Похожие презентации:
Inheritance, Variation and Evolution Variation
1.
Inheritance, Variation and EvolutionVariation
2.
Learning Objective• To voyage on the HMS Beagle and describe the variation that you find.
Targeting Assessment Objectives AO1, AO2 and AO3.
Success Criteria
• To identify variation between individuals in a species.
• To describe whether variation is due to environmental or genetic causes.
• To explain how variation arises.
3.
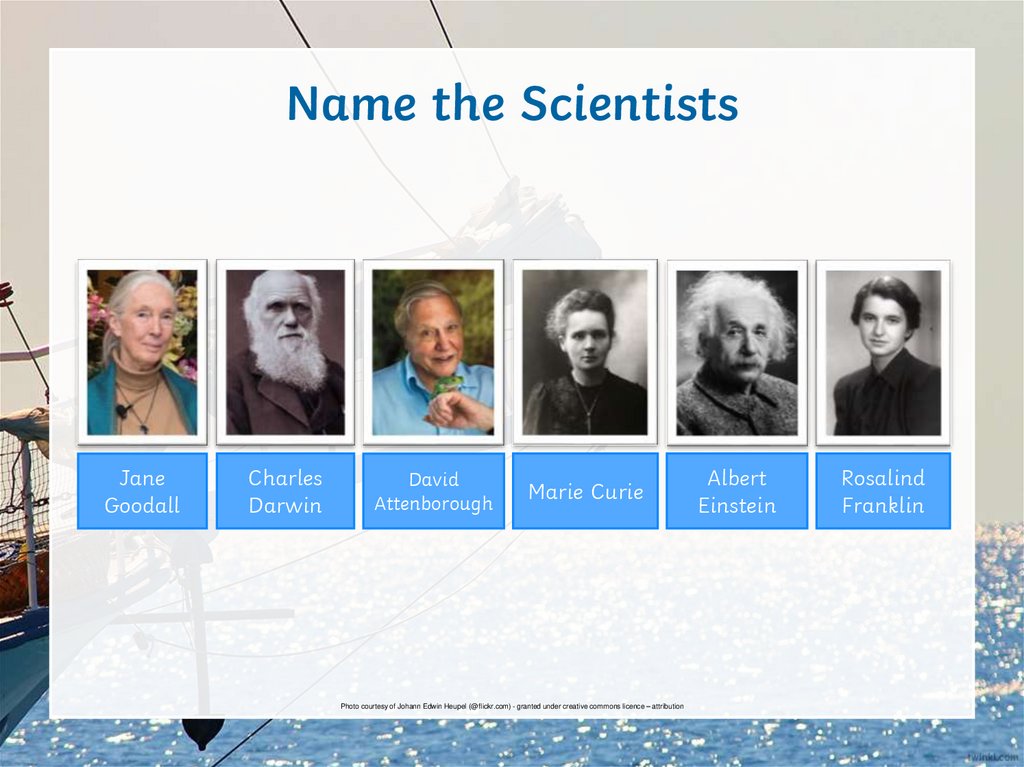
Name the ScientistsJane
Goodall
Charles
Darwin
David
Attenborough
Marie Curie
Photo courtesy of Johann Edwin Heupel (@flickr.com) - granted under creative commons licence – attribution
Albert
Einstein
Rosalind
Franklin
4.
Charles Darwin: True or FalseDarwin’s mother died when he was 8 years old
and he was raised by his 3 older sisters.
Darwin was condemned by his headmaster for
studying chemistry.
He studied medicine at Edinburgh University.
All true!
He spent a lot of his time at university collecting
sea slugs on the shoreline.
He hated studying anatomy.
He was educated in theology at Christ Church,
Cambridge University.
He set sale for a voyage on the HMS Beagle in
December 1831, at the age of 22.
5.
