Похожие презентации:
Pharmacists in Family Medicine 4.26.06
1. Pharmacists in Family Medicine: a New Model in Teaching & Practice
Pharmacists in Family Medicine: aNew Model in Teaching & Practice
John E. Delzell, Jr, MD, MSPH
L. Brian Cross, PharmD, CDE
Michelle Hilaire, PharmD, CDE
Oralia Bazaldua, PharmD
John Tovar, PharmD
Jeremy Thomas, PharmD
Andrea Franks, PharmD, BCPS
2. Introductions
John E. Delzell, Jr, MD, MSPHDepartment of Family Medicine
Kansas University School of Medicine
L. Brian Cross, PharmD, CDE
Holston Medical Group
University of Tennessee College of Pharmacy
Michelle Hilaire, PharmD, CDE
Fort Collins Family Medicine Residency
University of Wyoming
Oralia Bazaldua, PharmD & John Tovar, PharmD
Department of Family & Community Medicine
University of Texas Health Sciences Center at San Antonio
Jeremy Thomas, PharmD & Andrea Franks, PharmD, BCPS
Saint Francis Family Medicine Residency
University of Tennessee College of Pharmacy
3. Outline for this Lecture-Discussion
• Survey• Background
• Description of the speakers’ residency
programs
• Curricular Elements
• Audience Discussion
• Financial Issues
• How are we funded?
• Audience Discussion
• Final thoughts
4. Audience Survey
5. Audience Survey
Question #1• Does your hospital utilize clinical
pharmacists?
Question #2
• Does your department or residency program
utilize clinical pharmacists?
Question #3
• Have you worked with a pharmacist in the
inpatient setting?
6. Audience Survey
Question #4• Have you worked with a pharmacist in the
outpatient setting?
Question #5
• Does your hospital pay for a clinical
pharmacist?
Question #6
• Does your department or program pay for a
clinical pharmacist?
7. Audience Survey
Question #7• Can a PharmD see patients independently?
Question #8
• Can a PharmD bill independently for patient
care?
Question #9
• Does your residency program have a formal
curriculum for pharmacy teaching?
8. Audience Survey
Question #10• Are PharmDs involved in teaching your
residents or students?
Bonus Question
• Are pharmacists taking over the
WORLD?
9. Background
10. Background
Clinical pharmacist involvement in FPtraining programs first described in
1980’s
Increasing involvement as teachers since that
time
Clinical pharmacists in FP residency
programs:
Improve medication prescribing
Improve patient satisfaction
Improve patient outcomes
1. Geyman JP. J Fam Pract 1980;10:21-2; 2. Johnston TS, et al. J Fam Pract 1981;13:91-4.
3. Robinson JD, et al. Postgrad Med 1982;71(1):97-103; 4. Carter BL, et al. DICP 1984;18:817-21.
5. Helling DK, et al. Am J Hosp Pharm 1979;36:325-9; 6. Wilt DM, et al. Pharmacotherapy 1995;15(6):732-9.
11. Background
Clinical pharmacists in non-FPambulatory settings have improved
outcomes in:
Anticoagulation
Asthma
Diabetes
Heart Failure
Hypertension
These studies have helped to support
the role of clinical pharmacists as both
teachers & clinicians in FP residency
programs
Carter BL, et al. Ann Pharmacother 2000;34:772-86.
12.
Dickerson LM, et al. Fam Med 2002;34(9):653-7.13. Roles of Clinical Pharmacists in FP Residency Programs in the US
Survey of FPRPs to evaluateinvolvement of clinical pharmacists
579 programs identified
155 (27%) had a clinical pharmacist on faculty
• 56% in community-based programs
• 44% in university-based programs
Dickerson LM, et al. Fam Med 2002;34(9):653-7.
14. Current State of Clinical Pharmacists in FP Residency Programs in the US
130 pharmacists responded to aweb-based survey
Allocation of time/activities:
43% teaching
37% patient care
12% research
12% administration
<5% drug distribution
15.
