Похожие презентации:
Brainstem. Cerebellum. Reticular formation
1.
V.I.Vernadsky Federal University Medical Academy named after S.I. GeorgievskyHuman Anatomy Department ( Head of the Dpt. Prof. S.A. Kutia)
BRAINSTEM. CEREBELLUM.
RETICULAR FORMATION.
II semester
Lecturer: Associate Professor,
Lilia R. Shaymardanova, M.D., Ph.D.
2.
Germany, Max PlanckInstitute for Brain Research
The Institute of
neurophysiology, Russian
Academy of Sciences
The Zanvyl Krieger Mind/Brain
Institute, The Johns Hopkins
University
The European Brain
Research Institute in
Rome
The Paul-FlechsigInstitute for Brain
Research , institute of
Leipzig University
Hertie Institute for Clinical
Brain Research
3.
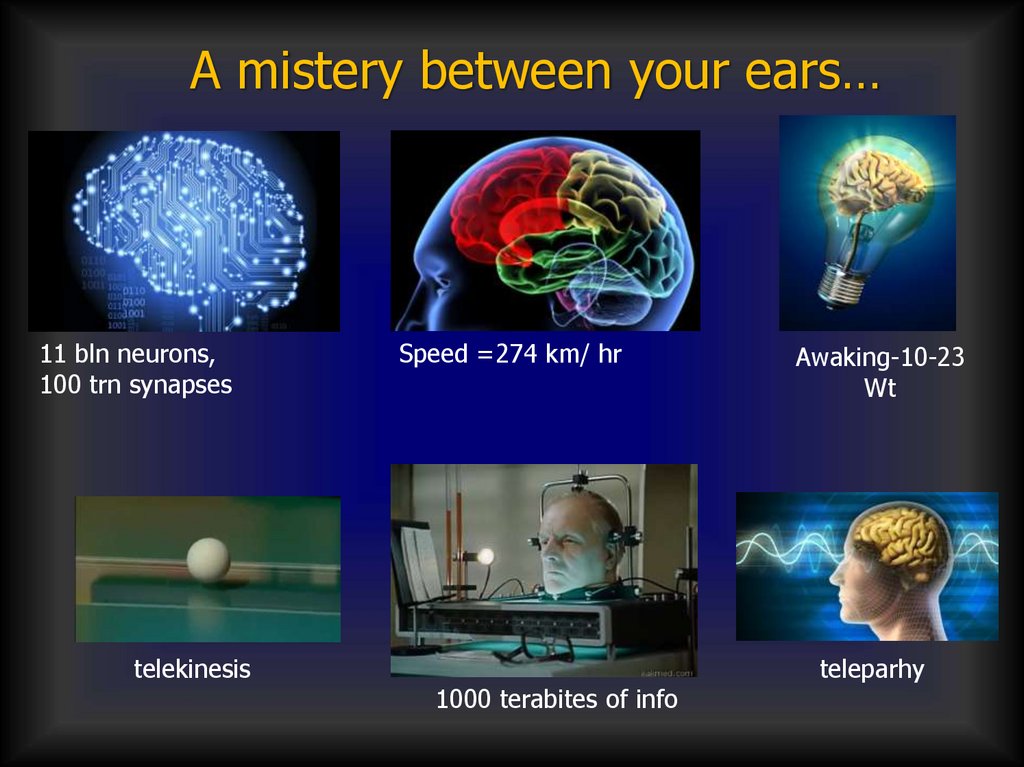
A mistery between your ears…11 bln neurons,
100 trn synapses
telekinesis
Speed =274 km/ hr
1000 terabites of info
Awaking-10-23
Wt
teleparhy
4.
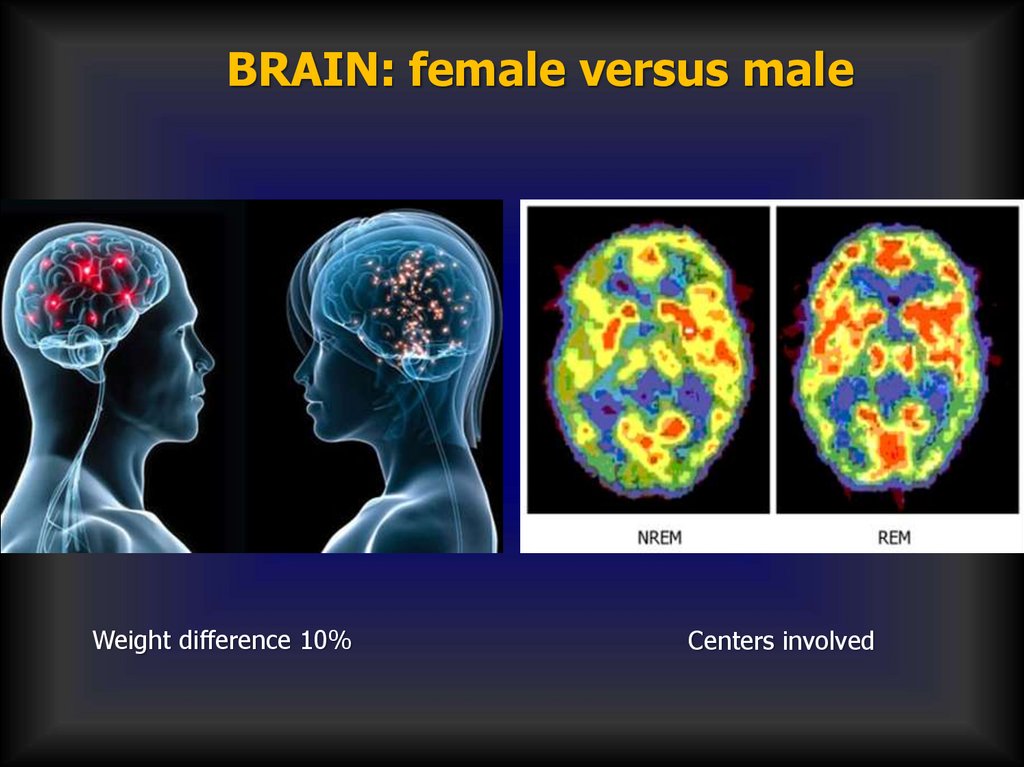
BRAIN: female versus maleWeight difference 10%
Centers involved
5.
6.
7.
8.
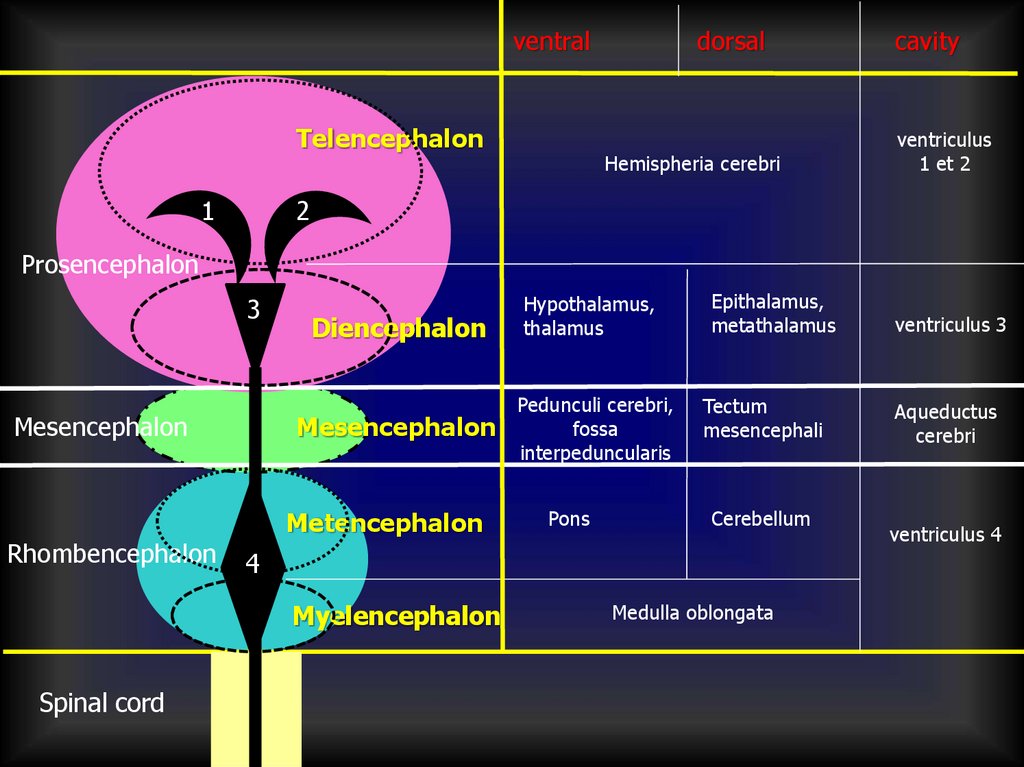
ventralTelencephalon
1
dorsal
Hemispheria cerebri
cavity
ventriculus
1 et 2
2
Prosencephalon
3
Mesencephalon
Rhombencephalon
Diencephalon
Mesencephalon
Metencephalon
Pedunculi cerebri,
fossa
interpeduncularis
Pons
Epithalamus,
metathalamus
Tectum
mesencephali
Cerebellum
4
Myelencephalon
Spinal cord
Hypothalamus,
thalamus
Medulla oblongata
ventriculus 3
Aqueductus
cerebri
ventriculus 4
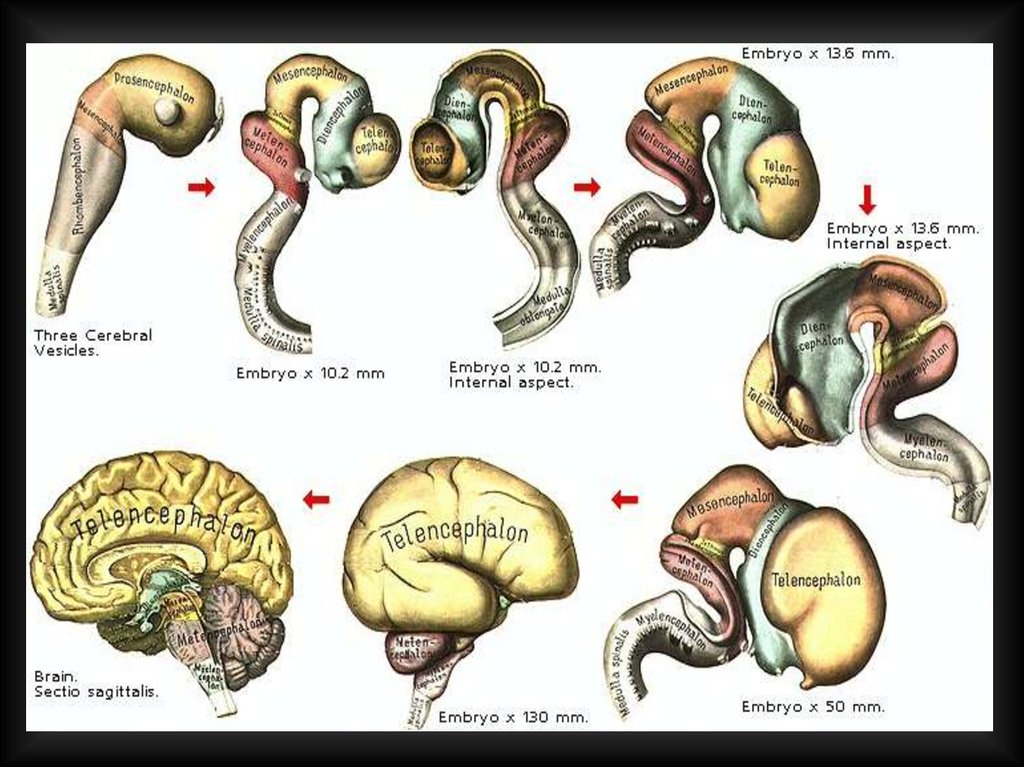
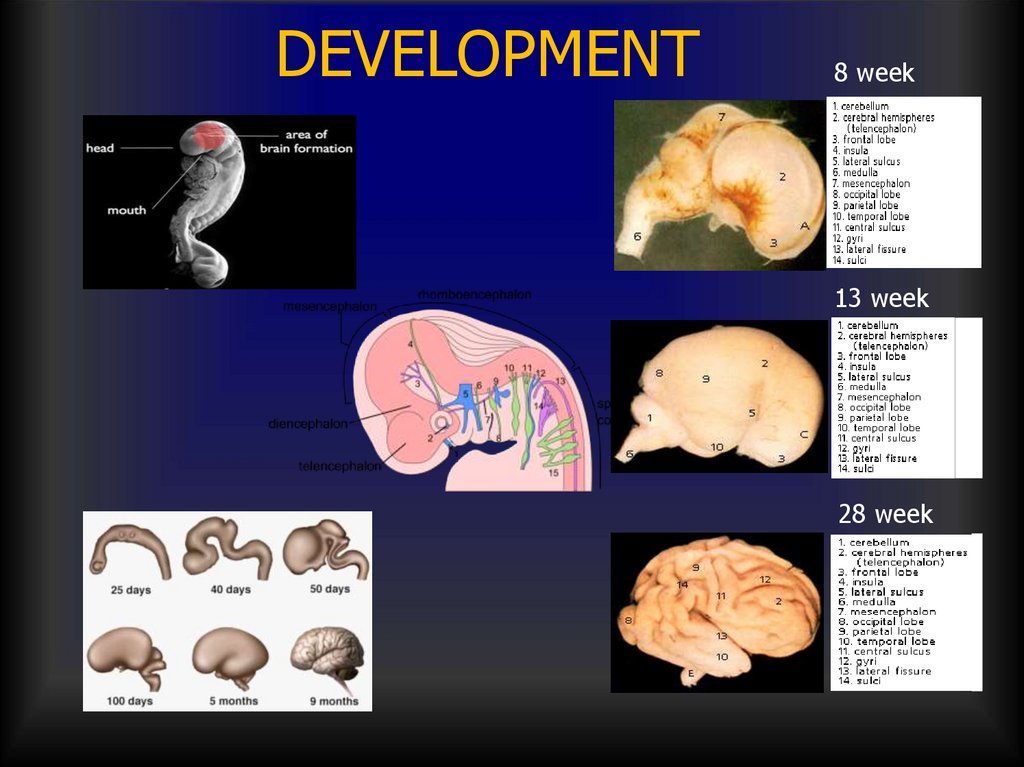
9. DEVELOPMENT
8 week13 week
28 week
10. DEVELOPMENT
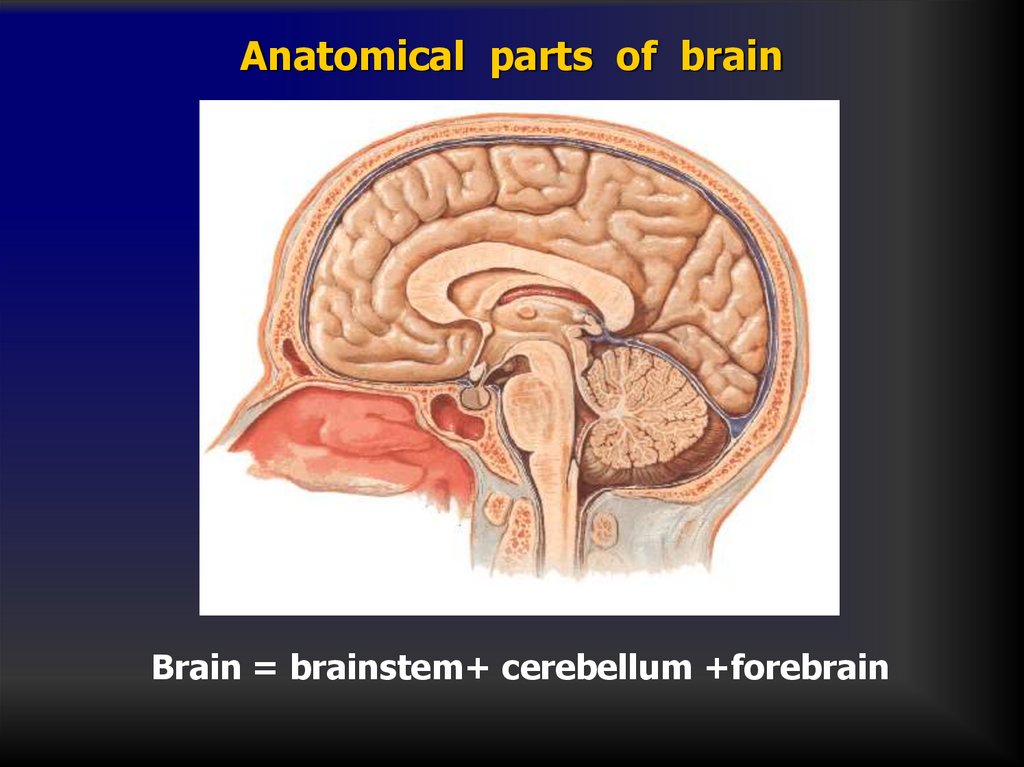
11. Anatomical parts of brain
Brain = brainstem+ cerebellum +forebrain12.
