Похожие презентации:
2. Java Basics. Java Statements
1. 2. Java Basics
2. Java Statements2. Comments
• /* . . . */ - multi line comment• // . . .
- single-line comment
• /** . . . */ - comment for documentation. It
can include some additional tags (e.g.
@version, @author, @param, @return).
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
2
3. How to Use Comments
• Comments should be used to give overviewsof code and provide additional information
that is not readily available in the code itself
• Comments should contain only information
that is relevant to reading and understanding
the program
• Doc comments describe Java classes,
interfaces, constructors, methods, and elds
• Java associates documentation comments
with the rst declaration after the comment
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
3
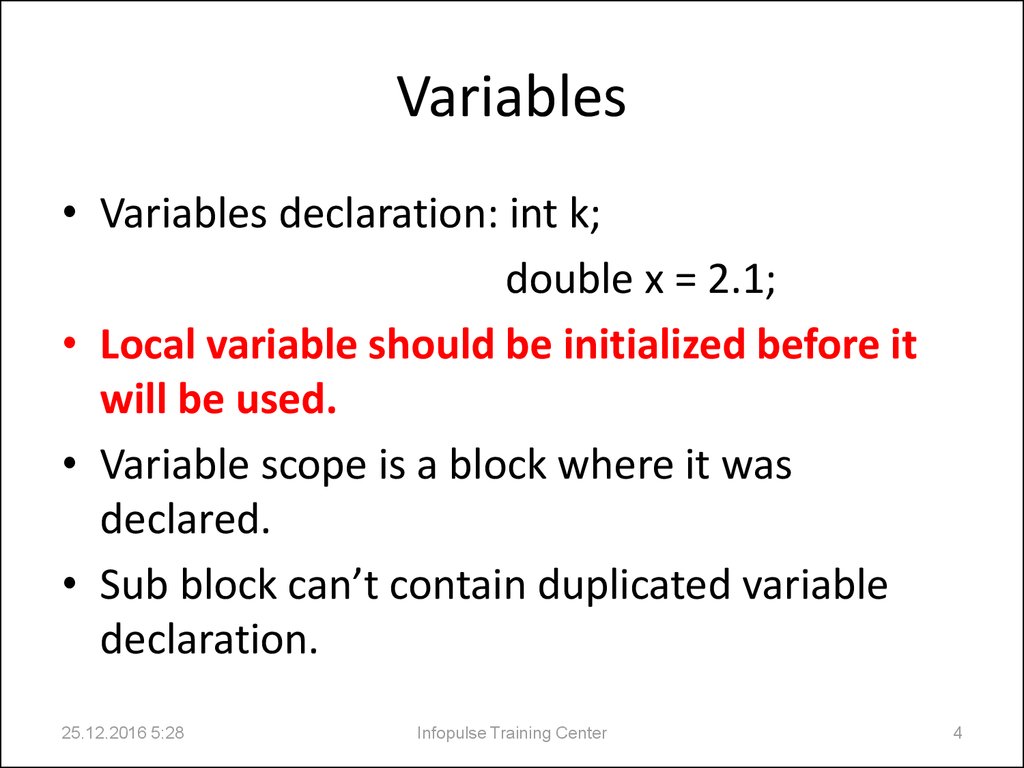
4. Variables
• Variables declaration: int k;double x = 2.1;
• Local variable should be initialized before it
will be used.
• Variable scope is a block where it was
declared.
• Sub block can’t contain duplicated variable
declaration.
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
4
5. 1. What will this program output?
