Похожие презентации:
Geography, climate and industry of Siberia
1.
Geography, climate and industry of siberiaPresentation was prepared
by Bansurov and Trofimov
2.
Siberia is a vast natural and the historicalregion in North Asia, bounded on the west
by the Ural Mountains, on the east by the
watershed ridges separating the basins of
the Arctic and Pacific Oceans (historically
by the Pacific Ocean), on the north by the
Arctic Ocean, on the south by the state
border of Russia.
3.
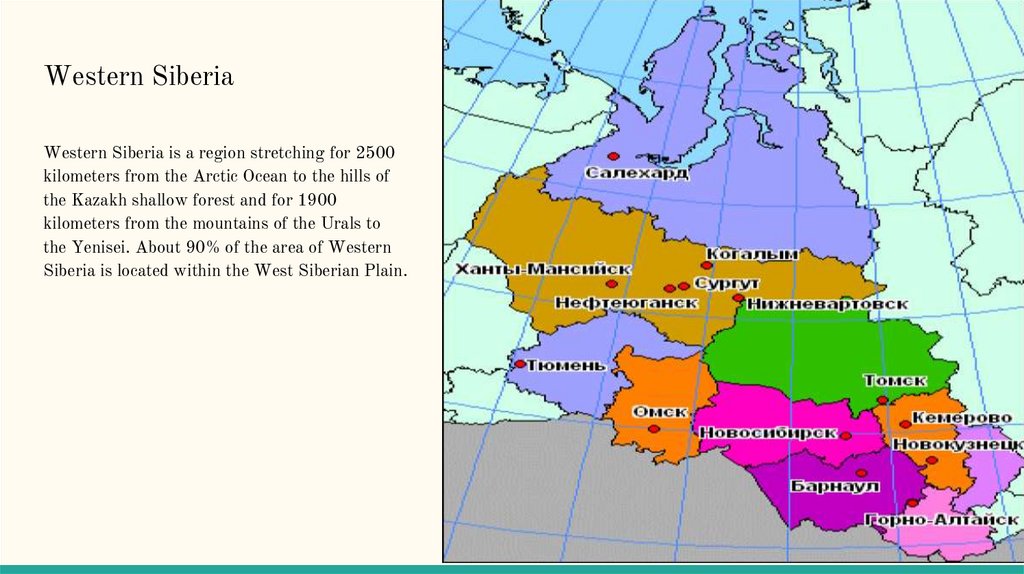
Western SiberiaWestern Siberia is a region stretching for 2500
kilometers from the Arctic Ocean to the hills of
the Kazakh shallow forest and for 1900
kilometers from the mountains of the Urals to
the Yenisei. About 90% of the area of Western
Siberia is located within the West Siberian Plain.
4.
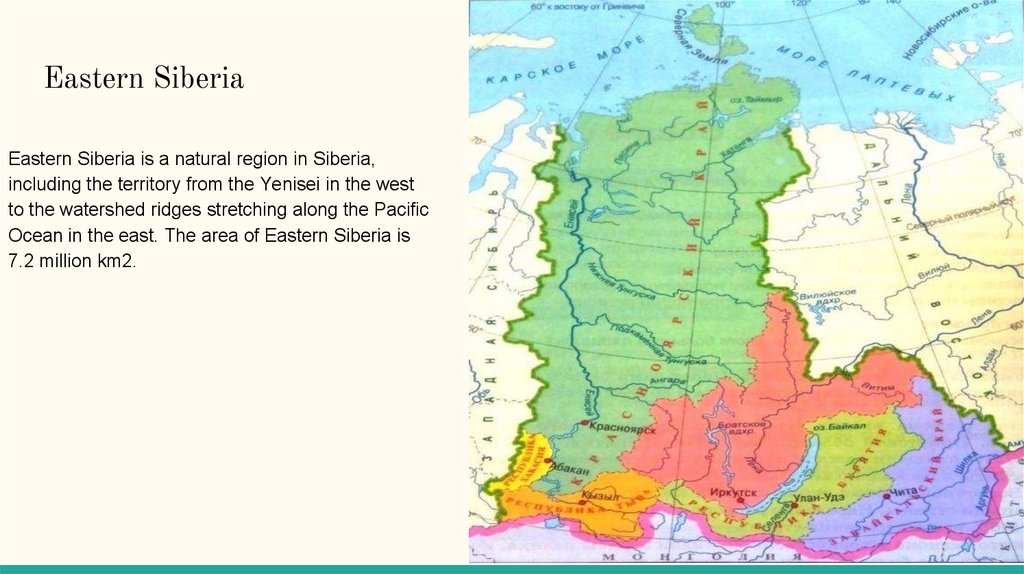
Eastern SiberiaEastern Siberia is a natural region in Siberia,
including the territory from the Yenisei in the west
to the watershed ridges stretching along the Pacific
Ocean in the east. The area of Eastern Siberia is
7.2 million km2.
5.
ClimateThe climate of Siberia is sharply
continental and harsh. There are two
main climatic zones: temperate in the
south and subarctic in the north.
Climate characteristics:
The average temperature in July: in
the south reaches +23 ° C, in the
north — about +5 °C.
The average thermometer in
January: -16 °C in the south, -48 °C
in the north.
6.
The climate of Western Siberiais predominantly continental.
The exception is mountainous
areas.
The northern regions are
characterized by cold, long
winters and cool, rainy summers.
In the southern regions, winters
are less severe, and summers are
warm and dry.
7.
The characteristic climate ofEastern Siberia is sharply
continental.
In winter, clear, cloudy and dry, but
very cold weather prevails. The
average air temperature in January
in the vast expanse of Eastern
Siberia varies from -26 ° C in the
southwest to -38...-42 ° C in the
Central Lowlands. In valleys and
hollows, the air temperature can
drop to -60 °C.
8.
IndustryNon ferrous metallurgy is one of
the most important branches of
the economy of Eastern Siberia.
1/3 of Russian non-ferrous metals
are produced here, primarily
aluminum (3/4 of Russian
production), as well as nickel and
copper.
9.
The electric power industry of Eastern Siberiais distinguished by the country's largest
hydroelectric power plants. They were built on
the Yenisei (Krasnoyarsk and SayanoShushenskaya with a capacity of over 6 million
kW) and on the Angara (Bratskaya, UstIlimskaya, Boguchanskaya, Irkutsk
hydroelectric power plants).
The district provides more than 13% of
Russia's total electricity production. A
significant proportion of energy is produced at
hydroelectric power plants, due to which it has
a relatively low cost. Energy-intensive
industries are developing on the basis of cheap
energy.
10.
Eastern Siberia ranks second interms of logging in Russia. The
main logging is carried out along
the Trans-Siberian railway, in the
Krasnoyarsk Territory and the
Angara region.
Large centers of woodworking
enterprises in the region are
located in Yeniseisk, Kansk,
Krasnoyarsk, Chita. 5 The pulp
and paper industry is developed in
Bratsk, Ust-Ilimsk, Baikalsk,
Krasnoyarsk, Selenginsk.









 География
География