Plan of description of brain parts1. The name
2. Development
3. Boundaries
4. External view
- ventral view
- dorsal view
5. Internal structure
- gray matter
- white matter
13.
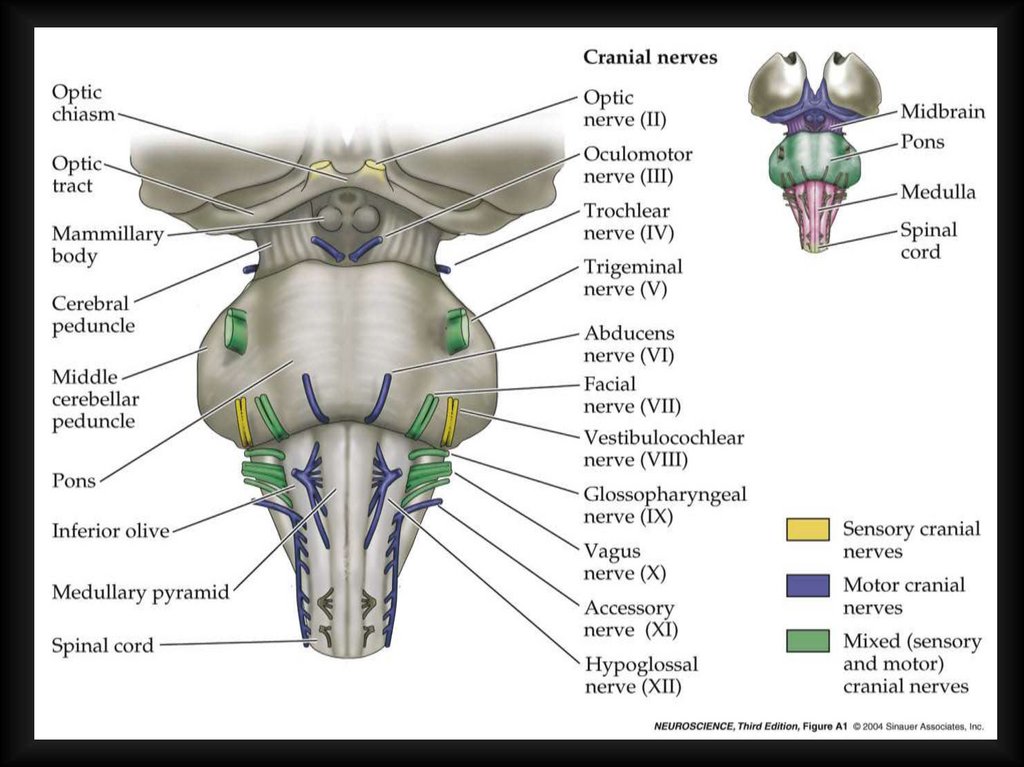
Brainstem14.
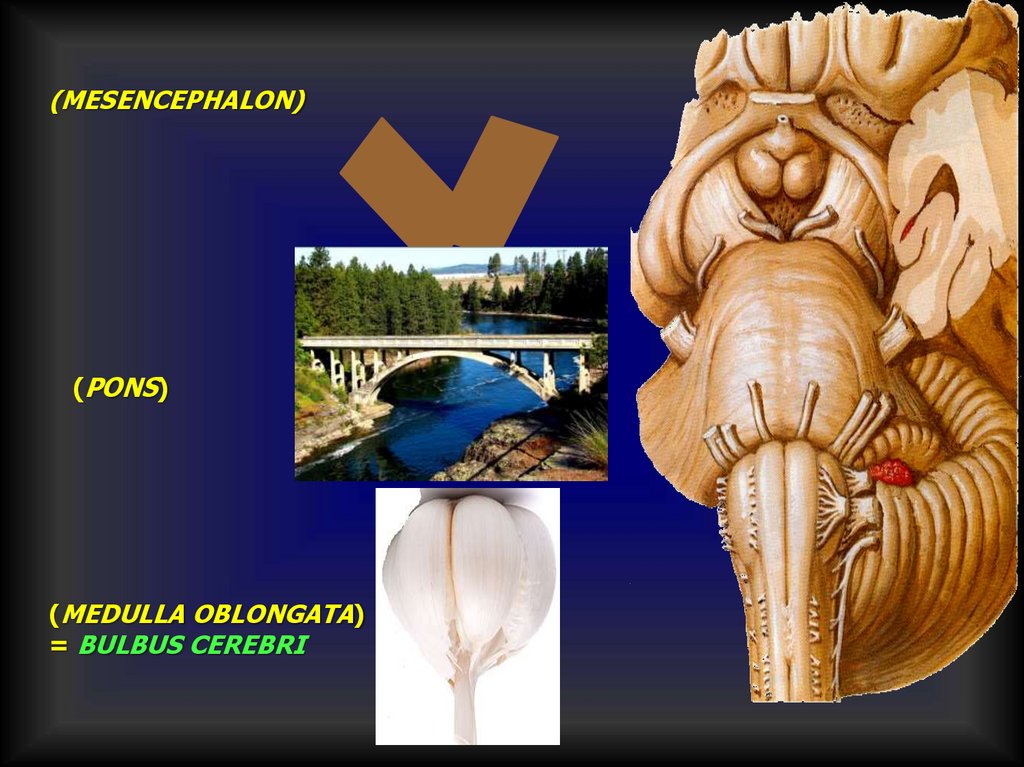
(MESENCEPHALON)(PONS)
(MEDULLA OBLONGATA)
= BULBUS CEREBRI
15.
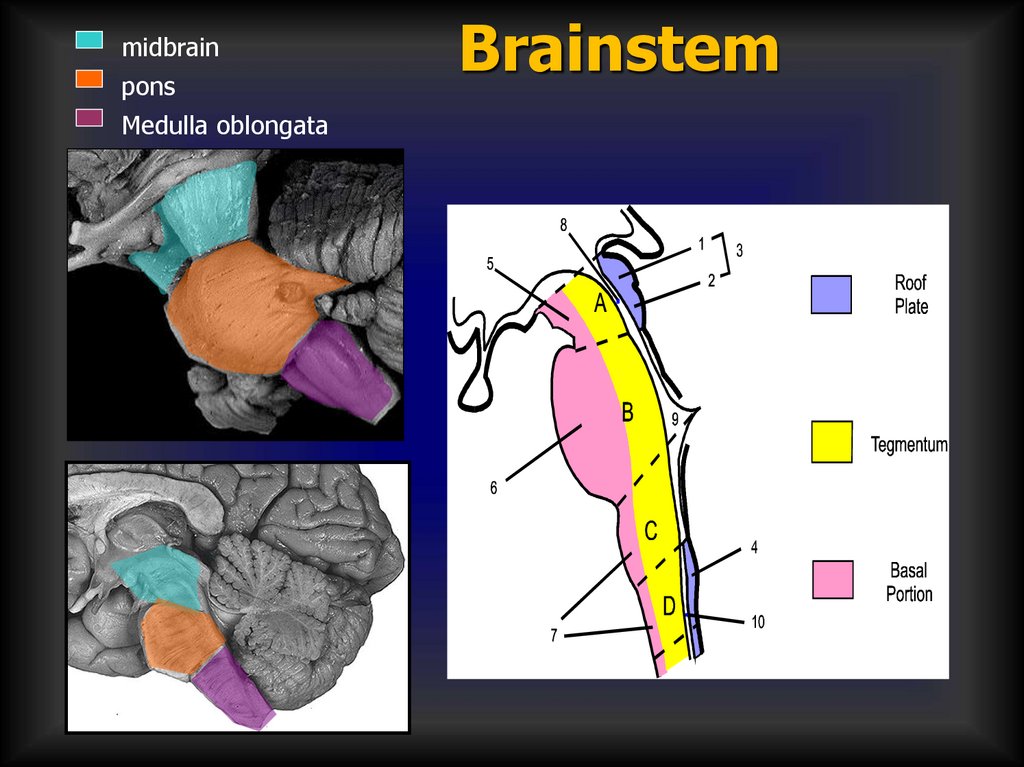
midbrainpons
Medulla oblongata
Brainstem
16.
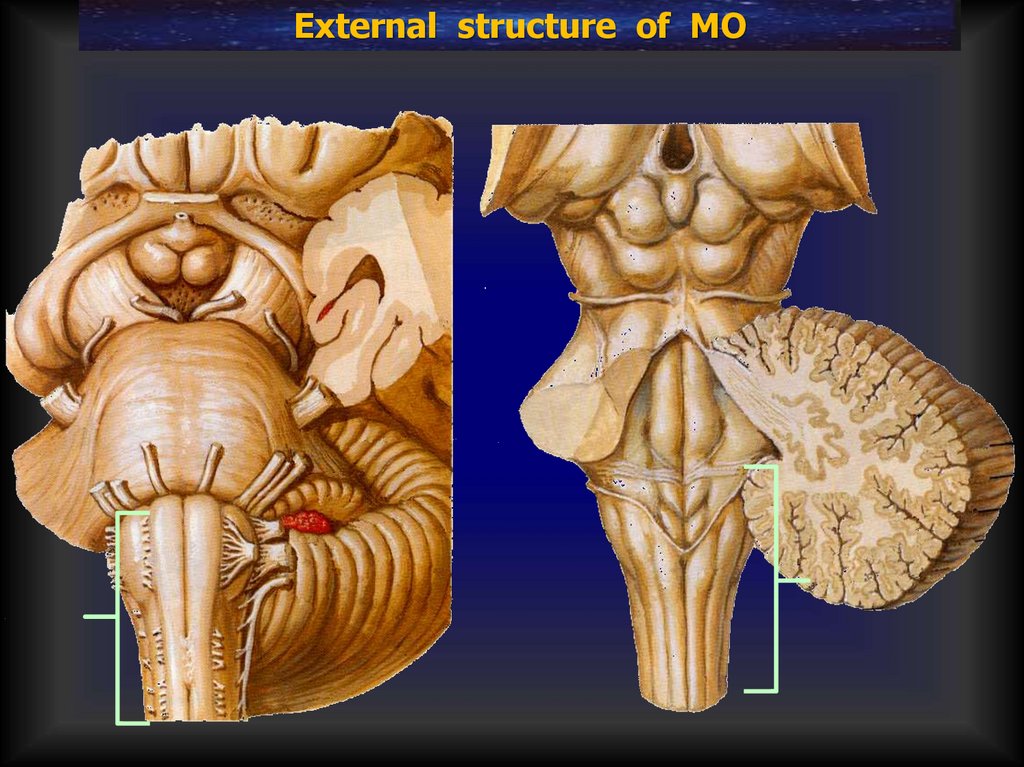
External structure of MO17.