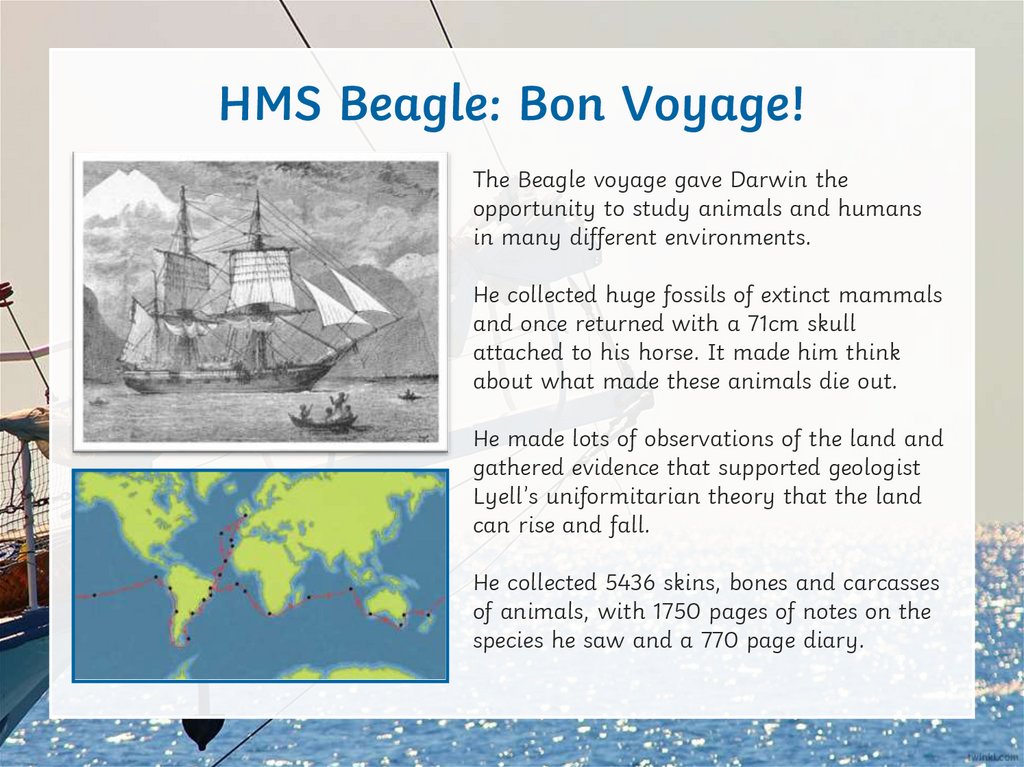
HMS Beagle: Bon Voyage!The Beagle voyage gave Darwin the
opportunity to study animals and humans
in many different environments.
He collected huge fossils of extinct mammals
and once returned with a 71cm skull
attached to his horse. It made him think
about what made these animals die out.
He made lots of observations of the land and
gathered evidence that supported geologist
Lyell’s uniformitarian theory that the land
can rise and fall.
He collected 5436 skins, bones and carcasses
of animals, with 1750 pages of notes on the
species he saw and a 770 page diary.
6.
Bon Voyage!Your bags are packed and you’re on board the HMS
Beagle, ready to help Darwin to collect information
about the species you encounter.
In each place you need to record the features of the
environment around you.
Darwin has pointed out some of the
interesting creatures in each place,
record as much information about
the animals as you can.
7.