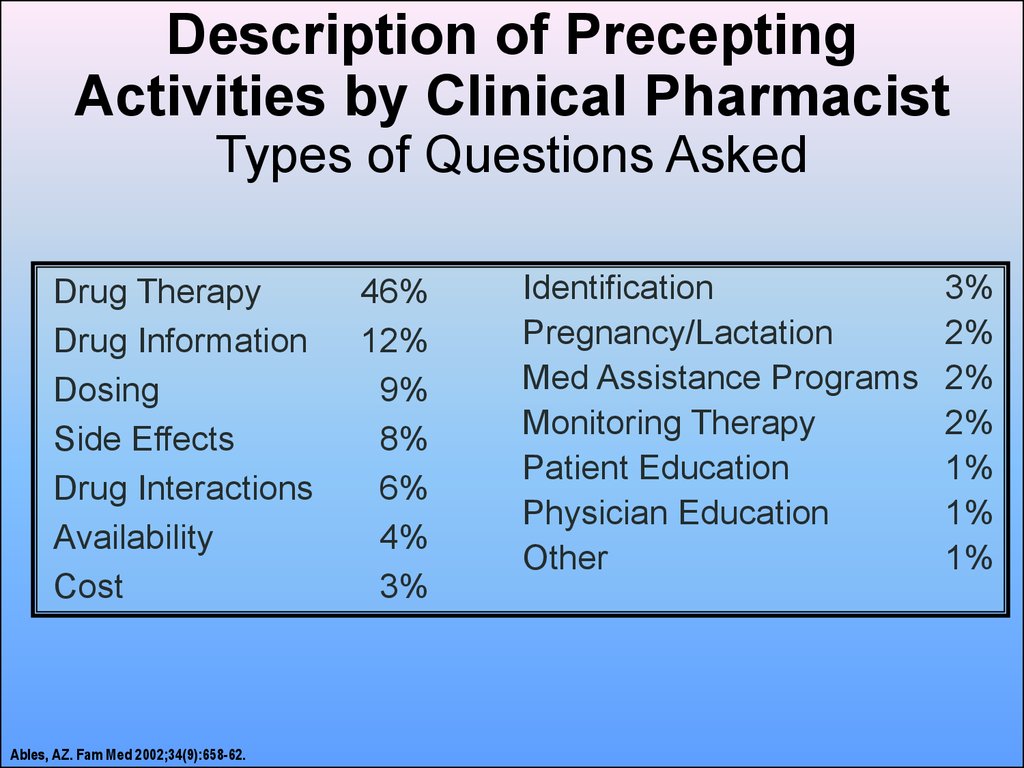
Ables, AZ. Fam Med 2002;34(9):658-62.16. Description of Precepting Activities by Clinical Pharmacist Types of Questions Asked
Drug TherapyDrug Information
Dosing
Side Effects
Drug Interactions
Availability
Cost
Ables, AZ. Fam Med 2002;34(9):658-62.
46%
12%
9%
8%
6%
4%
3%
Identification
Pregnancy/Lactation
Med Assistance Programs
Monitoring Therapy
Patient Education
Physician Education
Other
3%
2%
2%
2%
1%
1%
1%
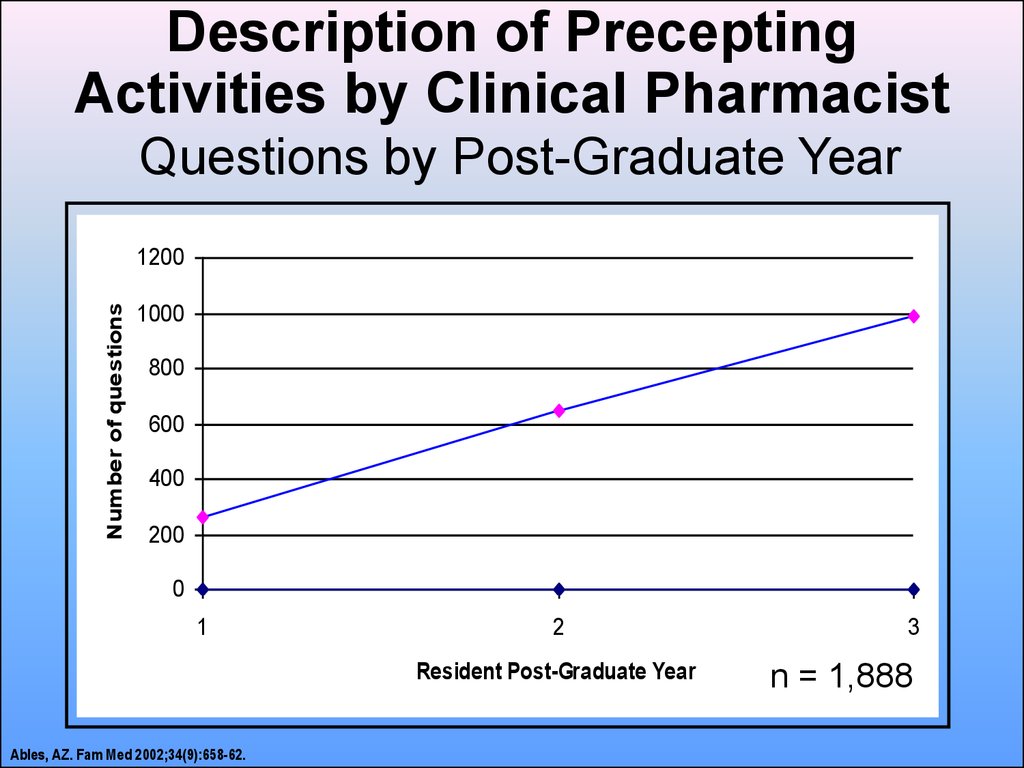
17. Description of Precepting Activities by Clinical Pharmacist Questions by Post-Graduate Year
Number of questions1200
1000
800
600
400
200
0
1
2
Resident Post-Graduate Year
Ables, AZ. Fam Med 2002;34(9):658-62.
3
n = 1,888
18. Other Clinical Pharmacist Responsibilities
Scholarly ActivitiesClinical Research
Quality Improvement Projects
Publications
Administrative Activities
Resident recruitment
Residency committees
Library maintenance
Pharmaceutical representative interactions
Didactic / evaluative program coordination
19. Group-on Pharmacotherapy
• 2005 Curricular Recommendations forPharmacotherapy education
20. Our Residency Programs
University of Kansas Family MedicineJohn E. Delzell, Jr, MD, MSPH
• University-based department and residency program
• KU College of Pharmacy-located in Lawrence
• PharmDs work with residents in hospital Family Medicine
(& other) service
• No formal curriculum
• PharmD salary paid by COP and hospital
21. Our Residency Programs
Fort Collins Family Medicine ResidencyMichelle Hilaire, PharmD, CDE
• Community-based residency program