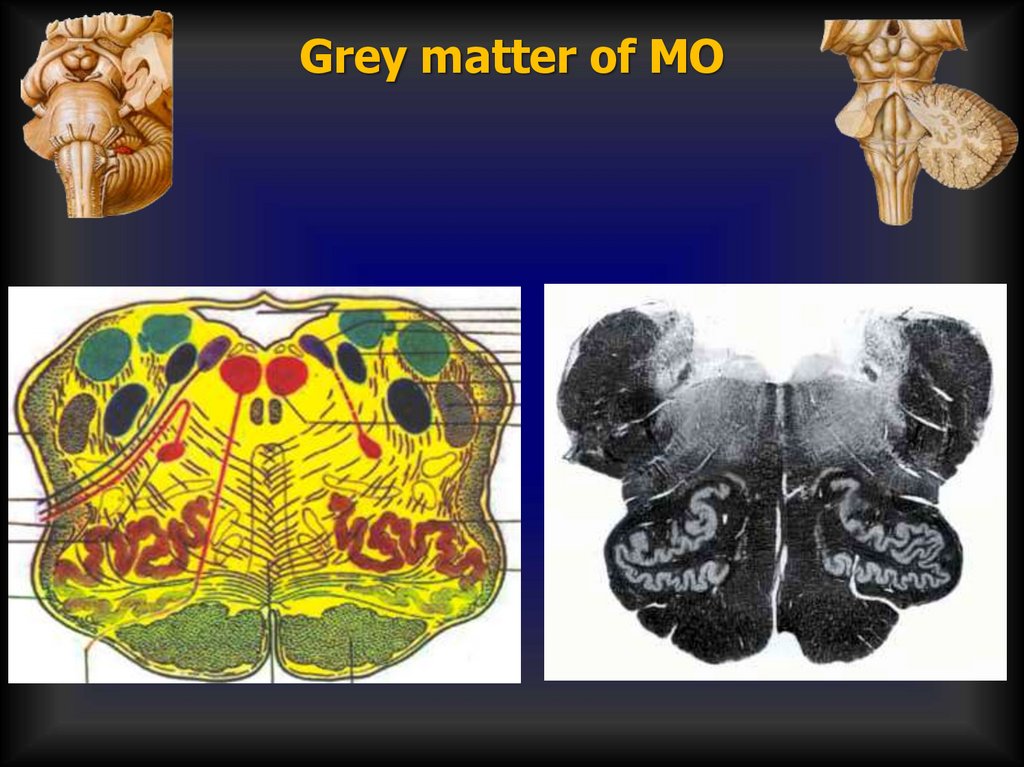
Grey matter of MO18.
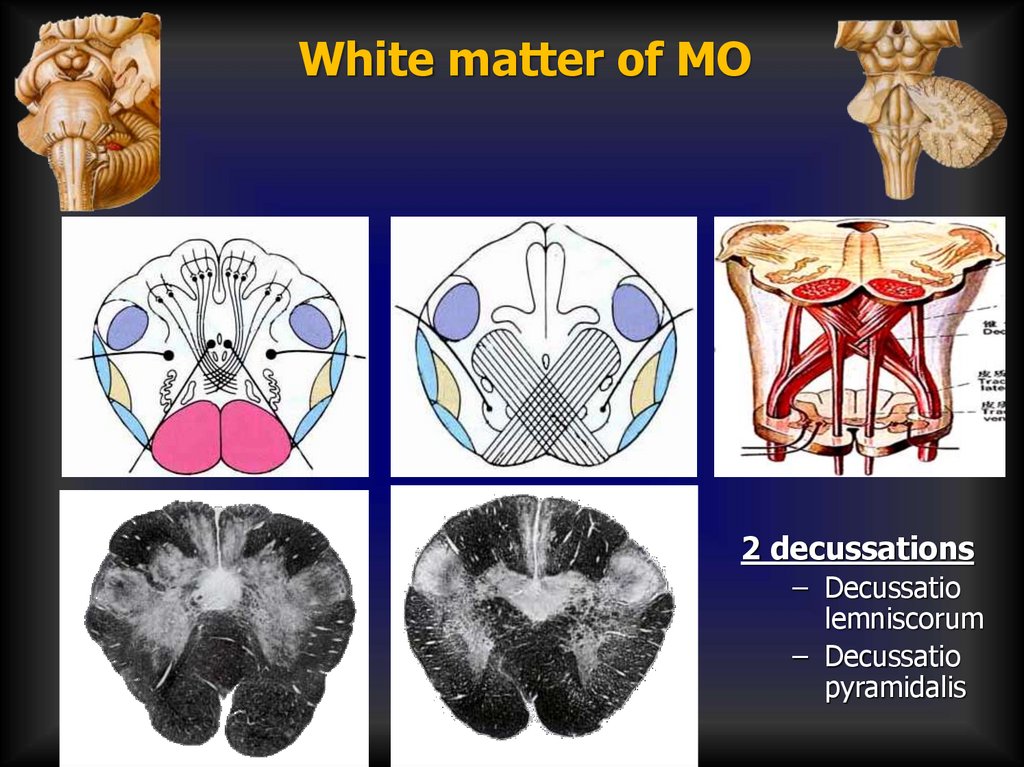
White matter of MO2 decussations
– Decussatio
lemniscorum
– Decussatio
pyramidalis
19.
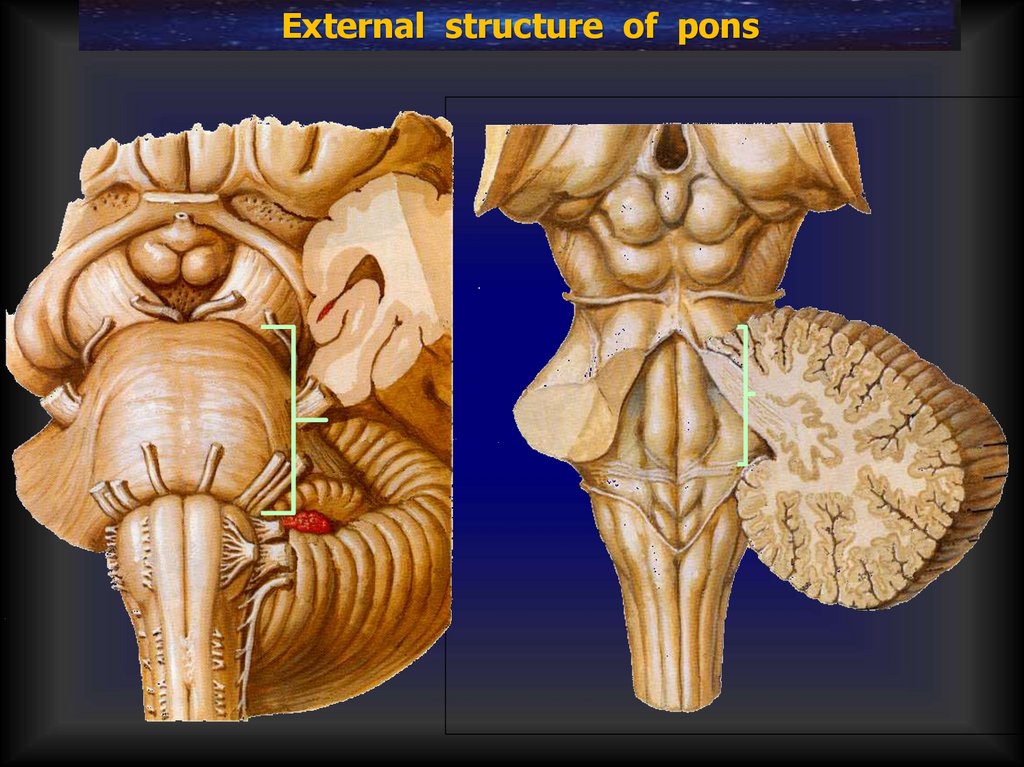
External structure of pons20.
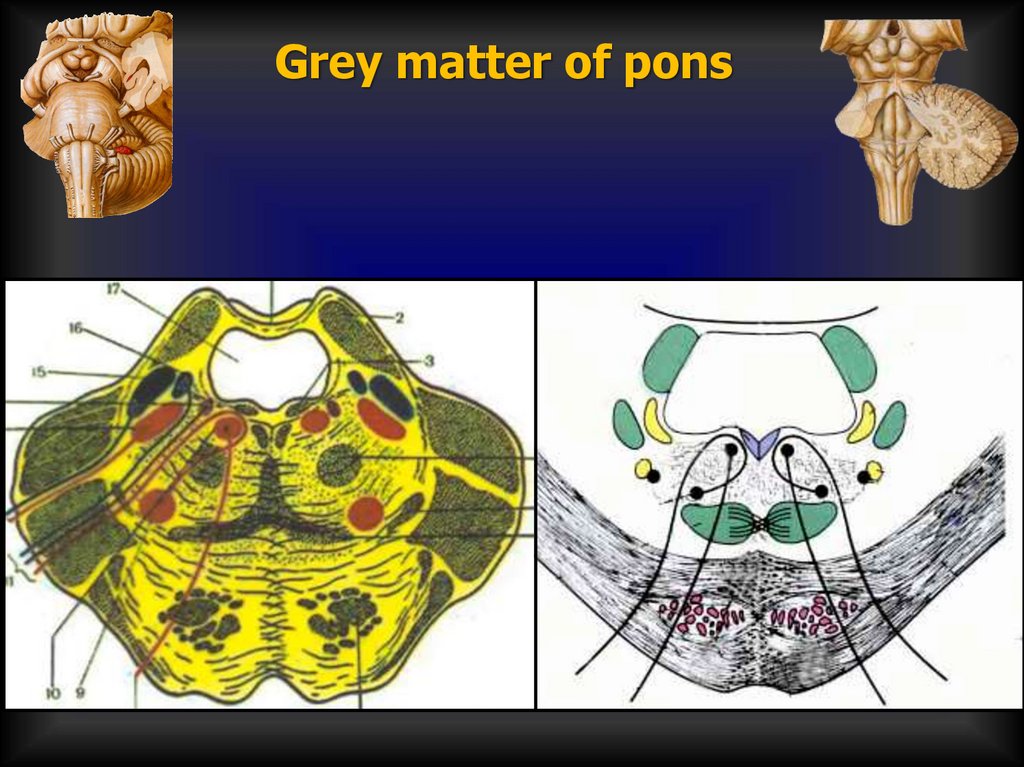
Grey matter of pons21.
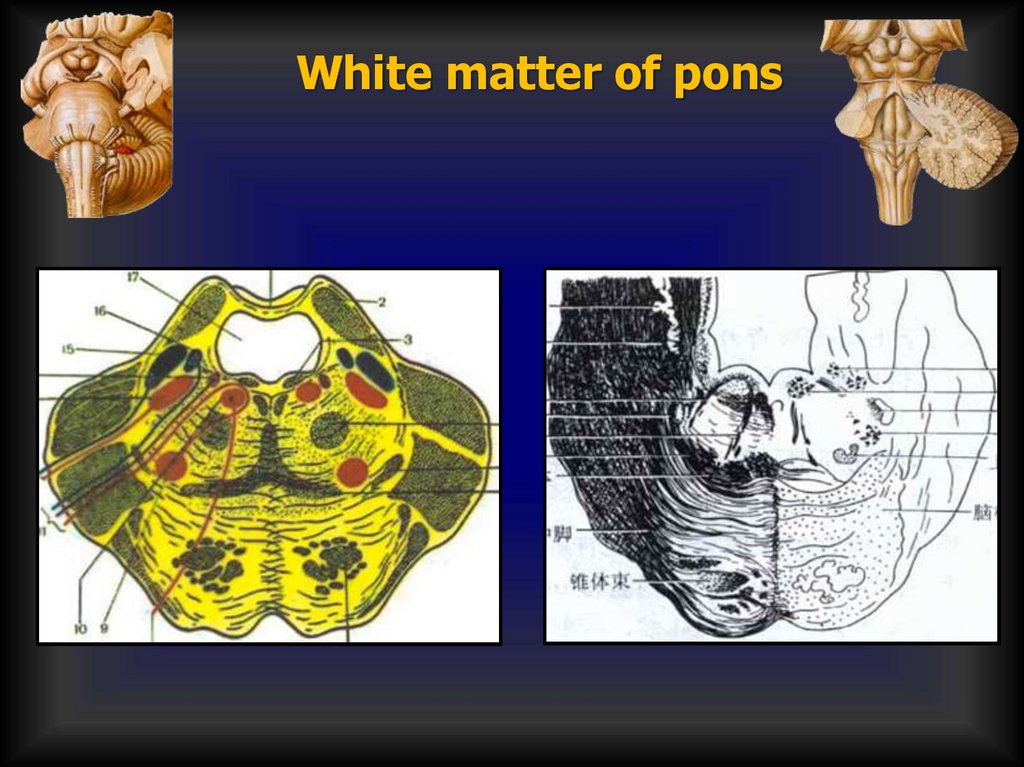
White matter of pons22.
