Похожие презентации:
Teaching and Learning Vocabulary
1.
Teaching and LearningVocabulary
December, 3, 2024
2.
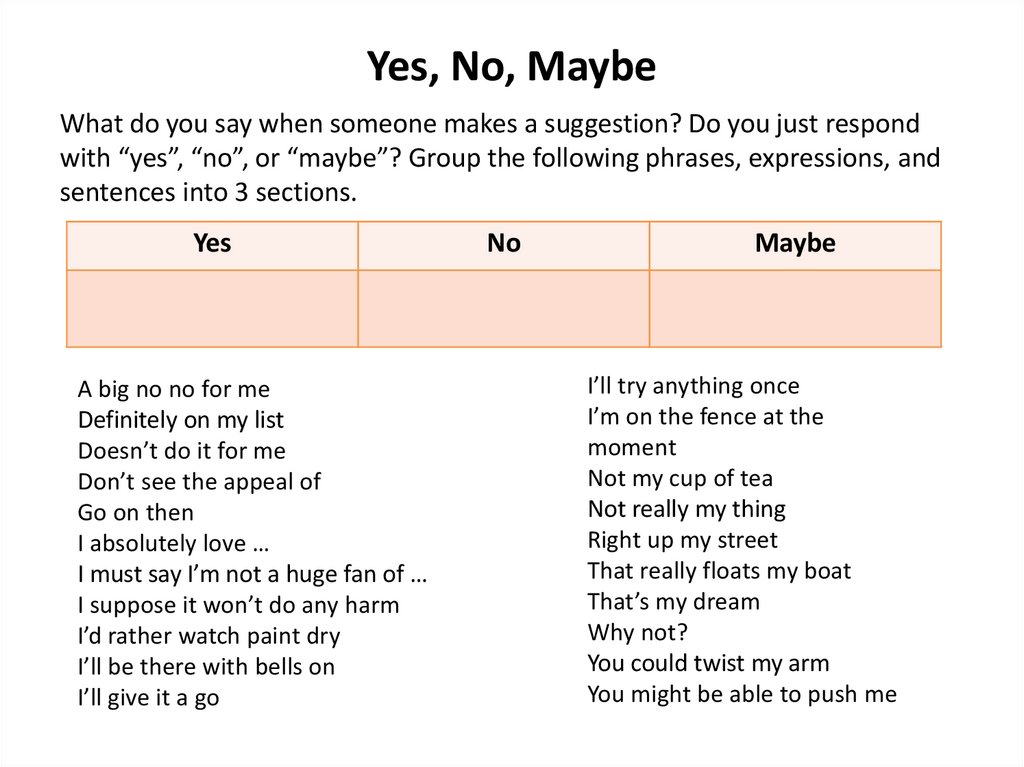
Yes, No, MaybeWhat do you say when someone makes a suggestion? Do you just respond
with “yes”, “no”, or “maybe”? Group the following phrases, expressions, and
sentences into 3 sections.
Yes
A big no no for me
Definitely on my list
Doesn’t do it for me
Don’t see the appeal of
Go on then
I absolutely love …
I must say I’m not a huge fan of …
I suppose it won’t do any harm
I’d rather watch paint dry
I’ll be there with bells on
I’ll give it a go
No
Maybe
I’ll try anything once
I’m on the fence at the
moment
Not my cup of tea
Not really my thing
Right up my street
That really floats my boat
That’s my dream
Why not?
You could twist my arm
You might be able to push me
3.
Yes, No, MaybeNow watch the video ‘Improve Your Vocabulary: 21 ways to say Yes, No,
Maybe’
https://www.engvid.com/improve-your-vocabulary-yes-no-maybe/
Do the quiz afterwards.
4.
