Похожие презентации:
Microscopy. Microscopy methods
1. Microscopy
MSU & SkolTechMicroscopy
1755
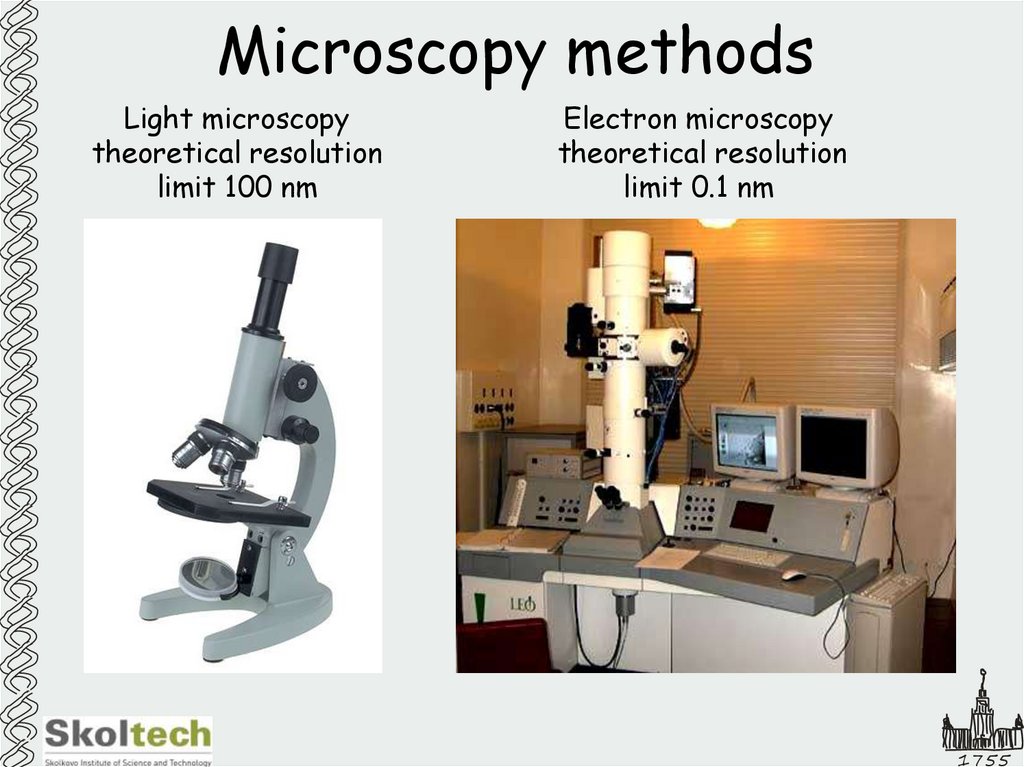
2. Microscopy methods
Light microscopytheoretical resolution
limit 100 nm
Electron microscopy
theoretical resolution
limit 0.1 nm
1755
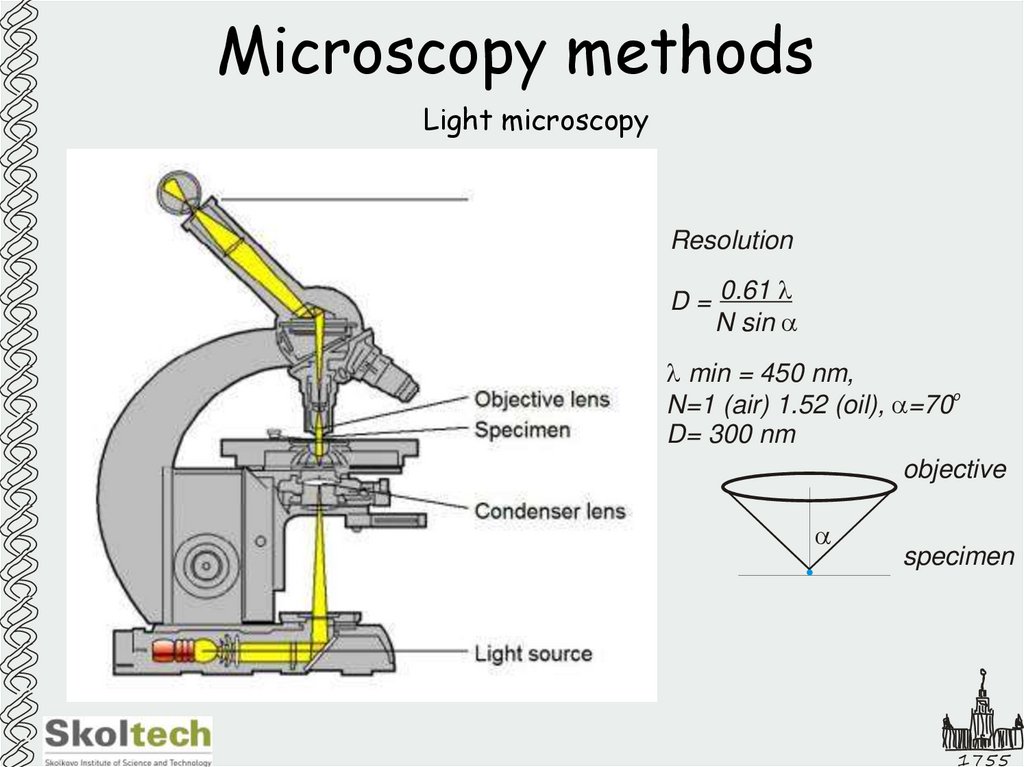
3. Microscopy methods
Light microscopyResolution
D = 0.61
N sin
min = 450 nm,
o
N=1 (air) 1.52 (oil), =70
D= 300 nm
objective
specimen
1755
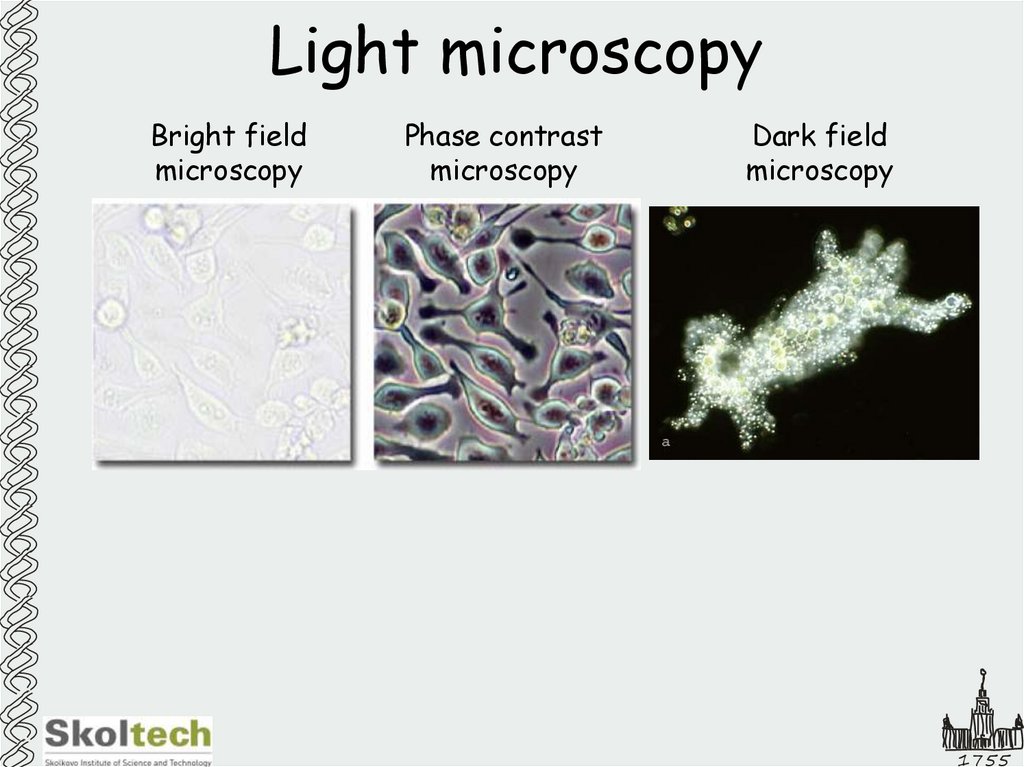
4. Light microscopy
Bright fieldmicroscopy
Phase contrast
microscopy
Dark field
microscopy
1755
5. Microscopy methods
Phase contrast microscopy1755
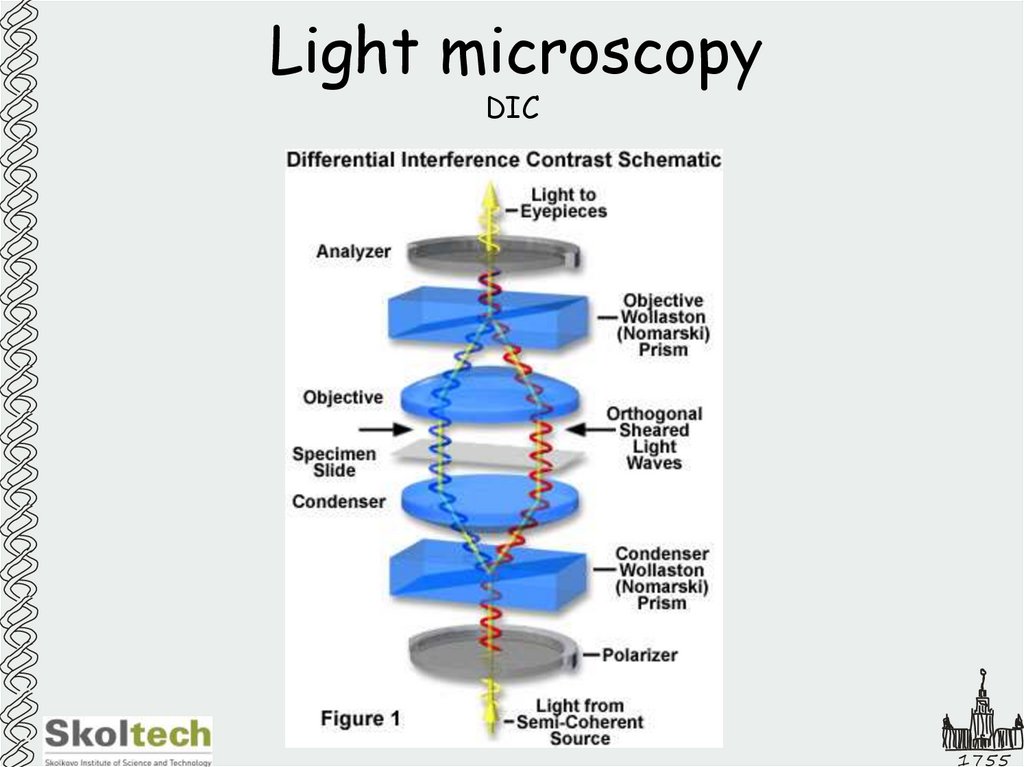
6. Light microscopy
DIC1755
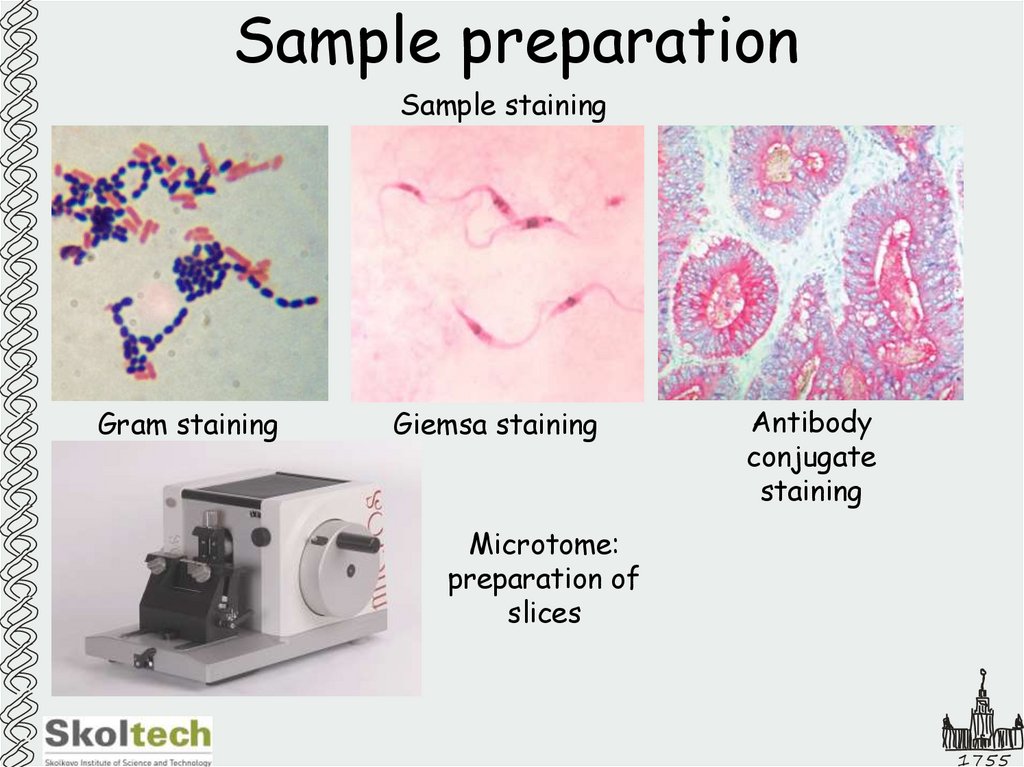
7. Sample preparation
Sample stainingGram staining
Giemsa staining
Antibody
conjugate
