Похожие презентации:
Intro to Geometric Modeling (GM)
1.
Week 4: Geometric Modeling –Parametric Representation of
Analytic Curves
Spring 2018, AUA
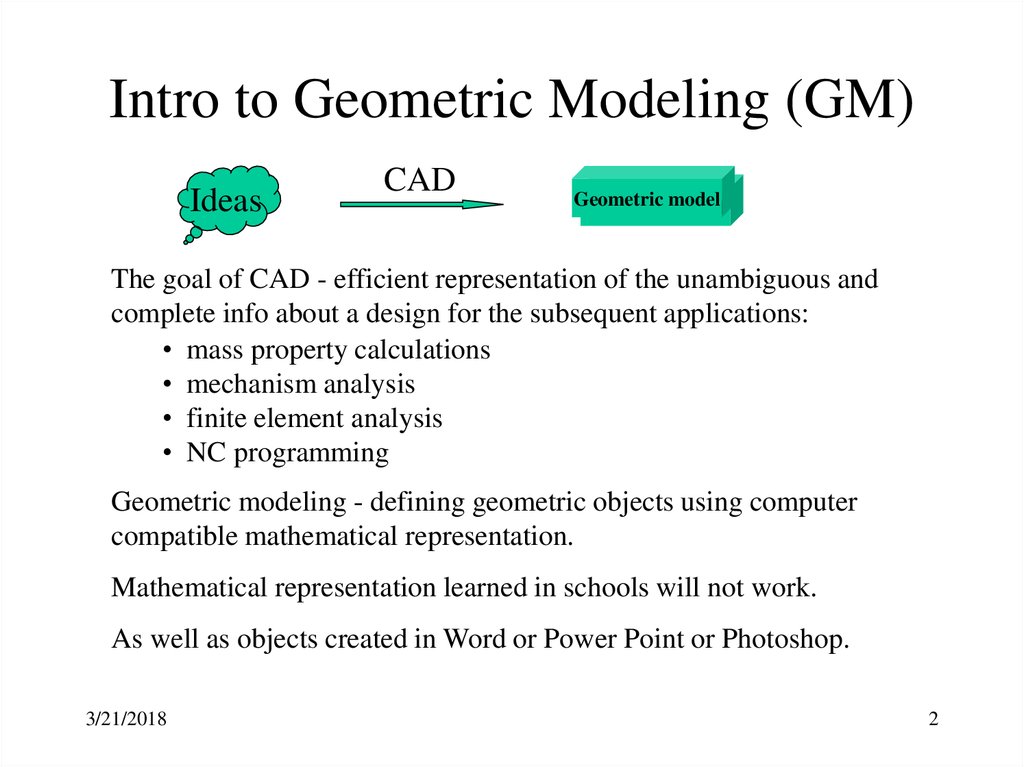
2. Intro to Geometric Modeling (GM)
IdeasCAD
Geometric
Geometricmodel
model
The goal of CAD - efficient representation of the unambiguous and
complete info about a design for the subsequent applications:
• mass property calculations
• mechanism analysis
• finite element analysis
• NC programming
Geometric modeling - defining geometric objects using computer
compatible mathematical representation.
Mathematical representation learned in schools will not work.
As well as objects created in Word or Power Point or Photoshop.
