Похожие презентации:
Managing people. (Lecture 3)
1.
Foundation Year ProgramLecture 3:
Managing people
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2. Learning outcomes
Foundation Year ProgramLEARNING OUTCOMES
After this lecture you should be able to:
• Identify different types of motivating factors
• Define the concept of organizational structure
• Recall the role of management
• Acknowledge different types of leadership
styles, their advantages and disadvantages
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
3. Lecture content
Foundation Year ProgramLECTURE CONTENT
What makes people work. Motivation theories
Factors that motivate workers
The organizational structure
The role of management
Leadership styles
Getting to know your leadership style
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
4. Why work?
Foundation Year ProgramWHY WORK?
Money is needed to buy needs and wants;
Sense of security;
Social need (affiliation);
Self-importance (feeling important);
Job satisfaction (self-actualization).
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
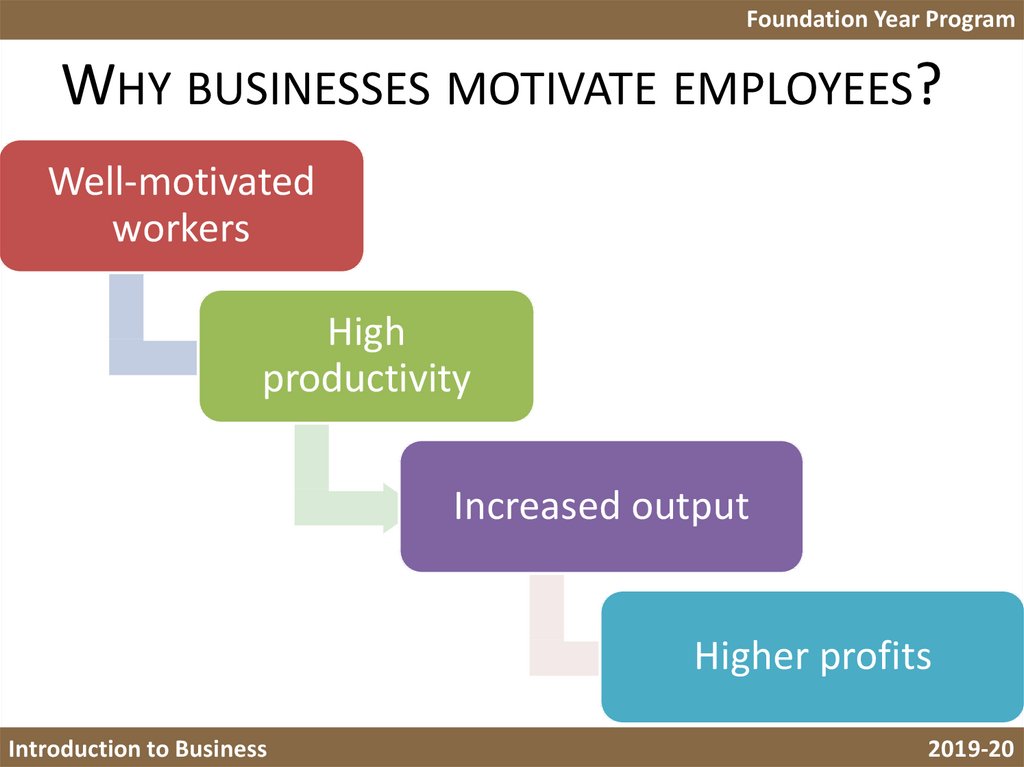
5. Why businesses motivate employees?
Foundation Year ProgramWHY BUSINESSES MOTIVATE EMPLOYEES?
Well-motivated
workers
High
productivity
Increased output
Higher profits
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
6. F.W. Taylor’s theory of motivation
Foundation Year ProgramF.W. TAYLOR’S THEORY OF MOTIVATION
• In 1880s a chief engineer introduced theory of
motivating employees solely by money.
• Employees were paid more for greater
physical output in factory.