staining
Microtome:
preparation of
slices
1755
8. Fluorescent microscopy
Fluorescent microscope construction1755
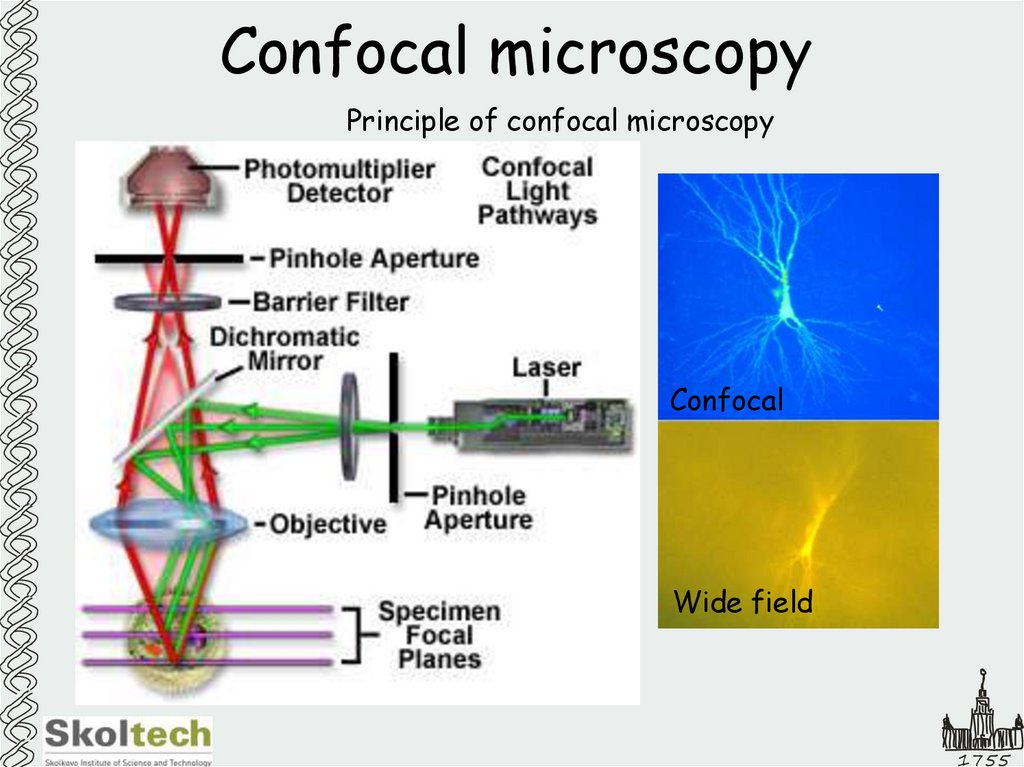
9. Confocal microscopy
Principle of confocal microscopyConfocal
Wide field
1755
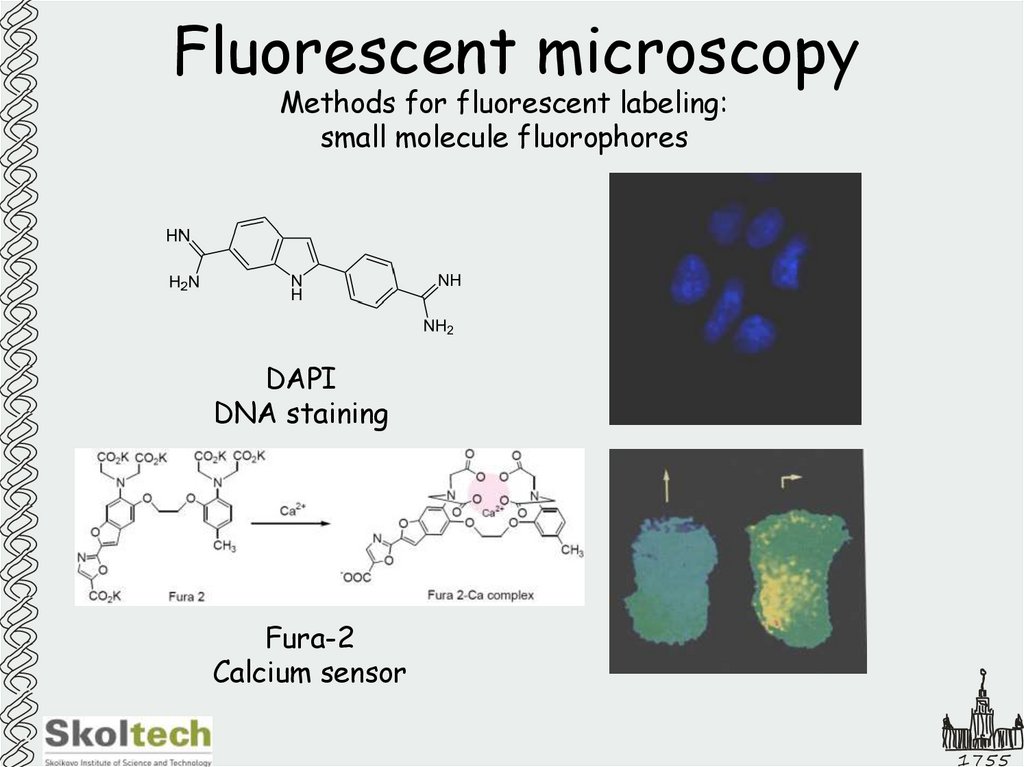
10. Fluorescent microscopy
Methods for fluorescent labeling:small molecule fluorophores
DAPI
DNA staining
Fura-2
Calcium sensor
1755
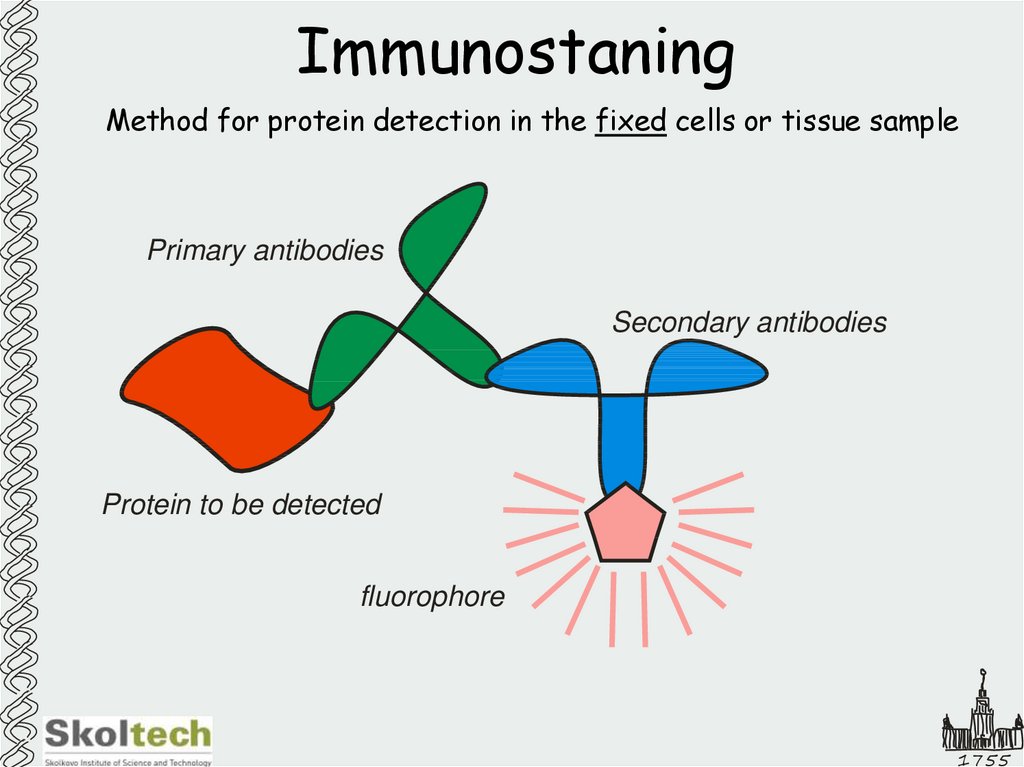
11. Immunostaning
Method for protein detection in the fixed cells or tissue samplePrimary antibodies
Secondary antibodies
Protein to be detected
fluorophore
1755
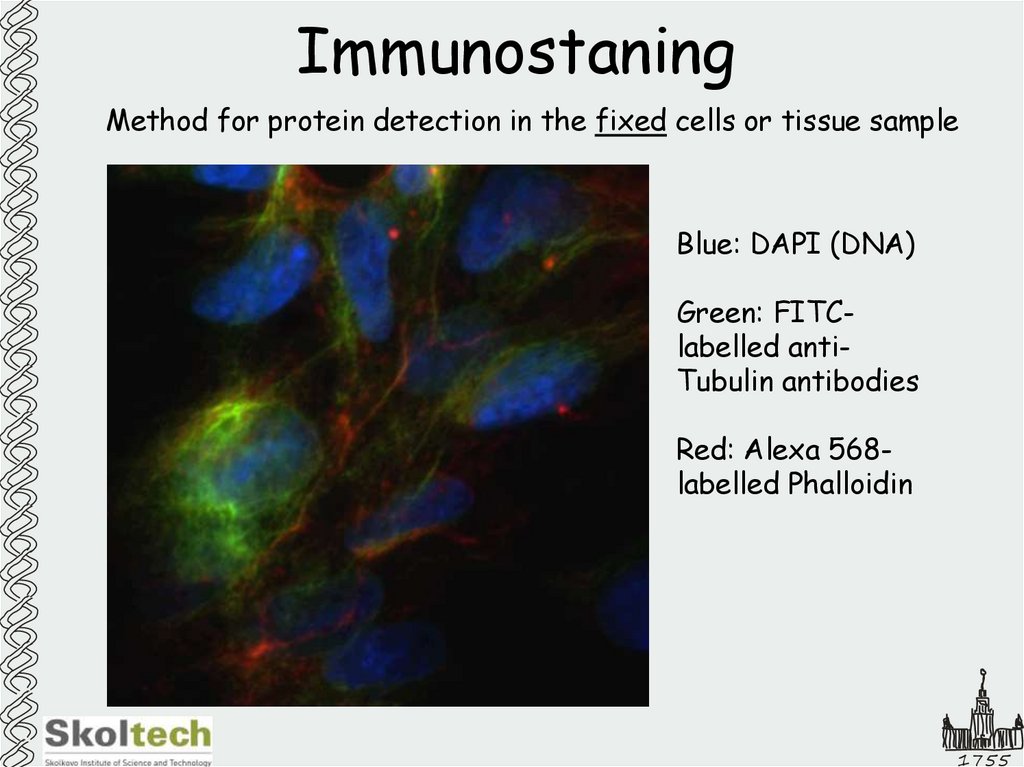
12. Immunostaning
Method for protein detection in the fixed cells or tissue sampleBlue: DAPI (DNA)
Green: FITClabelled antiTubulin antibodies
Red: Alexa 568labelled Phalloidin
1755