3/21/2018
2
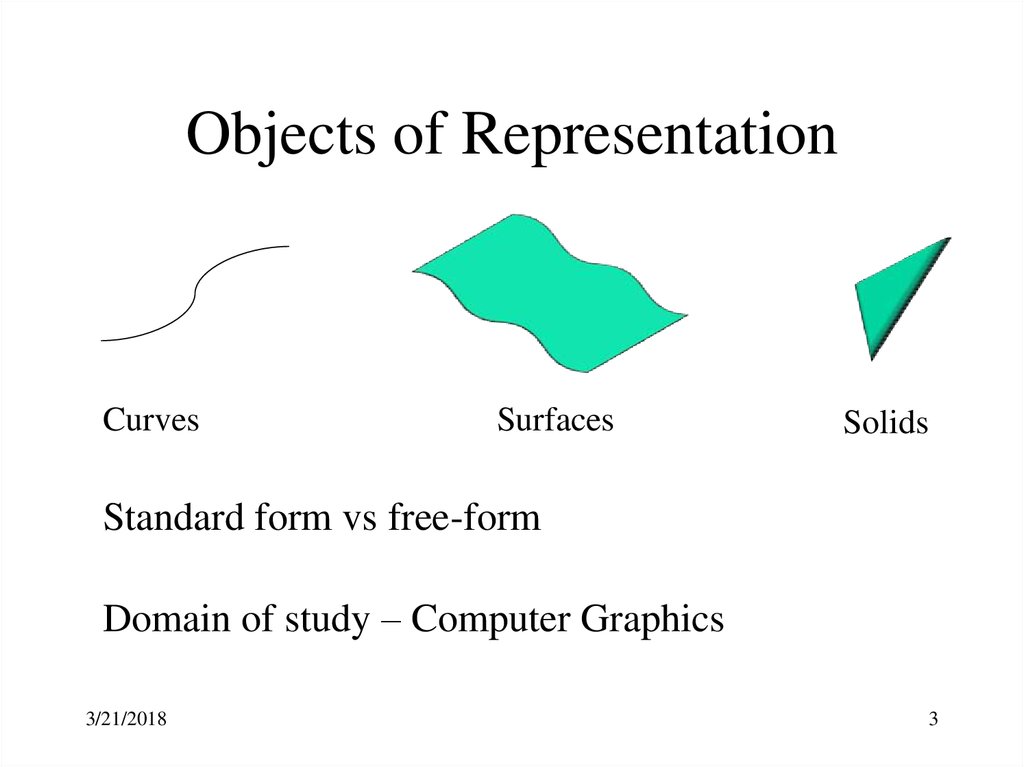
3.
Objects of RepresentationCurves
Surfaces
Solids
Standard form vs free-form
Domain of study – Computer Graphics
3/21/2018
3
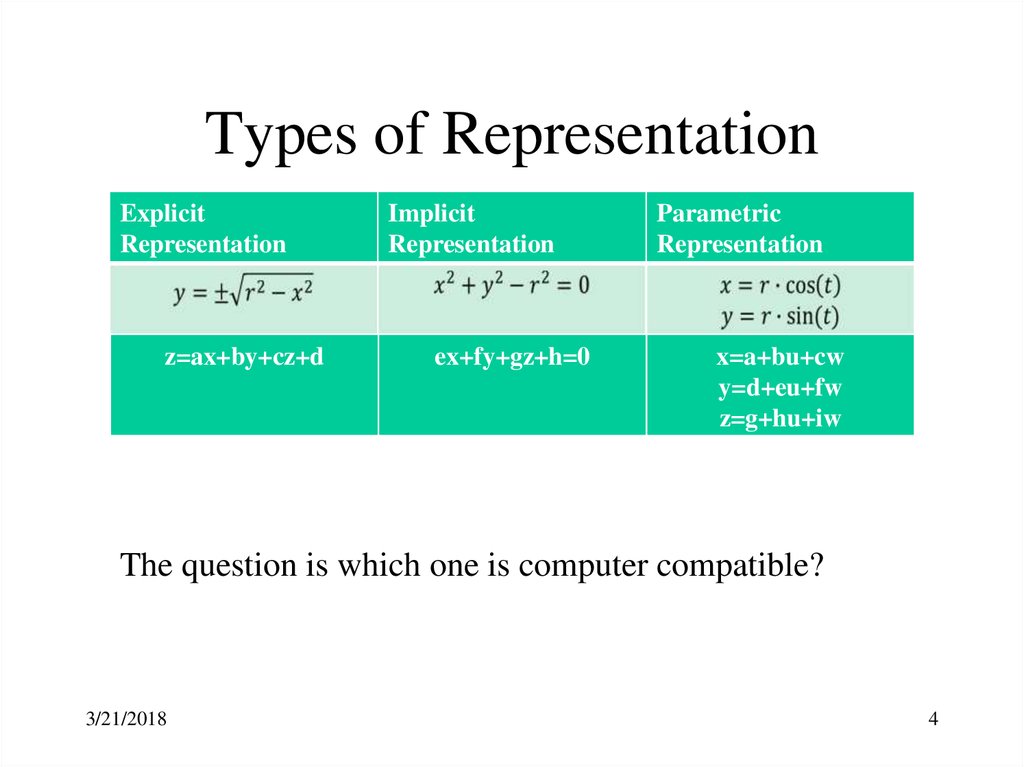
4.
Types of RepresentationExplicit
Representation
z=ax+by+cz+d
Implicit
Representation
ex+fy+gz+h=0
Parametric
Representation
x=a+bu+cw
y=d+eu+fw
z=g+hu+iw
The question is which one is computer compatible?
3/21/2018
4
5. Advantages of PR
• Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y, Z) from eachother.
