Похожие презентации:
Market structure, market power, and welfare ( lecture 2 )
1. Lecture 2: Market structure, market power, and welfare
2. Outline
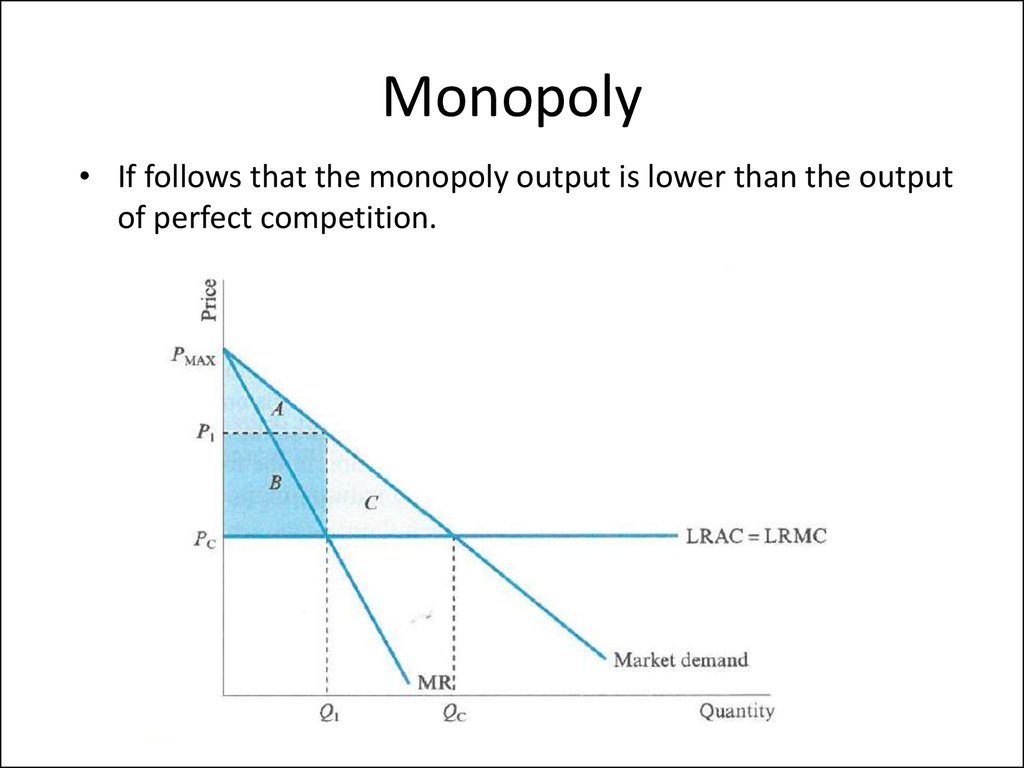
• Perfect competition and monopoly.• Welfare
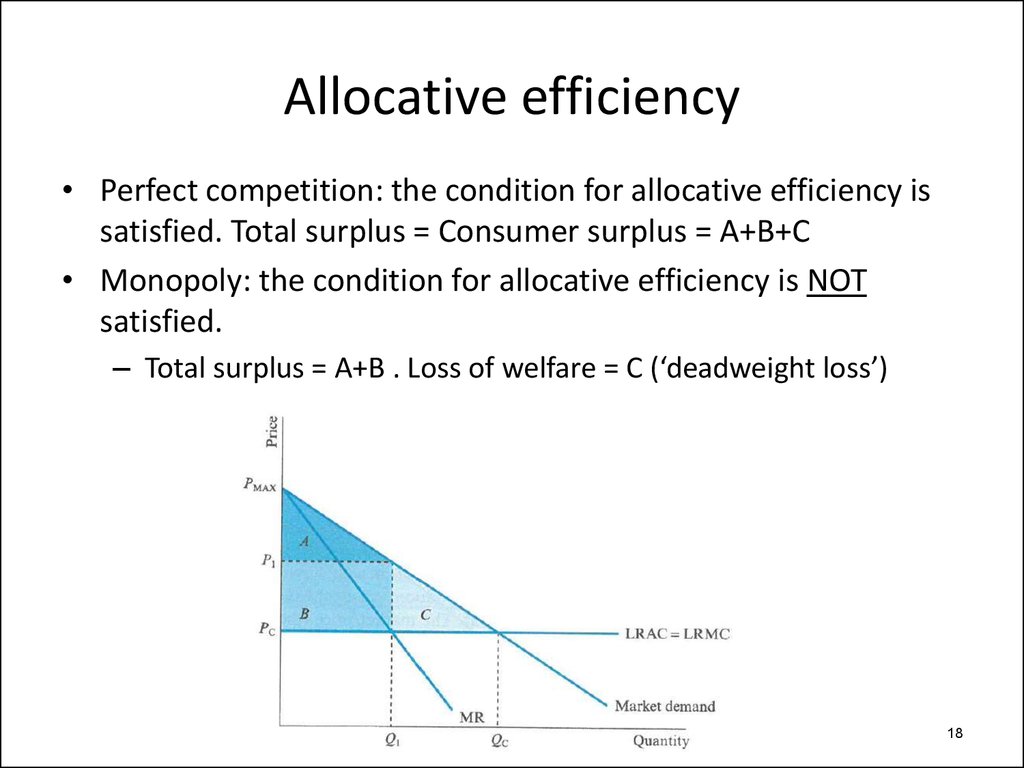