• BUT, people are not machines! Too simplistic
approach
• Not all people can be motivated by higher
paychecks, and should be motivated
differently depending on…
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
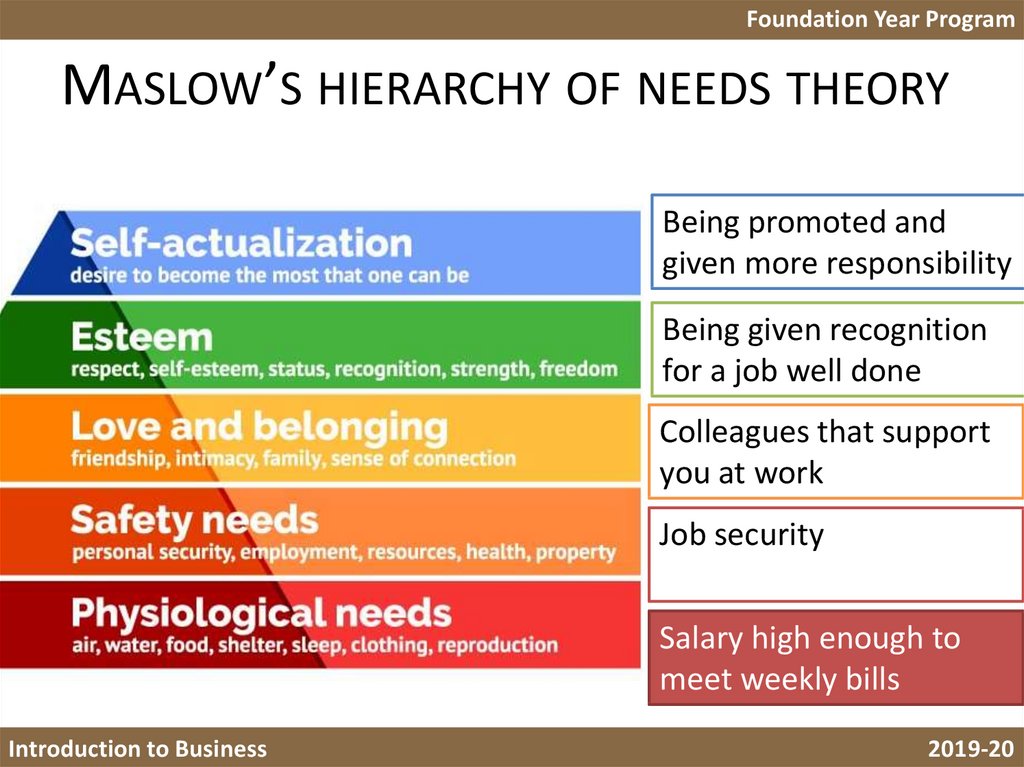
7. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory
Foundation Year ProgramMASLOW’S HIERARCHY OF NEEDS THEORY
Being promoted and
given more responsibility
Being given recognition
for a job well done
Colleagues that support
you at work
Job security
Salary high enough to
meet weekly bills
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
8. Herzberg’s theory of job satisfaction
Foundation Year ProgramHERZBERG’S THEORY OF JOB SATISFACTION
Hygiene
Factors that can demotivate if not present,
but do not actually
motivate employees to
work harder
Motivators
Factors that directly
motivate people to work
harder
Introduction to Business
• Financial rewards;
• Working conditions;
• Appropriate supervision
and policies.
• Job enrichment;
• Job empowerment.