public class InitTest {public static void main (String[] args) {
int a = 5;
int b;
if (a < 0) b = 10;
if (a >= 0) b = 50 ;
System.out.println(b);
}
}
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
5
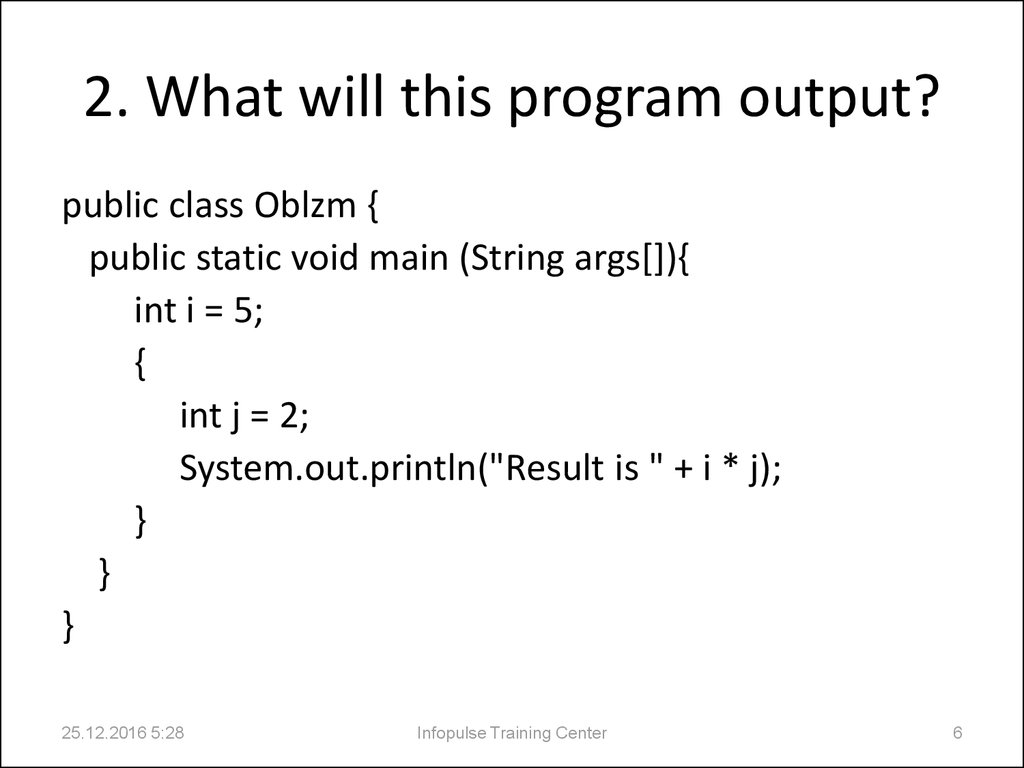
6. 2. What will this program output?
public class Oblzm {public static void main (String args[]){
int i = 5;
{
int j = 2;
System.out.println("Result is " + i * j);
}
}
}
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
6
7. 3. What will this program output?
public class Oblzm {public static void main (String args[]){
int i = 5;
{
int j = 2;
}
