Похожие презентации:
Responsibility of power engineers
1.
Responsibility of power engineersSudochakov Denis
ED 18-08B
2.
Who is a power engineer?• Power engineer is a specialist who is
responsible
for
the
operation,
maintenance, renovation, and repair of
mechanical systems in a facility;
Thermal power station;
Hydroelectric power stations;
Nuclear power plant;
Research institutes;
At different factories and enterprises;
Design and construction organizations;
Power engineer working with the control panel
of the NPP
Development [dɪ'veləpmənt] – разработка, создание;
Nuclear ['njuːklɪə] – ядерный;
3.
Power engineer tasks• Modernization of energy supply
systems;
• Installation of electrical equipment at
the enterprise;
• Creation of drawings;
• Installation and commissioning of the
system;
• Verification of relay protection
systems and automation;
• And other work related to power
supply;
Electric installation work
Equipment [ɪ'kwɪpmənt] – оборудование; Verification [ˌverɪfɪ'keɪʃ(ə)n] - контроль, проверка;
Related [rɪ'leɪtɪd] - связанный ; Commissioning [kəˈmɪʃnɪŋ] - введение в эксплуатацию;
4.
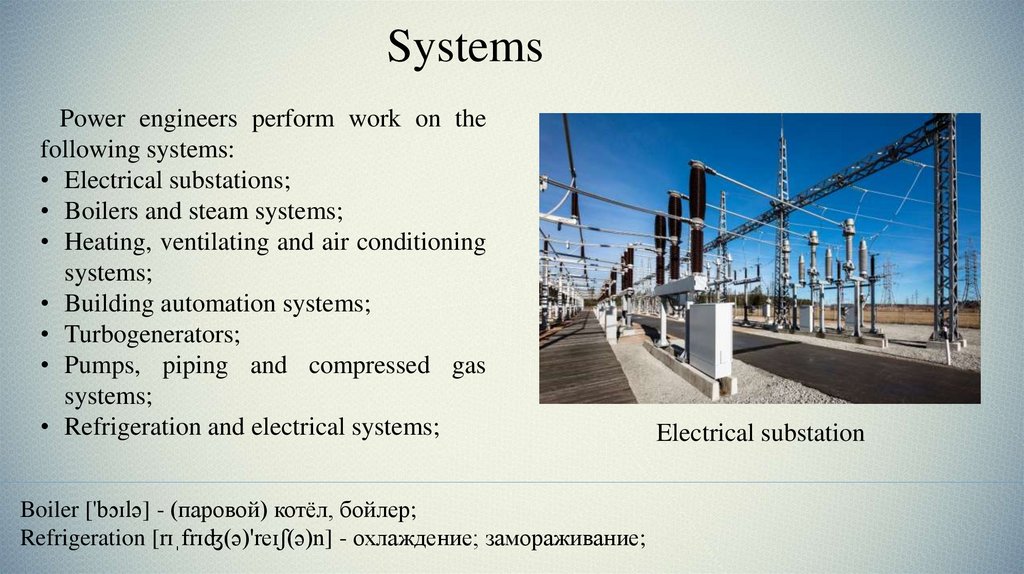
SystemsPower engineers perform work on the
following systems:
• Electrical substations;
• Boilers and steam systems;
• Heating, ventilating and air conditioning
systems;
• Building automation systems;
• Turbogenerators;
• Pumps, piping and compressed gas
systems;
• Refrigeration and electrical systems;
Boiler ['bɔɪlə] - (паровой) котёл, бойлер;
Refrigeration [rɪˌfrɪʤ(ə)'reɪʃ(ə)n] - охлаждение; замораживание;
Electrical substation
5.
Responsibility power engineering atthe enterprise
• Control of energy supply and
distribution;
• Scheduled inspection of equipment,
timely troubleshooting;
• Drawing up a plan of work for
repair, replacement of equipment;
• Emergency situations: explosions,
fires;
Electrical substation accident
Schedule ['ʃedjuːl] – График;
Emergency situations [ɪ'mɜːʤ(ə)n(t)sɪ, iː-] [ˌsɪʧu'eɪʃ(ə)n] – Аварийная ситуация;
troubleshooting [trʌ̱b(ə)lʃuːtɪŋ] – Исправление проблем; Accidents ['æksɪd(ə)nt] – Несчастный случай;
6.
