Похожие презентации:
Impact of the sanction on the Russian economy
1.
IMPACT OF THE SANCTIONON THE RUSSIAN ECONOMY
Maria Lukyanova
MSU Branch in Sevastopol
2.
The issues to be considered in the research1.
2.
3.
4.
Why were the sanctions imposed?
Types of sanctions and counter-sanctions.
Consequences of sanctions:
ruble devaluation;
capital outflow from Russia;
export of goods of the Russian Federation.
Government measures to minimize the negative impact of
sanctions.
5. Russia today.
3.
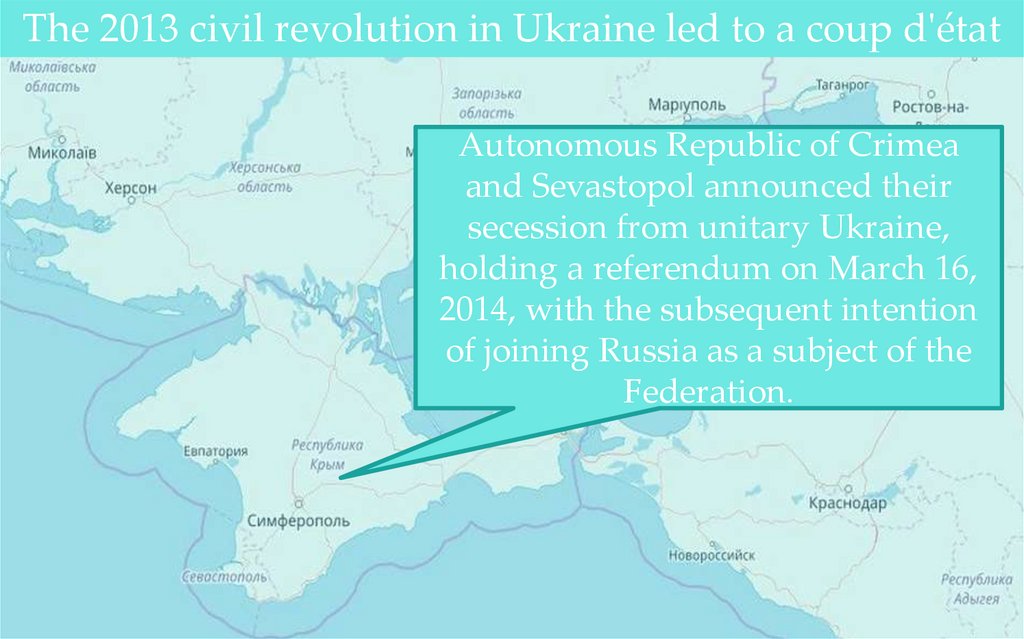
The 2013 civil revolution in Ukraine led to a coup d'étatAutonomous Republic of Crimea
and Sevastopol announced their
secession from unitary Ukraine,
holding a referendum on March 16,
2014, with the subsequent intention
of joining Russia as a subject of the
Federation.
4.
