Похожие презентации:
Introduction to the New Testament
1. Introduction to the New Testament
2. What is it?
27 different documentsWritten in Greek
Gathered together and
joined to the Old
Testament
This is the Bible as
Christians know it
3. Relationship to Old Testament
What is the Old Testament?Why is it called "Old"
Predates revelation of Christ
Do Jews call it old?
Where is the New Testament in
relationship to the Old?
4. Meaning of testament
Testament is another word forcovenant
Thus this is a book about a new
covenant
E.g.s of Old Covenant?
Jesus is the new covenant God makes
with humanity
Christians believe everything God
promises us in the Old Testament is
fulfilled in Jesus
5. Types of Writing
What type of writing is in the NT?Gospels (4)
gospel is a Greek word meaning
good news
Gospels are the specific gospels
of the Bible
Matt, Mark, Luke and John
6. A gospel
Not meant to be read as aliteral biography
Try to explain the teachings
of Jesus
Only period thoroughly
investigated is the last week
of Jesus' life
7. Types of writing
Second type of writing in the NT isHISTORY
Especially history of the early
church
Acts of the Apostles is the only
historical book in the NT
Speaks of the spread of the
Church up to Paul's visit to Rome
8. Types of writing
The third type of writing areletters aka epistles (21)
Written to various
communities by famous
apostles or their disciples
Paul wrote most of the
epistles
9. Types of writing
Apocalypse (1)Highly symbolic book
Signifies battle between God and
Satan
Evil is eventually defeated and
God's kingdom becomes reality
Book of Revelation
10. Daily life in the time of Christ
11.
12.
13.
14.
15. Major Groups
Priests: Acted as mediatorsbetween God and humans
Offered sacrifice in the
temple
High priest was very
important politically
E.g. Caiaphas
16. Major Groups
Sadducees: elite upperclass
Were very strong
politically and were
committed to the Temple
Didn't believe in life after
death
17. Major Groups
Pharisees: sect focusingon the law
The Law governs daily life
Rivals of Sadducees
Believed life after death is
possible
18. Major Groups
Zealots: revolutionarieswanting to overthrow the
Romans
At odds with Jewish leaders
because of their brutal tactics
Generally from poorer
classes
19. Major Groups
Sanhedrin: group ofcommunity elders
Priests, Pharisees and
Sadducees
Religious, political, judicial
body
20. Major Groups
Essenes: group thatwithdrew from society
Believed society was
impure
Believed the messiah
would soon arrive
21. Important places
The TempleDestroyed when Israelites
were exiled
Rebuilt by Herod
Handled sacrifice, prayer,
governance
22.
23.
24. Important places
SynagoguesPlace of daily, local
worship
25. Politics and Culture
Israel had been part of theGreek empire for years
Heavy Greek influence
Greek was the
commercial language
26. Politics and culture
Jews had a king - e.g. HerodAlso a Roman governor - e.g.
Pilate
Romans asked only for taxes
- didn't force conversions to
their religion
27. Politics and culture
Jews believed a messiah woulddeliver them
Messiah: Hebrew for "anointed
one"
From David's line
Would free Jews from foreign
oppression
NOT DIVINE BUT HUMAN - A
human can't be God
28. The Gospels
29. What are they
Four Gospels - who arethe authors?
Written at different times
with different objectives
No two gospels are
exactly the same
30. Timeline
Mark: 65-70 ADMatthew: 80-85 AD
Luke: 85-100 AD
John: 90-110 AD
31. Mark
Tradition says Mark was adisciple of St. Peter (I.e. He
never met Jesus)
Written for gentile Christians,
possibly in Rome
Message: be faithful to Jesus the road to heaven goes thru
suffering
32. Matthew
Matthew: Tax collector whobecame a disciple of Christ
Matt probably not the author
Written for Jewish converts to
Christianity
Message: Jesus is the fulfillment
of prophecies
33. Luke
Luke: Gentile Christian, doctor, friendof St. Paul (also didn't know Jesus)
Writer uses brilliant, clear language
Not from Palestine because of
geography errors
Written for non-Jewish Christians
Message: Jesus can save everyone
34.
35.
36. John
John: Disciple of JesusWritten for Jewish-Christians
expelled from synagogues
Interested in theology
Message: Jesus is God and
reveals his father
37. Synoptic Gospels
Mark, Matthew and Luke areknown as the SYNOPTIC
GOSPELS
Synoptic: Taking a common view
These three gospels are very
similar though not identical
John nothing like the other three
38.