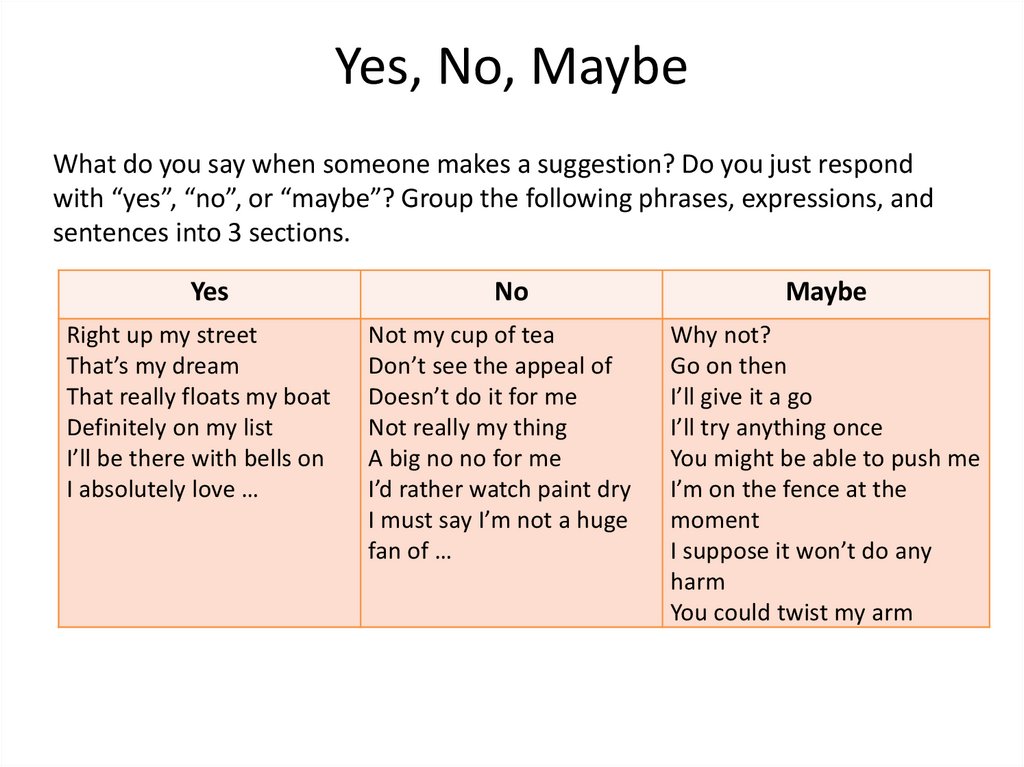
Yes, No, MaybeWhat do you say when someone makes a suggestion? Do you just respond
with “yes”, “no”, or “maybe”? Group the following phrases, expressions, and
sentences into 3 sections.
Yes
No
Maybe
Right up my street
That’s my dream
That really floats my boat
Definitely on my list
I’ll be there with bells on
I absolutely love …
Not my cup of tea
Don’t see the appeal of
Doesn’t do it for me
Not really my thing
A big no no for me
I’d rather watch paint dry
I must say I’m not a huge
fan of …
Why not?
Go on then
I’ll give it a go
I’ll try anything once
You might be able to push me
I’m on the fence at the
moment
I suppose it won’t do any
harm
You could twist my arm
5.
Yes, No, MaybeLet’s discuss the following questions:
• What is the topical vocabulary that the teacher introduces?
• What is the level of language learners the lesson is aimed at?
• In what way does the teacher introduce the vocabulary? Do you find it
effective? Did it work for you?
• Was the quiz difficult? Is it enough to have one video and one exercise to
acquire the vocabulary? What kind of activities could be added?
6.
Practice7.
