Похожие презентации:
Practical pharmacology. Part 3. Drug response
1.
Practical pharmacologyPart 3
2.
Drug response3. Drug reponse
Normal therapeutic responseSide effects
Exaggeration of pharmacological effect
Toxicities
Abnormal response
Tolerance
4. Drug reponse
Normal therapeutic responseSide effects
Exaggeration of pharmacological effect
Toxicities
Abnormal response
Tolerance
5.
AResponse
6. Drug reponse
Normal therapeutic responseSide effects
Exaggeration of pharmacological effect
Toxicities
Abnormal response
Tolerance
7.
Side effectsA
Response
Side effects
8. Drug reponse
Normal therapeutic responseSide effects
Exaggeration of pharmacological effect
Toxicities
Abnormal response
Tolerance
9. Intolerance
Exaggerated response(magnified pharmacological response)
resembling an overdose of a drug but at normal dose.
It is commonly observed in children
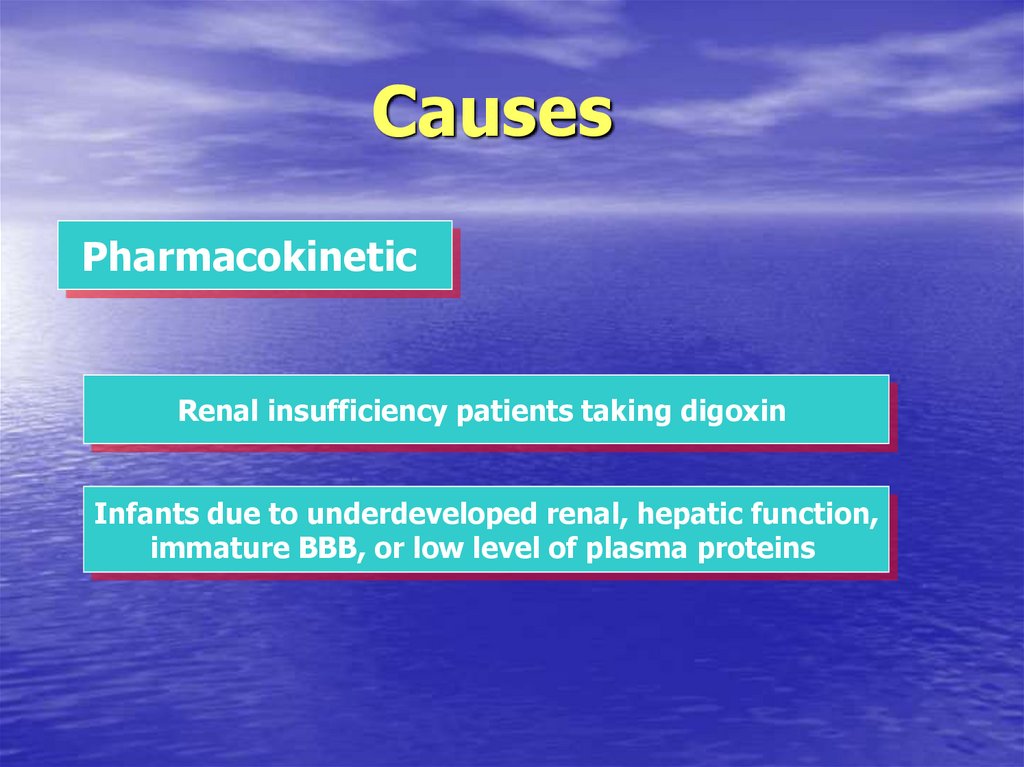
10. Causes
PharmacokineticRenal insufficiency patients taking digoxin
Infants due to underdeveloped renal, hepatic function,
immature BBB, or low level of plasma proteins
11. Causes
PharmacodynamicThyrotoxic patients, epinephrine
12.
Thyroxine13.