System.out.println("Result is “ + i * j);
}
}
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
7
8. 4. What will this program output?
public class Oblzm {public static void main (String args[]){
int i = 5;
{
int j = 2;
int i = 4;
System.out.println("Result is " + i * j);
}
}
}
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
8
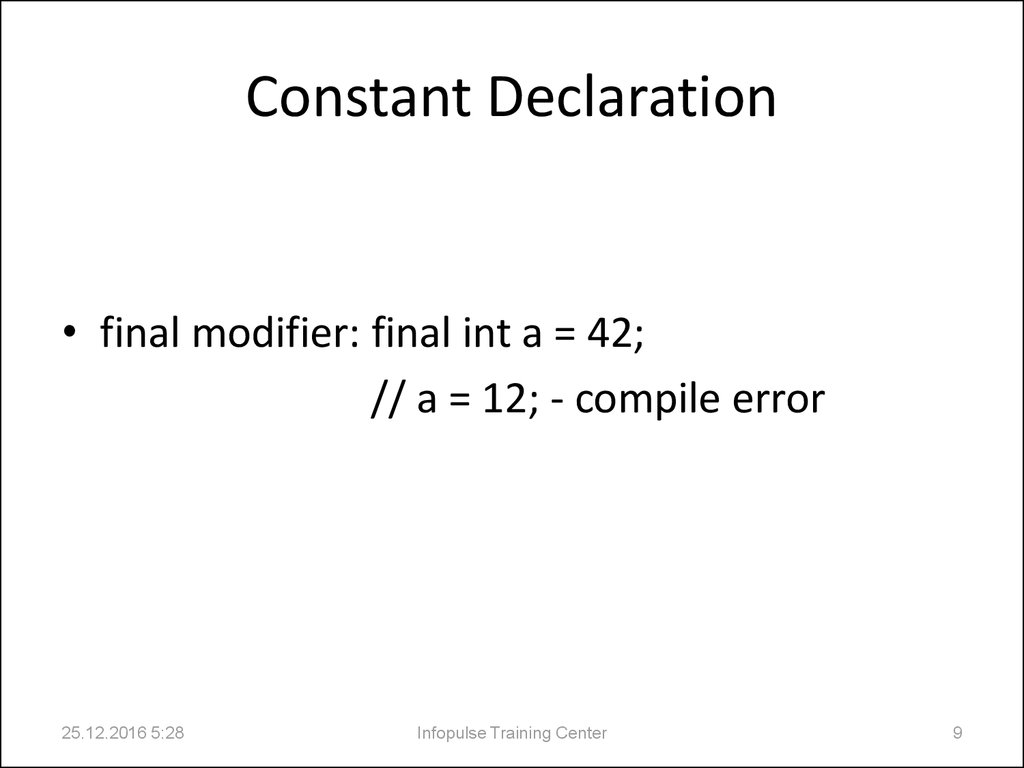
9. Constant Declaration
• final modifier: final int a = 42;// a = 12; - compile error
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
9
10. If-Then_Else Statement I
if (boolean_expression) {statements
}
if (boolean_expression) {
statements
} else {