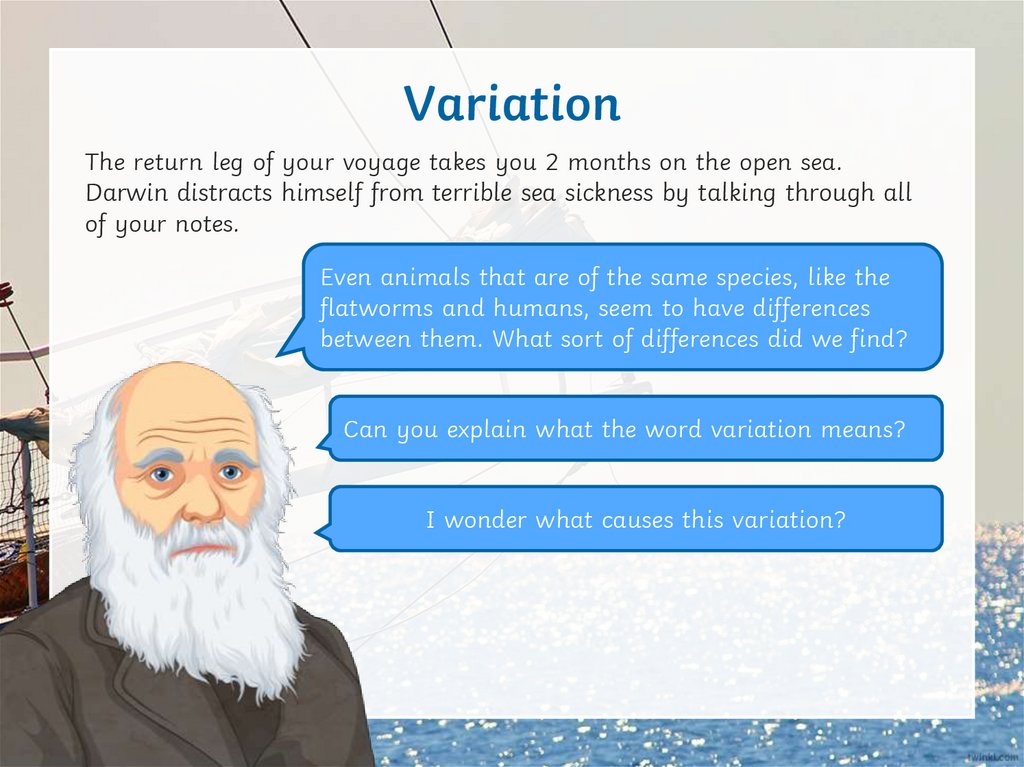
VariationThe return leg of your voyage takes you 2 months on the open sea.
Darwin distracts himself from terrible sea sickness by talking through all
of your notes.
Even animals that are of the same species, like the
flatworms and humans, seem to have differences
between them. What sort of differences did we find?
Can you explain what the word variation means?
I wonder what causes this variation?
8.
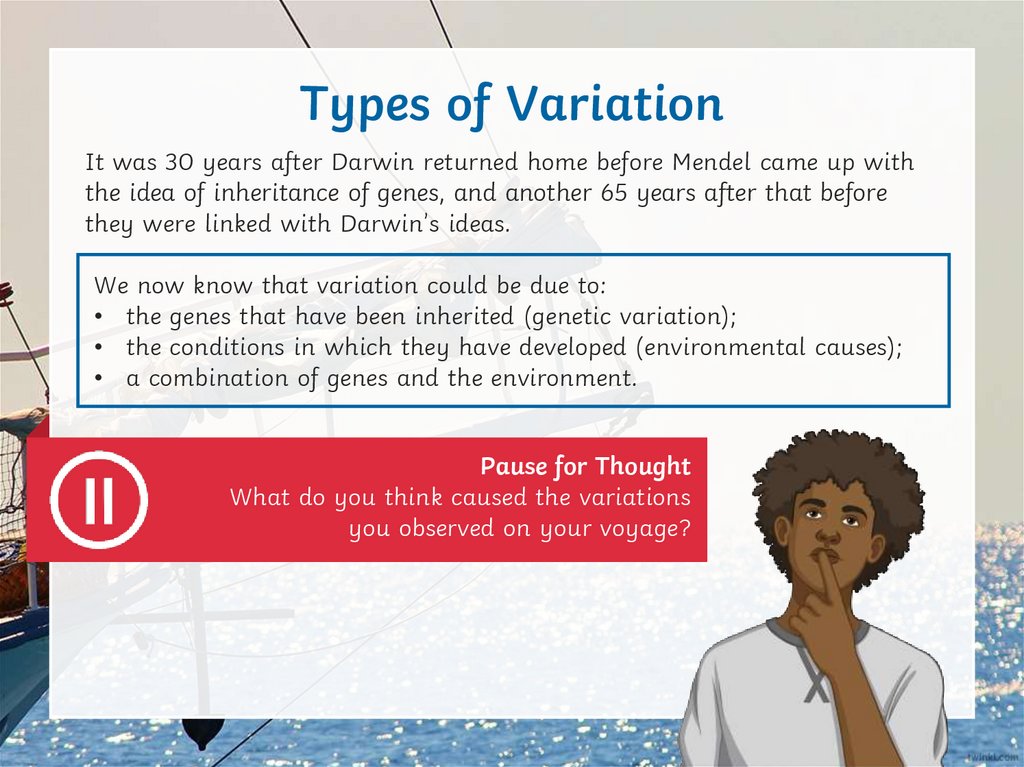
Types of VariationIt was 30 years after Darwin returned home before Mendel came up with
the idea of inheritance of genes, and another 65 years after that before
they were linked with Darwin’s ideas.