2019-20
2018-19
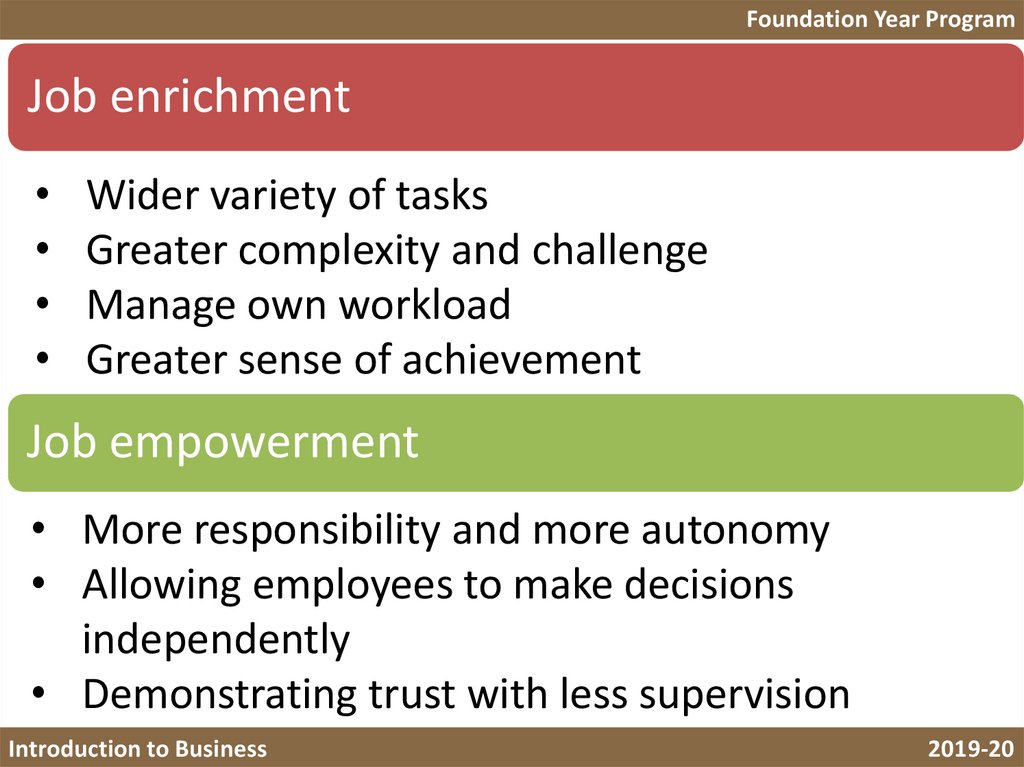
9.
Foundation Year ProgramJob enrichment
Wider variety of tasks
Greater complexity and challenge
Manage own workload
Greater sense of achievement
Job empowerment
• More responsibility and more autonomy
• Allowing employees to make decisions
independently
• Demonstrating trust with less supervision
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
10. Typical case study at work
Foundation Year ProgramTypical case study at work
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
11. Another interesting story by Mayo
Foundation Year ProgramANOTHER INTERESTING STORY BY MAYO
• The Hawthorne experiments were designed to study the effect
of shop-floor lighting on worker productivity at a telephone
parts factory in Hawthorne. However, the researchers were
perplexed to find that productivity improved, not just when
the lighting was improved, but also when the lighting was
diminished. Productivity improved whenever changes were
made in other variables such as working hours and rest