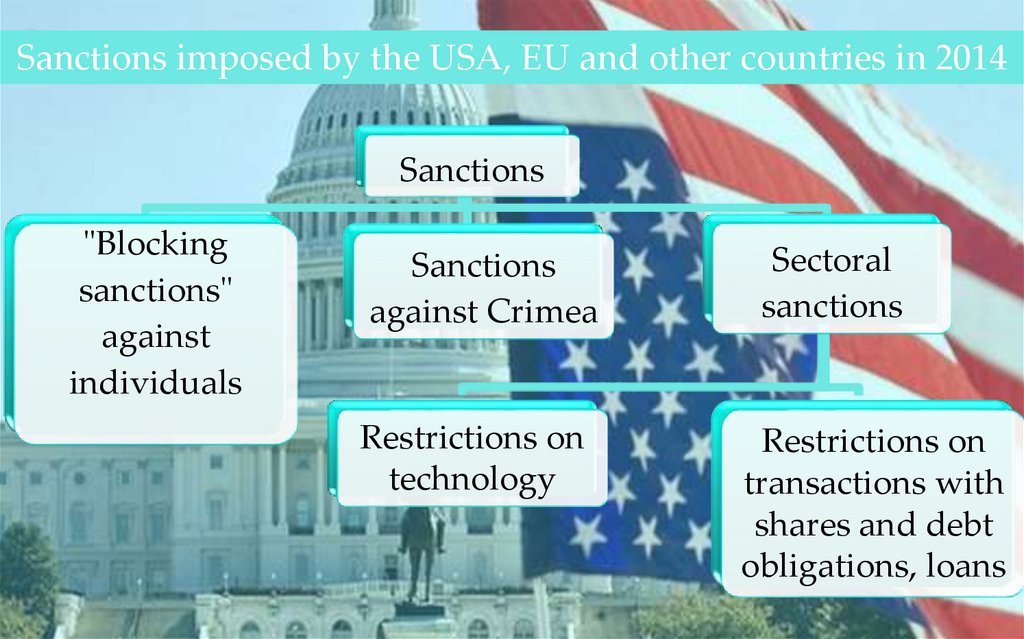
Sanctions imposed by the USA, EU and other countries in 2014Sanctions
"Blocking
sanctions"
against
individuals
Sanctions
against Crimea
Restrictions on
technology
Sectoral
sanctions
Restrictions on
transactions with
shares and debt
obligations, loans
5.
The Russian Federation counter-sanctionsCounter-sanctions:
food embargo
rejection of joint projects with unfriendly
partners
tightening of customs control, etc
6.
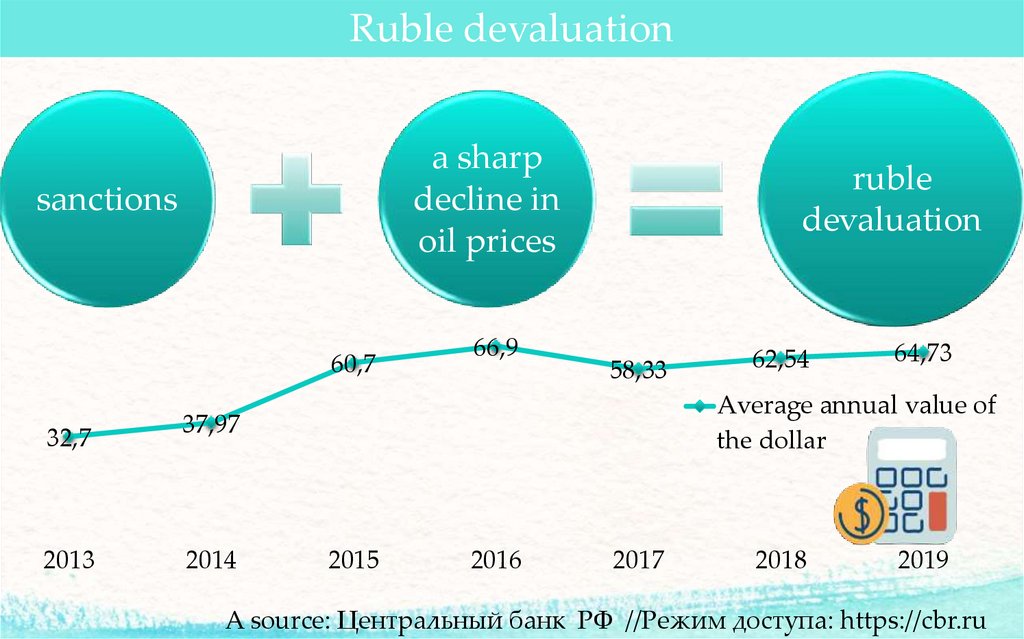
Ruble devaluationa sharp
decline in
oil prices
sanctions
60,7
32,7
2013
66,9
ruble
devaluation
58,33
64,73
Average annual value of
the dollar
37,97
2014
62,54
2015
2016
2017
2018
2019
A source: Центральный банк РФ //Режим доступа: https://cbr.ru
7.