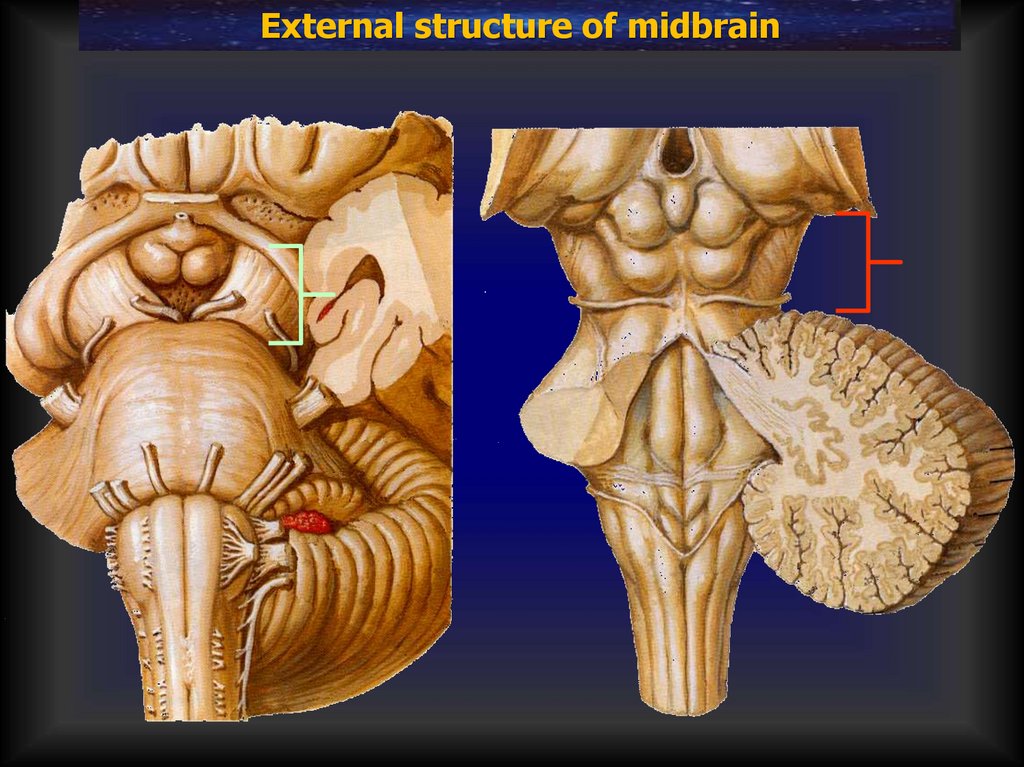
External structure of midbrain23.
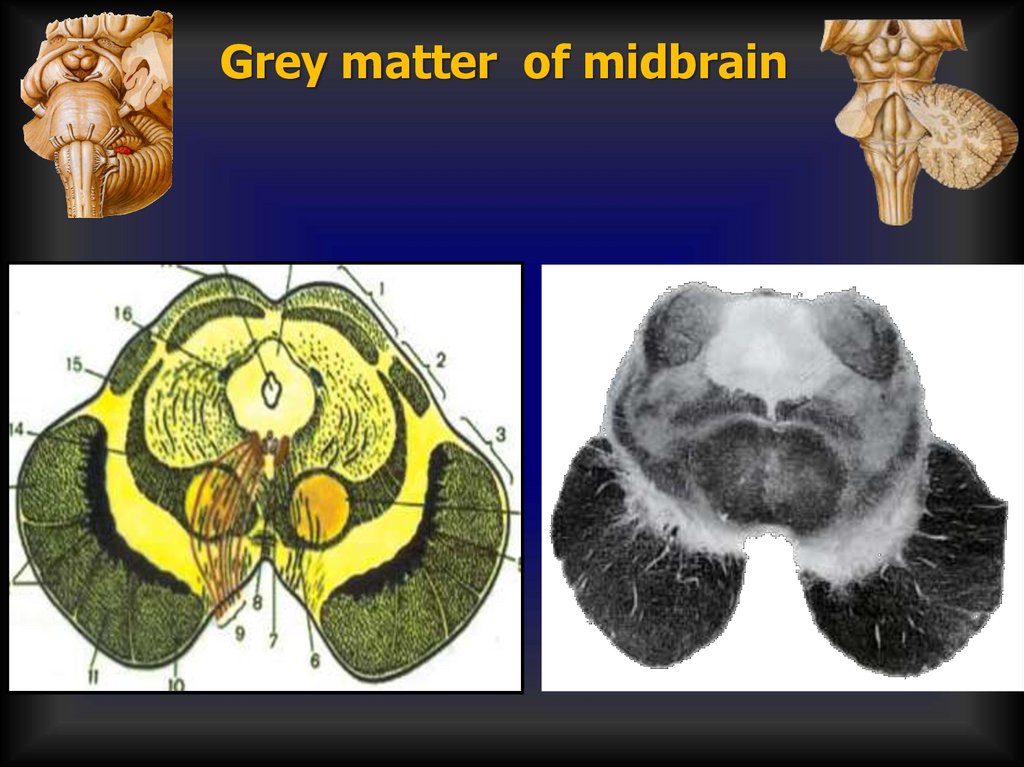
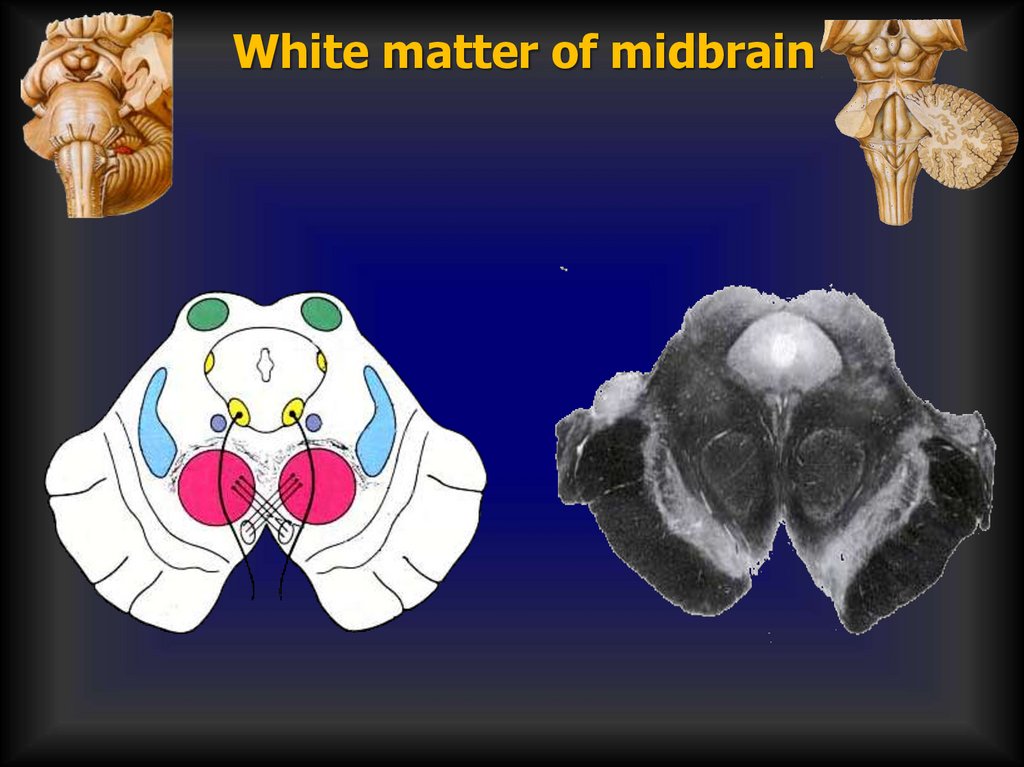
Grey matter of midbrain24.
White matter of midbrain25.
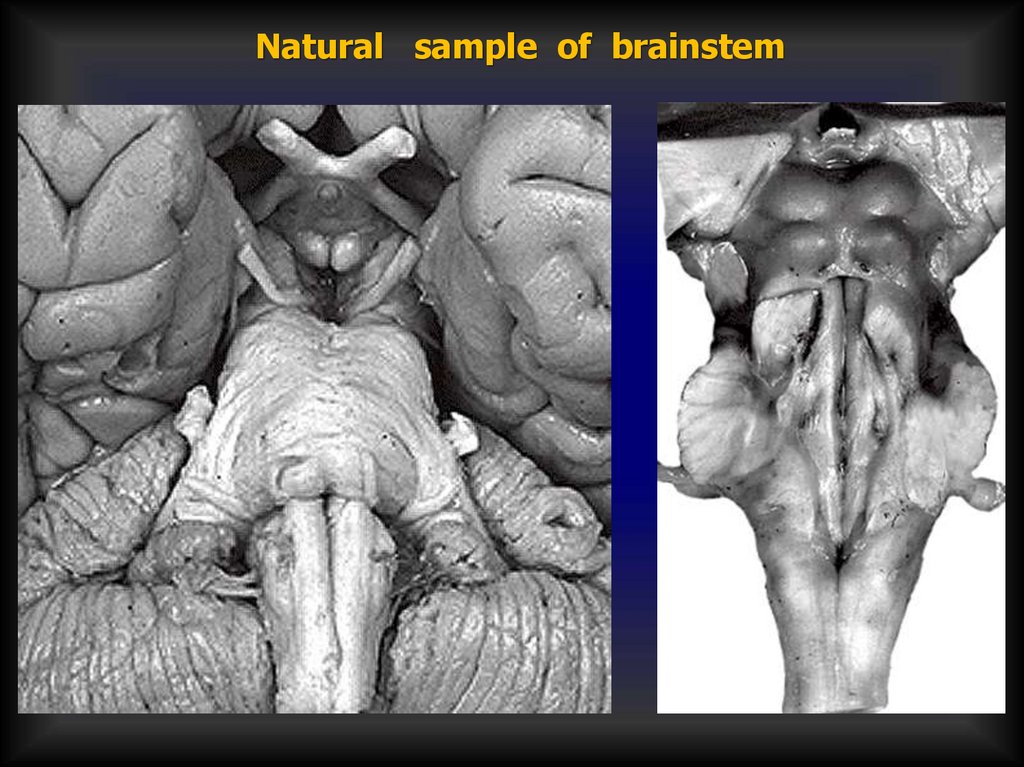
Natural sample of brainstem26.
General regularities27.
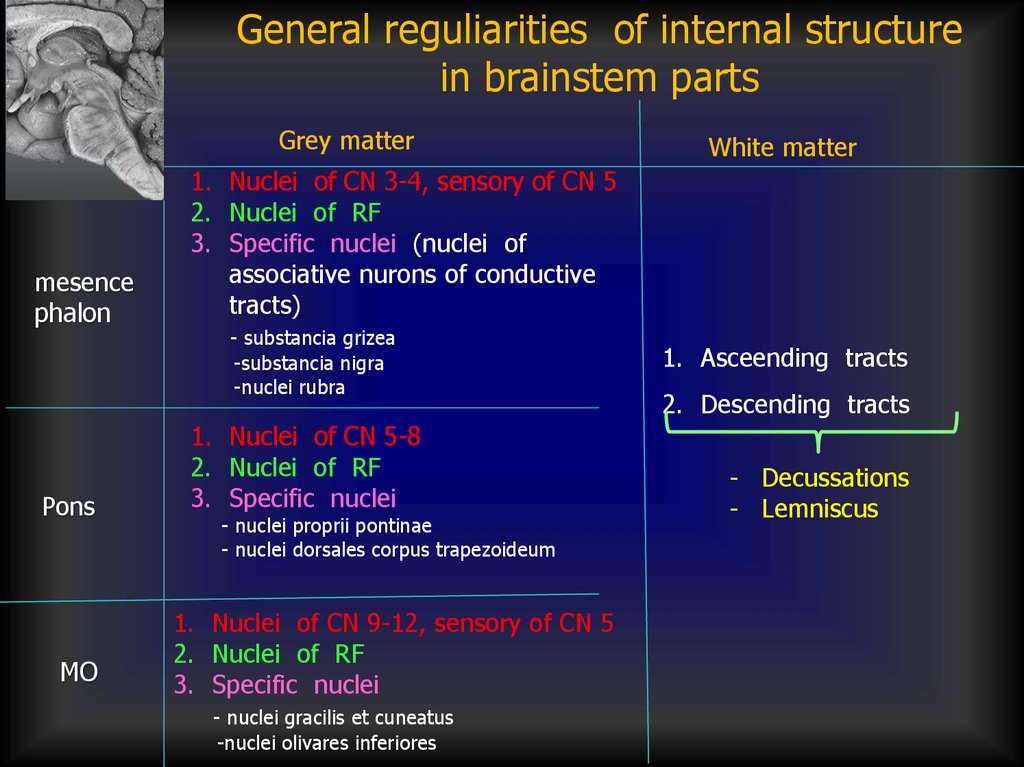
General reguliarities of internal structurein brainstem parts
Grey matter
mesence
phalon
Pons
МО
White matter
1. Nuclei of CN 3-4, sensory of CN 5
2. Nuclei of RF
3. Specific nuclei (nuclei of
associative nurons of conductive
tracts)
- substancia grizea
-substancia nigra
-nuclei rubra
1. Nuclei of CN 5-8
2. Nuclei of RF
3. Specific nuclei
- nuclei proprii pontinae
- nuclei dorsales corpus trapezoideum
1. Nuclei of CN 9-12, sensory of CN 5
2. Nuclei of RF
3. Specific nuclei
- nuclei gracilis et cuneatus
-nuclei olivares inferiores
1. Asceending tracts
2. Descending tracts
- Decussations
- Lemniscus
28.