3/21/2018
5
6. Advantages of PR
• Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y, Z) from each other.• Can be extended to higher objects. (4th parameter )
3/21/2018
6
7. Advantages of PR
• Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y, Z) from each other.• Can be extended to higher objects. (4th parameter )
• More DOF for controlling curves and surfaces.
3/21/2018
7
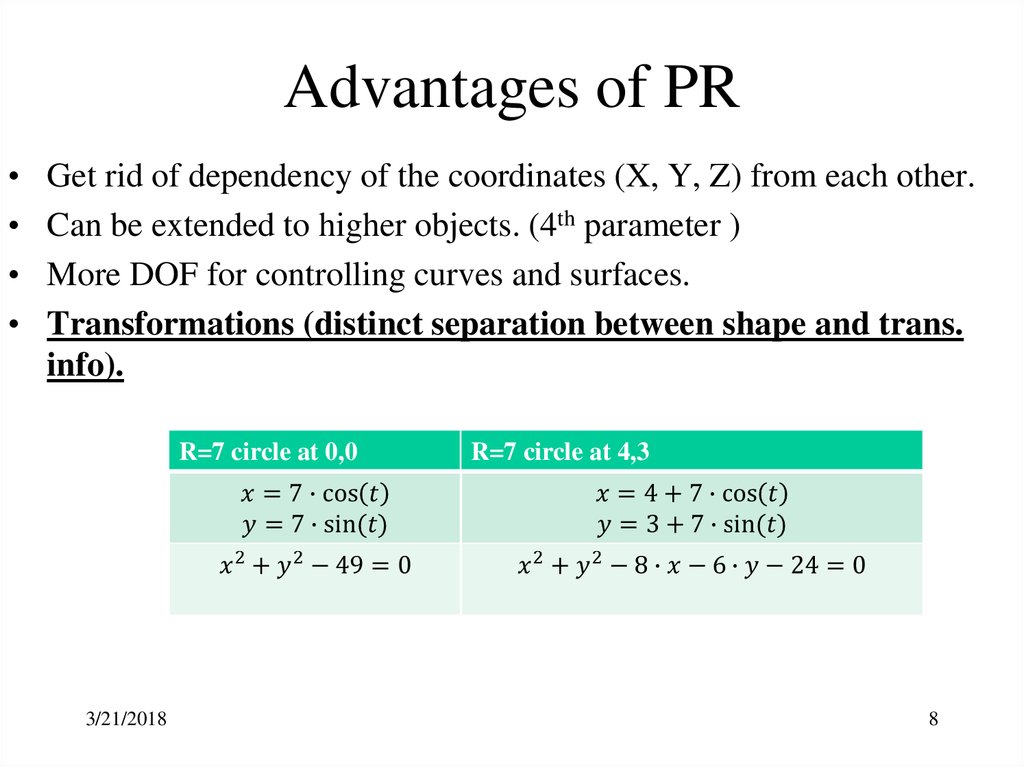
8. Advantages of PR
Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y, Z) from each other.
Can be extended to higher objects. (4th parameter )
More DOF for controlling curves and surfaces.
Transformations (distinct separation between shape and trans.
info).
R=7 circle at 0,0
3/21/2018
R=7 circle at 4,3
8
9. Advantages of PR
Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y, Z) from each other.
Can be extended to higher objects. (4th parameter )
More DOF for controlling curves and surfaces.
Transformations (distinct separation between shape and trans. info).
Vector – matrix multiplication (not good for you, good for comp).