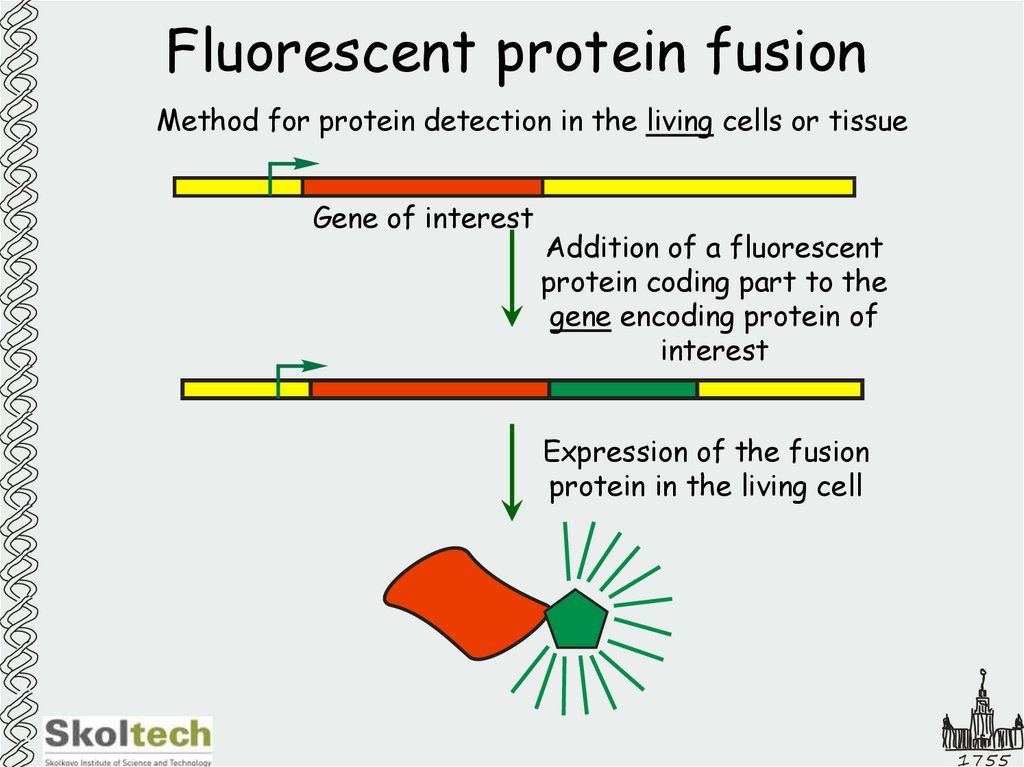
13. Fluorescent protein fusion
Method for protein detection in the living cells or tissueGene of interest
Addition of a fluorescent
protein coding part to the
gene encoding protein of
interest
Expression of the fusion
protein in the living cell
1755
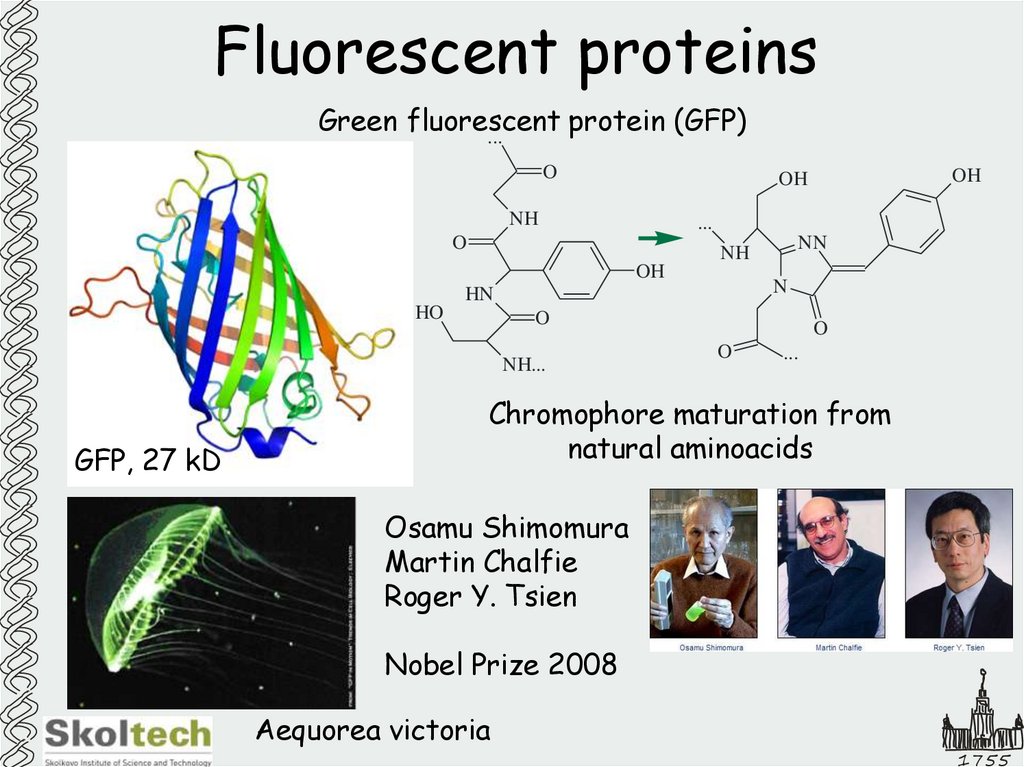
14. Fluorescent proteins
Green fluorescentprotein (GFP)
...
O
NH
...
O
OH
N
HN
O
NH...
GFP, 27 kD
NN
NH
HO
OH
OH
O
O
...
Chromophore maturation from
natural aminoacids
Osamu Shimomura
Martin Chalfie
Roger Y. Tsien
Nobel Prize 2008
Aequorea victoria
1755
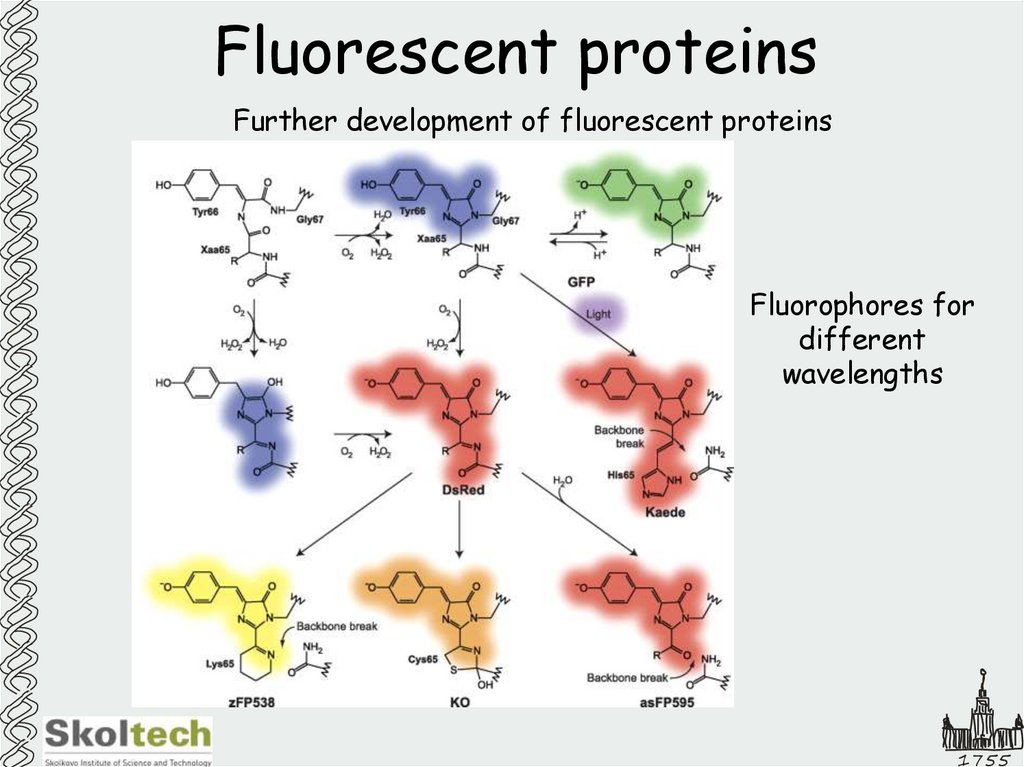
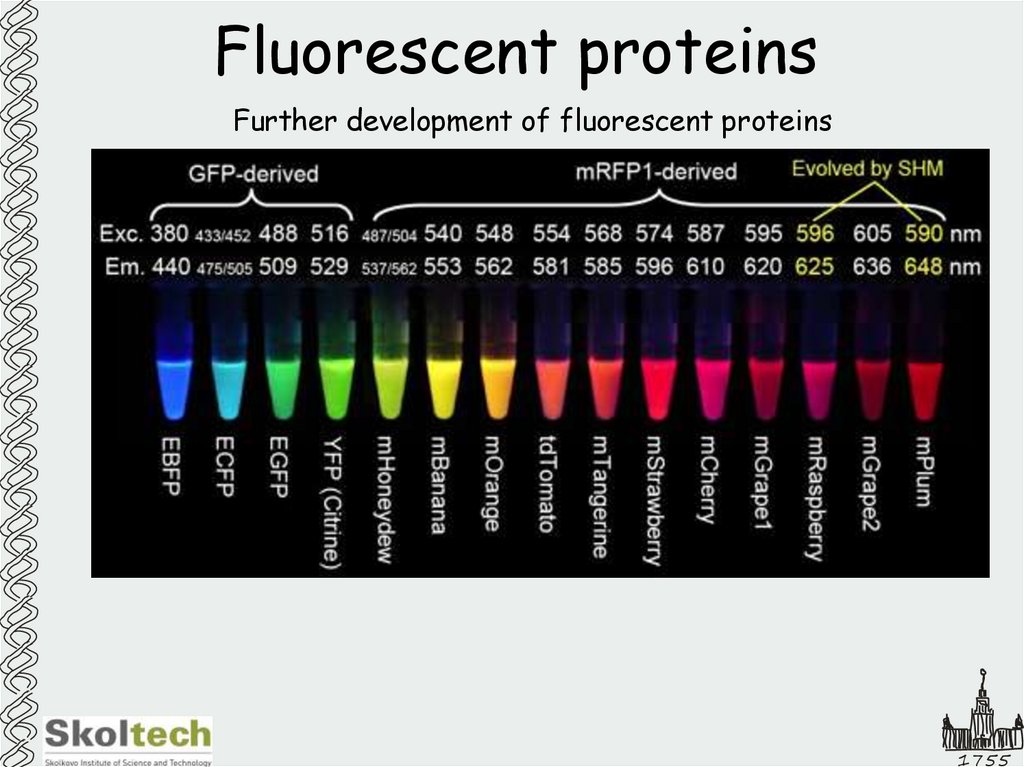
15. Fluorescent proteins
Further development of fluorescent proteinsFluorophores for
different
wavelengths
1755
16. Fluorescent proteins
Further development of fluorescent proteins1755