breaks. The researchers concluded that the workers’
productivity was not being affected by the changes in working
conditions, but rather by the fact that someone was
concerned enough about their working conditions to conduct
an experiment on it.
www.investopedia.com
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
12.
Foundation Year Program• Why do you think the workers might not be
happy in their jobs?
• Suggest ways the management might increase
the motivation of their employees.
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
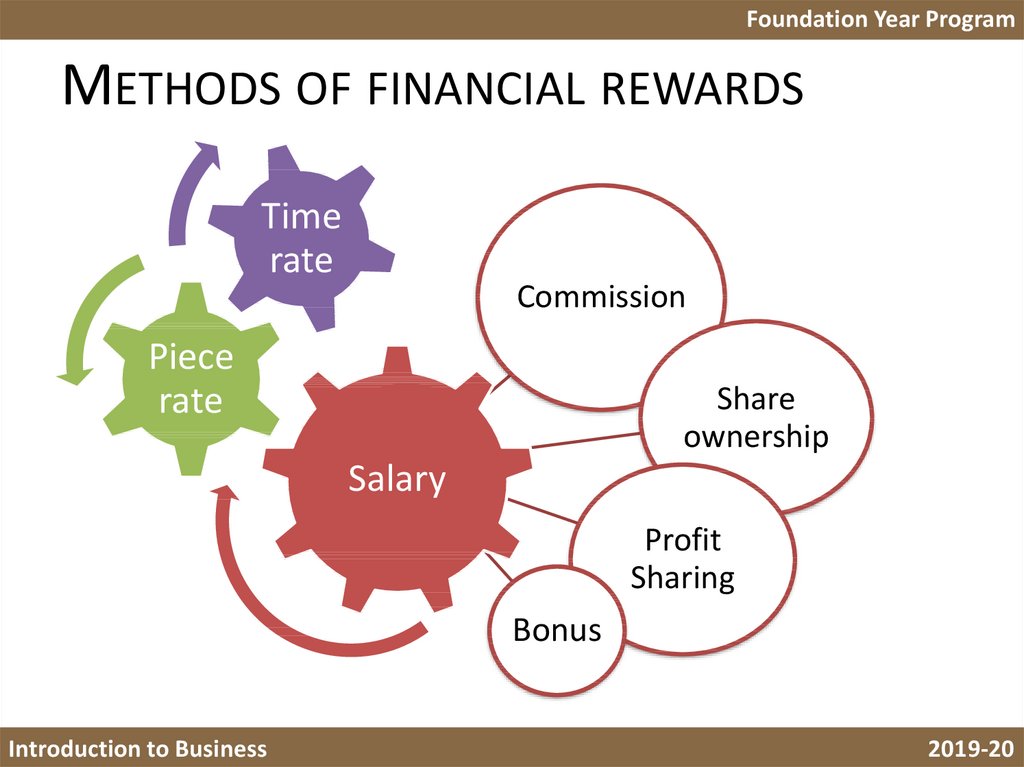
13. Methods of financial rewards
Foundation Year ProgramMETHODS OF FINANCIAL REWARDS
Time
rate
Commission
Piece
rate
Share
ownership
Salary
Profit
Sharing
Bonus
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
14.
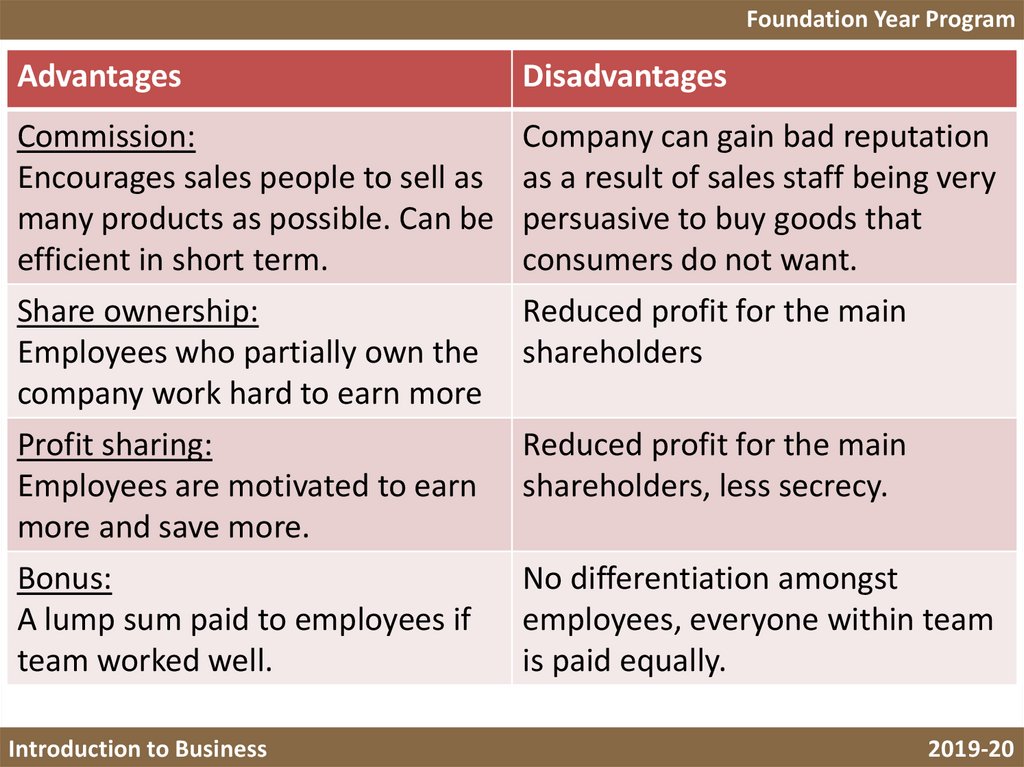
Foundation Year ProgramAdvantages
Disadvantages
Commission:
Encourages sales people to sell as
many products as possible. Can be
efficient in short term.