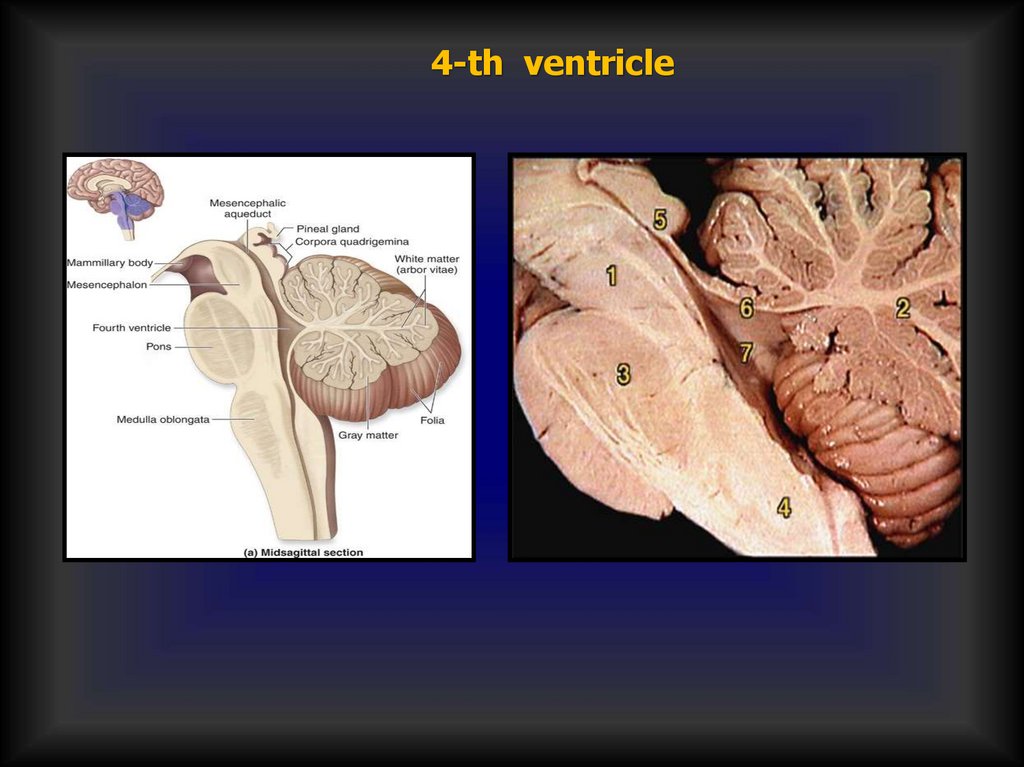
4-th ventricle29.
4-th ventricle30.
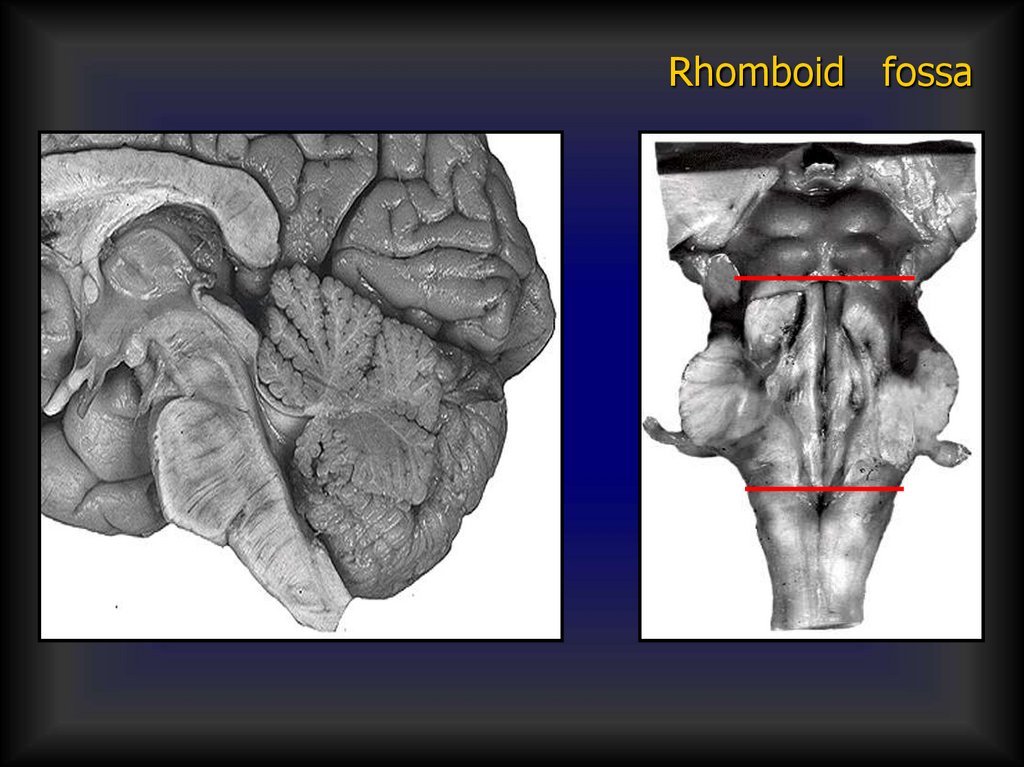
Rhomboid fossa31.
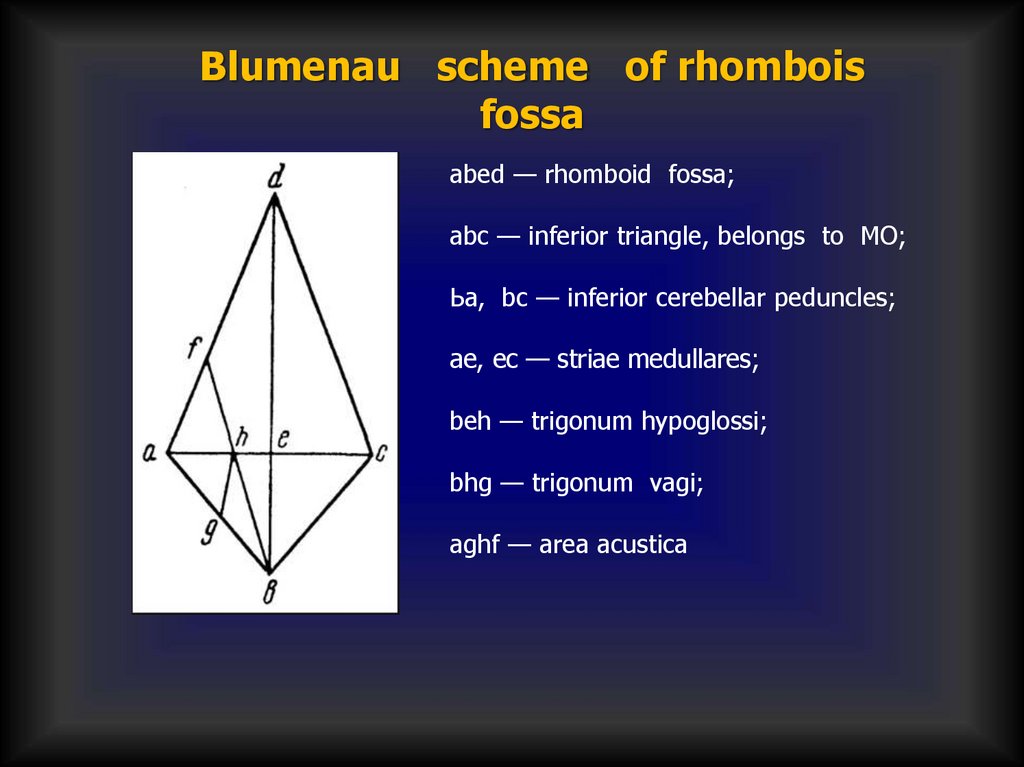
Blumenau scheme of rhomboisfossa
abed — rhomboid fossa;
abc — inferior triangle, belongs to MO;
Ьа, bс — inferior cerebellar peduncles;
aе, ес — striae medullares;
beh — trigonum hypoglossi;
bhg — trigonum vagi;
aghf — area acustica
32.
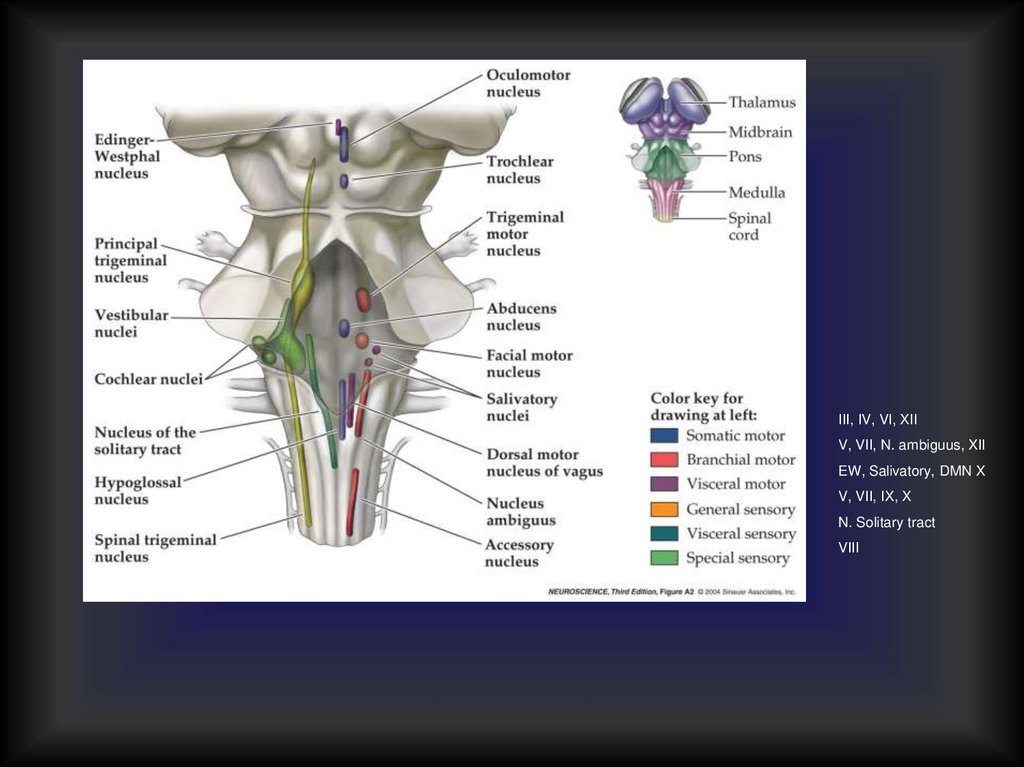
III, IV, VI, XIIV, VII, N. ambiguus, XII
EW, Salivatory, DMN X
V, VII, IX, X
N. Solitary tract
VIII
33.
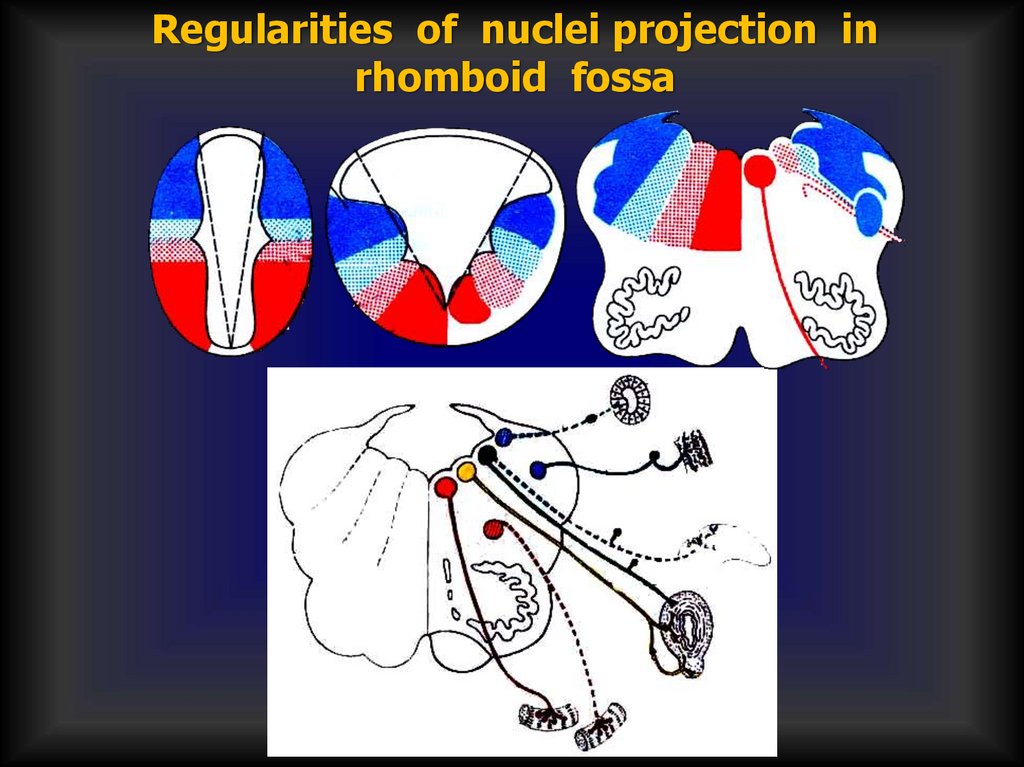
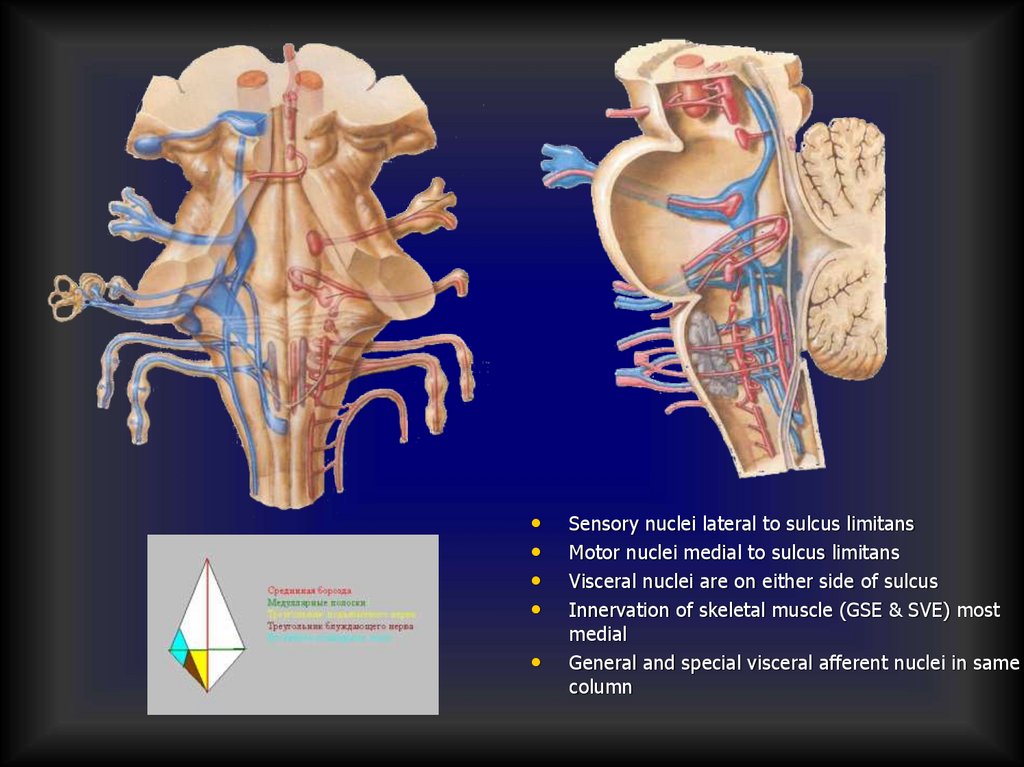
Regularities of nuclei projection inrhomboid fossa
34.