Toxicity14. Drug reponse
Normal therapeutic responseSide effects
Exaggeration of pharmacological effect
Toxicities
Abnormal response
Tolerance
15. Drug reponse
Normal therapeutic responseSide effects
Exaggeration of pharmacological effect
Toxicities
Abnormal response
Tolerance
16. Idiosyncrasy
Genetically determinedabnormal response to a drug
17. Example 1
Succinyl choline inpseudocholine esterase deficiency subjects
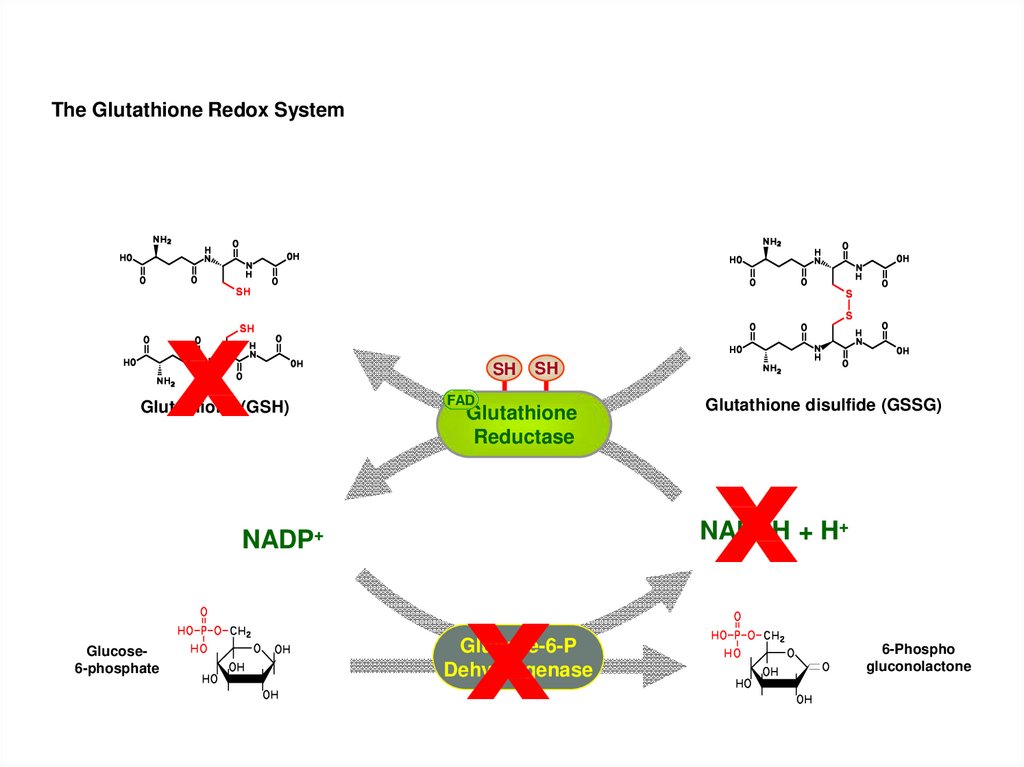
18. Example 2
Chloroquine, salicylates, sulfa drugs inglucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase
deficiency subjects
19.
The Glutathione Redox Systemx
Glutathione (GSH)
SH
SH
FAD
Glutathione
Reductase
x
NADPH + H+
NADP+
Glucose6-phosphate
Glutathione disulfide (GSSG)
x
Glucose-6-P
Dehydrogenase
6-Phospho
gluconolactone
20. Example 3
Isoniazide in slow, fast acetylators21.
Slow acetylatorIsoniazide
Isoniazide
metabolites
Fast acetylator
22. Drug reponse
Normal therapeutic responseSide effects
Exaggeration of pharmacological effect
Toxicities
Abnormal response
Tolerance
23. Tolerance
Decreased therapeutic efficacyon repeated administration over
days or months.
24. Tachyphylaxis (desensitization)
Rapidly developing tolerance25. Resistance (Refractoriness)
Loss of therapeutic efficacy26. Types of tolerance
AcquiredCongenital
27. Acquired tolerance
• Due to repeated administration of adrug
Pharmacokinetic
Pharmacodynamic
28. Pharmacokinetic tolerance
barbiturates cause toleranceof
concomitantly administered drugs
29. Pharmacodynamic tolerance
• Conformational changes in receptordue to long use of agonist, or
disruption of receptor effectors
linkage, or down regulation of
receptor
• Exhaustion of mediators in case of
amphetamine
30.