statements
}
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
10
11. If-Then_Else Statement II
if (boolean_expression) {statements;
} else if (boolean_expression) {
statements;
} else if (boolean_expression) {
statements;
}
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
11
12. If-Then-Else Example
int a = 10;if (a > 0) {
System.out.println("Positive");
}
else if (a < 0) {
System.out.println("Negative");
}
else {
System.out.println("Zero");
}
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
12
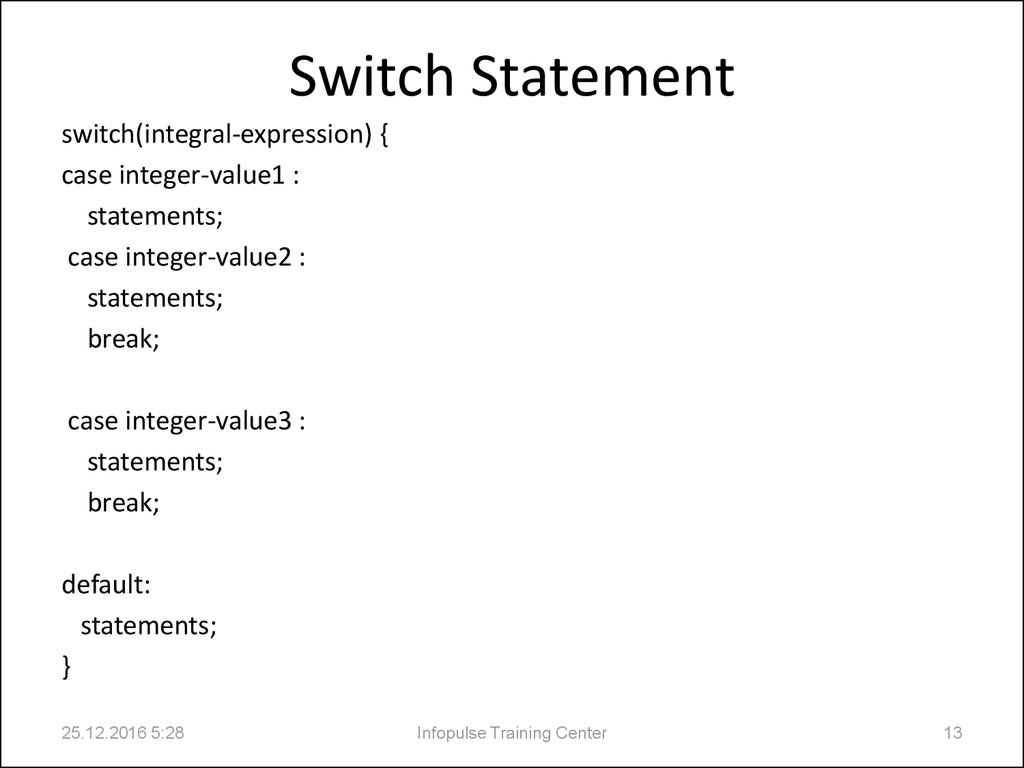
13. Switch Statement
switch(integral-expression) {case integer-value1 :
