Похожие презентации:
20 years from Сhernobyl
1. Folie 1
An IPPNW Presentation1
2. What really happened – the meltdown
The smoking reactor
Chernobyl Interinform
The exploded reactor
Igor Kostin (taken 12 hours after the catastrophe)
2
3. What really happened – the meltdown
• 26th of April, 198601:23:00: Start of an experiment in Block IV of the plant
01:23:40: The emergency shutdown fails
01:23:48: The reactor explodes, emitting radioactivity
• 28th of April, 1986
21:00:00: The Soviet news TASS first reports the accident
• 29th of April, 1986:
Western news first report of the meltdown
3
4. What really happened – measures taken
After 36 hours:
Evacuation of 45,000 people from the city of Pripjat
Until May 5th:
Evacuation of 130,000 people from within 30 km of ground zero
May 1st, 1986:
The state begins the control of water and milk
23. Mai 1986:
Iodine tablets start to be disseminated
4
5. What really happened – measures taken
• The plants‘ fire brigades try tocontrol the flames
• 600,000 – 860,000 young men
(so called liquidators) are drafted to clean
up the wreckage
Two men clean a vehicle
• Until May 5th: 4,200 tons of lead and sand
are dropped on the nuclear reactor
Source: Chernobyl Interinform
• May 6th: The fire is finally brought under control
5
6. What really happened – the so called death zone
EvacuatedKindergarten in Pripjat
Photo: Igor Kostin
6
7. What really happened – the so called death zone
Soldier guarding thedeath zone
Photo: Igor Kostin
7
8. What really happened – the so called death zone
In the death zonePhoto: Igor Kostin
8
9. What really happened – the so called death zone
Evacuated buildingPhoto: Igor Kostin
9
10. What really happened – radioactive pollution
• Death Zone:
30-Kilometer-radius around the reactor
• Contaminated regions:
Belarus: 30 percent
Ukraine: 7 percent
European Russia: 1,6 percent
Total of 162,000 km2 are contaminated
• Nine million people are affected. 400,000
loose their houses and properties
10
11. What really happened – radioactive pollution
Changing wind patterns spread the radioactive cloud all over Europe
Scandinavia, the Baltic States, Poland, Germany, Switzerland, Austria, Italy and other regions were
contaminated as well
Source:
UNESCEAR Report,
New York 2000;
Annex J.
April 26th, 00.00
April 27th, 00.00
11
April 27th,12.00
April 29th, 00.00
12. What really happened - Evacuation
A Belarus couple that had to be evacuated fromtheir irradiated village to a housing complex in
Minsk.
Photo: Martina Buchholz
12
13. Health effects of radioactivity
Radioactive elements dispersed by ChernobylIodine 131
Halftime: 8 days; stored in the thyriod gland,
causes thyroid cancer
Cesium 137
Halftime: 30 years; stored in all organs,
causes cancer, enters the food chain
Strontium 90
Halftime: 28 years; stored in teeth
and bones, causes leukaemia
Plutonium 239
Halftime: 24.000 years; contaminates
water reservoires, causes cancer
13
14. Health effects of radioactivity
Local farmer selling contaminated berriesPhoto: Martina Buchholz
14
15. Health effects of radioactivity
• High dosis starting with 0.5 Sievert (Sv)– Immediate breakdown of the immune system
– Uncontrollable bleeding and anemia
– Damage to the gastrointestinal tract
– Damage to internal organs and the central nervous system
– Tumors as long-term effects
15
16. Health effects of radioactivity
Low level radiation• Each dose, no matter how small, can cause cancer
• The question is how often this occurs and if other diseases can
also be attributed to it
• According to new studies, the effects of low-level radiation
include:
– Genome instabilities
– Mutations of DNA
– Malformations
– Increased cell aging
16
17. Health effects – the dispute
Numbers of the IAEA• Less than 50 deaths by mid-2005
• Approximately 4,000 cases of thyroid
cancer with only 9 deaths and healing
rates of 99% (with western standard
medicine)
• No proof of a rise in malformations,
sterility, leukaemie or other types of
cancer attributed to the meltdown
• Up to 4,000 possible deaths due to the
accident in Chernobyl
• The case of Chernobyl can be considered
closed. Poverty, unhealthy living
standards and the psychiatric impact of
the fall of the Soviet Union far exceed the
effects of radiation.