Sensory nuclei lateral to sulcus limitans
Motor nuclei medial to sulcus limitans
Visceral nuclei are on either side of sulcus
Innervation of skeletal muscle (GSE & SVE) most
medial
General and special visceral afferent nuclei in same
column
35.
36.
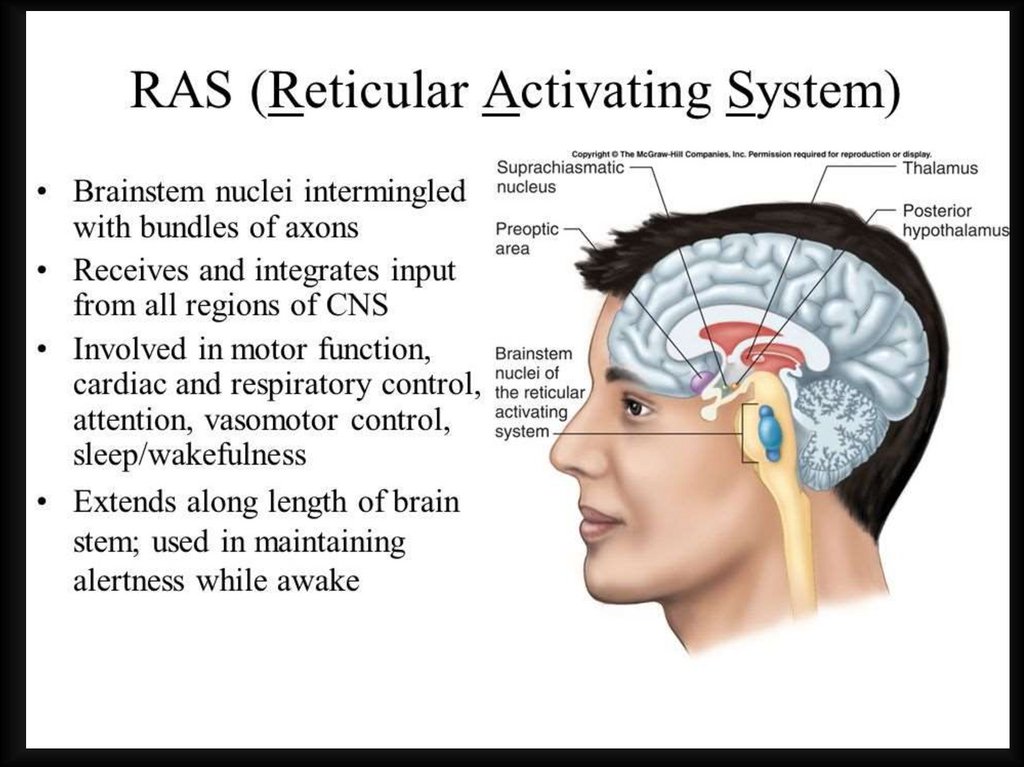
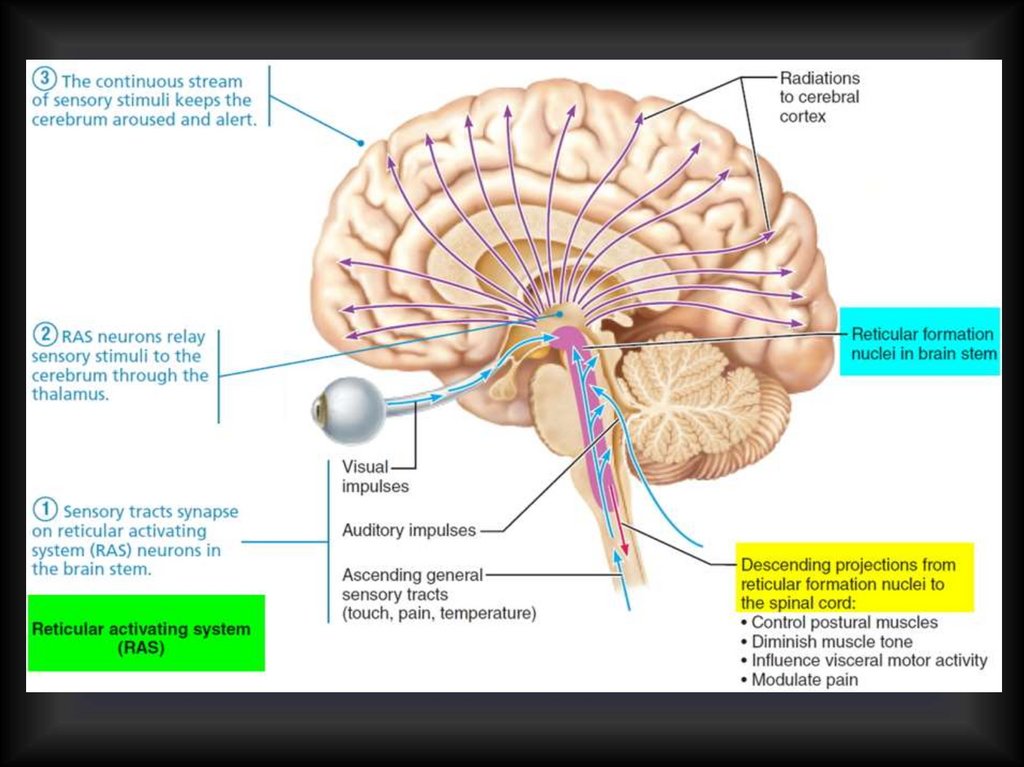
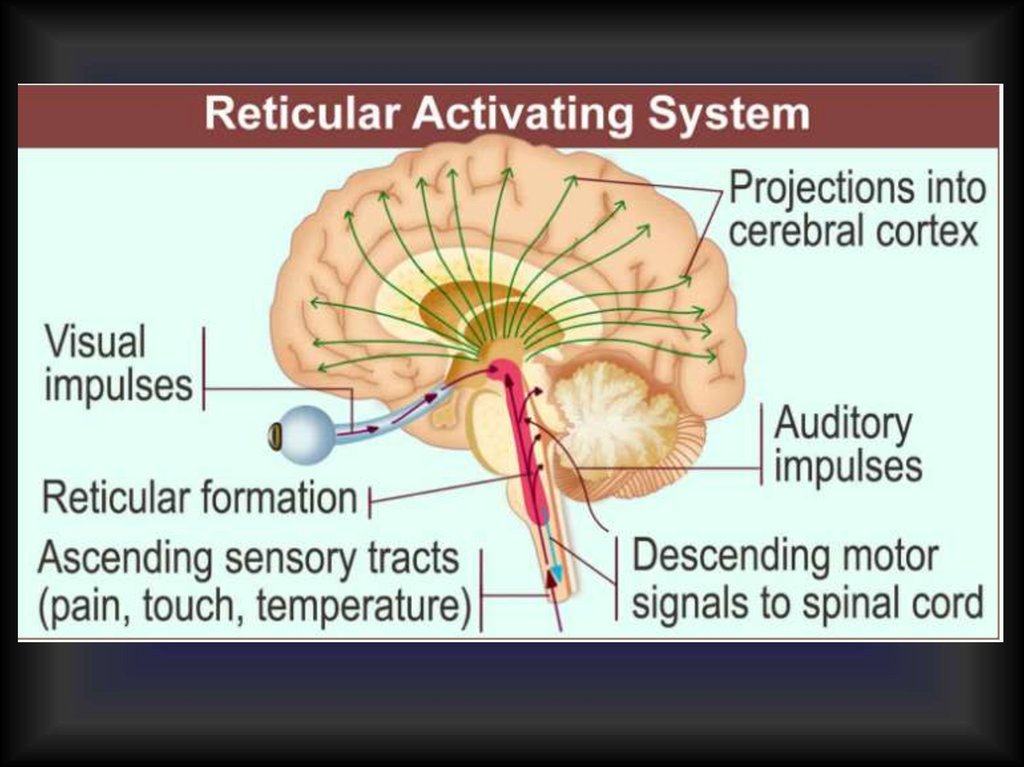
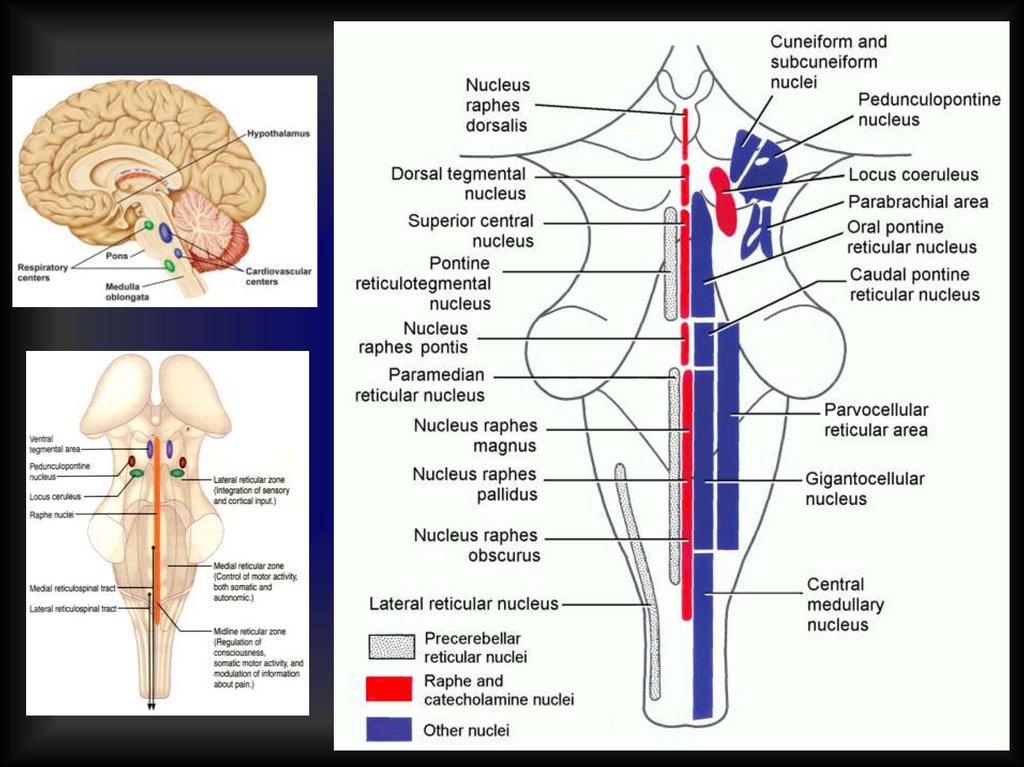
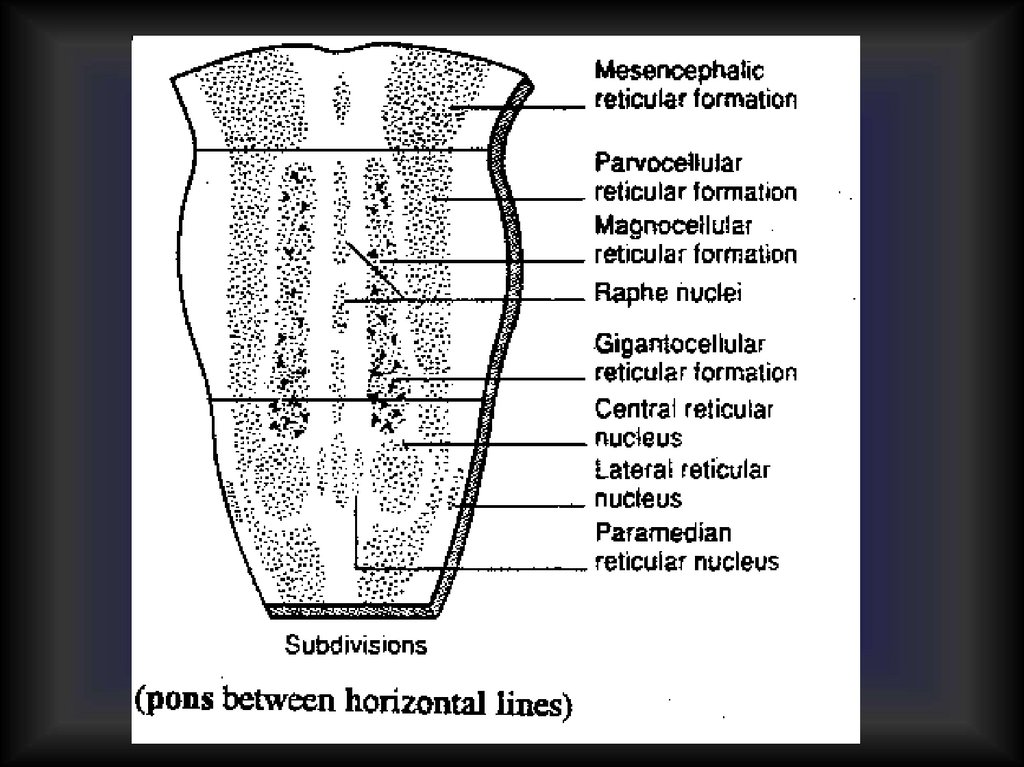
Reticular formation37.