Share ownership:
Employees who partially own the
company work hard to earn more
Profit sharing:
Employees are motivated to earn
more and save more.
Bonus:
A lump sum paid to employees if
team worked well.
Company can gain bad reputation
as a result of sales staff being very
persuasive to buy goods that
consumers do not want.
Reduced profit for the main
shareholders
Introduction to Business
Reduced profit for the main
shareholders, less secrecy.
No differentiation amongst
employees, everyone within team
is paid equally.
2019-20
2018-19
15. What is organizational structure?
Foundation Year ProgramWHAT IS ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE?
Organizational structure refers to the levels of
management and division of responsibilities
within an organization.
• Why businesses need hierarchy and division of
roles?
• To efficiently
perform different
pieces of work
utilizing best abilities
of participants
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
16.
Foundation Year ProgramArdak’s bakery has expanded and there are certain
tasks to be done, now she needs:
Operations manager
Human resources manager
Marketing and sales manager
Finance and accounting manager
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
17.
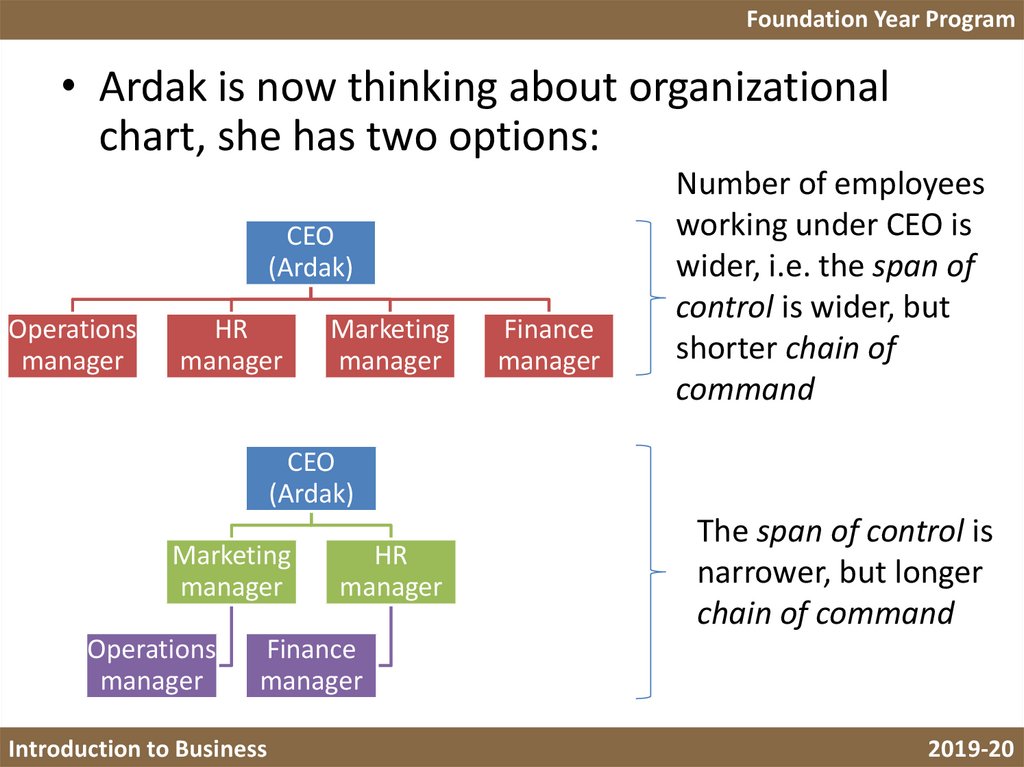
Foundation Year Program• Ardak is now thinking about organizational
chart, she has two options:
CEO
(Ardak)
Operations
manager
HR
manager
Marketing
manager
Finance
manager
Number of employees
working under CEO is
wider, i.e. the span of
control is wider, but
shorter chain of
command
CEO
(Ardak)
Marketing
manager
Operations
manager
HR
manager
The span of control is
narrower, but longer
chain of command
Finance
manager
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
18.
