Похожие презентации:
Carbon. Carbon cycle
1. Carbon Carbon cycle
2. Carbon
3. Carbon is…
All living things are made of carbon. Carbon is also apart of the ocean, air, and even rocks. Because the
Earth is a dynamic place, carbon does not stay still. It is
on the move!
In the atmosphere, carbon is attached to some oxygen
in a gas called carbon dioxide.
4.
5.
Plants use carbon dioxide and sunlight to make theirown food and grow. The carbon becomes part of the
plant. Plants that die and are buried may turn into
fossil fuels made of carbon like coal and oil over
millions of years. When humans burn fossil fuels,
most of the carbon quickly enters the atmosphere as
carbon dioxide.
6.
7.
Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas and traps heat inthe atmosphere. Without it and other greenhouse
gases, Earth would be a frozen world. But humans
have burned so much fuel that there is about 30%
more carbon dioxide in the air today than there was
about 150 years ago, and Earth is becoming a warmer
place. In fact, ice cores show us that there is now more
carbon dioxide in the atmosphere than there has been
in the last 420,000 years.
8.
9.
Global warming and climate change are terms forthe observed century-scale rise in the average
temperature of the Earth's climate system and its
related effects. Multiple lines of scientific evidence
show that the climate system is warming. Although the
increase of near-surface atmospheric temperature is
the measure of global warming often reported in the
popular press, most of the additional energy stored in
the climate system since 1970 has gone into the oceans.
The rest has melted ice and warmed the continents
and atmosphere. Many of the observed changes since
the 1950’s are unprecedented over tens to thousands of
years.
10.
The greenhouse effect is the process by whichradiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the
planet's surface to a temperature above what it would
be without its atmosphere.
11.
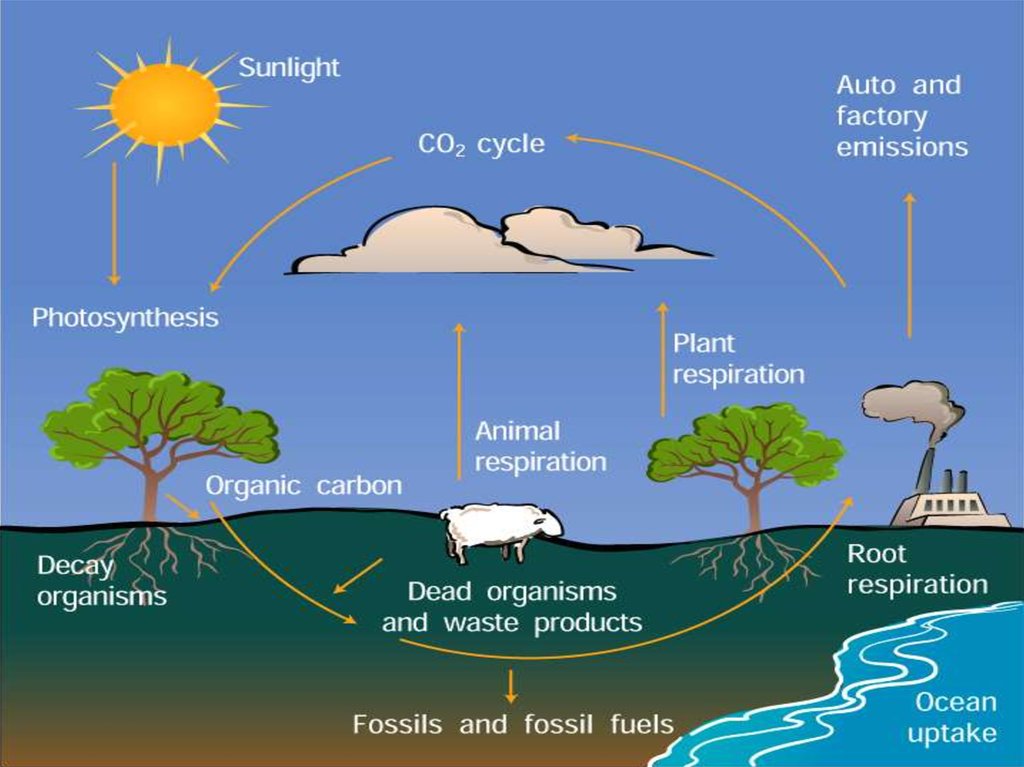
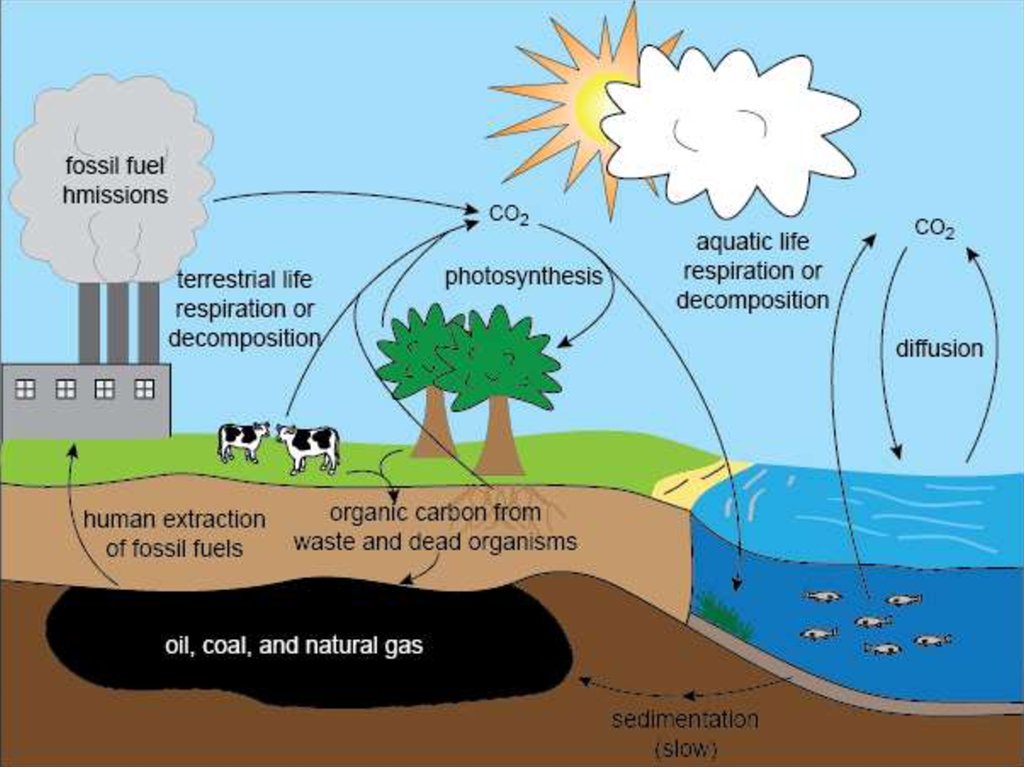
12. Carbon cycle is…
the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon isexchanged among
the biosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere,
and atmosphere of the Earth. Along with the nitrogen
cycle and the water cycle, the carbon cycle comprises a
sequence of events that are key to making the Earth
capable of sustaining life; it describes the movement
of carbon as it is recycled and reused throughout the
biosphere, including carbon sinks.











 Экология
Экология