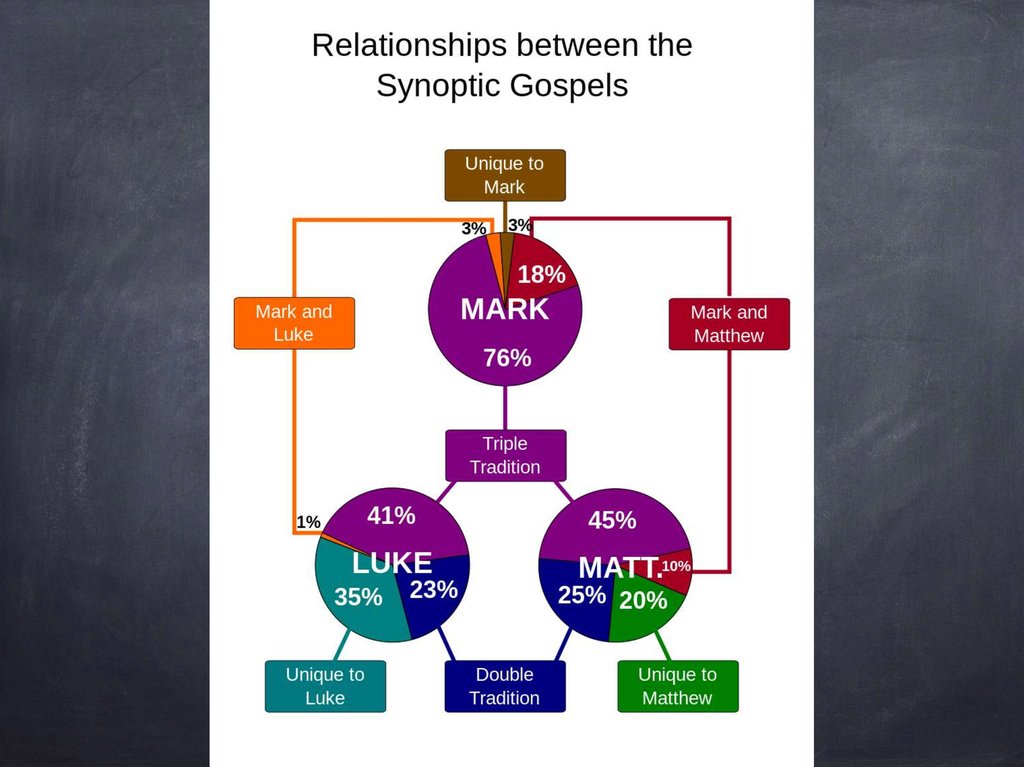
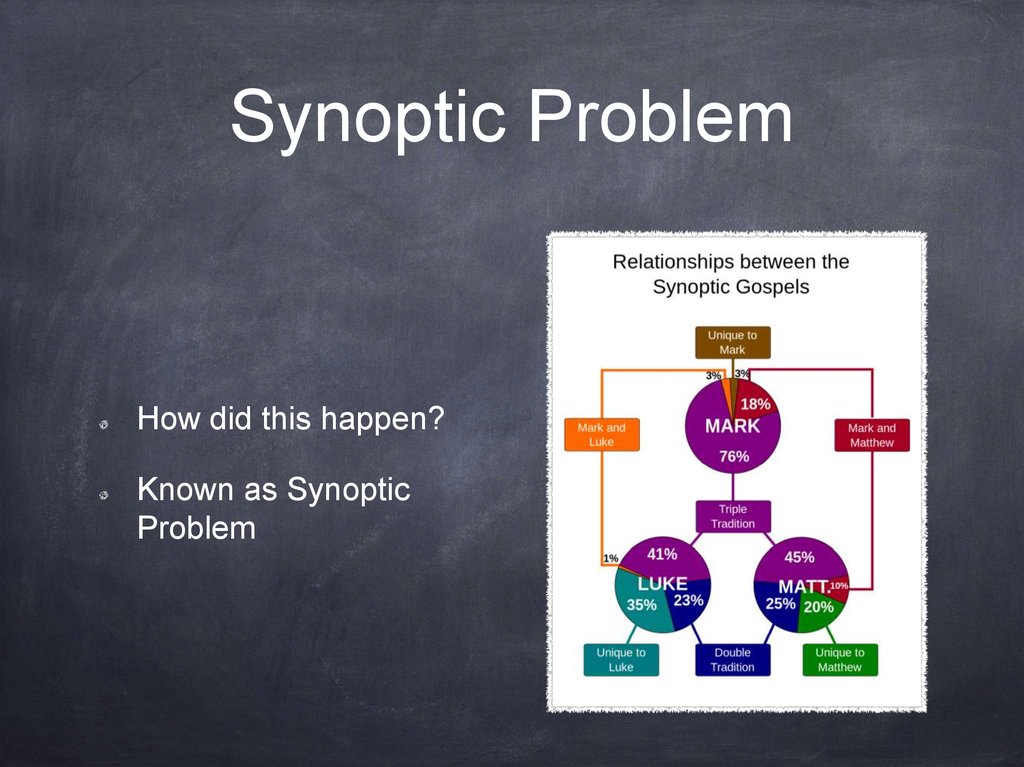
39. Synoptic Problem
How did this happen?Known as Synoptic
Problem
40. Synoptic Problem
Mark written firstLuke and Matthew both used
Mark and another source - the
Q Source
Q short for "Quelle"
Material from Q is in Matt and
Luke
But not Mark
41. Q Source
Q source thought to be acollection of sayings by
Jesus
No longer exists







































 Английский язык
Английский язык Религия
Религия