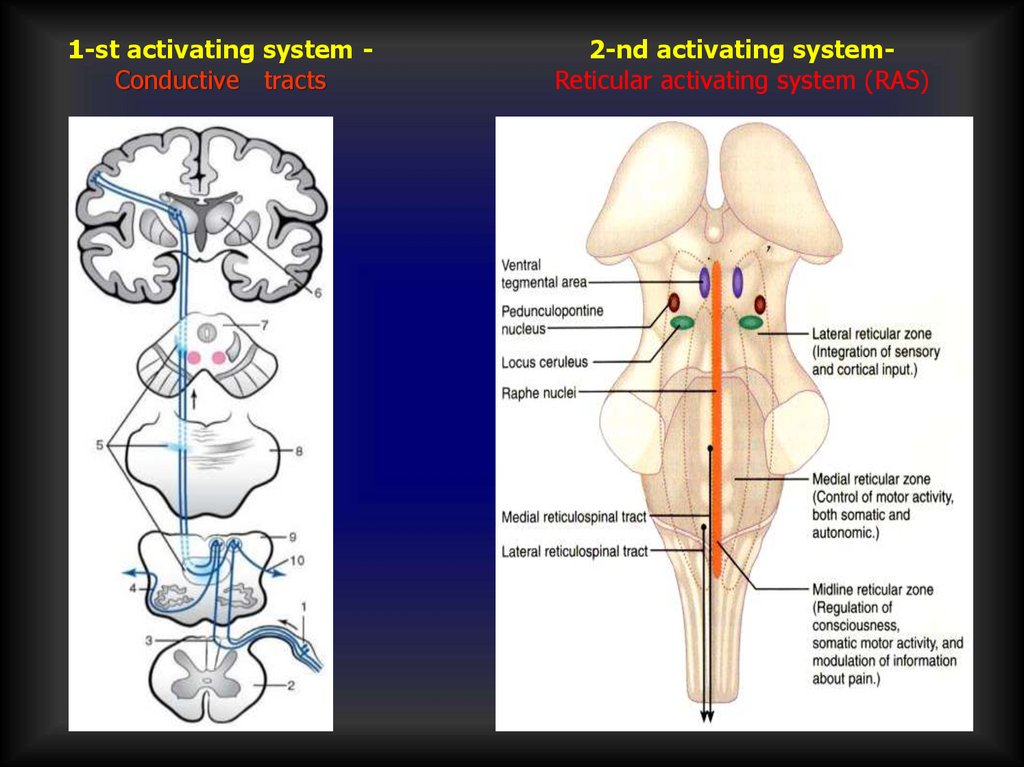
1-st activating system Conductive tracts2-nd activating systemReticular activating system (RAS)
38.
Effects of RAS1. Multiplication of stimuli
2. Amplification of stimuli
3. More generalized answer
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
cerebellum45.
46.
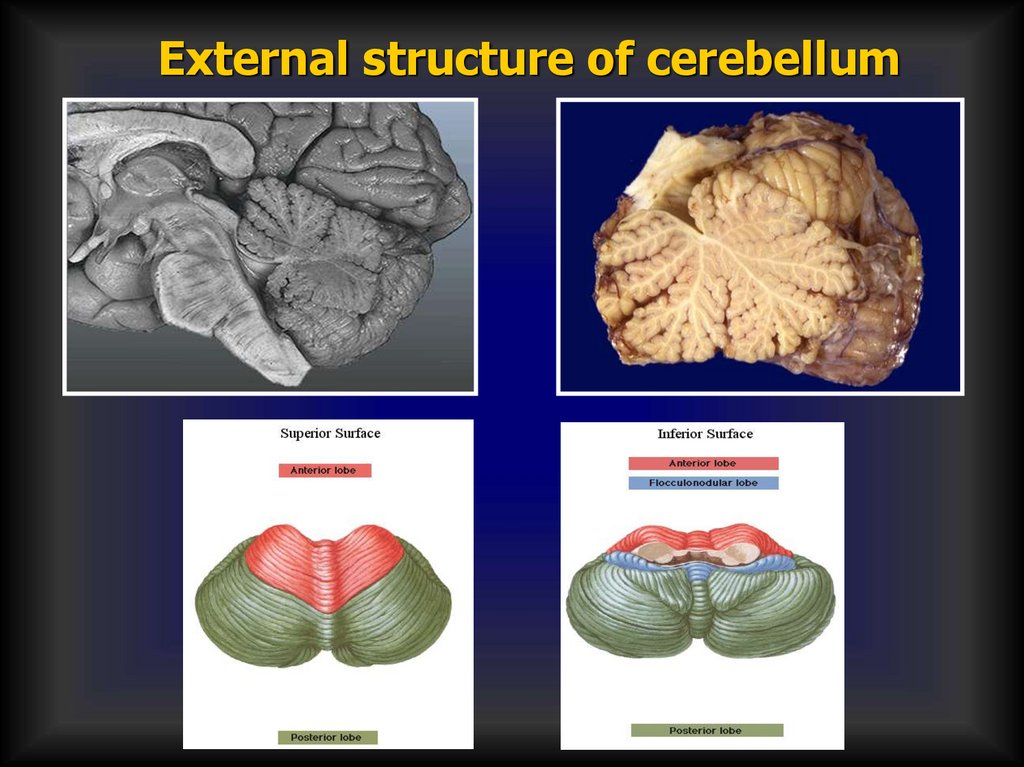
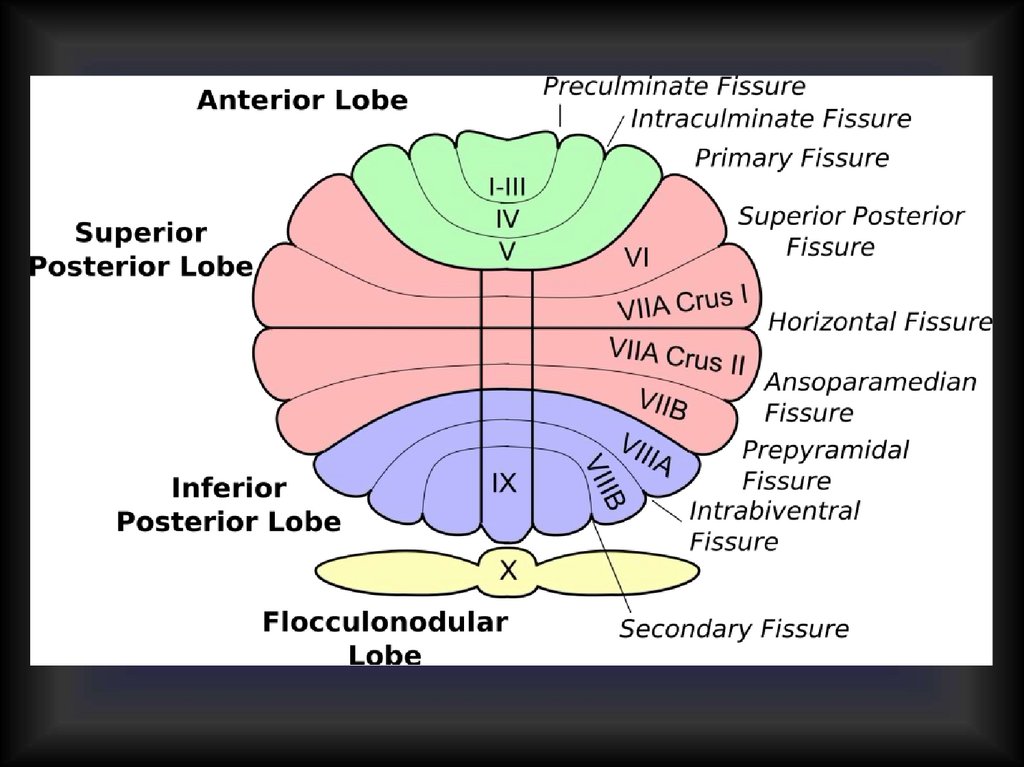
External structure of cerebellum47.
48.
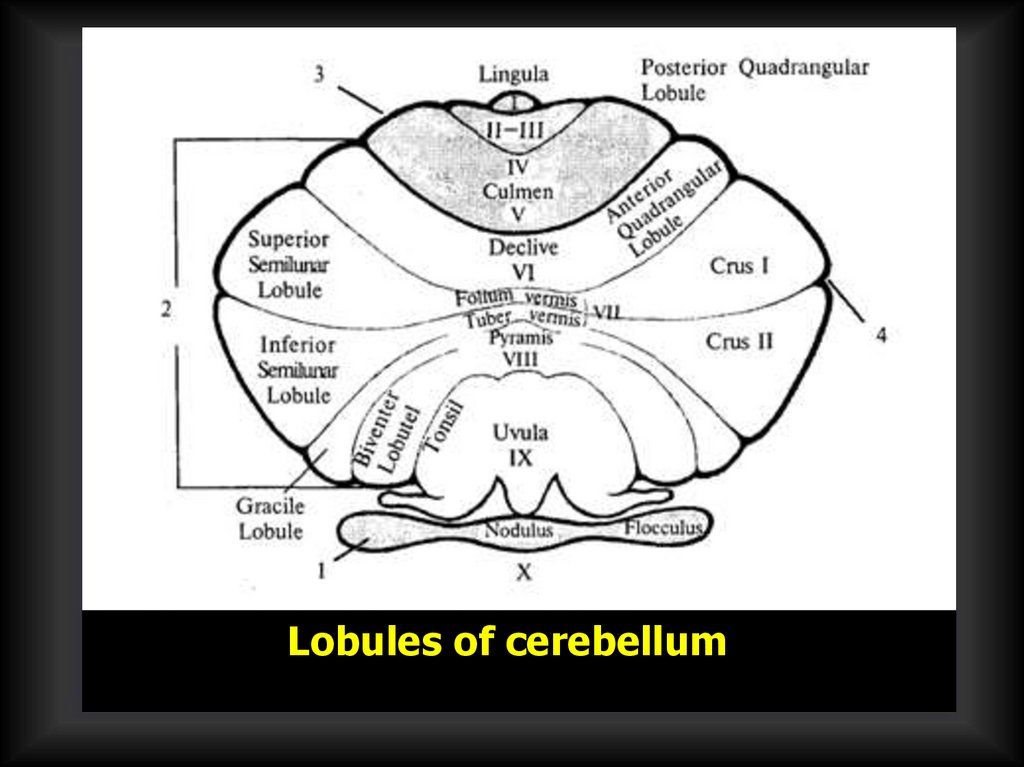
Lobules of cerebellum49.
50.
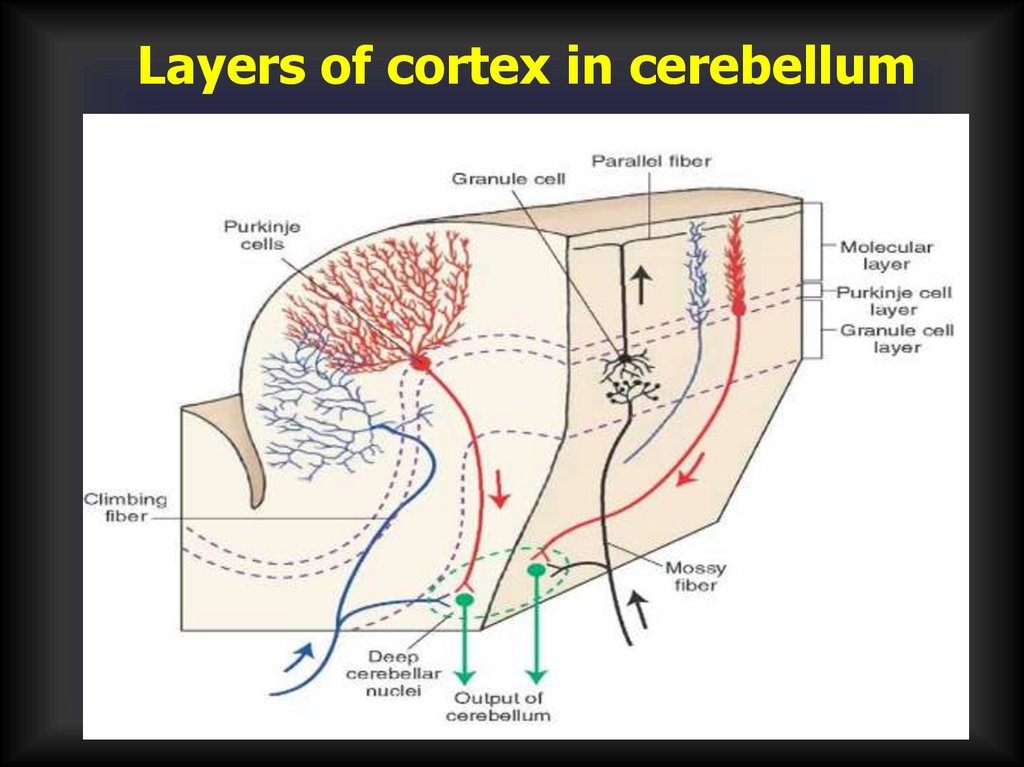
Layers of cortex in cerebellum51.