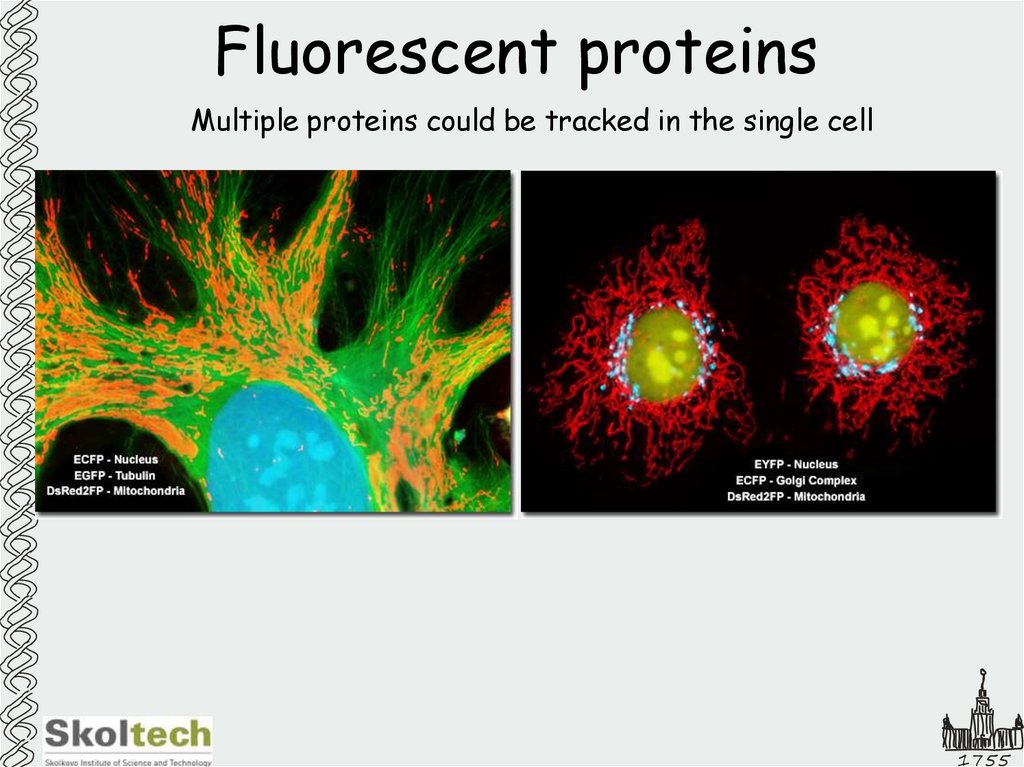
17. Fluorescent proteins
Multiple proteins could be tracked in the single cellGFP, 27 kD
1755
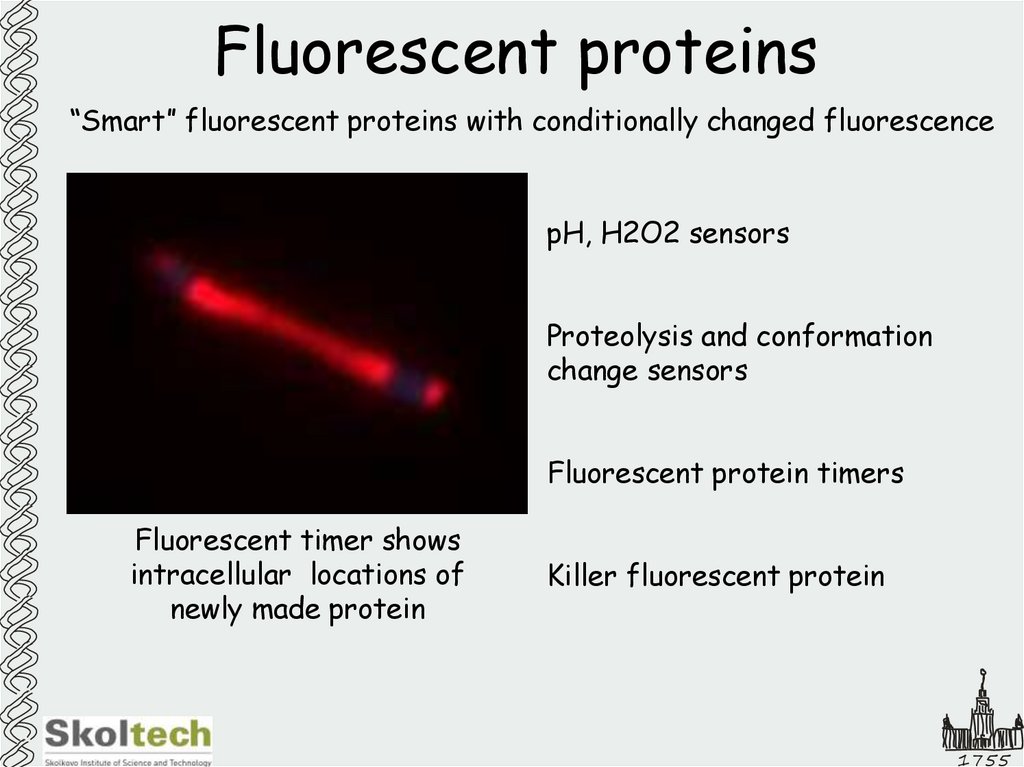
18. Fluorescent proteins
“Smart” fluorescent proteins with conditionally changed fluorescencepH, H2O2 sensors
Proteolysis and conformation
change sensors
Fluorescent protein timers
Fluorescent timer shows
intracellular locations of
newly made protein
Killer fluorescent protein
1755
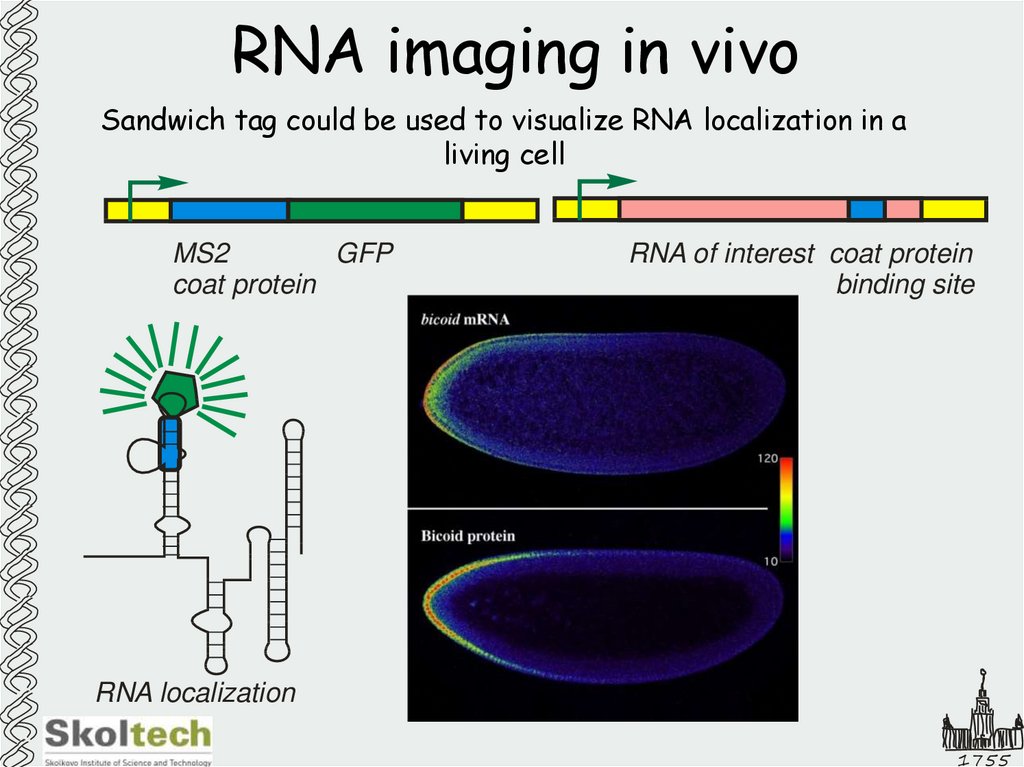
19. RNA imaging in vivo
Sandwich tag could be used to visualize RNA localization in aliving cell
MS2
GFP
coat protein
RNA of interest coat protein
binding site
RNA localization
1755
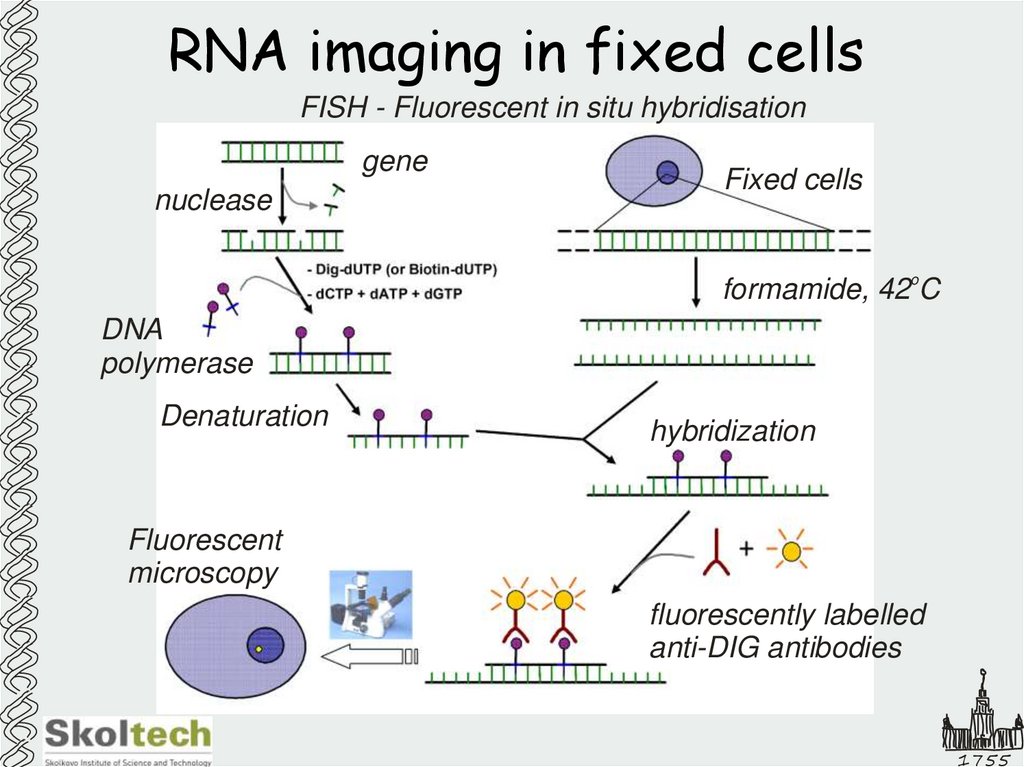
20. RNA imaging in fixed cells
FISH - Fluorescent in situ hybridisationgene
nuclease
Fixed cells
o
formamide, 42 C
DNA