EFFECTORRESPONSE
31. Congenital tolerance
Natural inborn tolerance to certain drugwhich has been never used before
32. Congenital tolerance
RacialEphedrine is not effective mydriatic in
black colored people
33. Congenital tolerance
SpeciesRabbits
tolerate large quantities of
atropine without toxicity
34. Congenital tolerance
Individual35.
Kymograph36.
Organ bathDrum
Water bath
37. Conditions
Physiological solutionTemperature
Aeration
38. Physiological solution
NaCl & KClCaCl2
Mg salt
NaHCO3
NaH2PO4
Glucouse
For isotonicity
39. Physiological solution
NaCl & KClCaCl2
Mg salt
NaHCO3
NaH2PO4
Glucouse
Contractility
40. Physiological solution
NaCl & KClCaCl2
Mg salt
NaHCO3
NaH2PO4
Glucouse
Contractility
41. Physiological solution
NaCl & KClCaCl2
Mg salt
NaHCO3
NaH2PO4
Glucouse
Buffering action
42. Physiological solution
NaCl & KClCaCl2
Mg salt
NaHCO3
NaH2PO4
Glucouse
Nutrition
43. Temperature
36-37˚C44. Aeriation
Pure O2Carbogen (90% O2 + 10% CO2)
Air
45. Our isolated organ
• Rabbit intestine• Tyrode‘s solution
• Temperature 37˚C
• Aeration by air pump
46.
47.
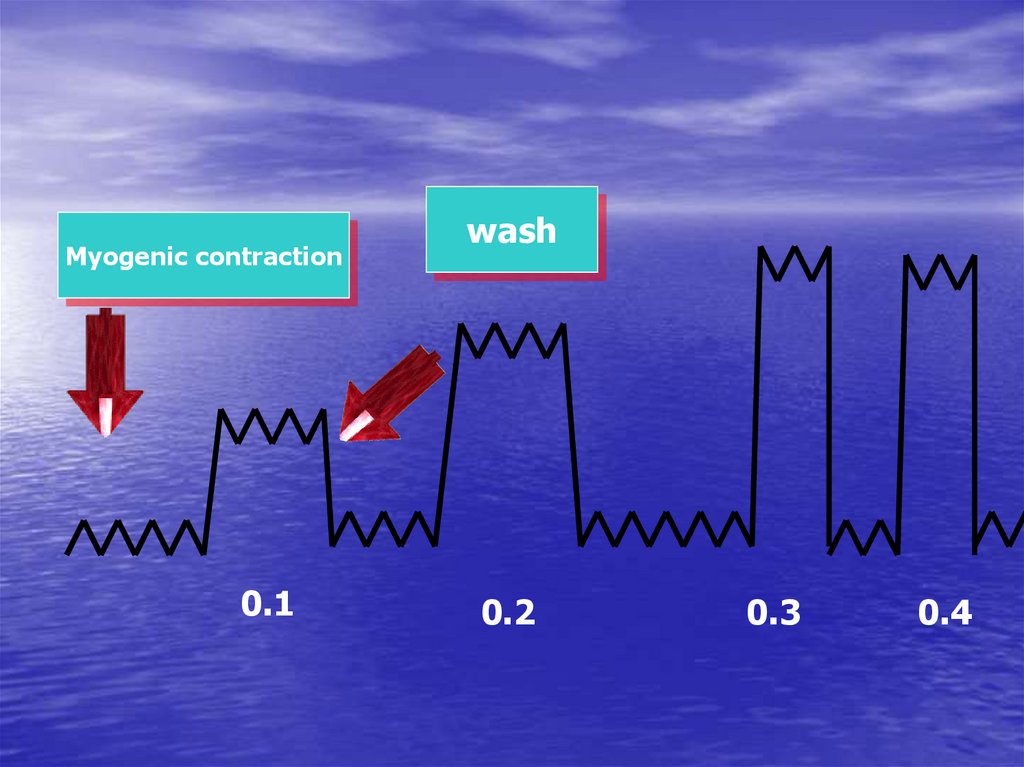
Myogenic contraction0.1
wash
0.2
0.3
0.4













































 Английский язык
Английский язык