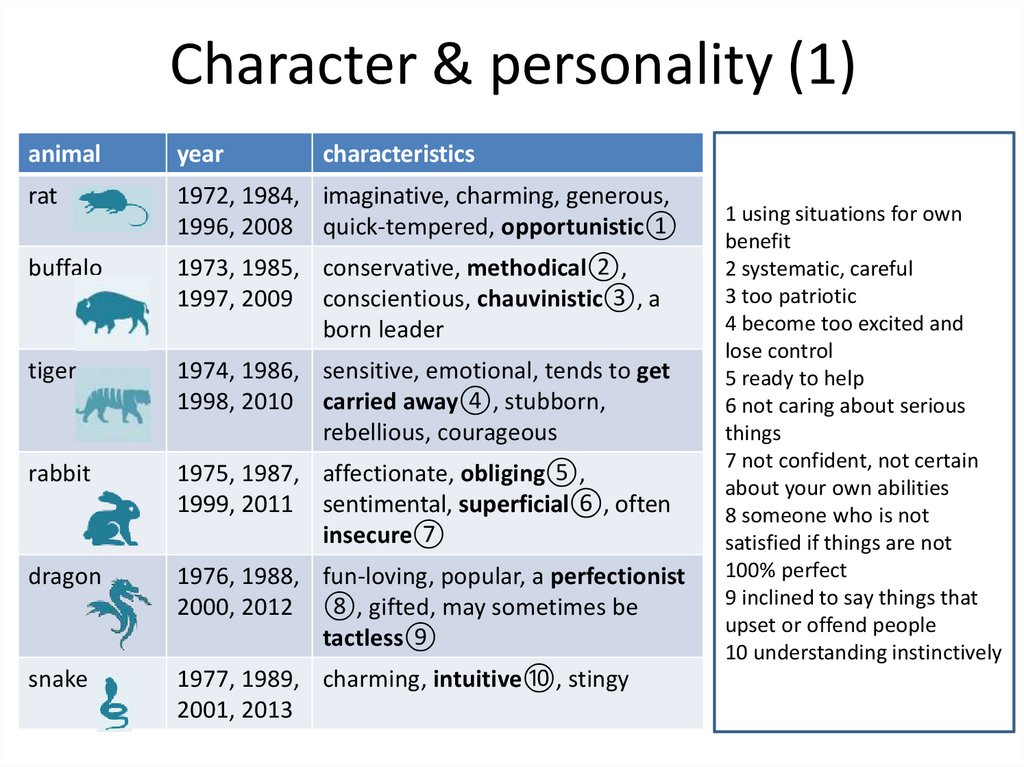
Character & personality (1)animal
year
characteristics
rat
1972, 1984, imaginative, charming, generous,
1996, 2008 quick-tempered, opportunistic①
buffalo
1973, 1985, conservative, methodical②,
1997, 2009 conscientious, chauvinistic③, a
born leader
tiger
1974, 1986, sensitive, emotional, tends to get
1998, 2010 carried away④, stubborn,
rebellious, courageous
rabbit
1975, 1987, affectionate, obliging⑤,
1999, 2011 sentimental, superficial⑥, often
insecure⑦
dragon
1976, 1988, fun-loving, popular, a perfectionist
2000, 2012 ⑧, gifted, may sometimes be
tactless⑨
snake
1977, 1989, charming, intuitive⑩, stingy
2001, 2013
1 using situations for own
benefit
2 systematic, careful
3 too patriotic
4 become too excited and
lose control
5 ready to help
6 not caring about serious
things
7 not confident, not certain
about your own abilities
8 someone who is not
satisfied if things are not
100% perfect
9 inclined to say things that
upset or offend people
10 understanding instinctively
8.
Character & personality (2)animal
year
characteristics
horse
1978, 1990,
2002, 2014
diligent⑪, independent, placid⑫,
outgoing, can be selfish and cunning
goat
1979, 1991,
2003, 2015
elegant, artistic, always ready to
complain, over-anxious
monkey
1980, 1992,
2004, 2016
witty, magnetic personality⑬,
good company, can be trustful⑭
rooster
1981, 1993,
2005, 2017
industrious, shrewd⑮, supportive
⑯, decisive, extravagant⑰
dog
1982, 1994,
2006, 2018
down-to-earth⑱, altruistic⑲,
morose⑳, sharp-tongued
pig
1983, 1995,
2007, 2019
intellectual, tolerant, naïve, often
materialistic
11 hard-working
12 calm, does not easily
become excited or angry
13 personality that attracts
people to you
14 not trusting, suspicious of
others
15 having good judgment
16 gives help or
encouragement
17 spends too much money
or uses too much of
something
18 practical and sensible
19 thinking of others rather
than yourself
20 gloomy
9.