Responsibility power engineer tohumanity and nature
• Atmospheric pollution;
• Pollution of rivers and lakes;
• Radioactive waste;
Combustible fuels: coal, oil and natural gas;
Draining warm water from power plants;
Radiation and toxic fumes;
Pollution [pə'luːʃ(ə)n] – загрязнение;
Combustible [kəm'bʌstəbl] - воспламеняемый, горючий
7.
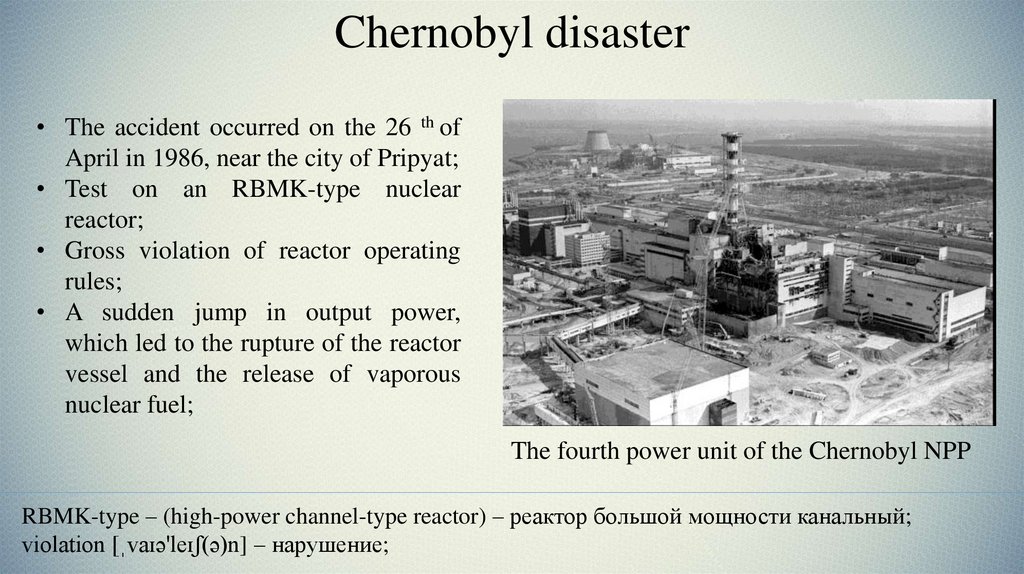
Chernobyl disaster• The accident occurred on the 26 th of
April in 1986, near the city of Pripyat;
• Test on an RBMK-type nuclear
reactor;
• Gross violation of reactor operating
rules;
• A sudden jump in output power,
which led to the rupture of the reactor
vessel and the release of vaporous
nuclear fuel;
The fourth power unit of the Chernobyl NPP
RBMK-type – (high-power channel-type reactor) – реактор большой мощности канальный;
violation [ˌvaɪə'leɪʃ(ə)n] – нарушение;
8.
Consequences of the accident• Exclusion zone within a
radius of 30 kilometers from
the station;
• Hundreds of firefighters and
medical workers who died
in the liquidation;
• Tens of thousands of cases
of radiation sickness among
the civilian population;
• Uninhabitable earth for 3000
years;
Abandoned city of Pripyat
House of culture
«Energetik» in Pripyat
Exclusion zone [ɪks'kluːʒ(ə)n zəun] - Зона отчуждения;
Radiation sickness [ˌreɪdɪ'eɪʃ(ə)n 'sɪknəs] – Лучевая болезнь;
Uninhabitable [ˌʌnɪn'hæbɪtəbl] – Непригодный для жилья;
9.
Conclusion• Electricity in homes, factories
and businesses;
• Heating in homes;
• Trolleybus, metro;
• Household
appliances:
washing machines, stoves,
refrigerators;
The City Of Krasnoyarsk
Household appliances ['haushəuld ə'plaɪən(t)s] – бытовая техника;
Green trolleybus








 Английский язык
Английский язык Педагогика
Педагогика