statements;
case integer-value2 :
statements;
break;
case integer-value3 :
statements;
break;
default:
statements;
}
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
13
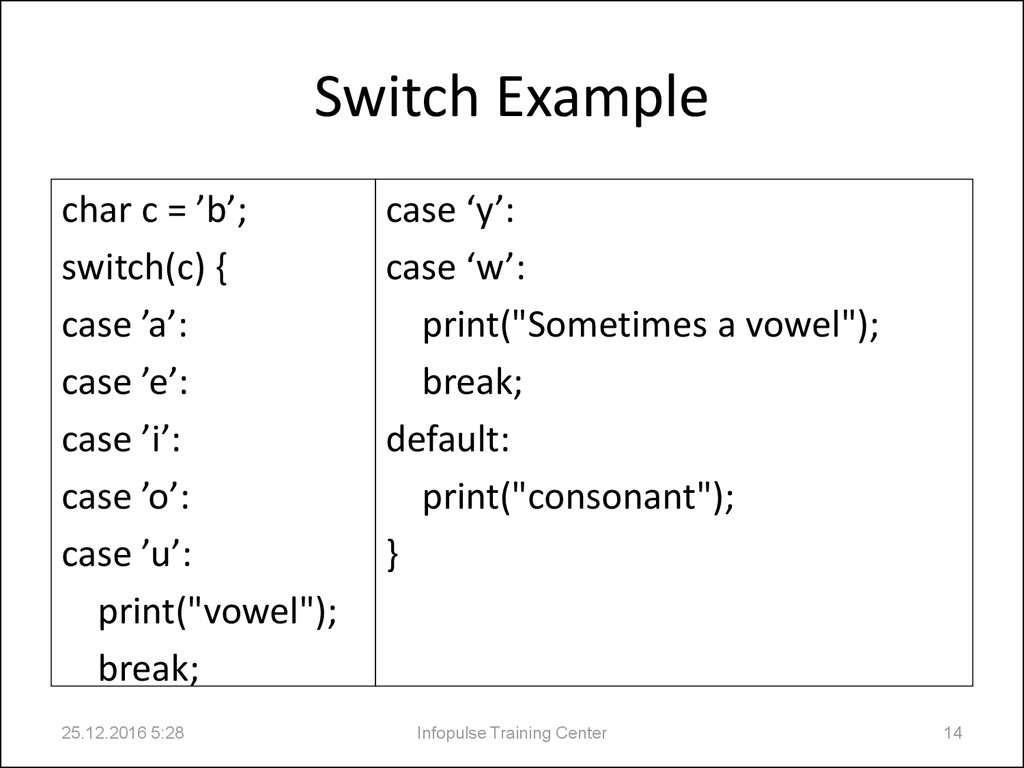
14. Switch Example
char c = ’b’;switch(c) {
case ’a’:
case ’e’:
case ’i’:
case ’o’:
case ’u’:
print("vowel");
break;
25.12.2016 5:28
case ‘y’:
case ‘w’:
print("Sometimes a vowel");
break;
default:
print("consonant");
}
Infopulse Training Center
14
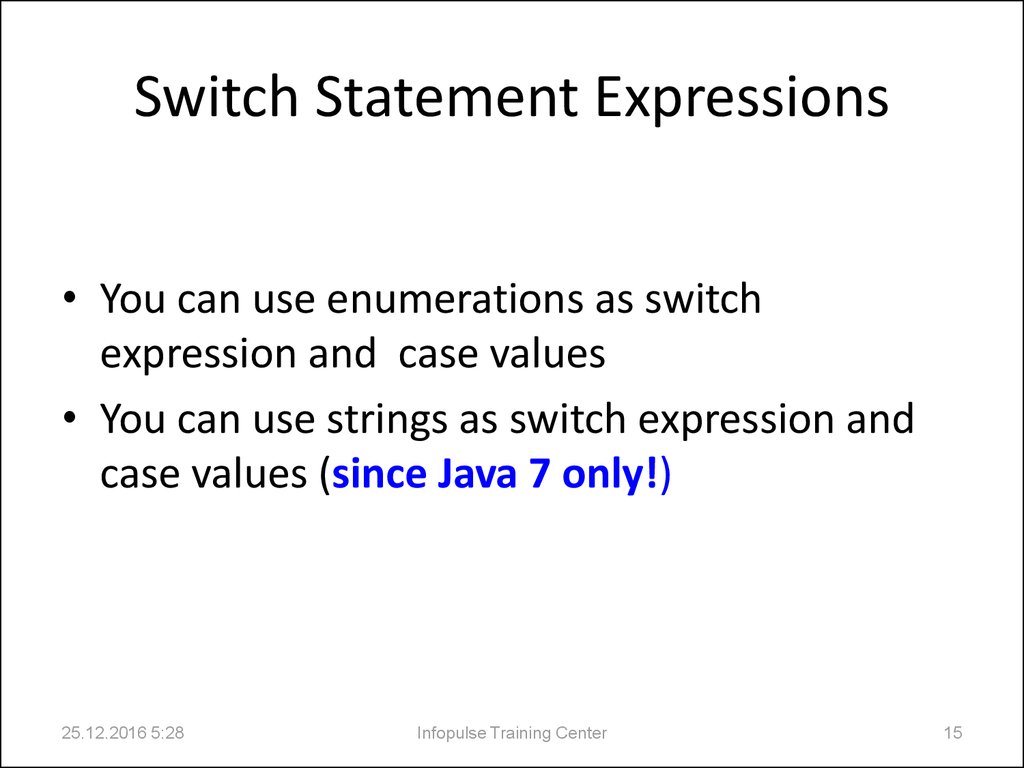
15. Switch Statement Expressions
• You can use enumerations as switchexpression and case values
