Похожие презентации:
Understanding Digitizers: Definition, Uses, and Applications
1.
Understanding Digitizers:Definition, Uses, and Applications
Digitizers are essential tools for converting physical designs and drawings into digital formats. They play a crucial
role in various industries by bridging the gap between the physical and digital worlds.
2.
What is a digitiser?A digitiser is a device that captures physical input, such as a pen stroke
or hand movement, and translates it into digital data. It essentially acts
as a bridge between the physical and digital realms.
Input
Conversion
Digitizers capture physical
The input is translated into
input, such as pen strokes or
digital data, such as
hand movements.
coordinates or pressure
values.
Output
The digital data is then used in software applications for various
purposes, such as design, editing, and analysis.
3.
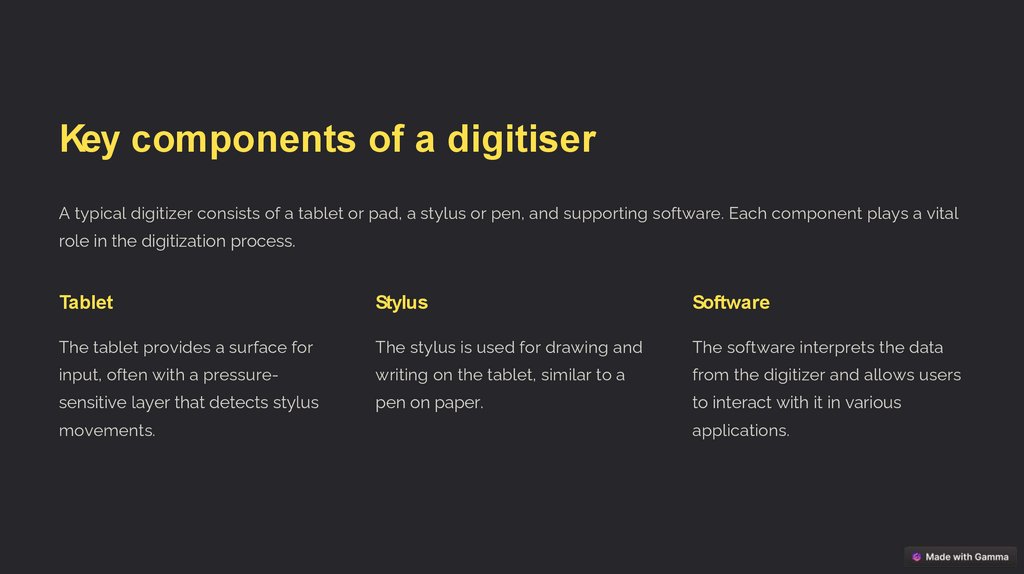
Key components of a digitiserA typical digitizer consists of a tablet or pad, a stylus or pen, and supporting software. Each component plays a vital
role in the digitization process.
Tablet
Stylus
Software
The tablet provides a surface for
The stylus is used for drawing and
The software interprets the data
input, often with a pressure-
writing on the tablet, similar to a
from the digitizer and allows users
sensitive layer that detects stylus
pen on paper.
to interact with it in various
movements.
applications.
4.
Digitis er input methodsDigitizers can employ different input methods to capture physical data.
Some commonly used methods include electromagnetic resonance,
pressure sensitivity, and optical tracking.
1
3
Electromagnetic
Res onance
2
Pres s ure Sens itivity
This method measures the
This method uses
force applied by the stylus
electromagnetic fields to
on the tablet, providing
track the stylus's position
varying levels of pressure
and pressure on the tablet.
input.
Optical Tracking
This method uses optical sensors to track the stylus's position
and orientation on the tablet.
5.
Applications of digitisersDigitizers have found widespread applications across various fields,
including graphic design, architecture, engineering, and medicine.
Industry
Application
Graphic Design
Creating digital artwork,
illustrations, and logos.
Architecture
Drawing floor plans, elevations,
and 3D models.
Engineering
Drafting technical drawings and
creating schematics.
Medicine
Annotating medical images and
creating digital anatomical
models.
6.
