relaxation
Training
Thorndike
& Skinner
Behaviour
therapy
environment
Techniques
Observalbe actions
and behavioural
Assertiveness
Training
Bandura
Wolpe
Eysenck
Systematic
Desentitisation
Effectiveness of
psychoanalysis?!
3.
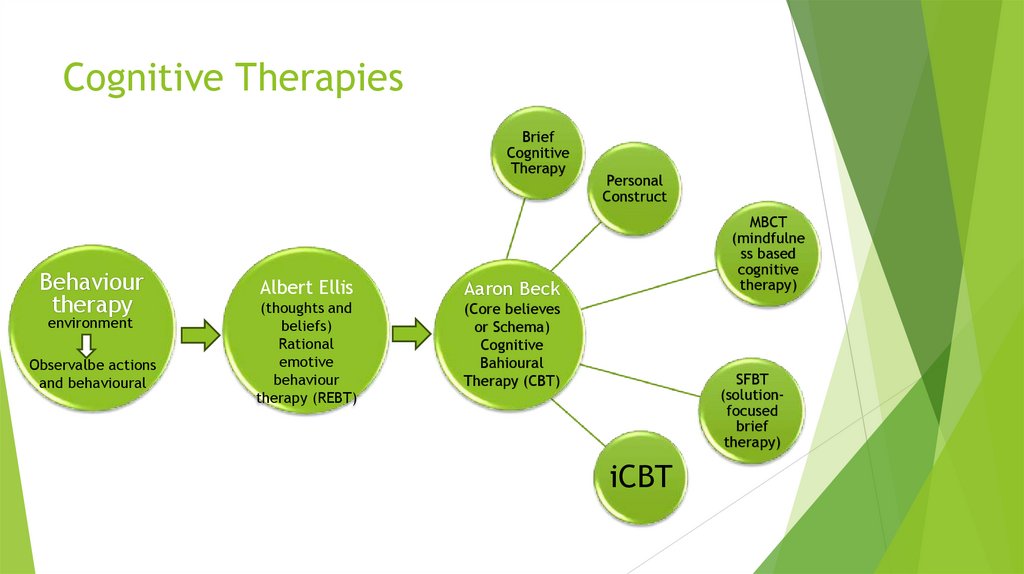
Cognitive TherapiesBrief
Cognitive
Therapy
Behaviour
therapy
environment
Observalbe actions
and behavioural
Albert Ellis
(thoughts and
beliefs)
Rational
emotive
behaviour
therapy (REBT)
Personal
Construct
MBCT
(mindfulne
ss based
cognitive
therapy)
Aaron Beck
(Core believes
or Schema)
Cognitive
Bahioural
Therapy (CBT)
SFBT
(solutionfocused
brief
therapy)
iCBT
4.
Techniques :Relaxation Training
1. Learn abdominal breathing
2. Progressive muscle relaxation
3. Visualisation and imagery
5.
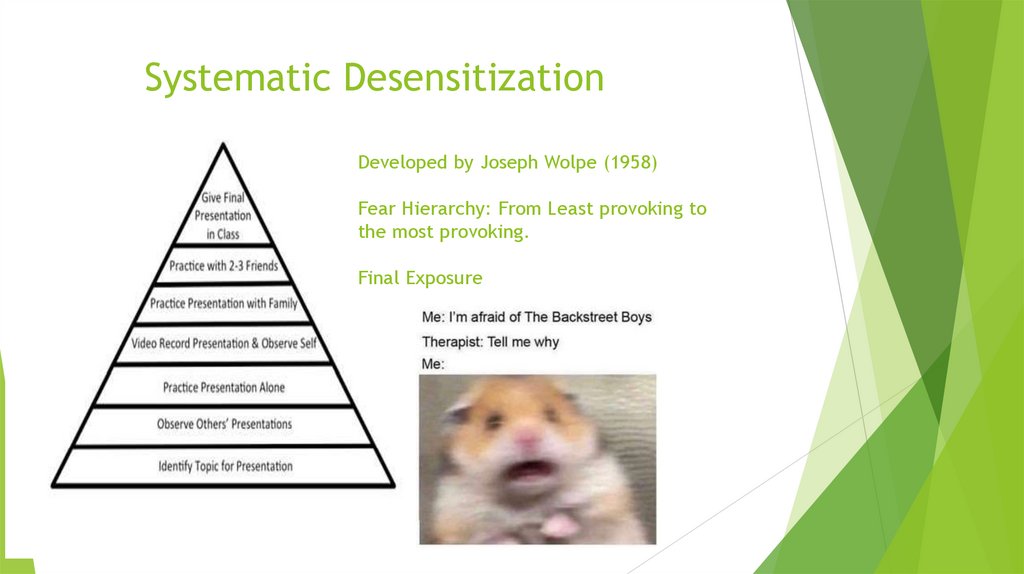
Systematic DesensitizationDeveloped by Joseph Wolpe (1958)
Fear Hierarchy: From Least provoking to
the most provoking.
Final Exposure
6.
Assertiveness TrainingFeelings
expression
The main
areas of
difficulty
Ask for
what you
need
Say
no
7.
Albert Ellis(1913-2007)
● Psychologist and psychotherapist who founded REBT
● Held MA and PhD in Clinical Psychology
● He was considered the second most influential
psychotherapist in history.
● Born in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, raised in the Bronx
● Parents divorced and he lived with his mother.
● Very sickly child, no emotional support from his mother
● Committed numerous sexual assaults against
women during his teens and early twenties.
● Phobias speaking in public, especially with women.
● Sex and love relations were his professional interests
from the beginning of his career.
8.
Rational Emotive Behaviour Therapy(REBT)
Ellis describes the sequence of events that lead to psychological disturbance:
A
B
C
• Activating event
• Exp. A friend refused to see me on the weekend
• Beliefs about what happened (rational vs
irrational)
• I am not interesting to her, does not value me
• Consequences (emotional or behavioural)
• Stop speaking to my ex friend.
Irrational thinking –main
Cause of all the disturbance
Worked on in REBT
9.
REBTHelping clients to change
Establish irrational belief by listening ( shoulds and musts)
Teach the ABC model at an early stage
Clients are encouraged to look at the activating event and the emotional
disturbance it produced
After attention is directed to the beliefs which caused such a powerful influence
Very active and direct approach. Involves persuasion, debate and humor as
therapeutic tool
Includes homework as self-monitoring, recording negative thoughts
Shame attacking exercises
Counsellors need to separate themselves from the irrational thoughts of the
clients. Debate has a central place in this model.
10.
Brief cognitive therapy & SolutionFocused therapy
Brief CT combines the two approaches ( the behavioral and the cognitive) and
is adaptable to be provided within even one session
SFBT encourages clients to think in terms of mental well-being and based on
four main assumptions:
1. Change is constant 2. Spend time on solutions
3. Small change needed for a greater change 4. Clients are the experts
Developed by Steve Shazer and colleagues at the Brief Family Center mid
1980s
Important figure Milton Erickson –unique approach-at the basis of modern
coaching
Skills: the use of matching the client’s language, open questions, establishing
rapport and goals . All positive changes acknowledged








 Психология
Психология