• You can use strings as switch expression and
case values (since Java 7 only!)
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
15
16. While and Do-While Statement
while (boolean_expression) {statements;
}
do {
statements;
} while (boolean_expression);
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
16
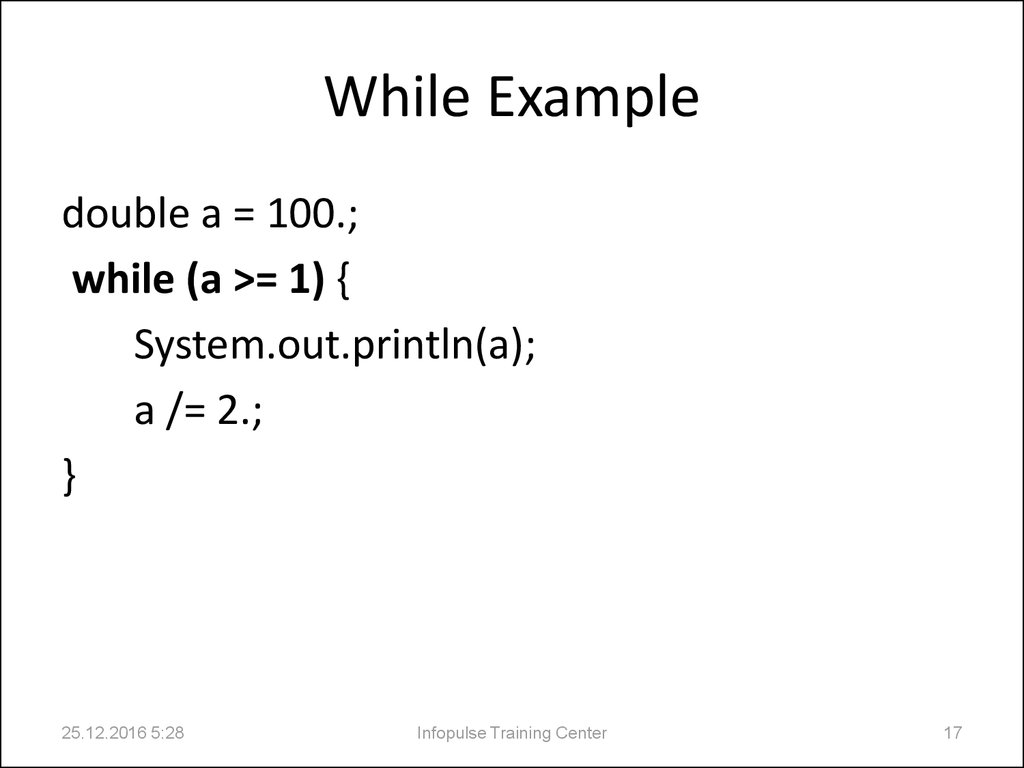
17. While Example
double a = 100.;while (a >= 1) {
System.out.println(a);
a /= 2.;
}
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
17
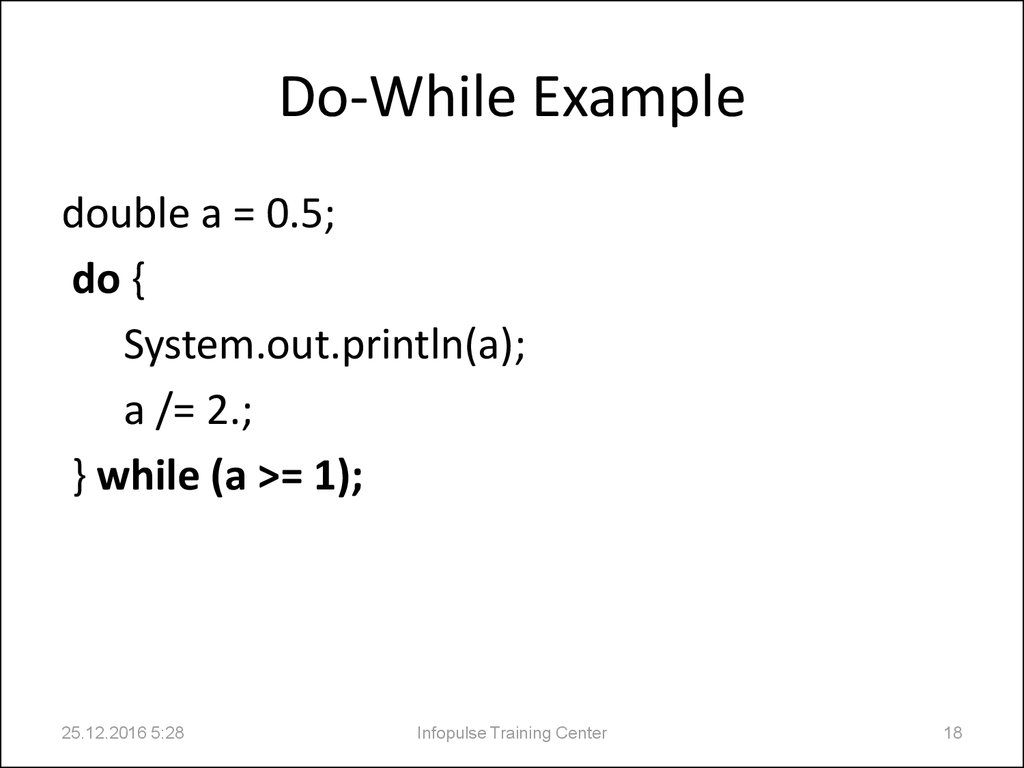
18. Do-While Example
double a = 0.5;do {
System.out.println(a);
a /= 2.;
