Похожие презентации:
Modern english lexicology. Lecture two : lexicography as a tool and the result of lexicological studies
1.
MODERN ENGLISHLEXICOLOGY
LECTURE TWO :
LEXICOGRAPHY AS A TOOL
AND
THE RESULT OF
LEXICOLOGICAL STUDIES
1
2. Topics for discussion:
• Lexicography as a science and a branchof Lexicology
• History of English Lexicography
• Problems of dictionary compiling
• Types of inquiry books /dictionaries
• Dictionaries in language teaching
2
3. Lexicography as a science
a branch of Linguisticsthe theory and practice
of compiling
dictionaries
is the activity or
profession of writing
dictionaries
The art of compiling
dictionaries
the practice of
compiling dictionaries
the activity or
occupation of compiling
dictionaries
3
4. Subject of lexicography
• The activity or profession of writingdictionaries (CollinsCobuild);
•The practice of compiling dictionaries (COD)
•The activity or occupation of compiling
dictionaries (OxfordAmerican)
• The art of compiling dictionaries
4
5. History of ENGLISH lexicography
• The oldest is a Latin-English "wordbook" bySir Thomas Elyot published in 1538.
•Cawdray English dictionary of so-called “hard
words” was published in 1604;
• In 1721, the Universal Etymological Dictionary was
published by Samuel Johnson;
• In 1755 S. Johnson’s Dictionary of the English
Language in 123 volumes;
• In 1811 a Concise Oxford Dictionary appeared;
• The completion of the English Language Dictionary
in 1928 , 173 years after its first edition.
5
6. Johnson's Dictionary Vol. 1 (1755) title page
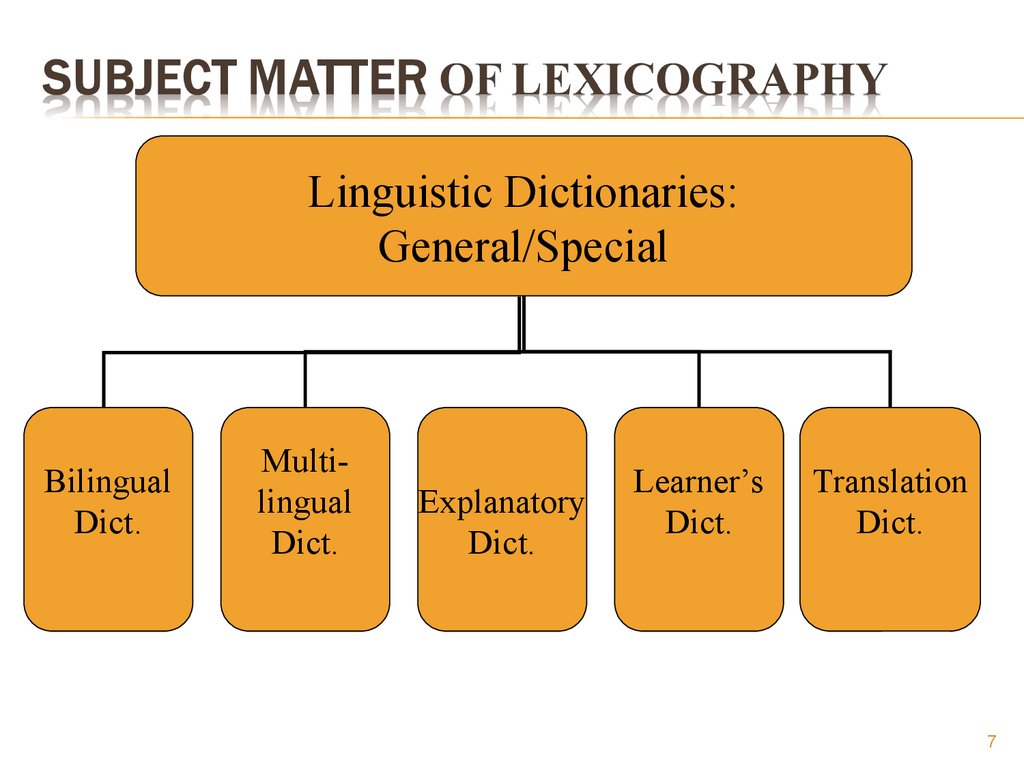
67. subject matter of Lexicography
Linguistic Dictionaries:General/Special
Bilingual
Dict.