3/21/2018
9
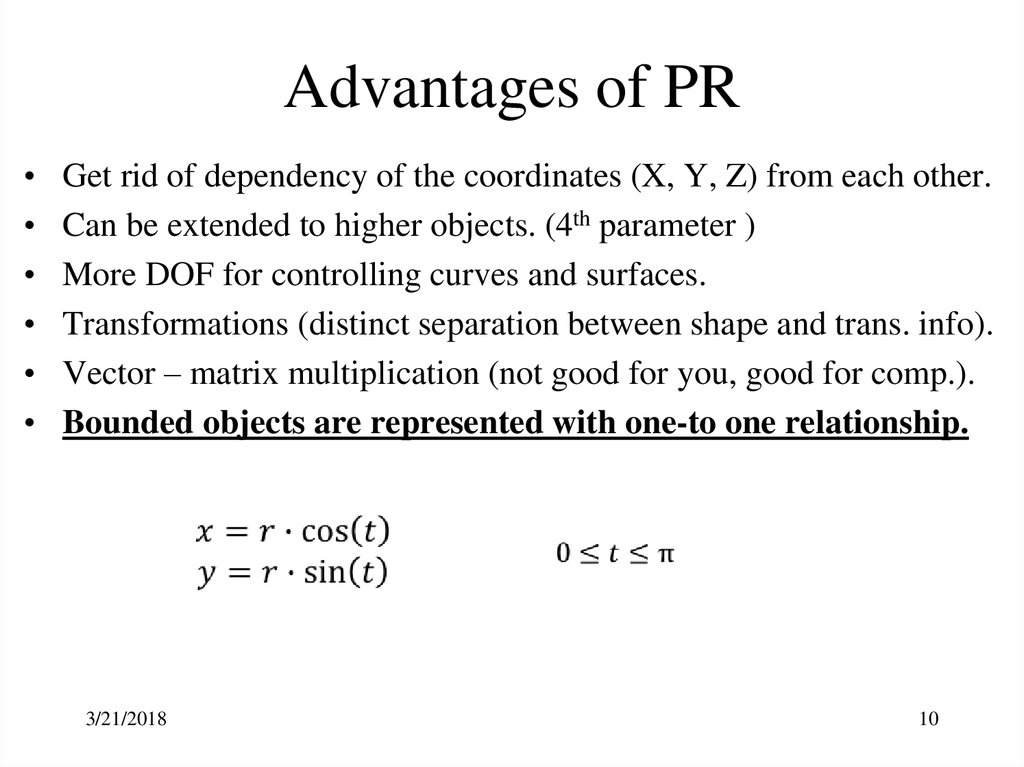
10. Advantages of PR
Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y, Z) from each other.
Can be extended to higher objects. (4th parameter )
More DOF for controlling curves and surfaces.
Transformations (distinct separation between shape and trans. info).
Vector – matrix multiplication (not good for you, good for comp.).
Bounded objects are represented with one-to one relationship.
3/21/2018
10
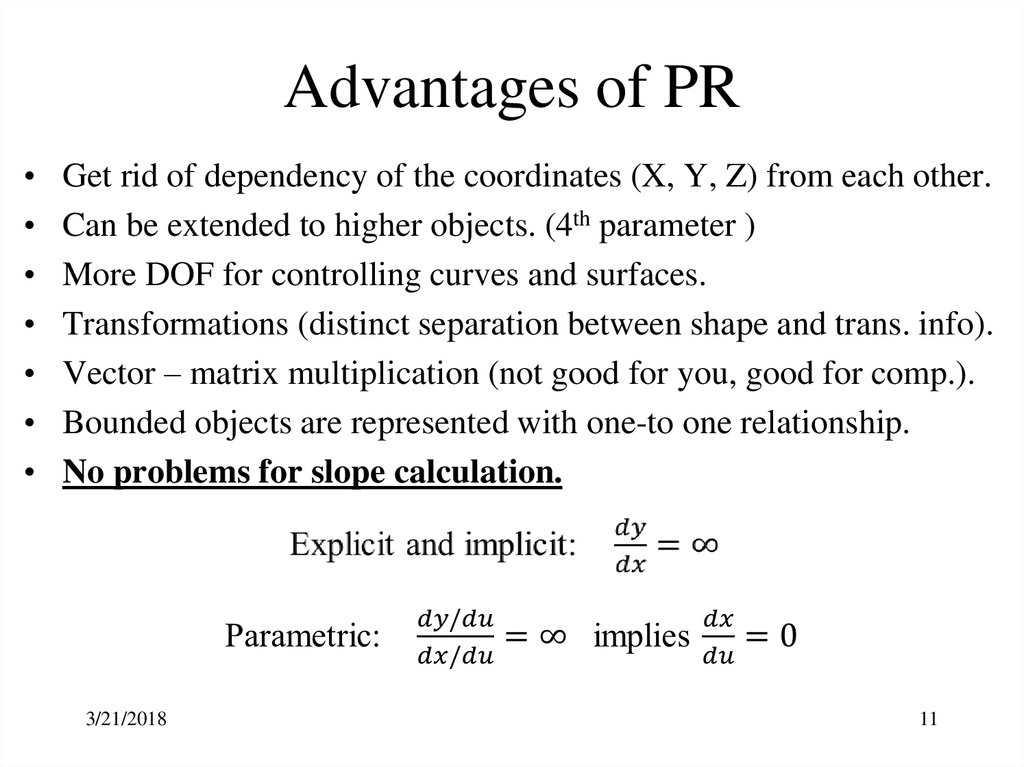
11. Advantages of PR
Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y, Z) from each other.