} while (a >= 1);
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
18
19. For Statement
for (initialization; Boolean-expression; step) {statements;
}
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
19
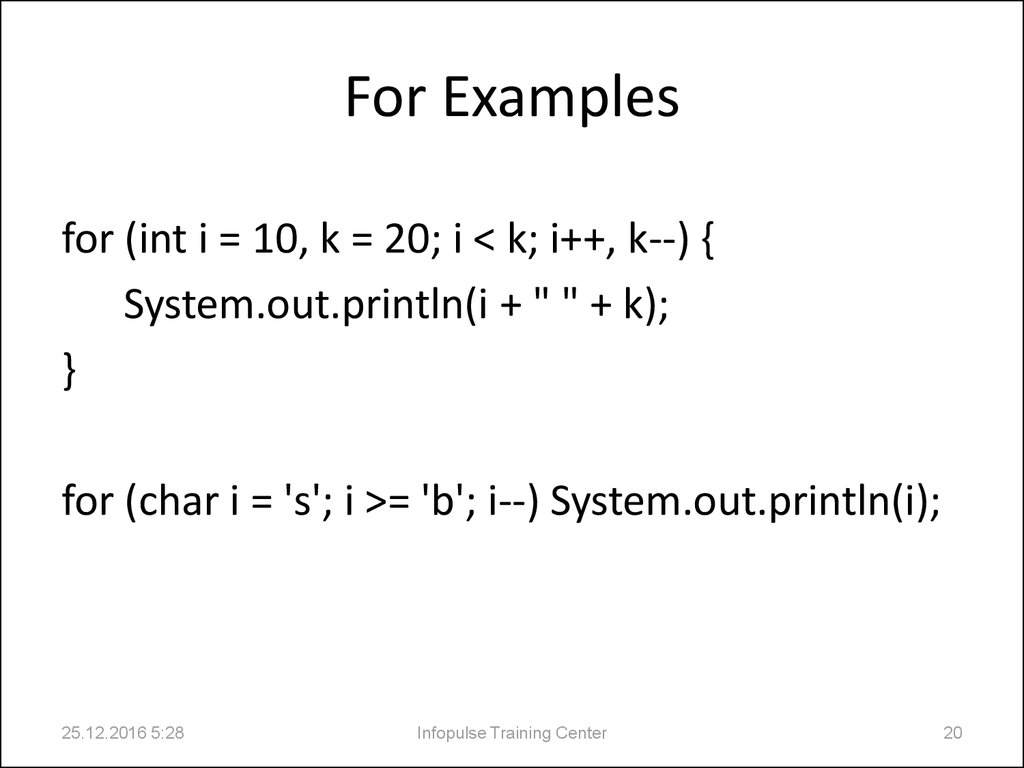
20. For Examples
for (int i = 10, k = 20; i < k; i++, k--) {System.out.println(i + " " + k);
}
for (char i = 's'; i >= 'b'; i--) System.out.println(i);
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
20
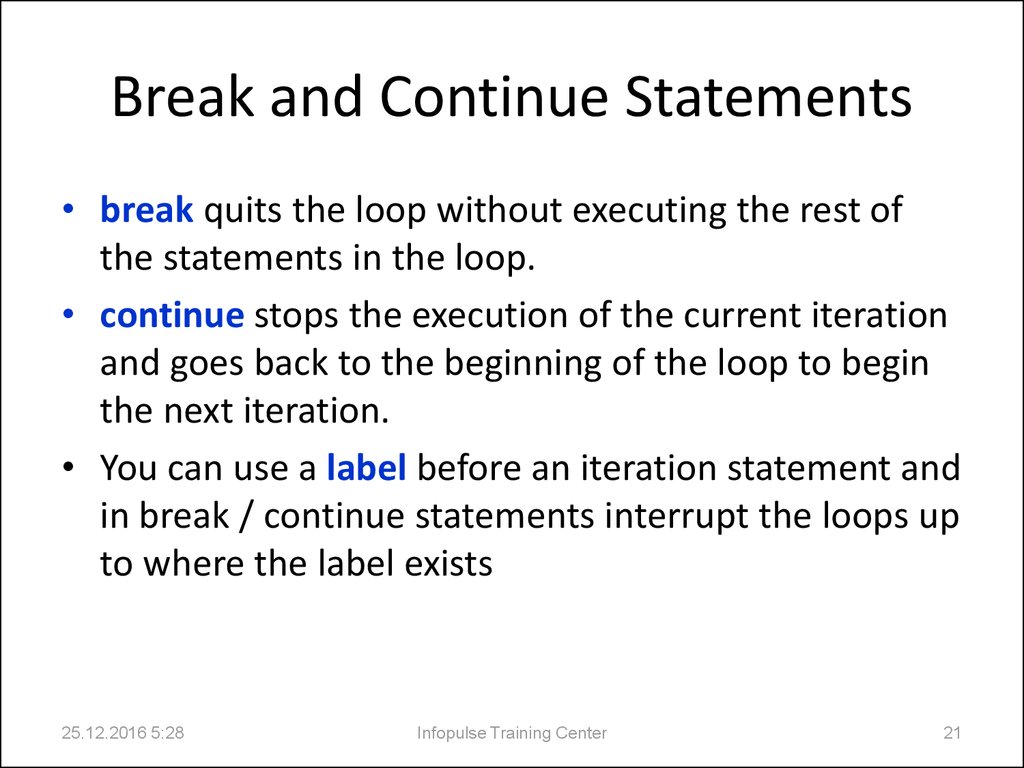
21. Break and Continue Statements
• break quits the loop without executing the rest ofthe statements in the loop.