Statistics of official institutions
• 25.000 deaths amongst the 800,000 Liquidatoren
(Source: state cancer registries in three states)
• 94 percent of liquiodators are ill
(Source: Ukrainian Embassy 2005)
• 84 percent of 3 million people exposed to
radioactivity in Ukraine are ill
(Source: Chernobyl Interinform)
• According to the Belarus cancer registry, the
cancer rate has increased by 40% since Chernobyl
• A working group of the WHO calculated 50,000
cases of thyroid cancer within the next 30-50 years
amongst children 0-4 years of age at the time of
the accident
Source: Chernobyl-Forum-Report Sept. 2005
17
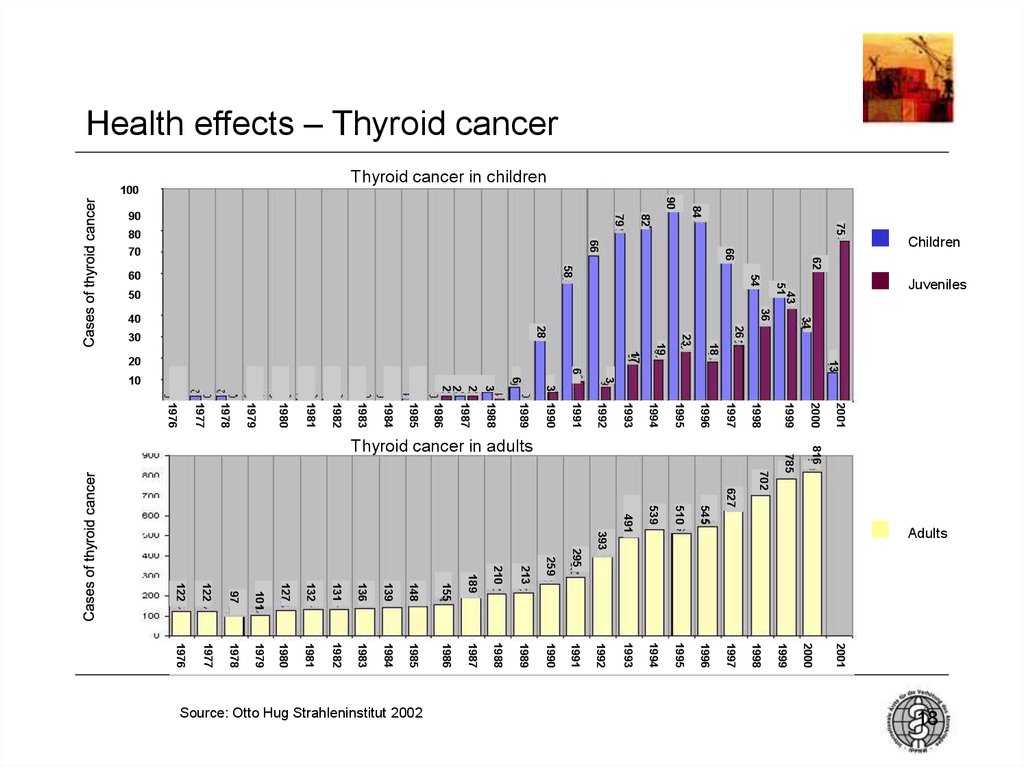
18. Health effects – Thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer in children100
75
62
66
34
36
26
18
13
6
3
6
2001
2000
1999
1998
816
785
702
545
627
1996
510
1997
1995
1985
1984
1983
1982
1981
1980
1979
1978
1977
1976
Adults
2001
2000
1999
1998
1997
1996
1995
1994
1993
1992
1991
1989
1990
213
1988
139
148
155
1983
1984
1985
1986
1987
136
1982
1979
131
101
1978
1981
97
1977
132
122
1976
1980
122
127
189
210
259
295
393
491
539
1989
3 1990
1991
1992
1993
1994
Thyroid cancer in adults
43
51
54
50
18
Source: Otto Hug Strahleninstitut 2002
3 1988
2
1987
2
2
1986
10
19
17
20
23
28
30
84
90
66
58
40
Juveniles
60
Children
80
70
82
79
90
19. Health effects – Thyroid cancer
Girl during an ultrasoundexamination (offered for
free by German IPPNW
doctor)
19
20. Health effects – cancer statistics
• Amongst liquidators: Rise in cancer rate by 20 %• In the region of Gomel, Belarus: rise in cancer rate by 55,9 %
• In the regions of Gomel and Mogilev: Doubling of breast cancer
rates, as well as a shift of 15 years towards younger women
• Rise of childhood leukaemia in the affected regions: 300%
• Rise of brain tumors amongst small children in Ukraine: 580%
Sources:
IPPNW & German Society for Radiation Protection
20
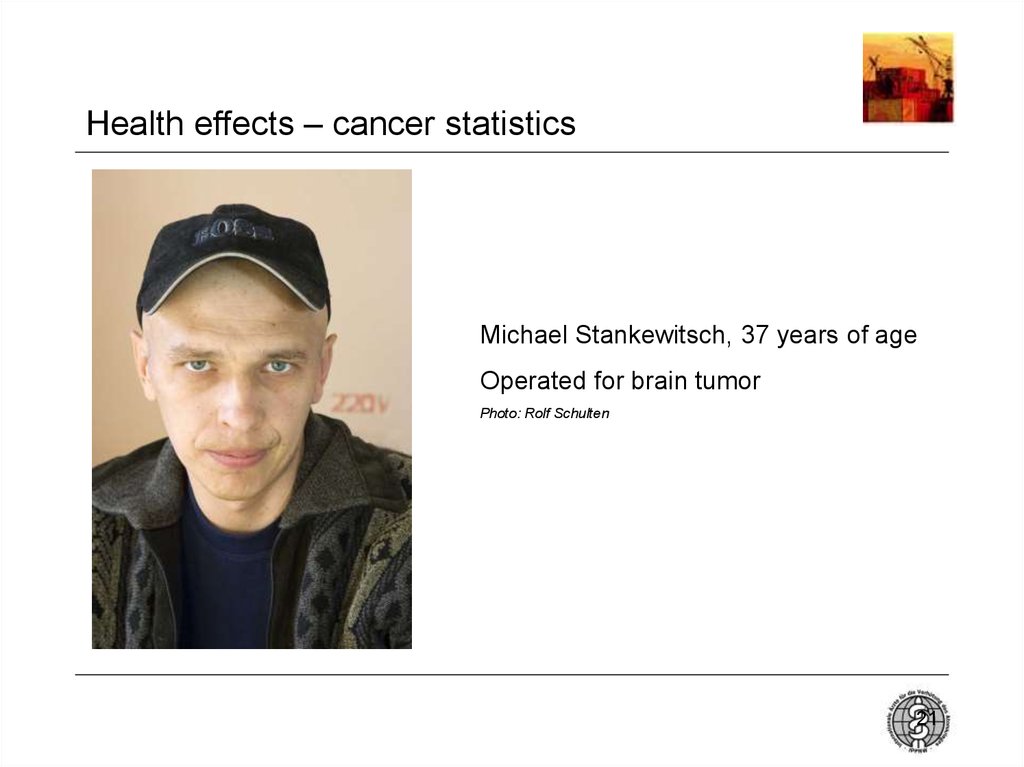
21. Health effects – cancer statistics
Michael Stankewitsch, 37 years of ageOperated for brain tumor
Photo: Rolf Schulten
21
22. Health effects on small children
• 5,000 additional deaths amongst small children in Europe• Significant rise in malformations in several European countries