Foundation Year ProgramCEO
Operations
manager
HR
manager
Marketing
manager
Finance
manager
Short chains of commands
Advantages
Disadvantages
Quicker and more accurate
communication
Less hierarchy, easier to identify and
fix problems
Span of control is wider, which
means more responsibility for each
employee
Potential loss of control over
employees due to increased
responsibility and duties
More satisfaction from the job
thanks to more trust with the wider
span of control
Wider span of control may incur
higher risks of making mistakes by
subordinates
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
19. The role of management
Foundation Year ProgramTHE ROLE OF MANAGEMENT
Planning (strategy)
Organizing (delegate)
Coordinating (bring together)
Commanding (lead)
Controlling (evaluate)
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
20. Delegation
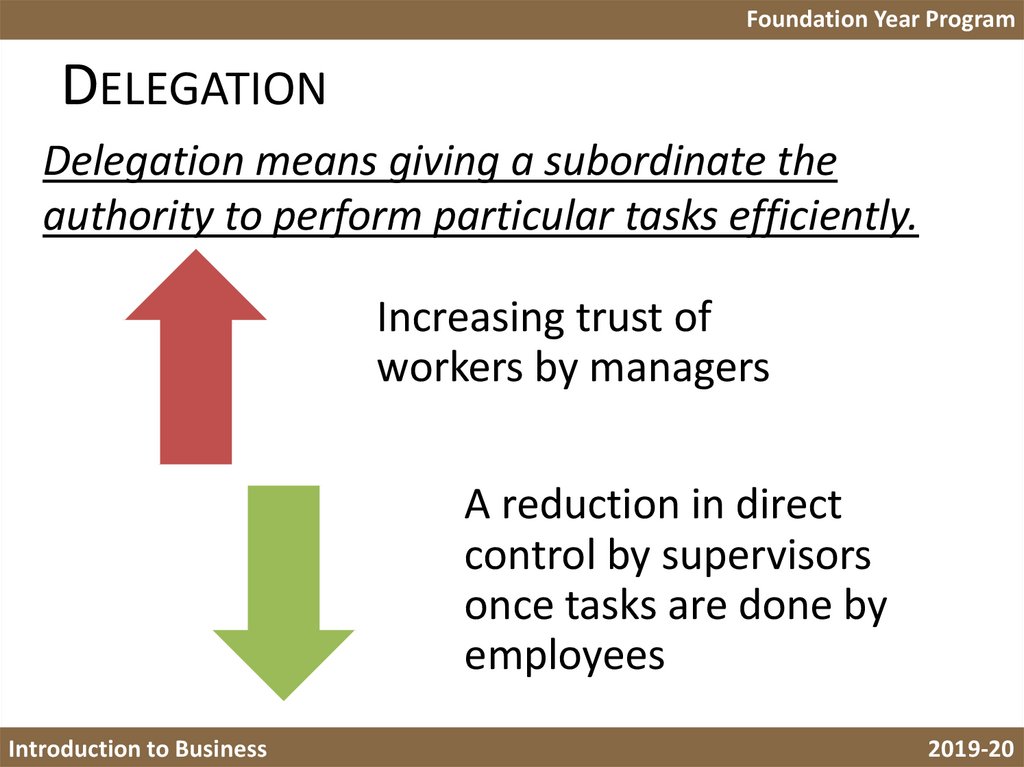
Foundation Year ProgramDELEGATION
Delegation means giving a subordinate the
authority to perform particular tasks efficiently.