We now know that variation could be due to:
• the genes that have been inherited (genetic variation);
• the conditions in which they have developed (environmental causes);
• a combination of genes and the environment.
Pause for Thought
What do you think caused the variations
you observed on your voyage?
9.
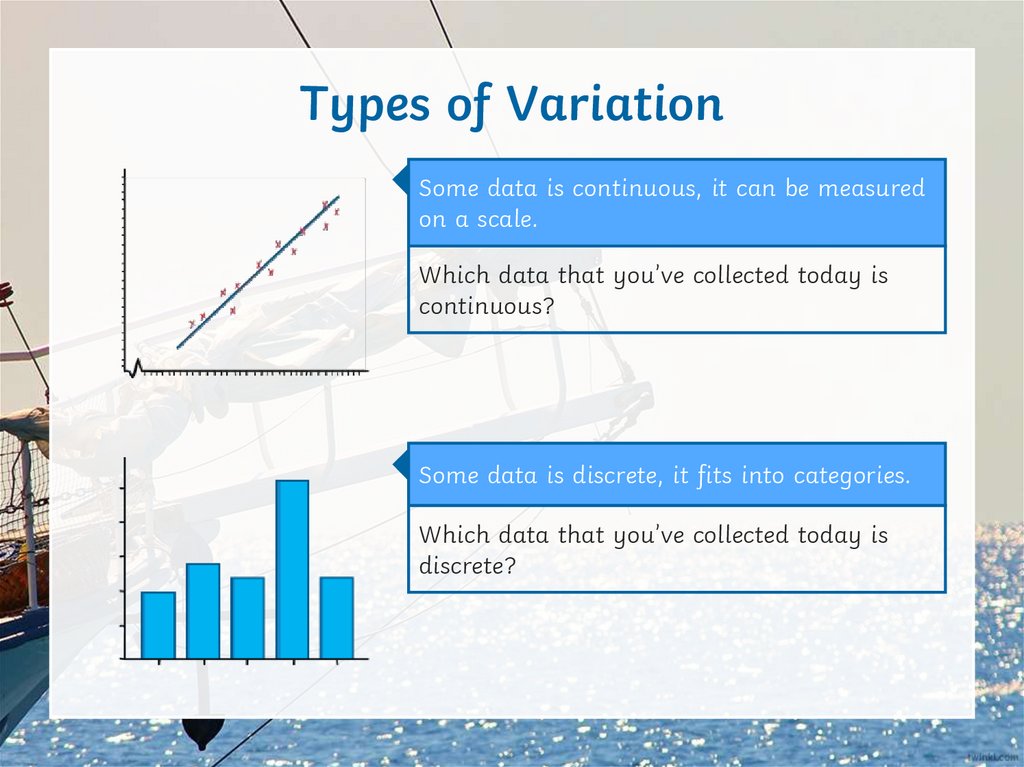
Types of VariationSome data is continuous, it can be measured
on a scale.
