Похожие презентации:
Hazardous waste
1. Lecture 8: Hazardous waste
13.10.2016Waste management and recycling incineration 2
1
2. Is the list definite?
If a material is listed in the list of hazardous wastesIt can be classified as non-hazardous if it has none of the listed dangerous
properties
If a material is not listed in the list of hazardous wastes
It can be classified as hazardous if it has even one of the listed dangerous
properties
http://ec.europa.eu/environment/waste/index.htm (general waste info)
http://www.environment-agency.gov.uk/business/topics/waste/32180.aspx
(classification)
In companies, records have to be kept and stored for any operations dealing
with hazardous waste (collection, transport)
quantity, nature and origin of hazardous waste
transport and treatment method foreseen
Directive 2008/98/EC provides additional obligations for labeling, record
keeping, monitoring and control from the "cradle to the grave", i.e., from the
waste producer to the final disposal or recovery.
20.10.2016
Waste management and recycling Hazardous waste
2
3. Types of hazardous waste
Solid wastesLiquid wastes
Chemicals
Industrial wastes
Well known; in environmental permits
Mainly taken to and treated by hazardous waste companies
Some can be treated in industrial plants
Examples of typical industrial hazardous wastes
metal refineries waste
chemical industry waste
waste oils (not edible oils!)
waste from thermal processes
solvents
20.10.2016
Waste management and recycling Hazardous waste
3
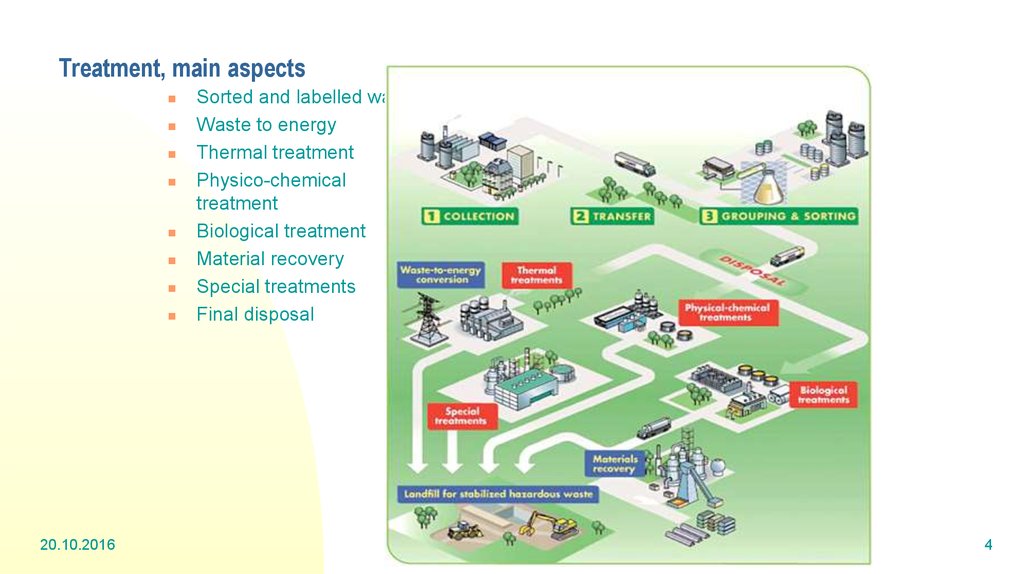
4. Treatment, main aspects
20.10.2016Sorted and labelled waste
Waste to energy
Thermal treatment
Physico-chemical
treatment
Biological treatment
Material recovery
Special treatments
Final disposal
Waste management and recycling Hazardous waste
4
5. 1 High temperature incineration
Process units at EkokemThe core unit is a 12-metre rotary kiln
1 300oC (Directive 2000/76/EU For Hazardous waste >1100 oC for 2 s )
Long delay time in kiln and after-burn complete decomposition and burning
Energy is recovered electricity and district heat
The slag can be used e.g. in soil construction
Flue gases are cleaned
• Cooling
• Acid gases washing by lime
• Particle removal by electrostatic precipitator
• Gaseous emissions: further scrubbing
• Dioxine and mercury removal by activated charcoal
At Riihimäki, the energy produced comparable to 43 milj. m3 natural gas.
20.10.2016
Waste management and recycling Hazardous waste
5
6. High temperature incineration of hazardous waste
Feeding packed wasteRotary kiln 1200-1350oC
After burner 900-1100oC
Feeding
solid waste
Steam production
Evaporation tower
Feeding
Liquid waste
c
Activated
carbon
Electrical
Precipitatori
Fiber filter
Slag
Ash
Ash silo
Heat exchanger
HCL scrubber
Flue gas
analysis
Filter press.
Solids to landfill
20.10.2016
Water
treatment
Flue gas fan
SO2
Waste managementscrubber
and recycling - Lime production
Hazardous waste
6
7. 4 Physico- chemical processes
Inorganic wastes, such as acids, bases and heavy metal containing liquids are made chemically safeMain methods
Neutralization of acid and bases
Precipitation of heavy metals
• The remaining water is purified for use in processes
Oxidation and reduction reactions
Notice: one type of waste can be used for processing another type of waste
Acid + base
Precipitating media
20.10.2016
Waste management and recycling Hazardous waste
7
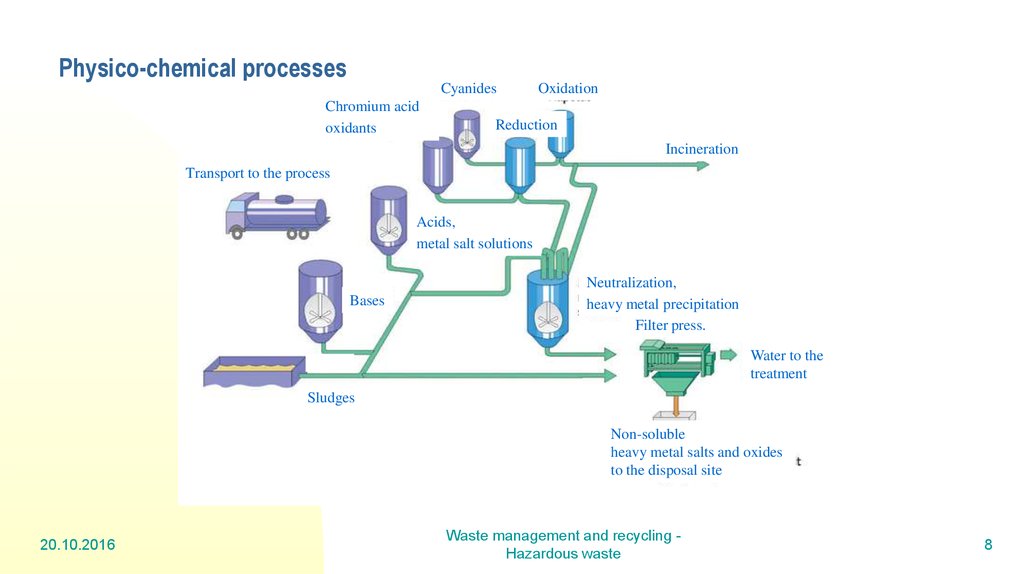
8. Physico-chemical processes
CyanidesChromium acid
oxidants
Oxidation
Reduction
Incineration
Transport to the process
Acids,
metal salt solutions
Bases
Neutralization,
heavy metal precipitation
Filter press.
Water to the
treatment
Sludges
Non-soluble
heavy metal salts and oxides
to the disposal site
20.10.2016
Waste management and recycling Hazardous waste
8






 Экология
Экология