Increasing trust of
workers by managers
A reduction in direct
control by supervisors
once tasks are done by
employees
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
21. Leadership styles
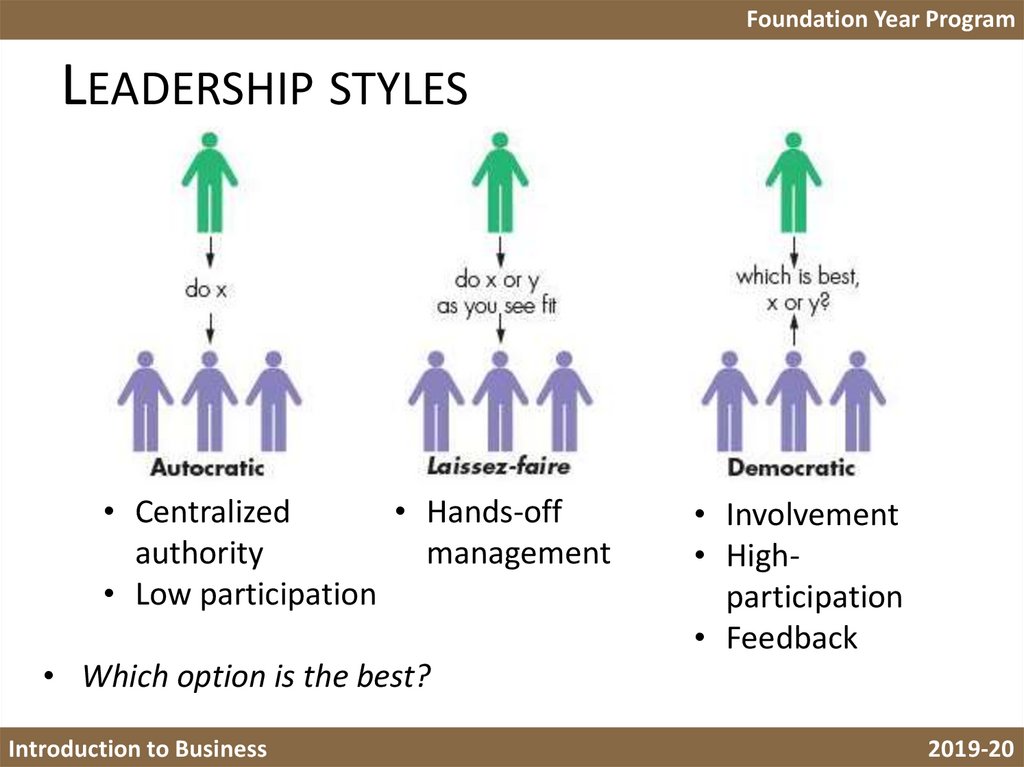
Foundation Year ProgramLEADERSHIP STYLES
• Centralized
• Hands-off
authority
management
• Low participation
• Which option is the best?
Introduction to Business
• Involvement
• Highparticipation
• Feedback
2019-20
2018-19
22.
Foundation Year Program• Autocratic leader makes all of the decisions on the production floor, leaving
no room for input from workers. This type of leadership works well with
unskilled workers performing work that does not require team involvement.
Autocratic leadership is difficult to work under and employees may feel
resentful. Skilled workers who can work with little supervision do not perform
well under an autocratic leader.
• Laissez-faire leadership style is the opposite of an autocratic approach. The
laissez-faire leader leaves workers to make decisions on their own and only
updates the team on progress. Highly skilled workers succeed under a laissezfaire leadership style. The hands-off approach requires little control from the
manager or supervisor, but it is important that leaders monitor work progress
to ensure the team meets goals.
• Democratic leadership style is a combination of autocratic and laissez-faire
approaches. The leader requires input from workers, but ultimately makes the
final decisions for the group. This style can work well with skilled and
unskilled workers. Unskilled workers have an opportunity to provide input
while still receiving direction and supervision. Working with employees
improves morale and gives workers a sense of satisfaction on the job.
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
23. Case study
Foundation Year ProgramCASE STUDY
• Which do you think will be the best leadership style for Bill
and his managers to use? Explain your answer
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
24.
Foundation Year Program• Getting to know your leadership style QUIZ!
• Follow the link:
https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/leadership-stylequiz.htm
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19
25.
Foundation Year ProgramReference list:
1) Borrington, K. and Stimpson, P.
(2013). Cambridge Igcse Business Studies. 4th
ed. London: Hodder Education, Ch. 6-7
Introduction to Business
2019-20
2018-19

















 Менеджмент
Менеджмент