Can be extended to higher objects. (4th parameter )
More DOF for controlling curves and surfaces.
Transformations (distinct separation between shape and trans. info).
Vector – matrix multiplication (not good for you, good for comp.).
Bounded objects are represented with one-to one relationship.
No problems for slope calculation.
3/21/2018
11
12. Advantages of PR
Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y, Z) from each other.
Can be extended to higher objects. (4th parameter )
More DOF for controlling curves and surfaces.
Transformations (distinct separation between shape and trans. info).
Vector – matrix multiplication (not good for you, good for comp.).
Bounded objects are represented with one-to one relationship.
No problems for slope calculation.
Discretizing entities
3/21/2018
12
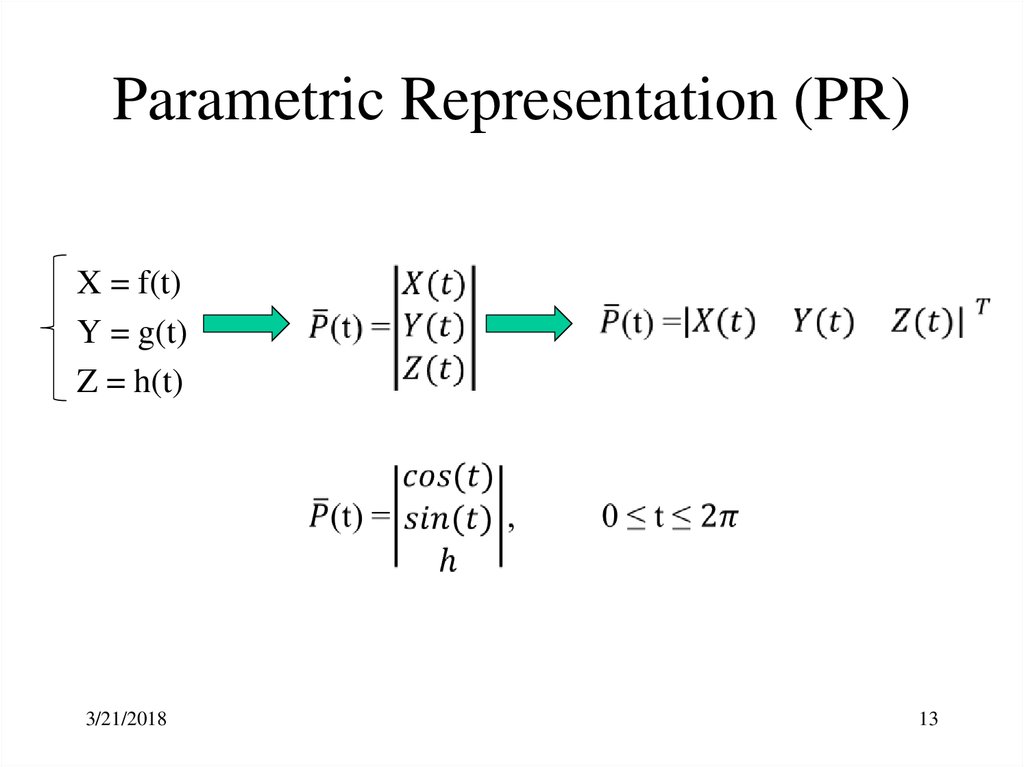
13.