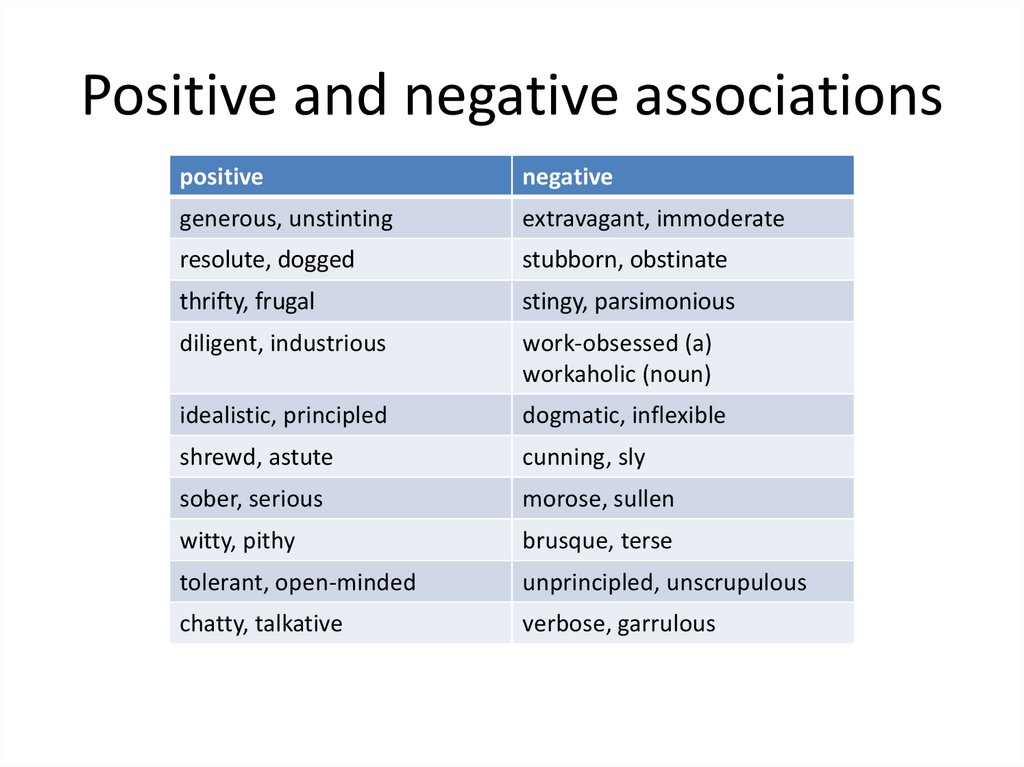
Positive and negative associationspositive
negative
generous, unstinting
extravagant, immoderate
resolute, dogged
stubborn, obstinate
thrifty, frugal
stingy, parsimonious
diligent, industrious
work-obsessed (a)
workaholic (noun)
idealistic, principled
dogmatic, inflexible
shrewd, astute
cunning, sly
sober, serious
morose, sullen
witty, pithy
brusque, terse
tolerant, open-minded
unprincipled, unscrupulous
chatty, talkative
verbose, garrulous
10.
Read the comments and then answerthe questions
I wish Tatyana would calm down and
not get so over-excited about things.
Tom thinks that his country is better
than any other country and doesn’t
listen to reason.
Alice can always be relied upon to make
the right decision.
Sophie is always so calm.
Harry is such a practical and sensible
person.
Andrey has a tendency to say things
that upset people.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Who is placid?
Who is down-to-earth?
Who tends to get carried away?
Who is often tactless?
Who is shrewd?
Who is chauvinistic?
11.
Which colleagues does the speakerhave a positive opinion of and which a
negative one?
‘Ellie, my boss, is very astute and she can be
very witty, but I find her assistant, David, a bit
sullen and obstinate. Julia, who I sit next to, is a
bit stingy and extremely work-obsessed. I do a
lot of work with Marco, who is very obliging,
supportive and tolerant.’
12.
Fill the gaps with proper words. You’regiven the first letter(s) and clues to the
meaning in brackets (1).
1. He’s rather o___________ . He always tries to use
situations to his own advantage. (devious)
2. She has an i___________ approach to life rather than
a rational one. (instinctive)
3. My father was a somewhat quick-tempered and
m___________ sort of person. (gloomy)
4. He was a very altruistic person, almost to the point of
being n___________. (too trusting)
5. Aisha has a m___________ personality. Everyone is
drawn to her. (attractive)
6. Rob is very a conscientious and m___________
worker. (careful, systematic)
13.