• continue stops the execution of the current iteration
and goes back to the beginning of the loop to begin
the next iteration.
• You can use a label before an iteration statement and
in break / continue statements interrupt the loops up
to where the label exists
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
21
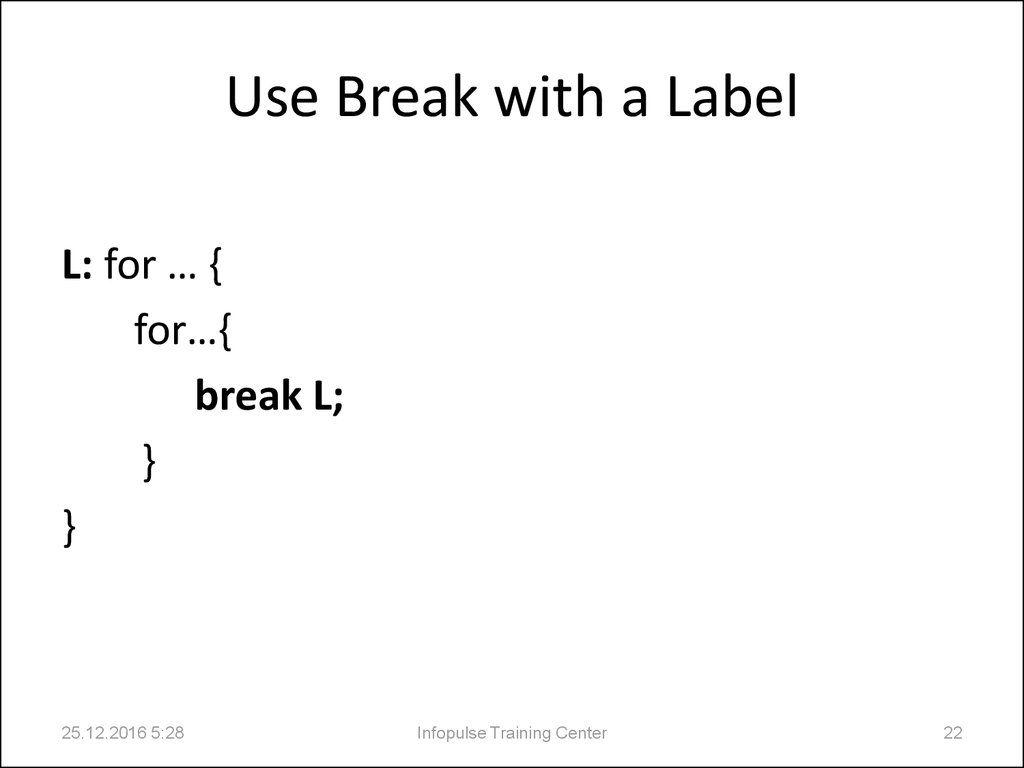
22. Use Break with a Label
L: for … {for…{
break L;
}
}
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
22
23. Exercise 2.2.1.
• Find and print all divisors of a given naturalnumber n.
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
23
24. Exercise 2.2.1.
• See 221Divisors project for the full text.25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
24
25. Exercise 2.2.2.
• Find and print all prime divisors of a givennatural number n.
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
25
26. Exercise 2.2.3.
• Find sum of an infinite row for a given xx x2
x3
xn
1
...
...
1
2!
3!
n!
• Compare result with a Math.exp(x) method
value
25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
26
27. Manuals
• Learning the Java Language. Language Basics25.12.2016 5:28
Infopulse Training Center
27
















 Программирование
Программирование