• At least 10,000 additional Malformations in Europe
Sources:
IPPNW & German Society for Radiation Protection
22
23. Health effects – other diseases
Liquidators• Increase in lethal cardio-vascular diseases by 22%
• Sharp rise in gastrointestinal and CNS-diseases
• 95% of liquidators suffer from ocular diseases
• Accelerated aging due to damage to antioxidant systems
Children
• 70% of children of affected parents are registered as chronically
ill (Ukraine, 1996)
• 13x rise in childhood diseases in the region of Gomel
23
24. Health effects – the IPPNW study
LiquidatorsSeveral 100.000 liquidators are affected
Several 10.000 Liquidatoren have died from radiation
Thyroid cancer
More than10.000 cases of thyroid cancer in the normal
population
More than 50.000 expected cases of thyroid cancer in the
near future
Malformations
10,000 severe cases of malformations in Europe
Neonatal mortality
5,000 additional childhood deaths in Europe
Sources:
IPPNW & German Society for Radiation Protection
24
25. Health effects – the IPPNW study
Cancer, leukaemiaand other diseases
Rise in cancer and leukaemia cases in several states. No
metanalysis to date.
13x rise in childhood manifestation of diseases in affected
regions
Genetische Schäden
Einschätzung
Bei Kindern von Liquidatoren und Menschen in belasteten
Gebieten wurden Erbgutveränderungen festgestellt
Dies sind sehr konservative Zahlen. Das russische Umweltministerium bezifferte die Zahl der durch Tschernobyl kranken
Menschen Anfang der 90er Jahre auf über 1,3 Millionen
Source:
IPPNW & German Society for Radiation Protection
25
26. Health effects – the children
Young cancer patientPhoto: Hermine Oberück
26
27. Criticism of the IAEA/WHO Study
• New and significant studies were ignored.• More than 100,000 people left out of the calculations.
• The calculations did not include non-cancer diseases.
• 5,000 casualties are missing from the original study in the press
release.
27
28. Other effects
The nuclear accident led to a forced evacuation of people:Source: UNDP, 2002
28
29. Conclusion
There are no final answers on ChernobylThe case „Chernobyl“ cannot be closed!
29


























 Английский язык
Английский язык Экология
Экология