Fill the gaps with proper words. You’regiven the first letter(s) and clues to the
meaning in brackets (2).
7. I find Eva a bit b___________ and rude. (speaks in a quick
and rude way)
8. She’s fun-loving but she can be a bit s___________ at
times. (doesn’t care about serious things)
9. I think Max is i___________ . (doesn’t have much
confidence, not really sure of himself)
10. I’m always happy to go out for a meal with Kerstin. She’s
such g___________ c___________ . (pleasant and
entertaining to spend time with)
11. She was very c___________ in speaking out against
corruption. (brave, unafraid to speak or act)
12. Owen’s a p___________. He’s never happy if he doesn’t
get an A-grade in every test.
14.
Write adjectives related to theseabstract nouns.
1. altruism
2. parsimony
3. diligence
4. placidity
5. industriousness
6. rebellion
7. distrust
8. terseness
9. naivety
10.unscrupulousness
15.
Give a synonym that would be morelikely to be used in informal situations
1. altruistic
2. parsimonious
3. diligent
4. placid
5. industrious
6. rebellious
7. distrustful
8. terse
9. naive
10.unscrupulous
16.
Which adjectives would you use todescribe you, your friends and your
family members?
17.
18.
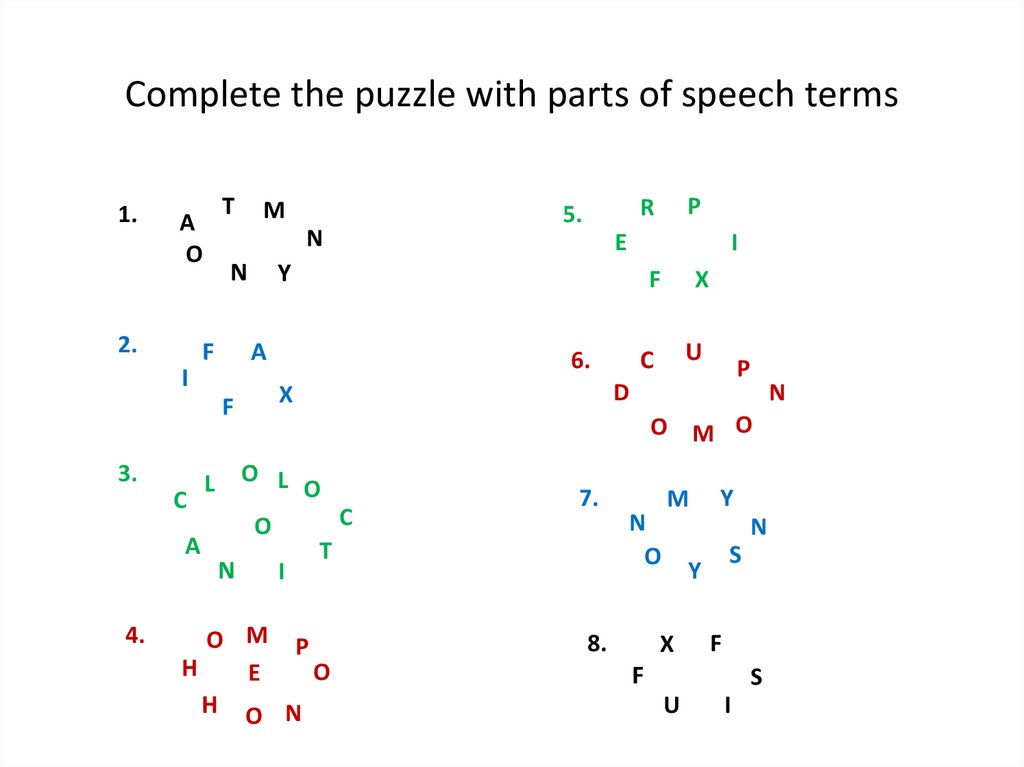
Complete the puzzle with parts of speech terms1.
A
O
2.
T
N
N
F
F
4.
E
I
6.
O M P
H
O
E
H O N
F
X
C
U
P
D
X
L O L O
C
C
O
A
T
N
I
P
R
5.
Y
A
I
3.
M
O M O
7.
N
O
8.
M
Y
N
S
Y
X
F
F
S
U
I
N
19.