Parametric Representation (PR)X = f(t)
Y = g(t)
Z = h(t)
3/21/2018
13
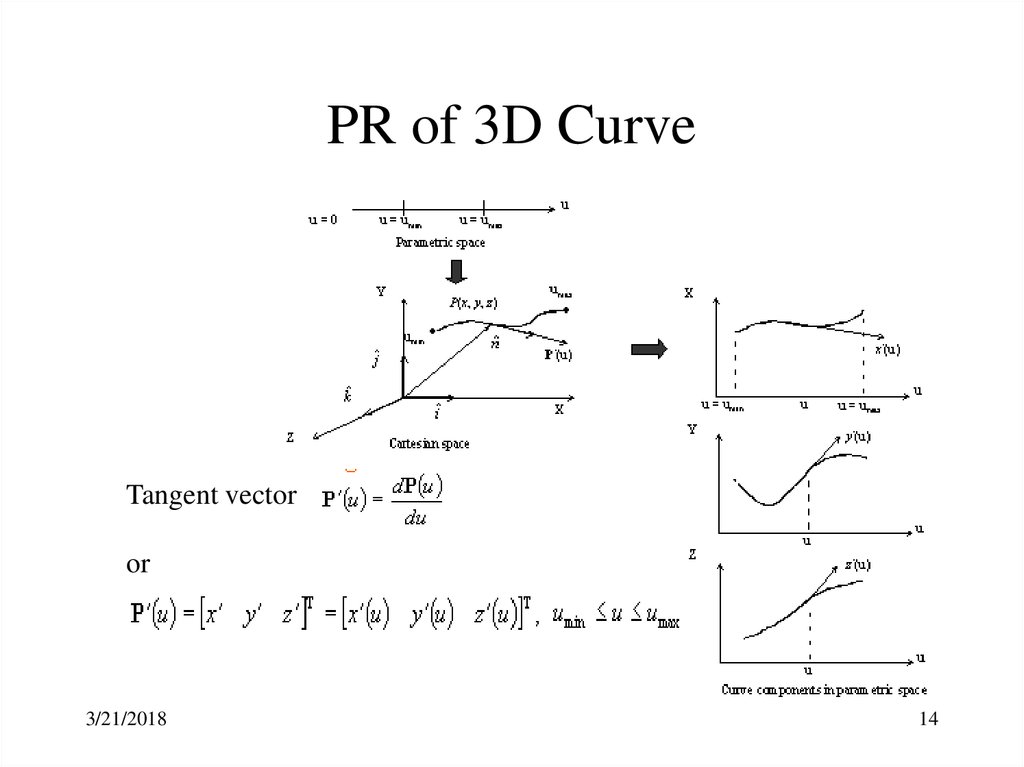
14. PR of 3D Curve
Tangent vectoror
3/21/2018
14
15. PR of Analytic Curves
Analytic curves are defined by analytic equations•Compact form for representation
•Simple computation of properties
3/21/2018
•Little practical use
•No local control
15
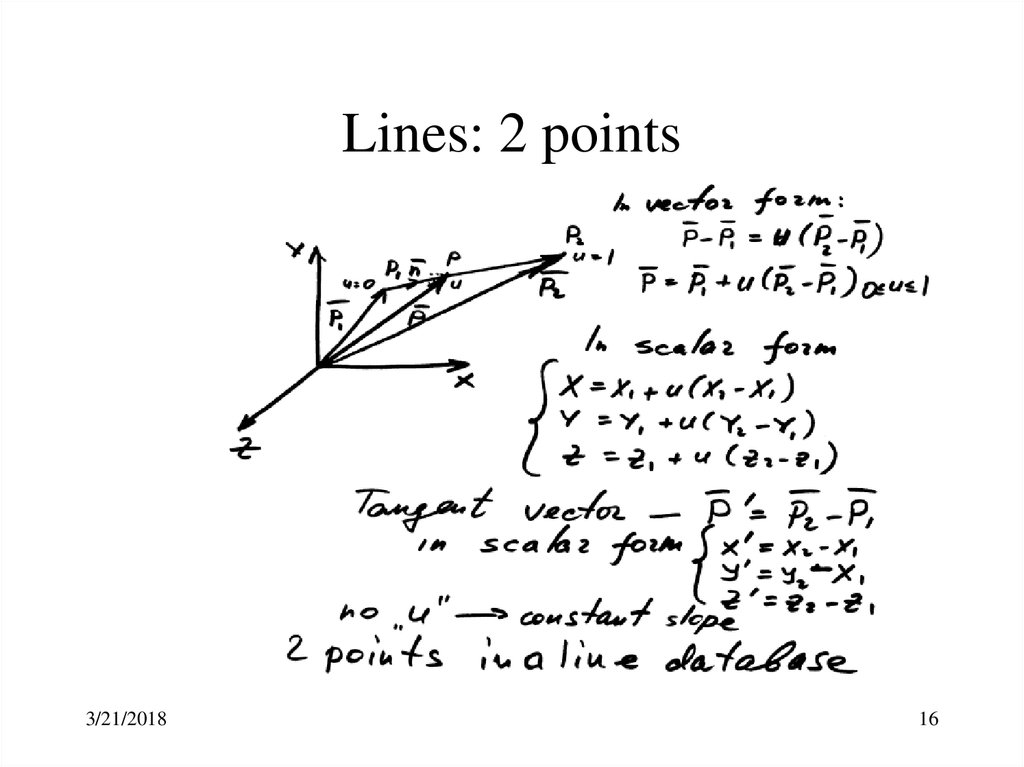
16. Lines: 2 points
3/21/201816
17. Lines: point and direction
