Похожие презентации:
Corrosion of metals and alloys as result of pollution, prevention
1.
CORROSION OF METALS ANDALLOYS AS RESULT OF
POLLUTION,PREVENTION
By:Issadilov Ersain and Alpysbaev Bekzat
2. WHAT IS THE CORROSION?
Corrosion is a natural process, which converts arefined metal to a more stable form, such as its
oxide, hydroxide, or sulfide. It is the gradual
destruction of materials (usually metals) by
chemical reaction with their environment.
Metals and alloys are constantly in contact with
various substances.They can interact with
substances by forming different compounds.As a
result properties of metal may change,or total
destruction of metal structures occurs.It is very
harmful and dangerous process that is called
corrosion(lat.Corrosion-attack).
3. alloy
ALLOYAn alloy is a mixture of metals or a mixture of a metal
and another element. Alloys are defined by metallic
bonding character. An alloy may be a solid solution of
metal elements (a single phase) or a mixture of
metallic phases (two or more solutions).
Alloys are used in a wide variety of applications. In
some cases, a combination of metals may reduce the
overall cost of the material while preserving
important properties. In other cases, the combination
of metals imparts synergistic properties to the
constituent metal elements such as corrosion
resistance or mechanical strength. Examples of alloys
are steel,solder,brass,pewter,duralumin,phosphor
bronze and amalgams.
4. FORMS OF CORROSION
General corrosionHigh-temperature corrosion
Atmospheric corrosion
Galvanic corrosion
Stray-current corrosion
General biological corrosion
Molten salt corrosion
Corrosion in liquid metals
Oxidation
Sulfidation
Carburization
Other forms(a)
Localized corrosion
Filiform corrosion
Crevice corrosion
Pitting corrosion
Localized biological corrosion
5. FORMS OF CORROSION
Metallurgically influenced corrosionMechanically assisted degradation
Intergranular corrosion
Dealloying corrosion
Erosion corrosion
Fretting corrosion
Cavitation and water drop impingement
Corrosion fatigue
Environmentally induced cracking
Stress-corrosion cracking
Hydrogen damage
Liquid metal embrittlement
Solid metal induced embrittlement
6. WHY METALS CORRODE?
Metals corrode because we use them inenvironments where they are chemically
unstable. Only copper and the precious metals
(gold, silver, platinum, etc.) are found in nature in
their metallic state. All other metals, to include
iron-the metal most commonly used-are
processed from minerals or ores into metals
which are inherently unstable in their
environments.
7. Corrosion is divided as chemical and electrochemical
CORROSION IS DIVIDED AS CHEMICAL AND ELECTROCHEMICALElectrochemical
corrosion
Occurs in electrolytic solutions,is amplified in the
presence of less active metals,at the same time metal
that more active aredestroyed.Accompained by
transition of electrons,the emergence of micro
Oxidizing agent: hydrated ions of electrolytes
Examples:destruction of pipelines,the ship’s
hulls,constructions
Chemical
corrosion
Occurs under the action of oxidants nonelectrolytes
at high temperatures
Oxidizing agent:O2,Cl2,SO2 and other gases,different
type of fuel,water vapor
Examples:destruction of parts of internal combustion
engine,chemical devices,turbine parts in power
plants
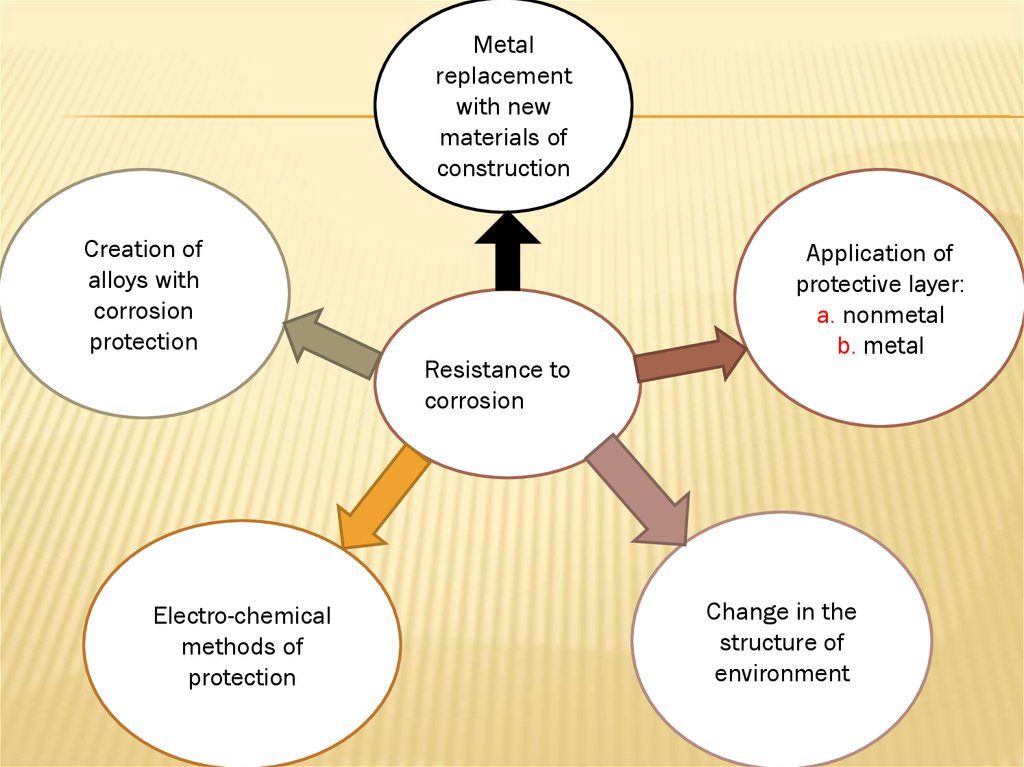
8.
Metalreplacement
with new
materials of
construction
Creation of
alloys with
corrosion
protection
Electro-chemical
methods of
protection
Resistance to
corrosion
Application of
protective layer:
a. nonmetal
b. metal
Change in the
structure of
environment
9.
10. Prevent rust(Предотвращение ржавления)
PREVENT RUST(ПРЕДОТВРАЩЕНИЕ РЖАВЛЕНИЯ)Rust is permeable to air and water , so iron
continues to corrode . rust prevention ,
therefore, requires a coating that eliminates
the formation of rust . On the surface of
stainless steel passivation layer is formed of
chromium oxide (III). This manifestation of
passivation occurs with magnesium, titanium ,
zinc , zinc oxide , aluminum , polyaniline and
other conductive polymers .
11.
12. qUESTIONS
QUESTIONS❶What is the corrosion?
❷Corrosion in latin.
❸Why metals corrode?
❹On what types of corrosion are divided?
❺
13.
THANK YOU FORWATCHING!!!












 Английский язык
Английский язык