Match the definitions below with the terms for the lexical items1.
a word which has the same or nearly the same meaning as
another word
2.
a meaningful group of letters added to the beginning of a root or
base word to make a new word, which can be a different part of
speech from the original word
3.
a word in the target language which looks or sounds as if it has
the same meaning as a similar word in the learner’s first
language but does not
4.
a meaningful group of letters added to the beginning or end of a
word to make a new word, which can be a different part of
speech from the original word
5.
a verb which is made up of more than one word (e.g. a verb +
adverb particle or preposition) which has a different meaning
from each individual word
6.
a word with the same spelling as another word, but which has a
different meaning
7.
a group of words that are related to each other by their root or
base word
8.
a meaningful group of letters added to the end of a root or base
word to make a new word, which can be a different part of
speech from the original word
A. Affix
B. Antonym
C. Collocation
D. Compound
E. False friend
F. Homophone
G. Homonym
H. Idiom
I. Lexical set
J. Prefix
K. Phrasal verb
L. Register
M. Root word, base word
N. Suffix
O. Synonym
P. Word family
20.
Match the definitions below with the terms for the lexical items9.
the opposite of another word
10.
a group of words or phrases that are about the same content
topic or subject
11.
nouns, verbs, adjectives or prepositions that are made up of two
or more words with one unit of meaning
12.
a basic word or part of a word from which other words can be
made by adding a prefix or suffix or in some other way
13.
words which are regularly used together. The relation between
the words may be grammatical or lexical
14.
a group of words that are used together, in which the meaning of
the whole word group is different from the meaning of each
individual word
15.
a word which sounds the same as another word, but has a
different meaning or spelling
16.
the formality or informality of the language used in a particular
situation
A. Affix
B. Antonym
C. Collocation
D. Compound
E. False friend
F. Homophone
G. Homonym
H. Idiom
I. Lexical set
J. Prefix
K. Phrasal verb
L. Register
M. Root word, base word
N. Suffix
O. Synonym
P. Word family
21.
For questions 1–7 match the examples of vocabulary with the categorieslisted A–H. There is one extra option which you do not need to use.
Examples of vocabulary
Categories
1. colour, color; realise, realize; theatre, theater
A synonyms
2. traffic lights; alarm clock; seat belt
B lexical set
3. childish; successfully; dependable
C collocations
4. turn up; turn off; turn into
D word + suffix
5. catch a cold; catch a bus; catch a thief
E prefix + word
6. sad; miserable; unhappy
F compounds
7. ankle; stomach; knee; heart
G phrasal verbs
H American and British English
22.
What do you need to consider when you are teachingvocabulary?
Watch the video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=91CgQ5Vah-k
Answer the following questions:
• How many words does the average English speaker know?
• How many words do they use on a regular basis?
• What does knowing a word mean?
• What are the problems related to the meaning of the word?
• What are the problems related to the form of the word?
• What does the speaker mean by ‘collocation’ and ‘colligation’?
• What are the problems related to the pronunciation of the word?
23.