Multilingual
Dict.
Explanatory
Dict.
Learner’s
Dict.
Translation
Dict.
7
8. BEST ONLINE Dictionaries
American Heritage Dictionary American Heritage Dictionary of theEnglish Language, Fifth Ed.
Collins Online Dictionary Collins Unabridged English Dictionary; Collins
Unabridged Thesaurus; Collins Webster's American English Dictionary
Dictionary.com Dictionary.com Unabridged, based on the Random
House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary
Merriam-Webster OnLine Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary
Oxford Dictionaries Online Oxford Dictionary of English; New Oxford
American Dictionary; Oxford Thesaurus of English; Oxford American
Writer's Thesaurus
Advanced learner dictionaries:
Cambridge Dictionaries Online Cambridge Advanced Learner's
Dictionary
Longman Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English
Macmillan Macmillan English Dictionary for Advanced Learners
Oxford University Press Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary
8
9. What is a dictionary?
1) A dictionary is abook in which the
words and phrases of
a language are listed
alphabetically,
together with their
meanings or their
translations in
another language.
E.G. Uzbek-English
Dictionary
2) A dictionary is an
alphabetically ordered
reference book on one
particular subject or
limited group of
subjects, a reference
book on any subject,
E.G. Dictionary of
quotations, Who’s Who,
Shakespeare’s
Glossary
9
10. Types of dictionaries
Two major types:Encyclopedic (thing books) and
Linguistic (word books) dictionaries
Linguistic dictionaries can be:
• Unilingual – present definitions in the same language, and
are explanatory;
•Bilingual – words and their equivalents in another
language, called translation dictionaries;
•Multilingual – present words in several usually genetically
related languages;
•Diachronic –vocabulary units are presented throughout
their etymological history;
•Synchronic – concern with the present day meaning and
usage of vocabulary units;
•General – the general bulk of the vocabulary;
•Special(ised) – various classes of vocabulary units
(synonyms, antonyms, idioms, terminology, etc.)
10
11. problems of dictionary compiling:
1.2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Selection of vocabulary units - listemes;
Ways of their arrangement;
Setting of the entries – graphics and order;
Selection and arrangement of the LSVs in the
semantic structure;
Use of illustrative examples to show the contextual
variations of meanings;
Presentation of the phonetic and grammatical
features;
Inclusion of stylistic, etymological, phraseological
characteristics, etc.
11
12. A Good dictionary :
• describes the composition of the English vocabulary;•presents various types of vocabulary units: morphemes, words
and set expressions;
•presents vocabulary units usually in alphabetical order;
•provides derivational relations of listemes in their entries;
•presents meanings in accordance with its frequency of use;
•presents the etymological data of the listemes;
•gives functional, regional and territorial variations of the
listemes;
•provides set expressions/idioms with listed words
•marks stylistic, slang and other specific features;
•provides clear instructions for the use of the dictionary and the
list of labels, symbols to be used, etc.
12
13. Role of dictionary in flt:
•to be used as a handbook for consulting the English vocabulary;•to advise on the choice of synonyms, antonyms, etc.
•to check the right pronunciation of the vocabulary units;
•to consult derivational and compositional peculiarities of
listemes in their entries;
•to find out meanings in accordance with frequency of use;
•to check the etymological features of the listemes;
•to find out functional and territorial variations of the listemes;
•to learn about stylistic, slang and other specific features;
•to apply in research work and selection of language units for
diploma and course papers and dissertations,
•helps with translation work, etc.
13



















 Английский язык
Английский язык