Which data that you’ve collected today is
continuous?
Some data is discrete, it fits into categories.
Which data that you’ve collected today is
discrete?
10.
New VariationMutations are
changes in the
DNA, they occur
continuously.
Most have no
effect on the
phenotype.
If the new
phenotype is
suited to the
environment, it
can lead to a
change in the
species.
Very rarely
one will
change the
phenotype.
11.
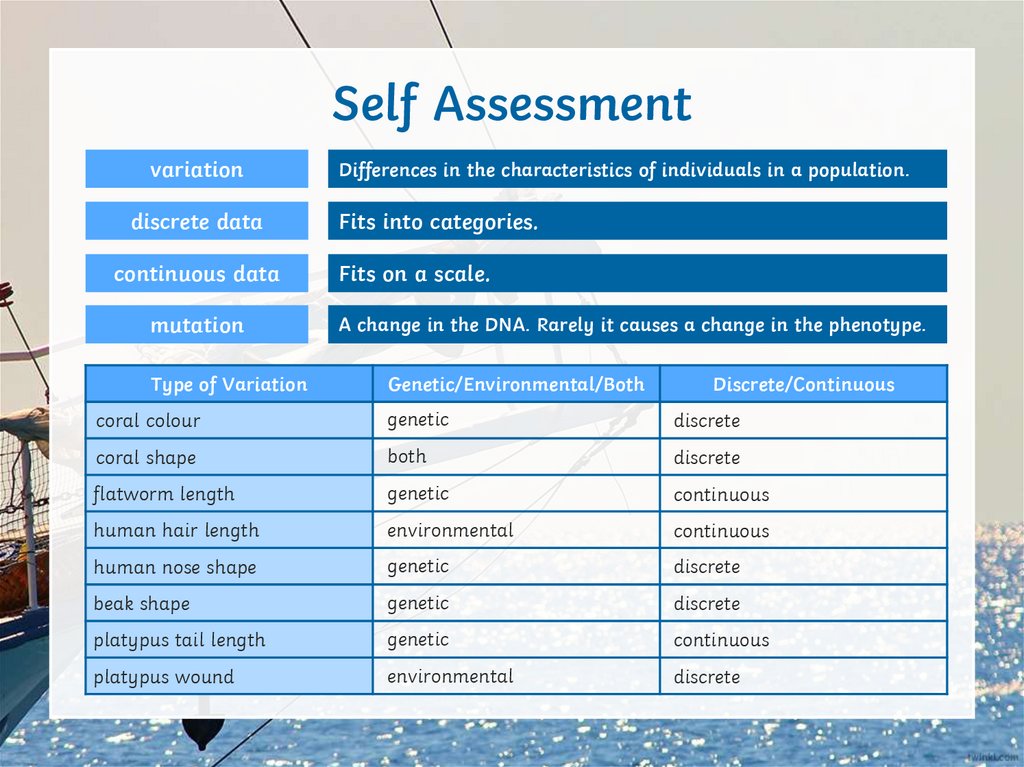
Self Assessmentvariation
discrete data
continuous data
mutation
Type of Variation
Differences in the characteristics of individuals in a population.
Fits into categories.
Fits on a scale.
A change in the DNA. Rarely it causes a change in the phenotype.
Genetic/Environmental/Both
Discrete/Continuous
coral colour
genetic
discrete
coral shape
both
discrete
flatworm length
genetic
continuous
human hair length
environmental
continuous
human nose shape
genetic
discrete
beak shape
genetic
discrete
platypus tail length
genetic
continuous
platypus wound
environmental
discrete
12.
Exam Question PracticeThe picture shows a horse
and its foals (babies), they
have similar characteristics.
How is the information for a characteristic passed on? genes
These foals may not grow up to be the same height, give two reasons why.
They may have inherited different genes from their parents (genetic cause).
They may not have the same supply of food (environmental cause).







 Биология
Биология