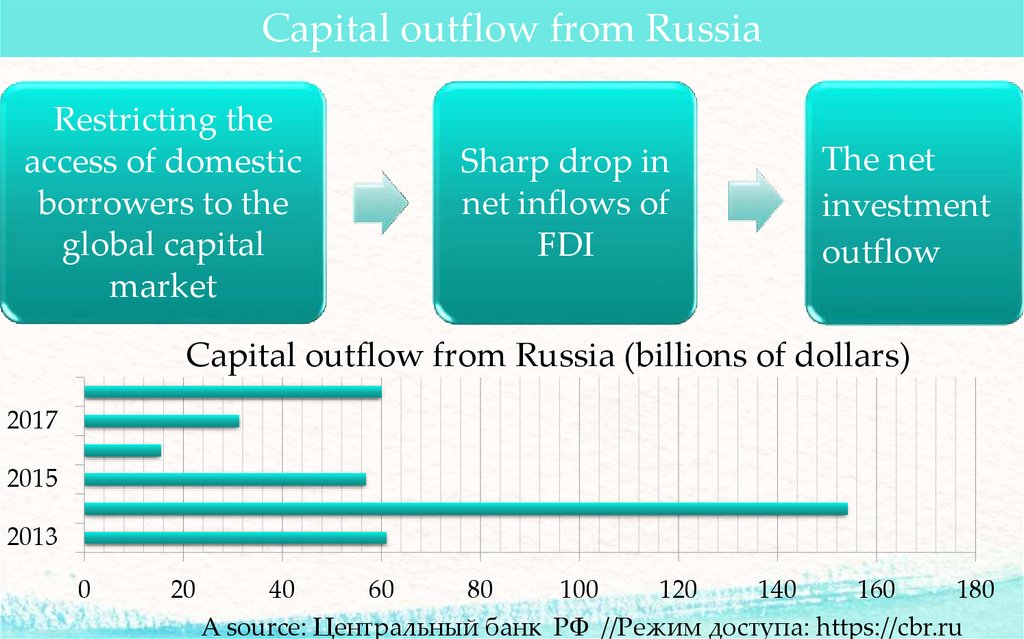
Capital outflow from RussiaRestricting the
access of domestic
borrowers to the
global capital
market
Sharp drop in
net inflows of
FDI
The net
investment
outflow
Capital outflow from Russia (billions of dollars)
2017
2015
2013
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
180
A source: Центральный банк РФ //Режим доступа: https://cbr.ru
8.
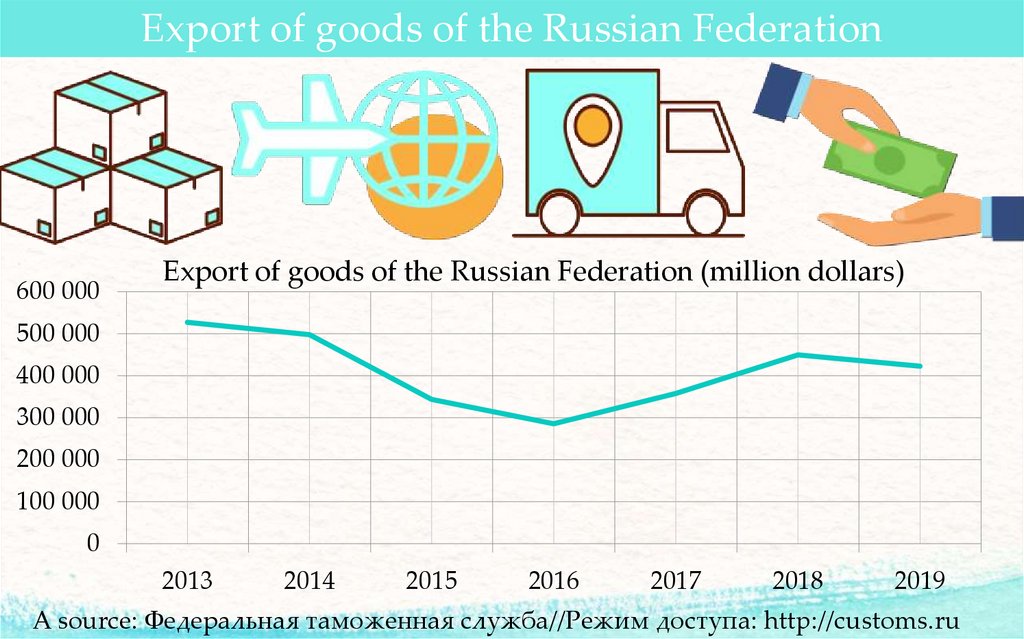
Export of goods of the Russian Federation600 000
Export of goods of the Russian Federation (million dollars)
500 000
400 000
300 000
200 000
100 000
0
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
2019
A source: Федеральная таможенная служба//Режим доступа: http://customs.ru
9.