polymerase
Denaturation
hybridization
Fluorescent
microscopy
fluorescently labelled
anti-DIG antibodies
1755
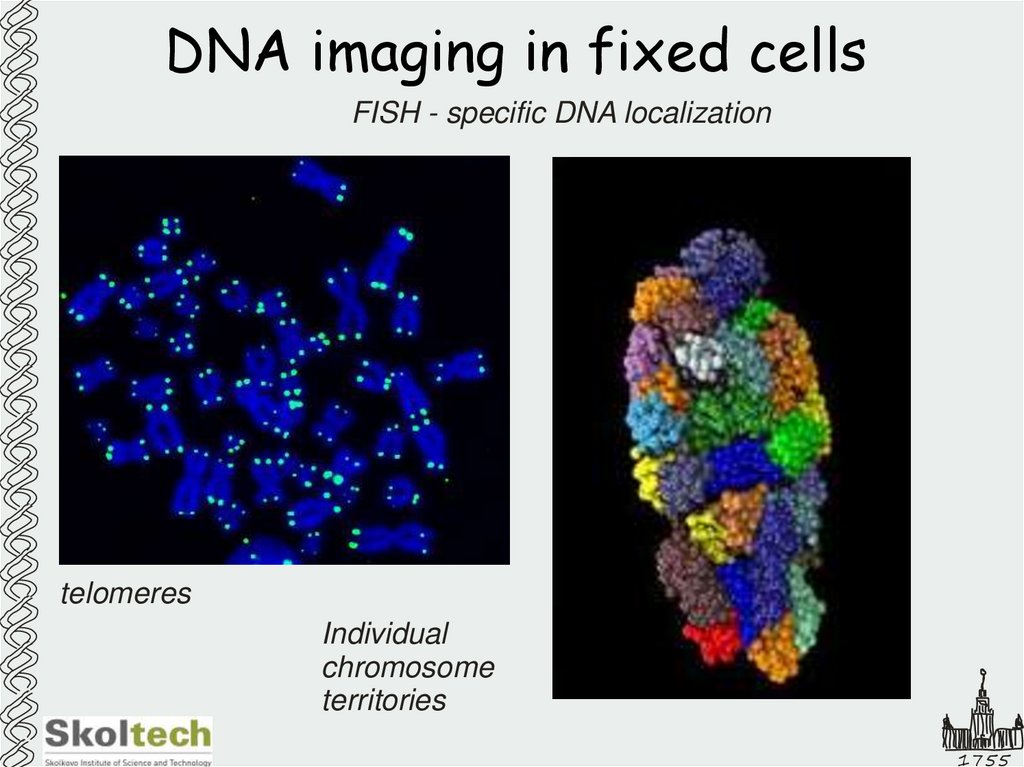
21. DNA imaging in fixed cells
FISH - specific DNA localizationtelomeres
Individual
chromosome
territories
1755
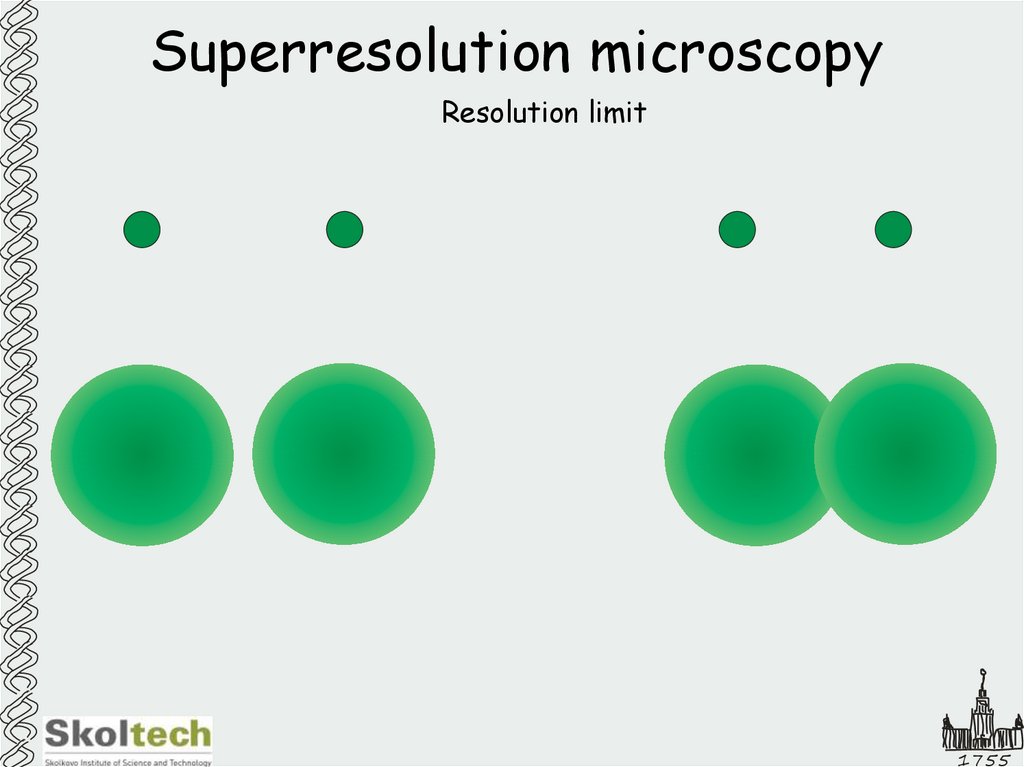
22. Superresolution microscopy
Resolution limit1755
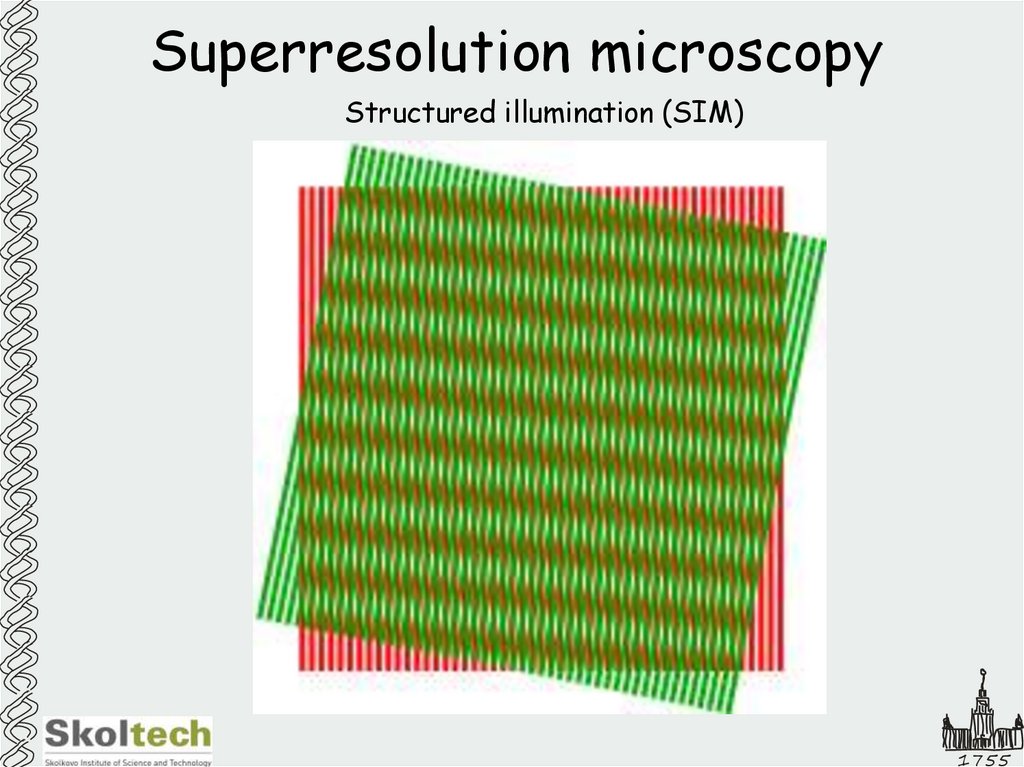
23. Superresolution microscopy
Structured illumination (SIM)1755
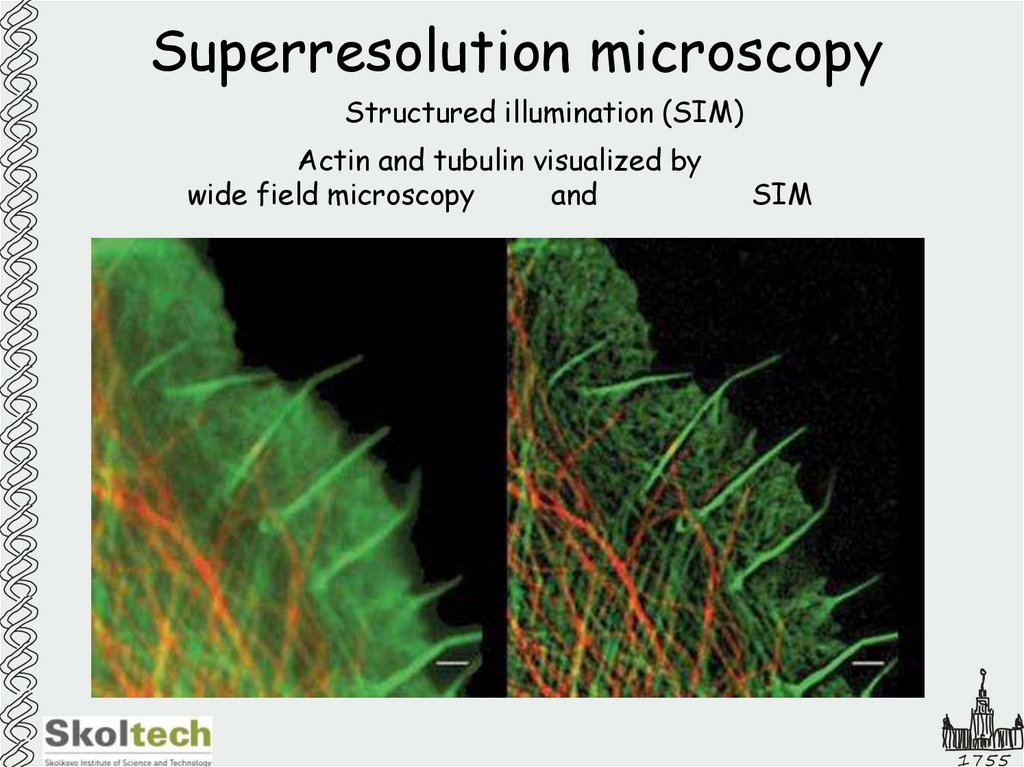
24. Superresolution microscopy
Structured illumination (SIM)Actin and tubulin visualized by
wide field microscopy
and
SIM
1755
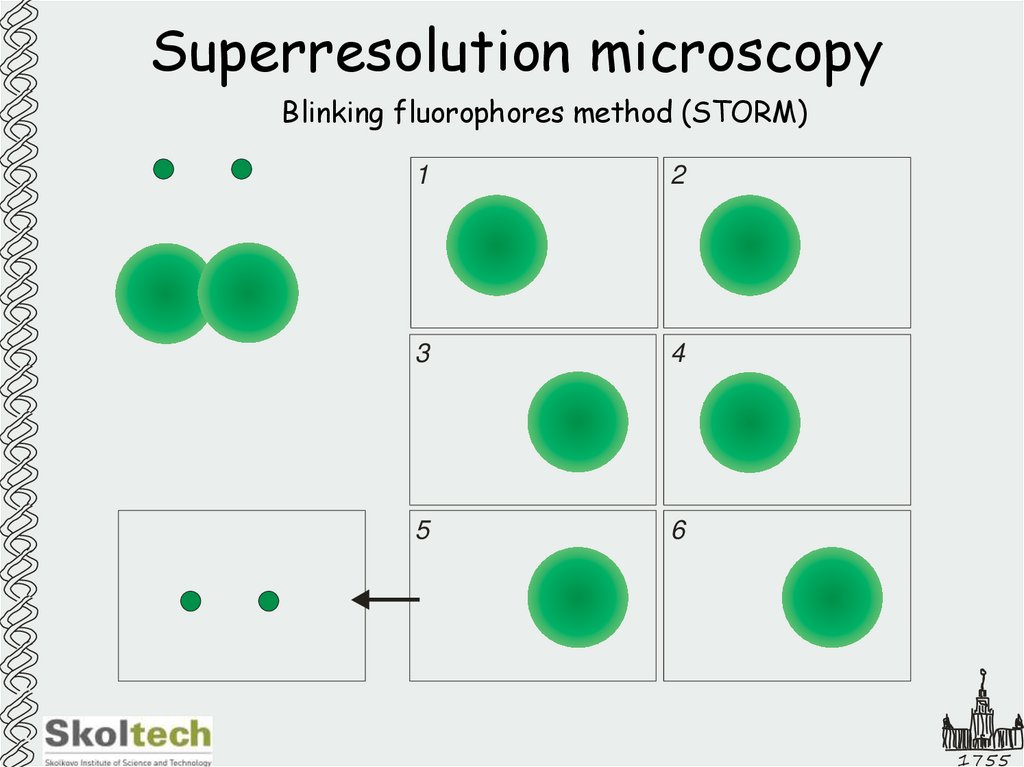
25. Superresolution microscopy
Blinking fluorophores method (STORM)1
2
3
4
5
6
1755
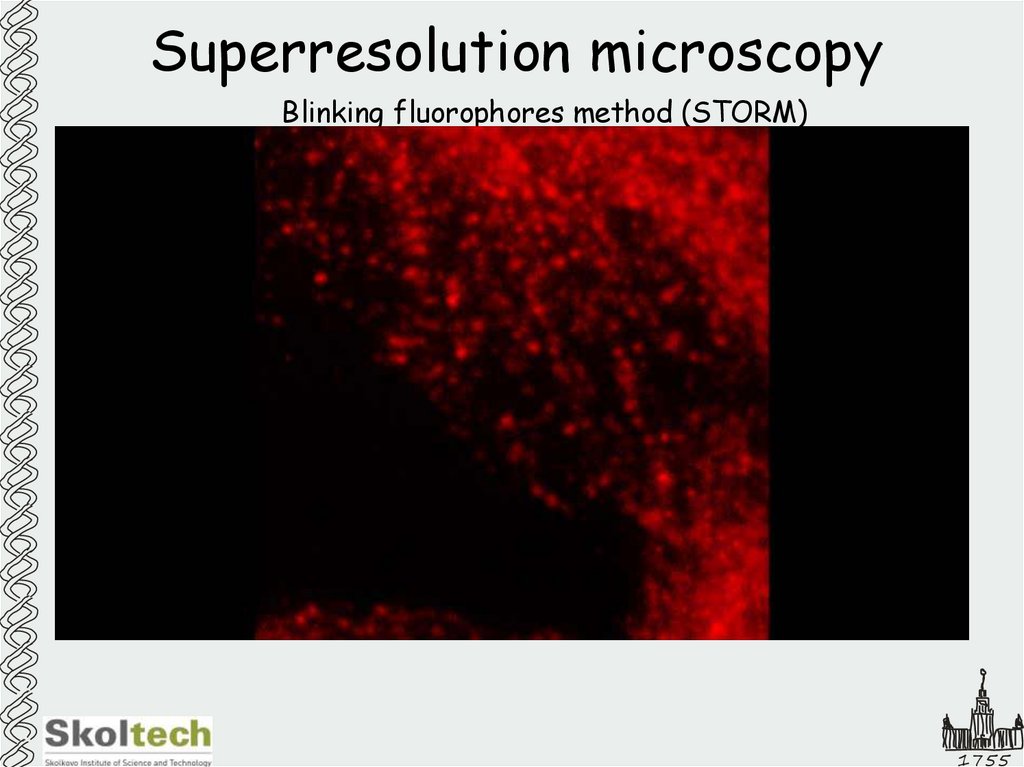
26. Superresolution microscopy