• University of Wyoming COP located in Laramie
• PharmD works with residents in FPC and another
PharmD who works with residents in the hospital
• Incorporated into existing residency curriculum
• PharmD salary paid by University of Wyoming COP
22. Our Residency Programs
University of Texas Health Sciences Centerat San Antonio
Oralia Bazaldua, PharmD & John M. Tovar, PharmD
• University-based department and residency
• University of TX COP located in Austin
• PharmDs work with residents in FPC & hospital
• There is a formal curriculum
• PharmD salaries paid by Hospital, FM Department &
COP
23. Our Residency Programs
UT / Saint Francis Family MedicineResidency Program
Jeremy Thomas, PharmD &, Andrea Franks PharmD
• Community-based, University run residency program
• University of Tennessee COP located in Memphis
• PharmDs work with residents in FPC and hospital
• There is a formal rotation
• PharmDs salaries paid by COP
24. Round Table Discussion
Curricular Elements• Pharmacotherapy rotation
Required or elective
• Didactics / conferences
• Precepting in Family Practice Center
• Journal Club
• Morning report
• Consultations
• Shadowing
• Other educational opportunities
25. Round Table Discussion
What are the funding models that are outthere?
• Hospital funding
• Department funding
• College of Pharmacy funding
• Joint arrangement
• LIMITED clinical revenue generated
26. Round Table Discussion
Actual Pay• Varies by institution
• Varies by experience of the pharmacist
• Varies by training (residency or fellowship
training, advanced certification, etc)

























 Медицина
Медицина