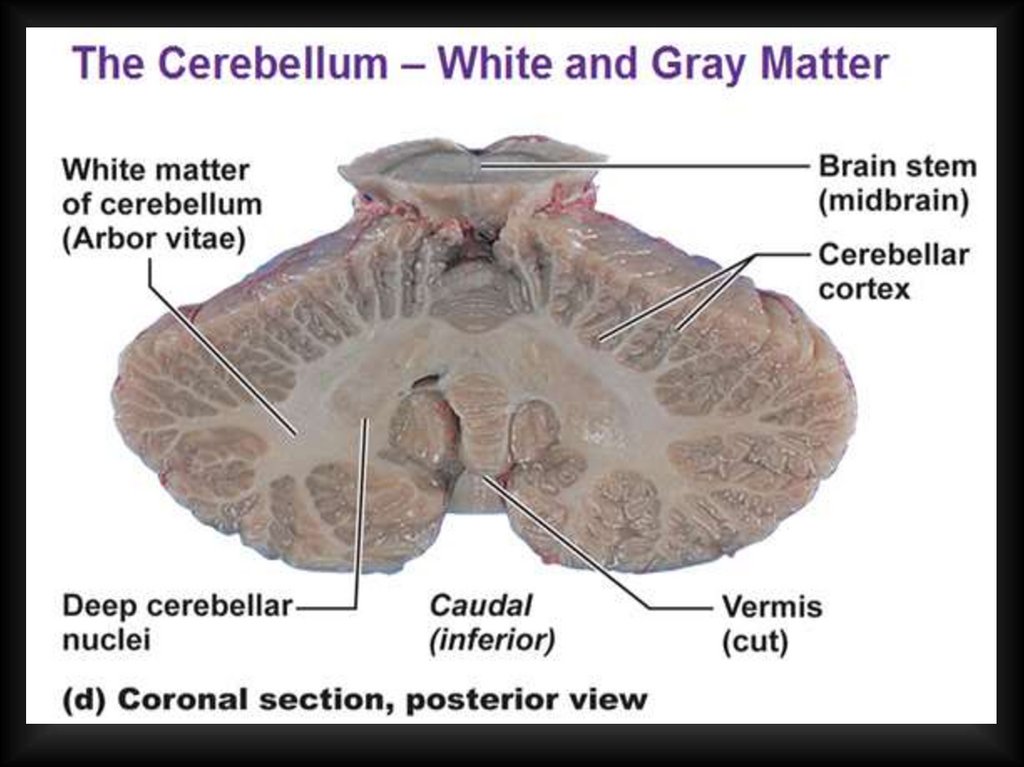
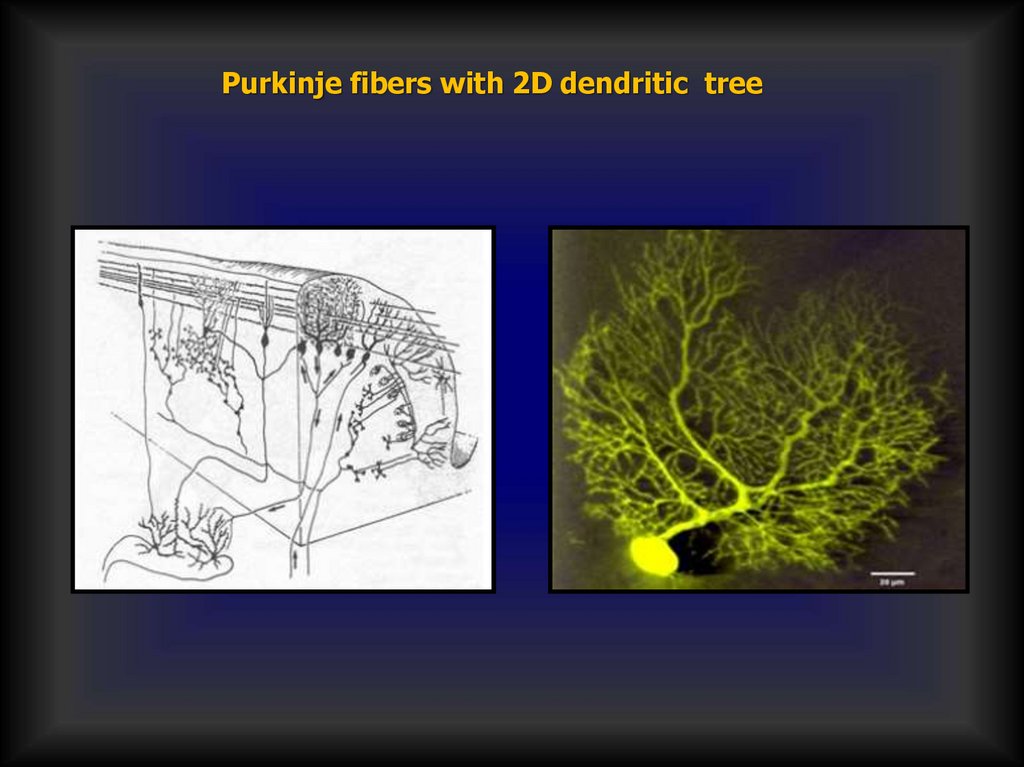
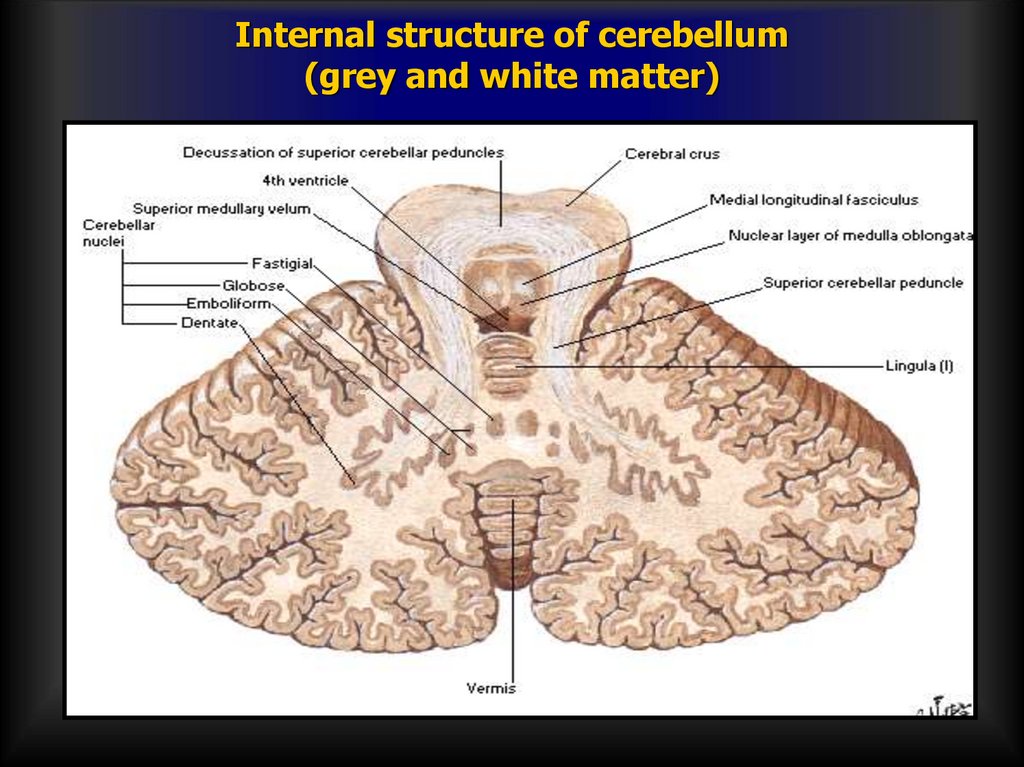
Purkinje fibers with 2D dendritic tree52. Internal structure of cerebellum (grey and white matter)
53.
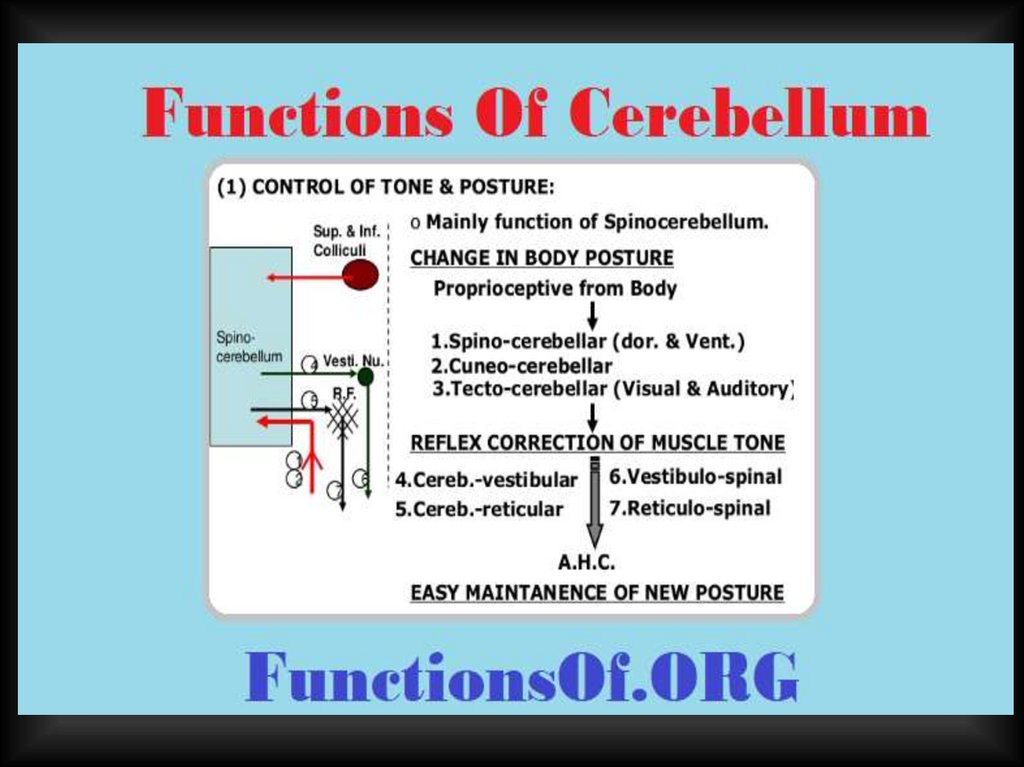
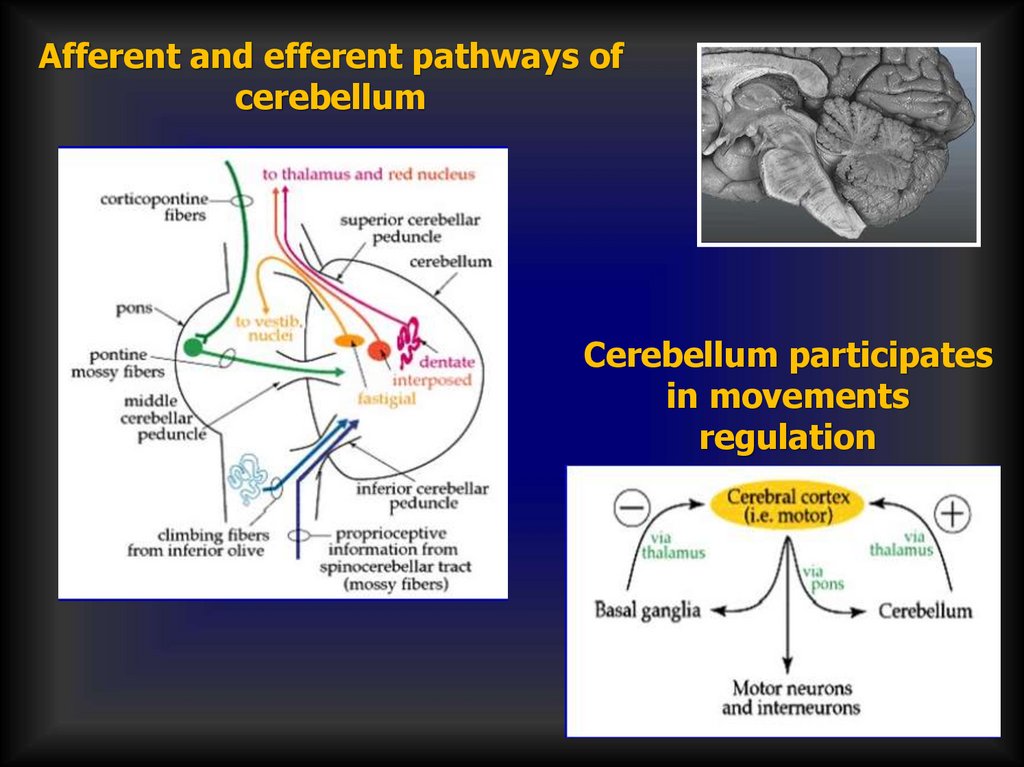
Afferent and efferent pathways ofcerebellum
Cerebellum participates
in movements
regulation
54.
Methods of study55.
Thank you forattention!





 Биология
Биология