Blinking fluorophores method (STORM)1755
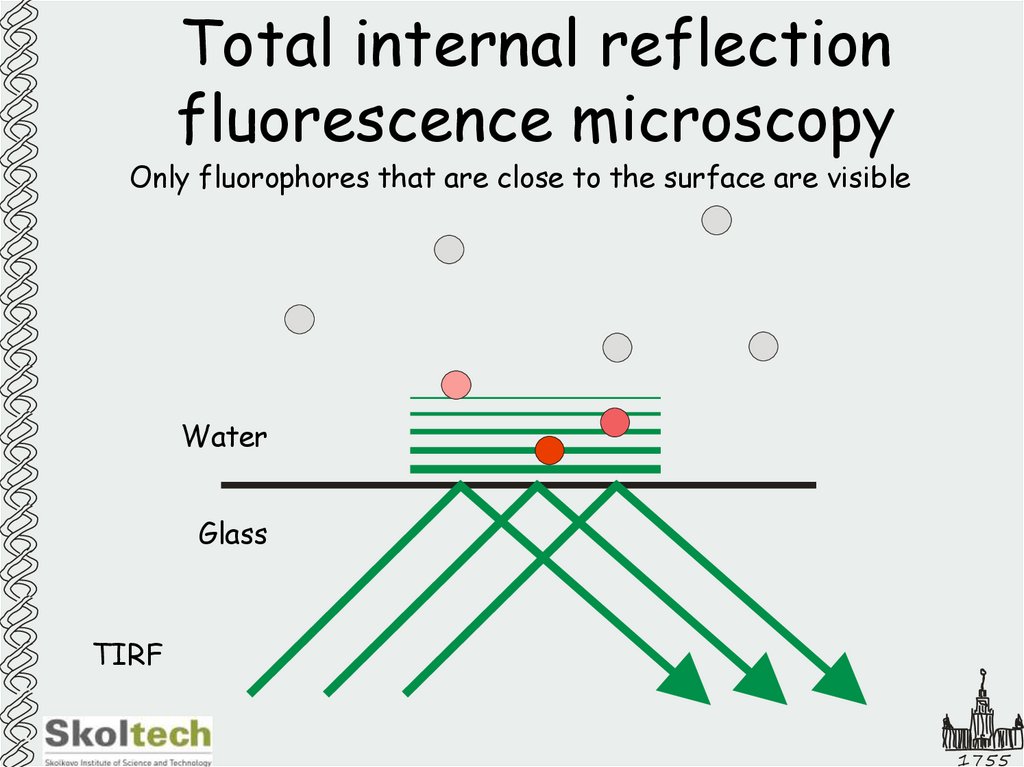
27. Total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy
Only fluorophores that are close to the surface are visibleWater
Glass
TIRF
1755
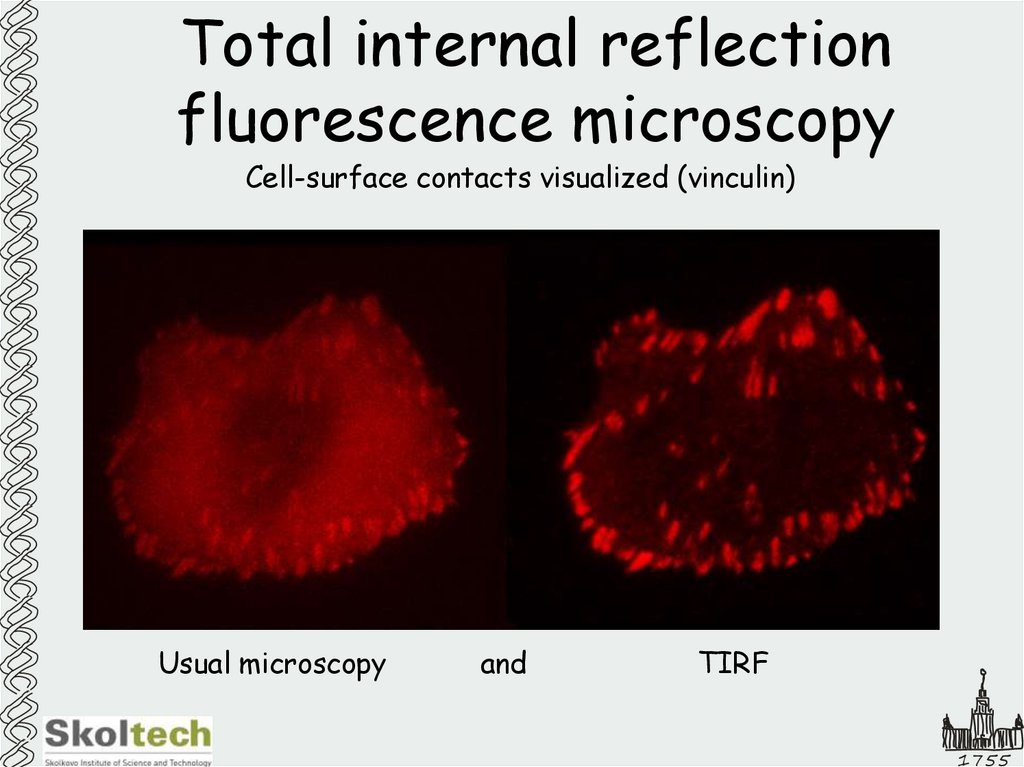
28. Total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy
Cell-surface contacts visualized (vinculin)Usual microscopy
and
TIRF
1755
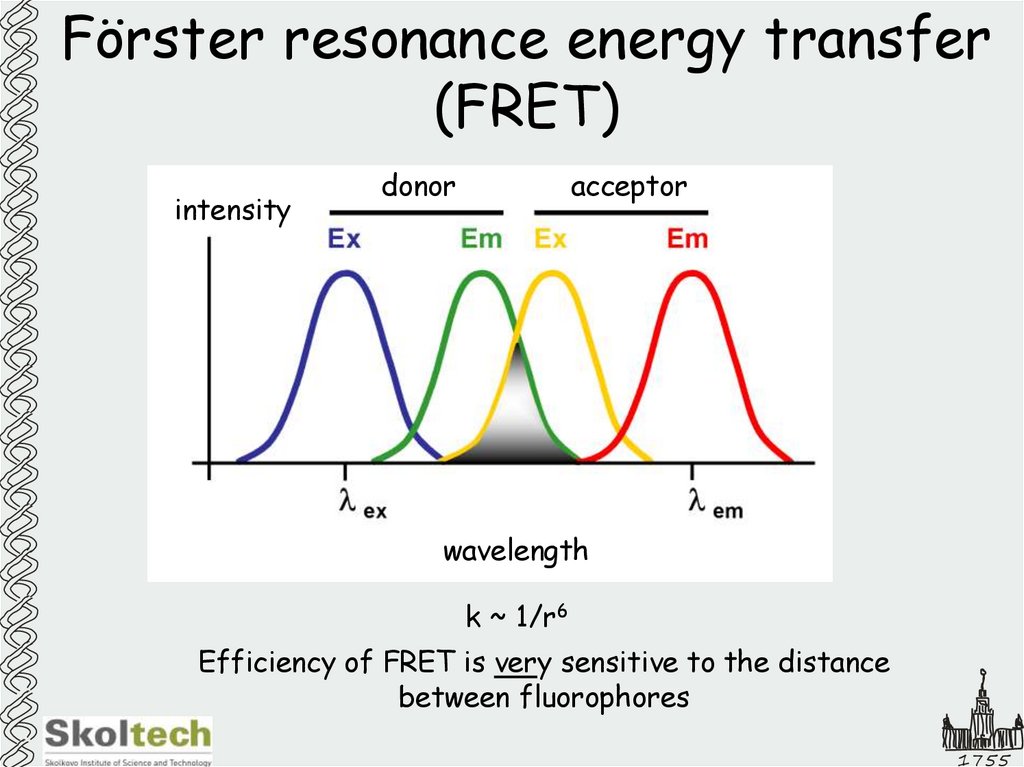
29. Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET)
intensitydonor
acceptor
wavelength
k ~ 1/r6
Efficiency of FRET is very sensitive to the distance
between fluorophores
1755
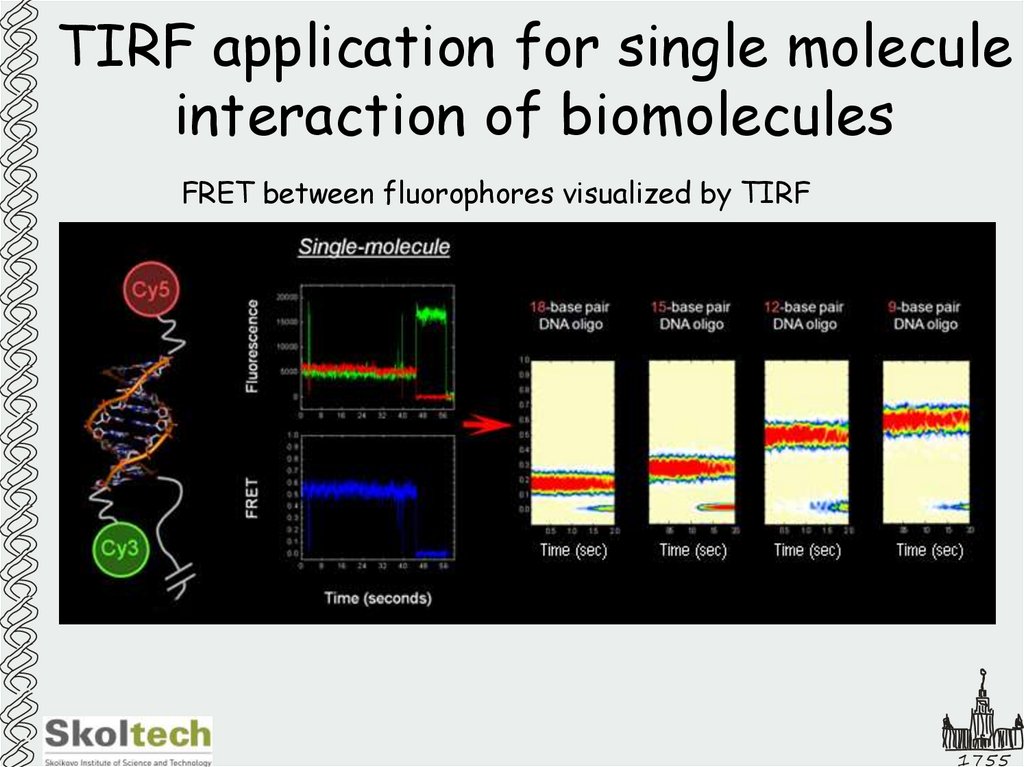
30. TIRF application for single molecule interaction of biomolecules
FRET between fluorophores visualized by TIRF1755
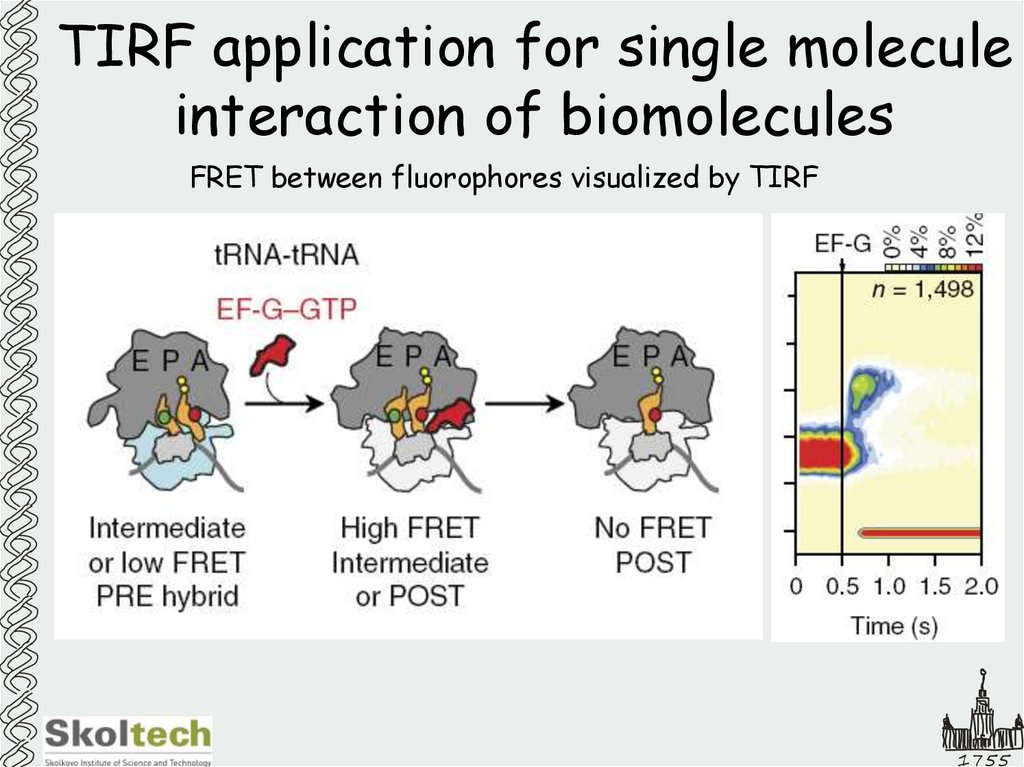