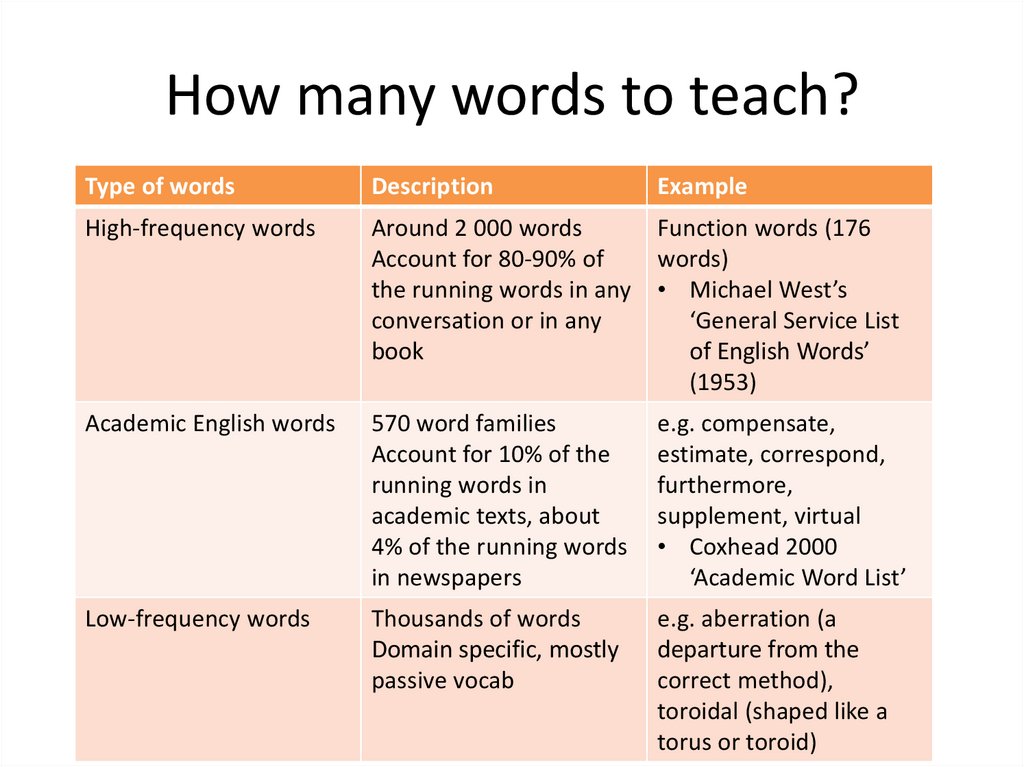
How many words to teach?Type of words
Description
Example
High-frequency words
Around 2 000 words
Account for 80-90% of
the running words in any
conversation or in any
book
Function words (176
words)
• Michael West’s
‘General Service List
of English Words’
(1953)
Academic English words
570 word families
Account for 10% of the
running words in
academic texts, about
4% of the running words
in newspapers
e.g. compensate,
estimate, correspond,
furthermore,
supplement, virtual
• Coxhead 2000
‘Academic Word List’
Low-frequency words
Thousands of words
Domain specific, mostly
passive vocab
e.g. aberration (a
departure from the
correct method),
toroidal (shaped like a
torus or toroid)
24.
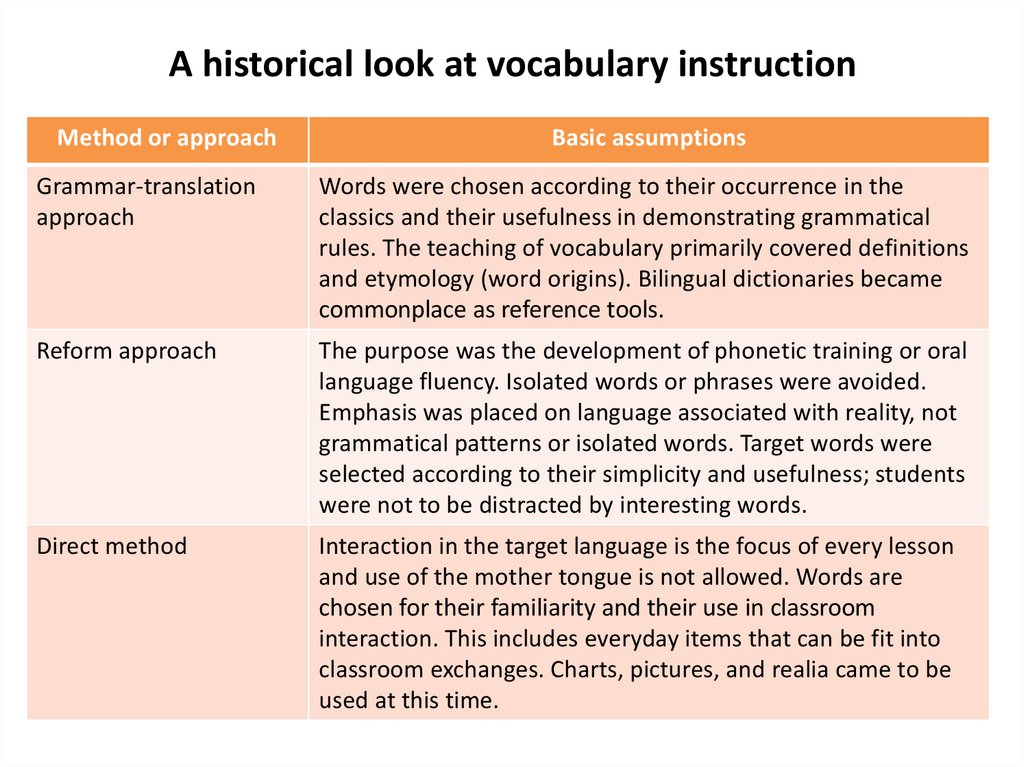
A historical look at vocabulary instructionMethod or approach
Basic assumptions
Grammar-translation
approach
Words were chosen according to their occurrence in the
classics and their usefulness in demonstrating grammatical
rules. The teaching of vocabulary primarily covered definitions
and etymology (word origins). Bilingual dictionaries became
commonplace as reference tools.