n0 ≤ L ≤ Lmax
3/21/2018
17
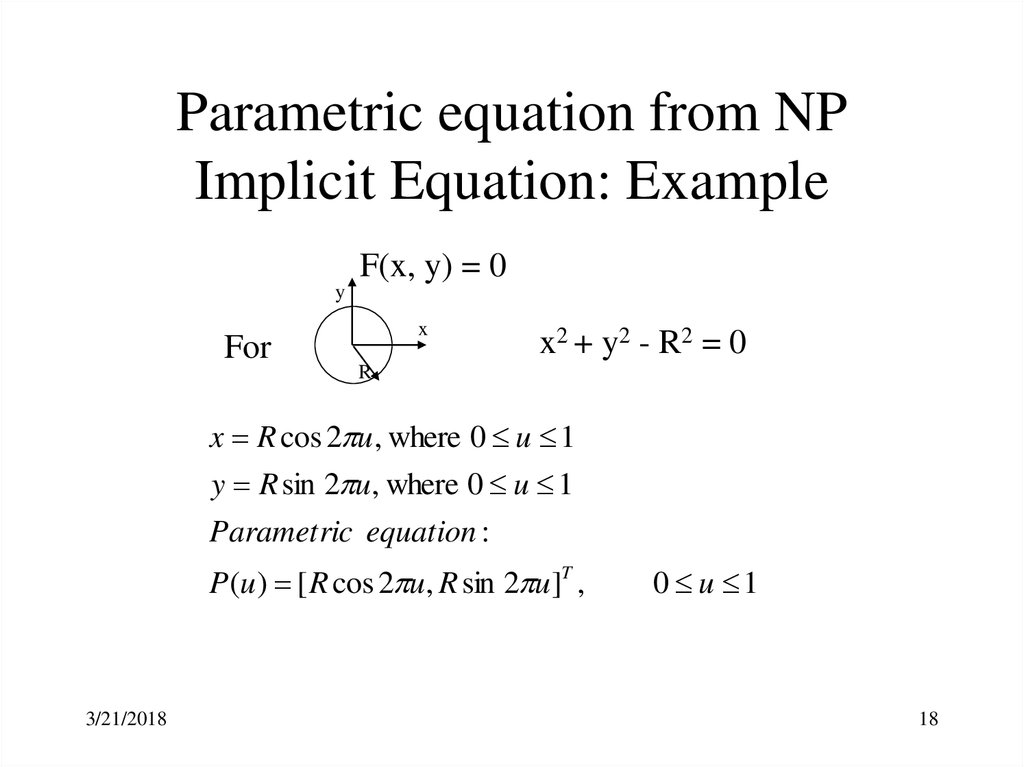
18. Parametric equation from NP Implicit Equation: Example
F(x, y) = 0y
For
x
x2 + y2 - R2 = 0
R
x R cos 2 u, where 0 u 1
y R sin 2 u, where 0 u 1
Parametric equation :
P(u ) [ R cos 2 u, R sin 2 u ]T ,
3/21/2018
0 u 1
18
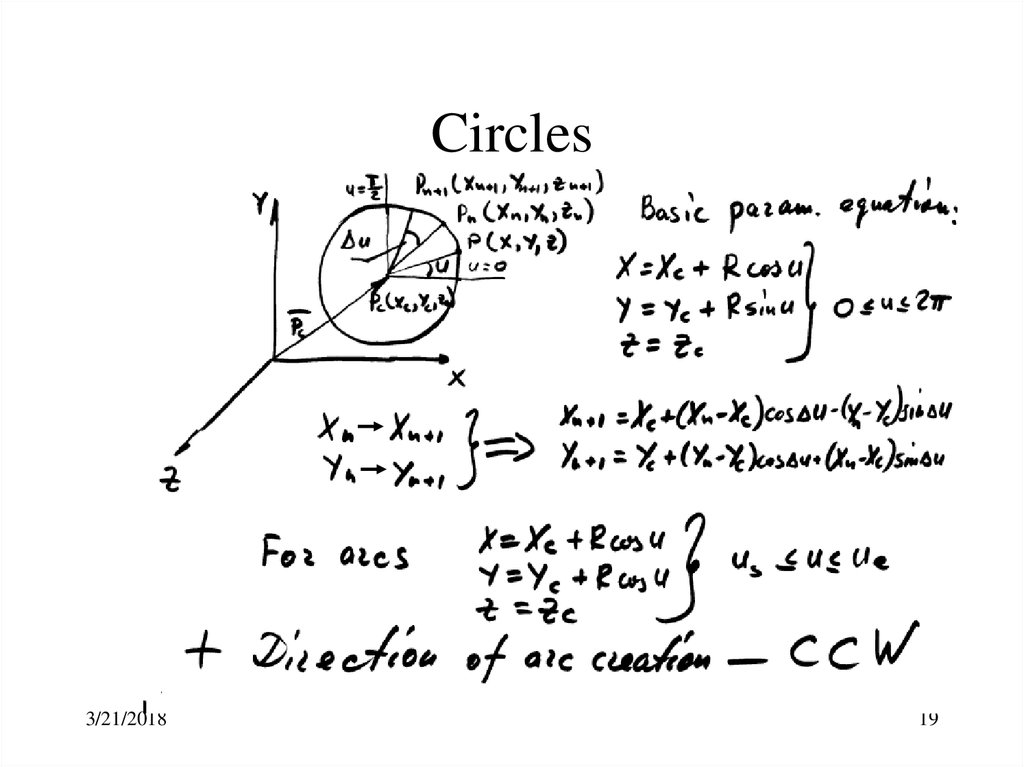
19. Circles
3/21/201819
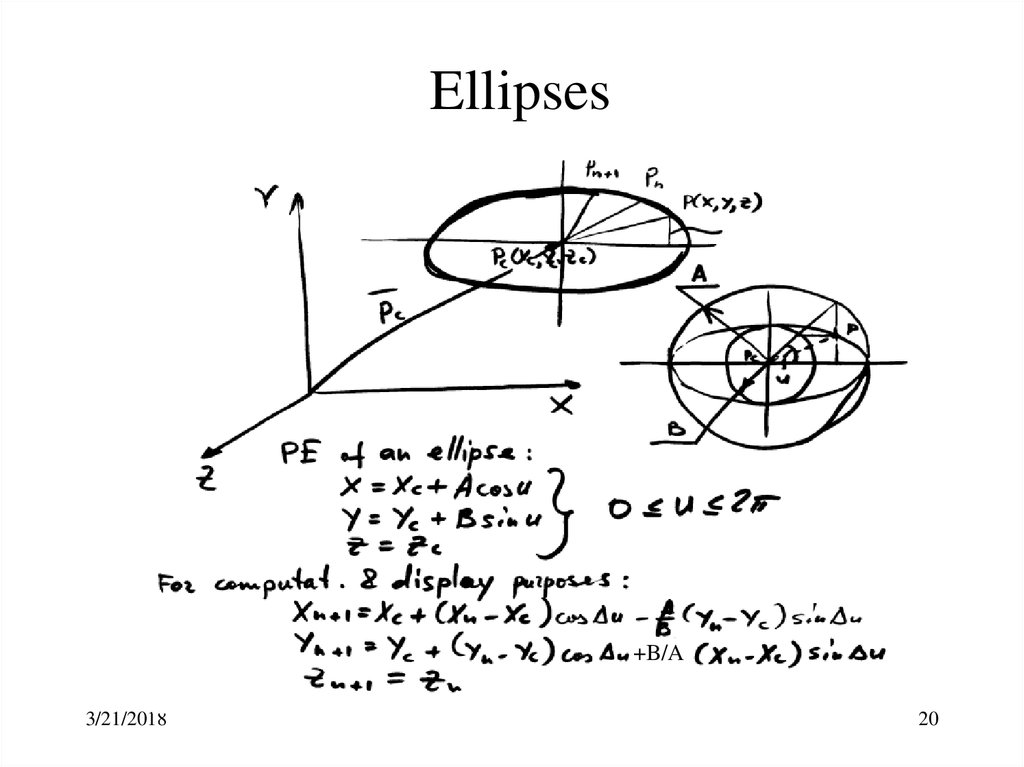
20. Ellipses
+B/A3/21/2018
20
21. Examples
• Find the equation and endpointsof a line that passes through point
P1, parallel to an existing line,
and is trimmed by point P2.
• Relate the following CAD
commands to their mathematical
foundations:
– The command to measure the
angle between two
intersecting lines.
– The command to find the
distance between a point and
a line.
3/21/2018
P4
y
P5
n1
n1
P3
P2
P1
x
z
P2
P1
P4
P3
P2
P3
D
P4
n1
21








 Математика
Математика