31. TIRF application for single molecule interaction of biomolecules
FRET between fluorophores visualized by TIRF1755
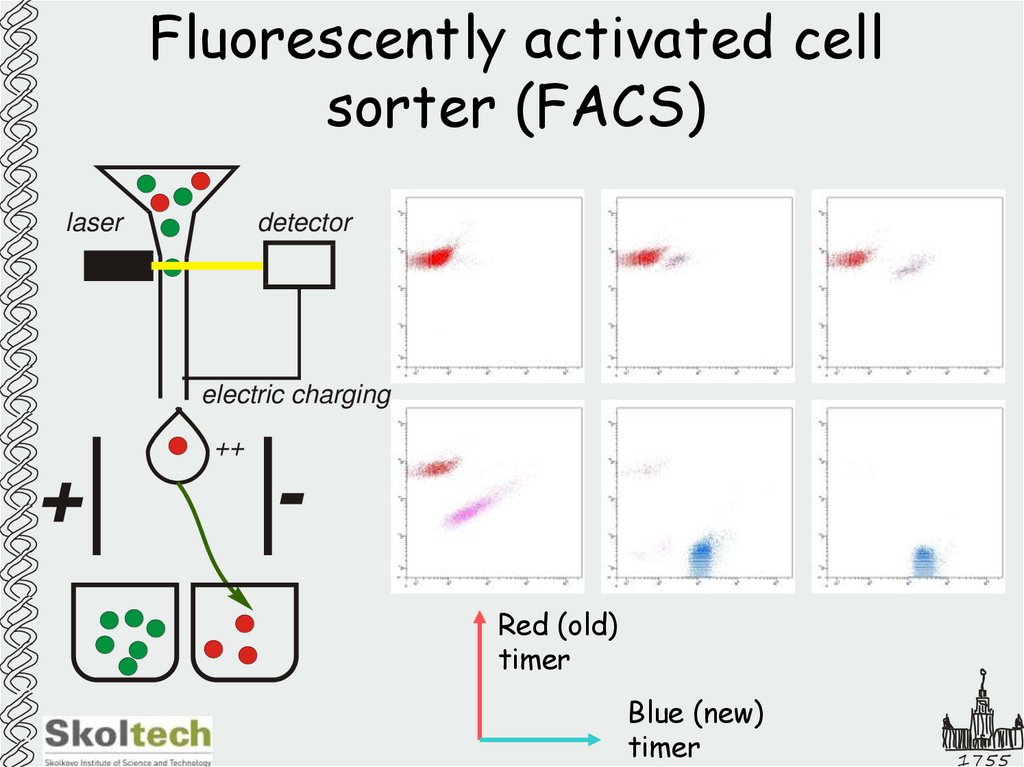
32. Fluorescently activated cell sorter (FACS)
laserdetector
electric charging
++
+
Red (old)
timer
Blue (new)
timer
1755
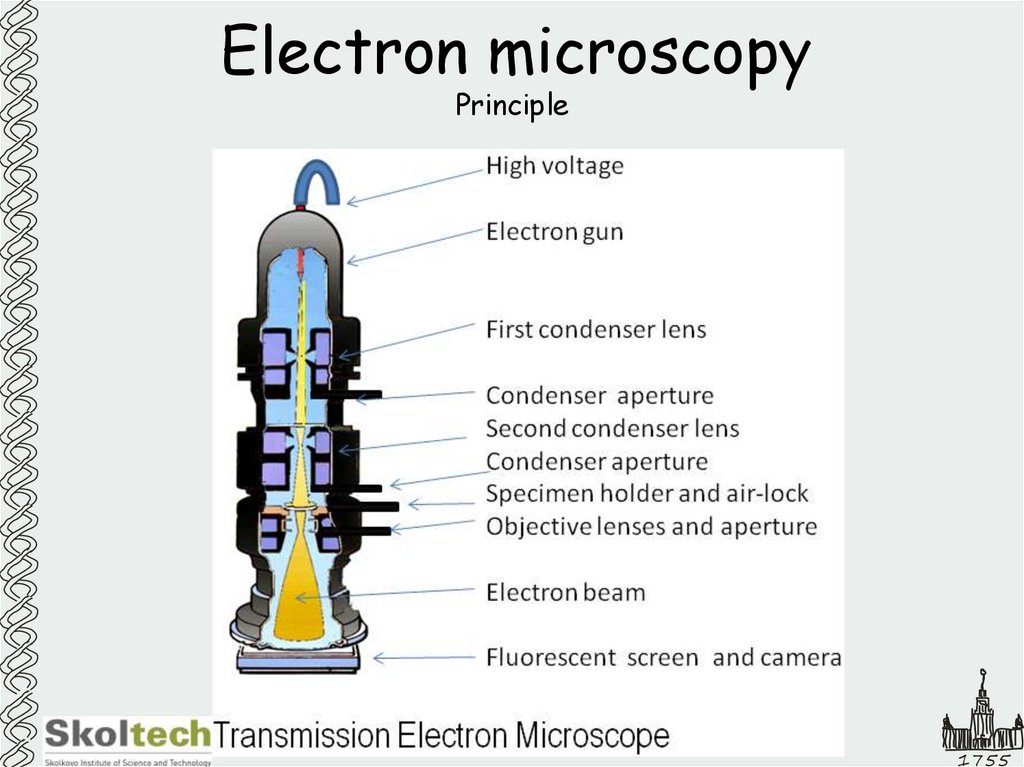
33. Electron microscopy
Principle1755
34. Electron microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy1755
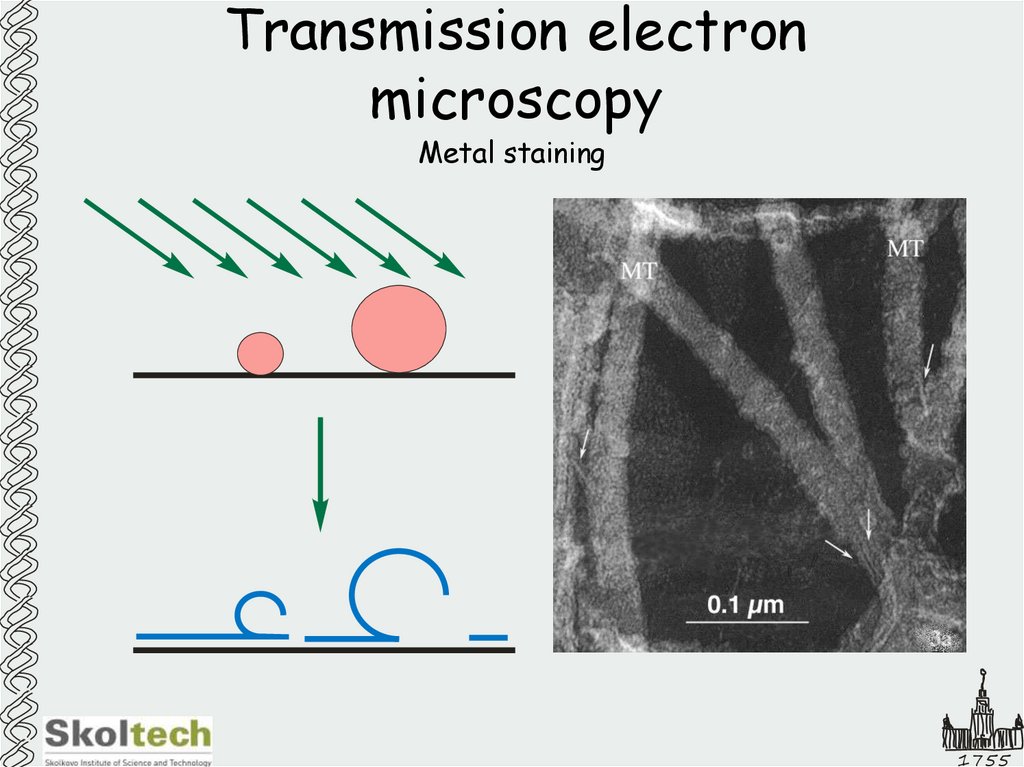
35. Transmission electron microscopy
Metal staining1755
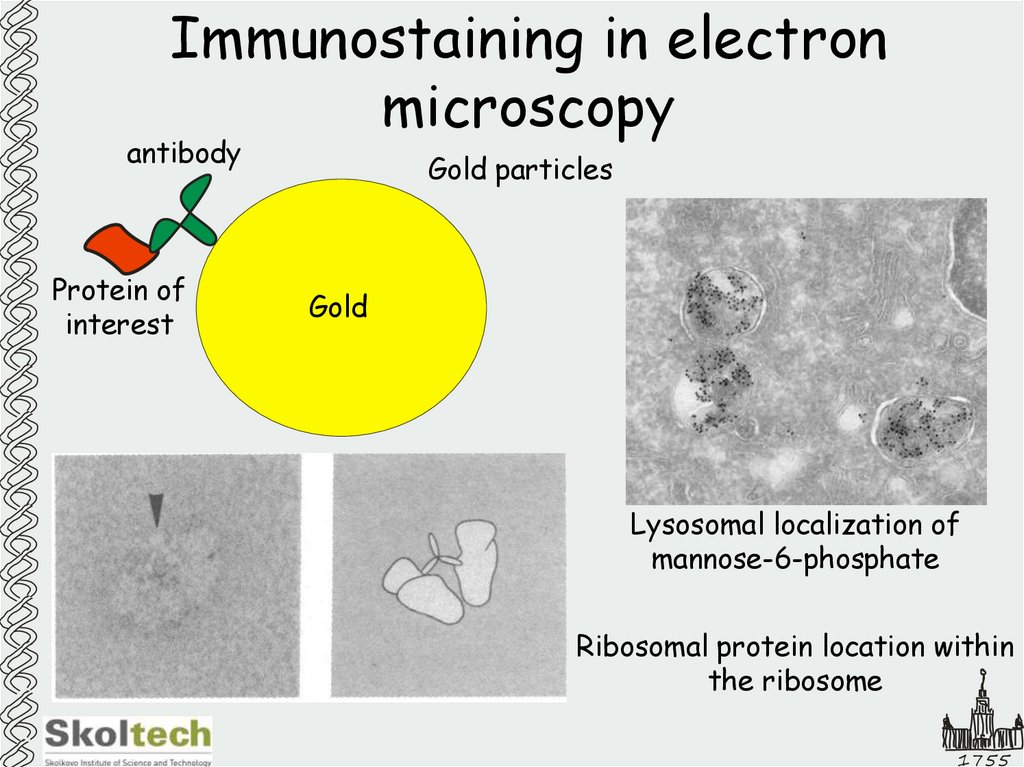
36. Immunostaining in electron microscopy
antibodyProtein of
interest
Gold particles
Gold
Lysosomal localization of
mannose-6-phosphate
Ribosomal protein location within
the ribosome
1755
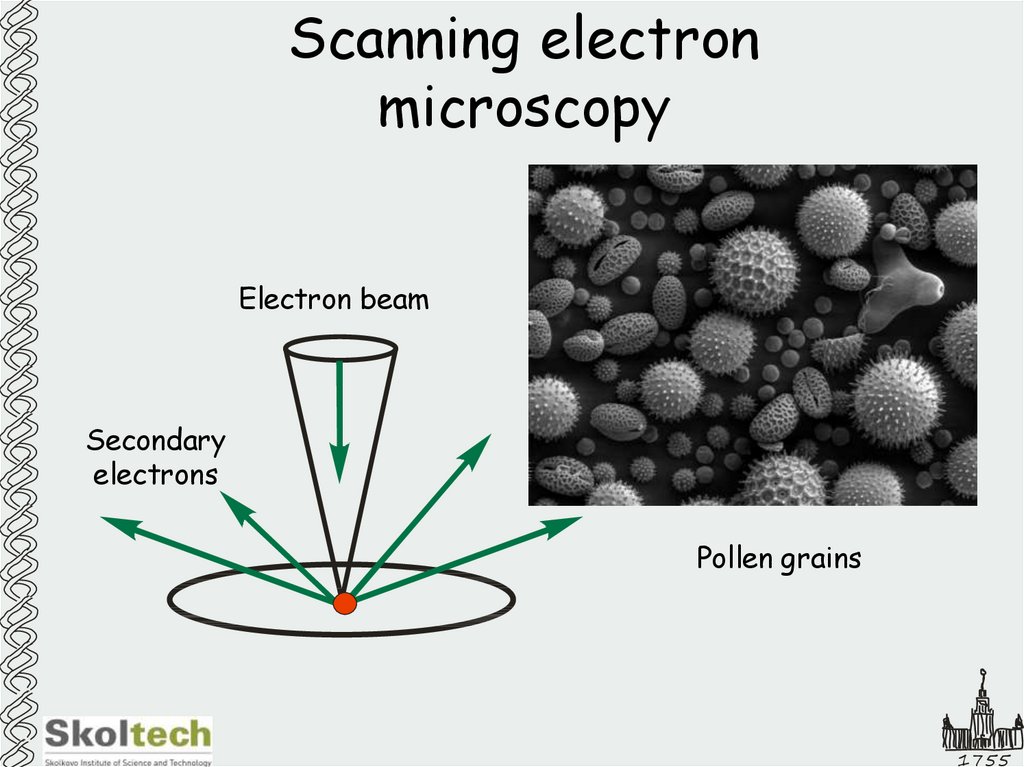
37. Scanning electron microscopy
Electron beamSecondary
electrons