Government measures to minimize the negative impact of sanctions:1. Providing financial risk
management assistance to banks.
2. Additional capitalization of
systemic banks.
3. Creation the national payment
system "Mir“.
10.
4. A transition to inflation targeting.5. Refraining the growth of the
monetary aggregate through
cutting budget spending.
6. Development of import-
substitution.
11.
Import substitution has its drawbacks:Low quality of Russian equipment.
The dependence on imported supplies of equipment, food
staff, seedlings, and components .
Financial resources are distributed in favor of foreign producers.
12.
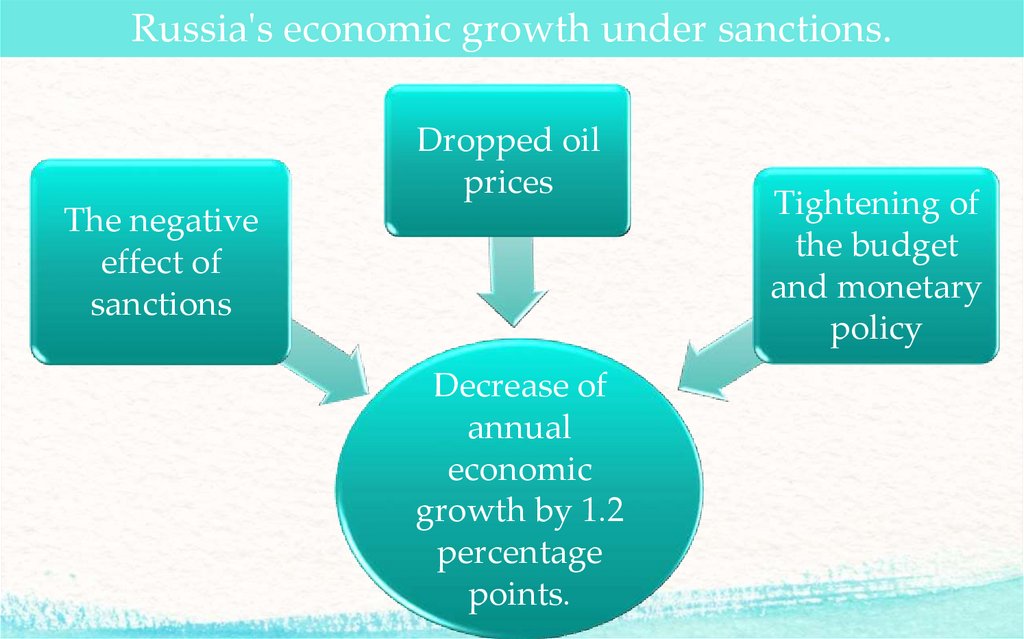
Russia's economic growth under sanctions.Dropped oil
prices
The negative
effect of
sanctions
Decrease of
annual
economic
growth by 1.2
percentage
points.
Tightening of
the budget
and monetary
policy
13.
Russia today.seek new ways
of its
development
Russia is
able to
fully cover the
external debt
increase
resistance to
possible
increase in
sanctions
the fifth-largest
national
economy in
Europe
the eleventhlargest nominal
GDP in the
world
The
economy
of Russia
is
14.
Thank youfor attention!








 Экономика
Экономика Английский язык
Английский язык