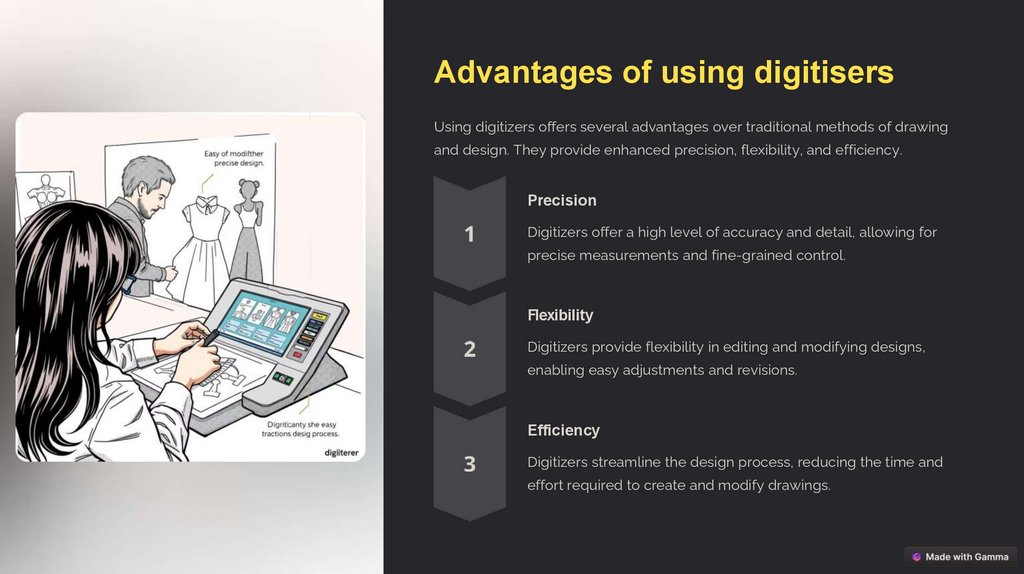
Advantages of using digitisersUsing digitizers offers several advantages over traditional methods of drawing
and design. They provide enhanced precision, flexibility, and efficiency.
Precision
Digitizers offer a high level of accuracy and detail, allowing for
precise measurements and fine-grained control.
Flexibility
Digitizers provide flexibility in editing and modifying designs,
enabling easy adjustments and revisions.
Efficiency
Digitizers streamline the design process, reducing the time and
effort required to create and modify drawings.
7.
Emerging trends in digitiser technologyDigitiser technology is constantly evolving, with new advancements driving innovation and expanding its
capabilities. Trends such as wireless connectivity, enhanced pressure sensitivity, and integration with AI are
reshaping the landscape.
Wireless Connectivity
Modern digitizers are increasingly adopting wireless connectivity, allowing for greater mobility and freedom
of movement.
Enhanced Pressure Sensitivity
Advanced pressure sensitivity capabilities allow for more realistic and nuanced digital strokes, mimicking the
feel of traditional art tools.
AI Integration
AI algorithms are being integrated into digitizers, enabling features such as automatic line correction, stroke
prediction, and intelligent colour palettes.
8.
Cons iderations for s electing a digitis erWhen choosing a digitiser, it's crucial to consider factors such as resolution, pressure sensitivity, active
area size, and compatibility with your software and workflow.
1
Res olution
The resolution determines the level of detail the digitizer can capture, with higher
resolution offering greater precision.
2
P res s ure Sens itivity
Pressure sensitivity allows for varying line thickness and shading, mimicking the feel of
traditional pen and paper.
3
Active Area Size
The active area size refers to the usable drawing surface, which should be sufficient for
your intended use.
4
Software Compatibility
Ensure that the digitizer is compatible with the software you use for design and editing.
9.
Conclus ion and key takeawaysDigitizers are versatile tools that bridge the gap between physical and digital worlds. They offer a powerful way to
create, edit, and share designs with enhanced precision, flexibility, and efficiency.
Precis ion
Flexibility
E fficiency
Digitizers offer a high level of
Digitizers provide flexibility in
Digitizers streamline the design
accuracy and detail.
editing and modifying designs.
process.







 Программирование
Программирование Право
Право