Pollen grains
1755
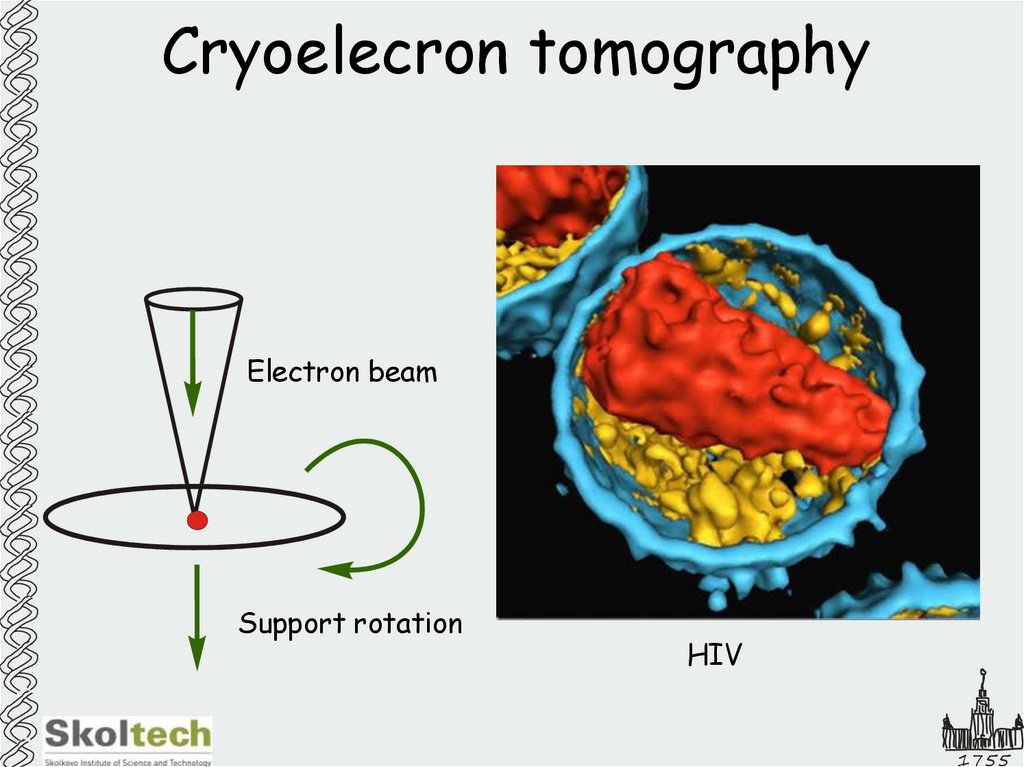
38. Cryoelecron tomography
Electron beamSupport rotation
HIV
1755
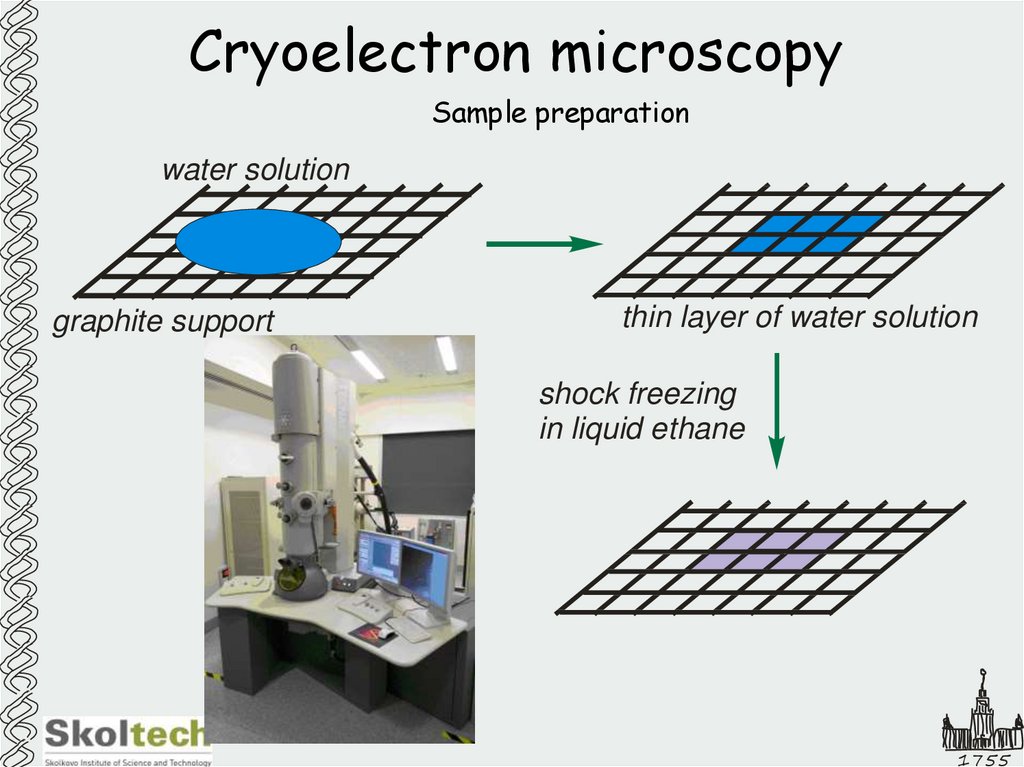
39. Cryoelectron microscopy
Sample preparationwater solution
graphite support
thin layer of water solution
shock freezing
in liquid ethane
1755
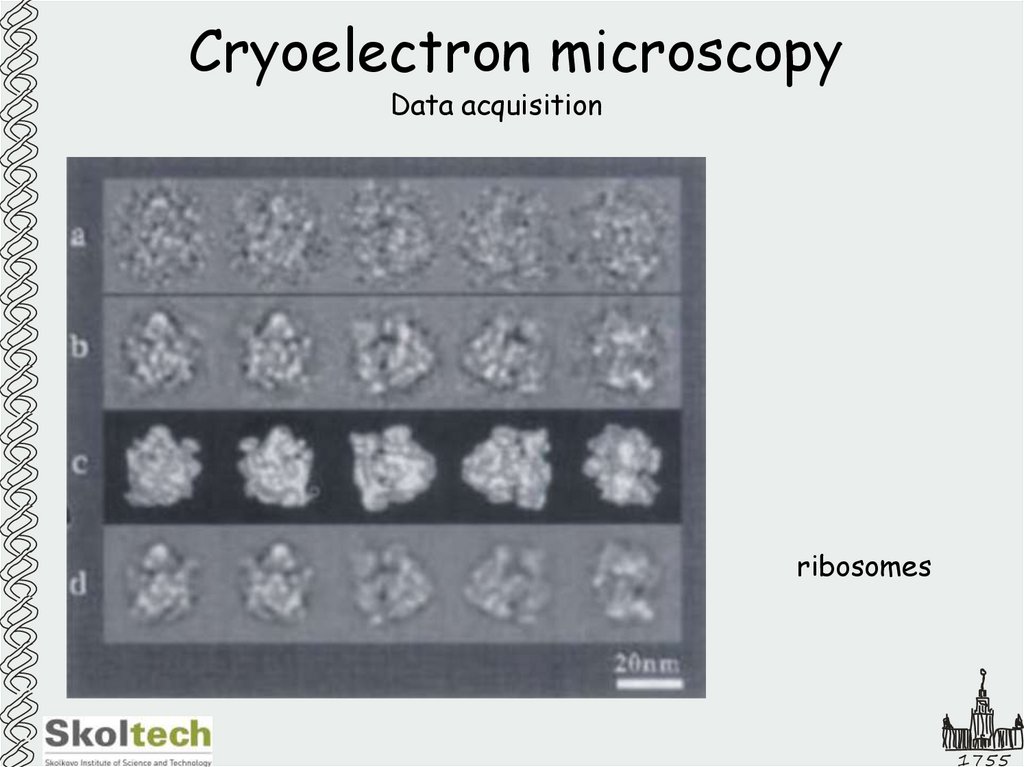
40. Cryoelectron microscopy
Data acquisitionribosomes
1755
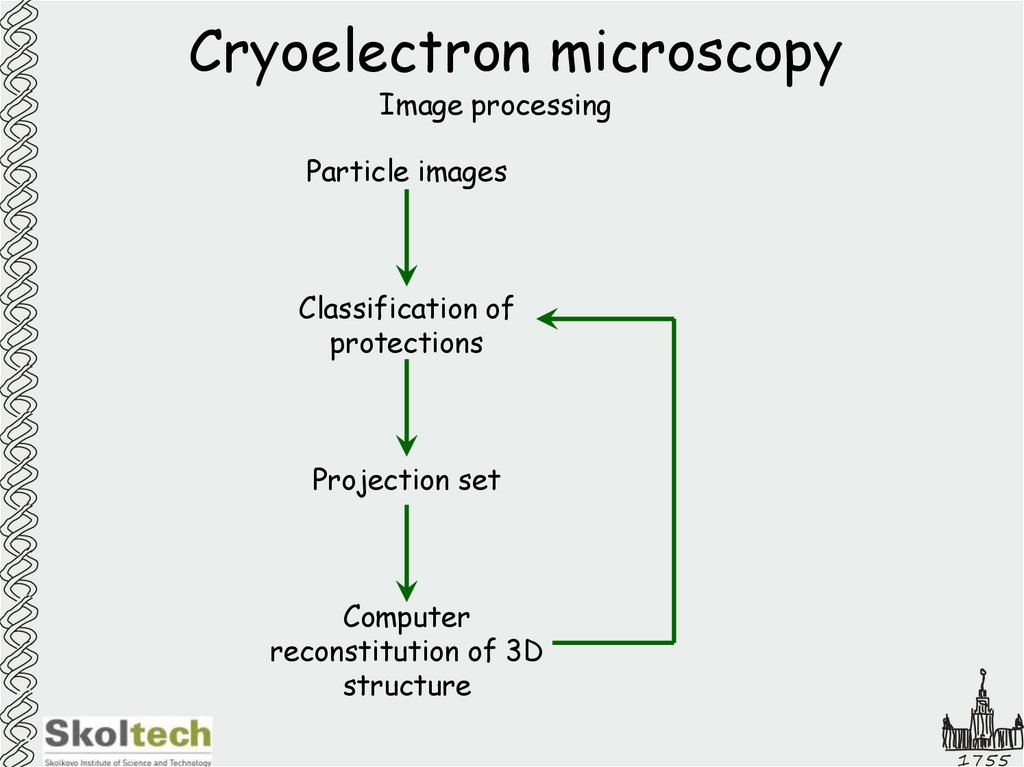
41. Cryoelectron microscopy
Image processingParticle images
Classification of
protections
Projection set
Computer
reconstitution of 3D
structure
1755
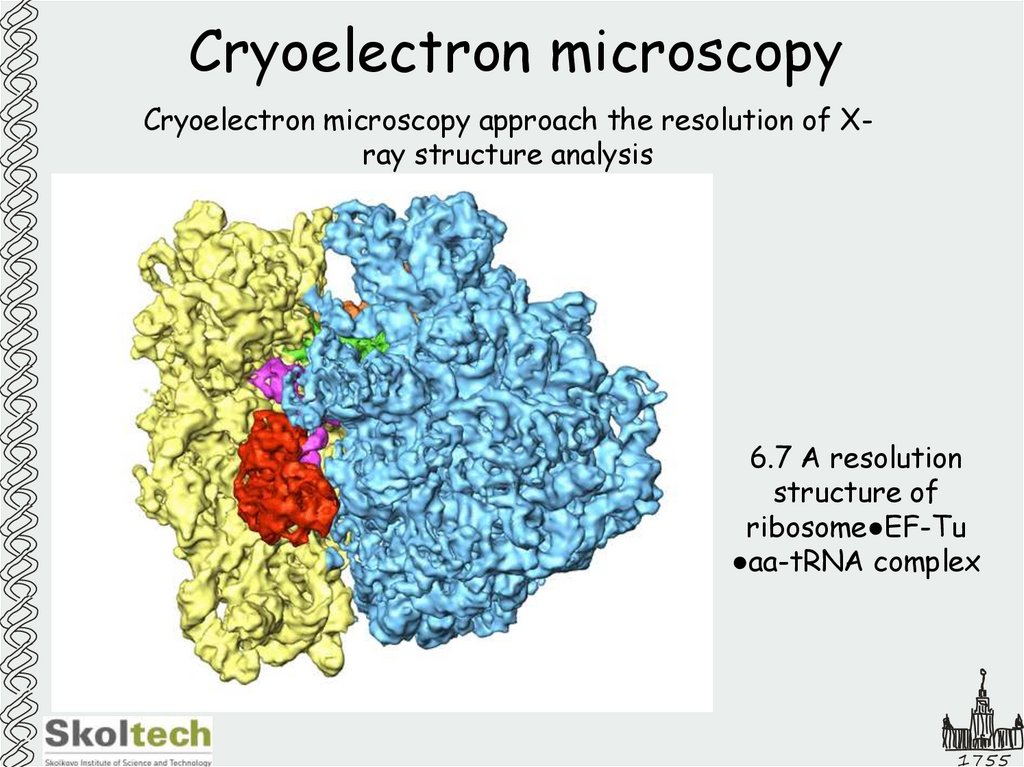
42. Cryoelectron microscopy
Cryoelectron microscopy approach the resolution of Xray structure analysis6.7 A resolution
structure of
ribosome●EF-Tu
●aa-tRNA complex
1755




 Физика
Физика