Reform approach
The purpose was the development of phonetic training or oral
language fluency. Isolated words or phrases were avoided.
Emphasis was placed on language associated with reality, not
grammatical patterns or isolated words. Target words were
selected according to their simplicity and usefulness; students
were not to be distracted by interesting words.
Direct method
Interaction in the target language is the focus of every lesson
and use of the mother tongue is not allowed. Words are
chosen for their familiarity and their use in classroom
interaction. This includes everyday items that can be fit into
classroom exchanges. Charts, pictures, and realia came to be
used at this time.
25.
A historical look at vocabulary instructionMethod or approach
Basic assumptions
Reading approach
It suggested that reading skill could be improved by the
development of vocabulary, and it criticized stressing speech
without selecting content in a principled way. Vocabulary was
considered primary in language instruction, and words were
chosen according to their usefulness and frequency. A General
Service List of English Words was published by Michael West
(1953). This list of 2000 most frequently used words in English is
still widely used today in research and course materials.
Audiolingualism
It was based on behaviorist view of habit formation and featured
modeling, drills, memorization and feedback. Charles Fries, the
ALM founder, believed that too much focus on words could give
learners the false impression that they knew the language because
they knew some words. His solution was to choose simple and
familiar words so students would not put too much faith in their
word knowledge.
Communicative
language teaching
Language is meant for communication. Vocabulary is chosen from
authentic materials according to their usefulness. Corpora have
recently played a role in identifying target words as they are
authentically used.
26.
4 most important vocab learning strategies• Guessing from context
• Learning using word cards
• Using word parts to help remember words
• Using a dictionary
27.
The role of the vocab teacherRank the vocab teacher's actions in order of
importance:
to teach vocab
to test
to plan
to train learners in the most useful
strategies for vocab learning
28.
The role of the vocab teacher1. to plan
2. to train learners in the most useful strategies for vocab
learning
3. to test
4. to teach vocab
29.
Watch the video ‘How to Teach Vocabulary- Teacher Trainer reacts to a Vocabulary
Lesson’
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FSgfjPdwetA
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
What does the teacher trainer mean by ‘eliciting
vocabulary from students’?
What is a concept checking question?
Should the vocabulary teacher drill pronunciation?
Is body language important in teaching vocabulary? Why?
How can we personalize the topic studied?
30.
Discussion1. What does it mean to know a word?
2. As a learner of a foreign language, which strategies did you use
to learn vocabulary? Which were more successful? Less
successful?
3. In your opinion, what are the primary benefits of using
communicative activities to teach vocabulary?
4. What do you think is most difficult about vocabulary teaching
and learning?
5. How would you go about selecting the words you should teach?
6. As a teacher, are you more concerned about the quality of word
learning or quantity? How will you divide your teaching time
between teaching words and teaching word-learning strategies?
31.
Home assignmentHave you tried these practical
activities to help students with
vocabulary learning?
https://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/
teaching-resources/teachingsecondary/activities/beginnera1/vocabulary-activities
Make a presentation on a vocabulary
activity which you find most
effective (2-3 slides).
32.
Reflection• Have you learnt anything new today?
• Has anything surprised you about what you learned?
• What do you disagree with?
• Was the lesson useful?
• If given the opportunity, one thing you would change
about this lesson is …























 Английский язык
Английский язык