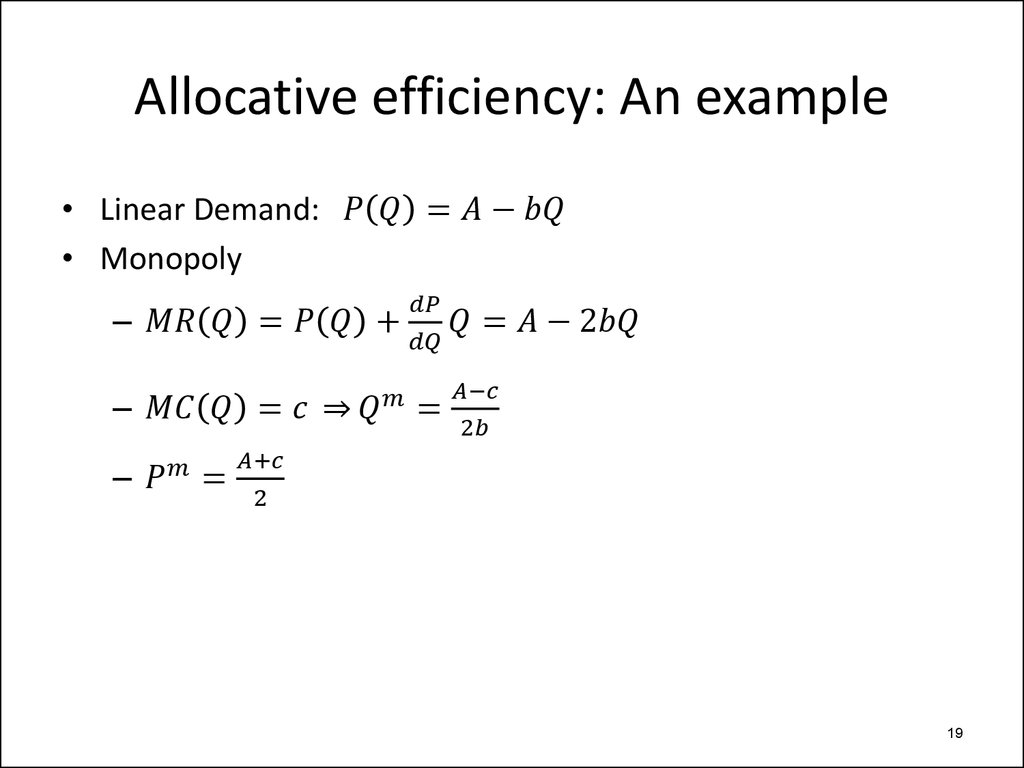
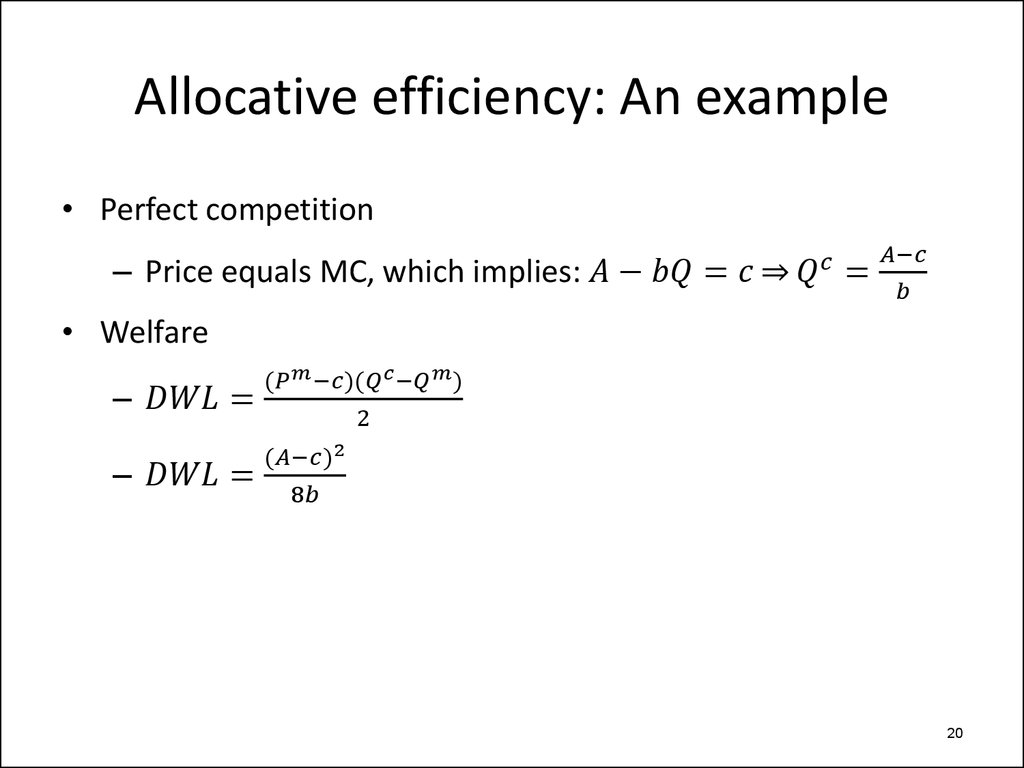
– Allocative efficiency
• Surplus standard
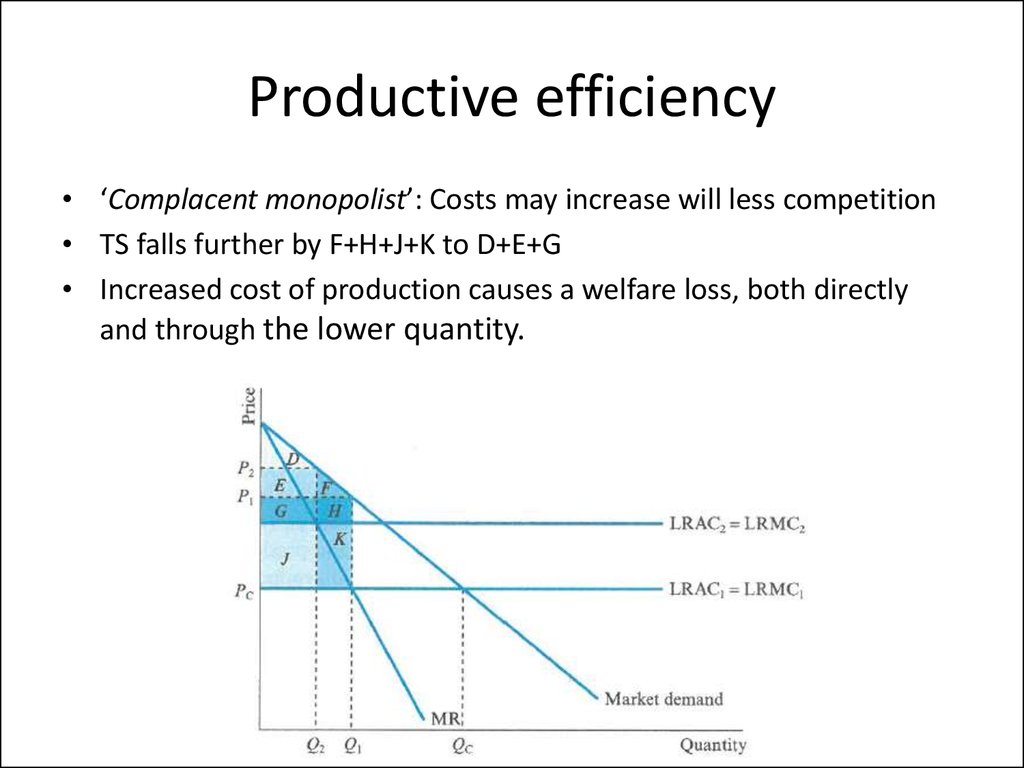
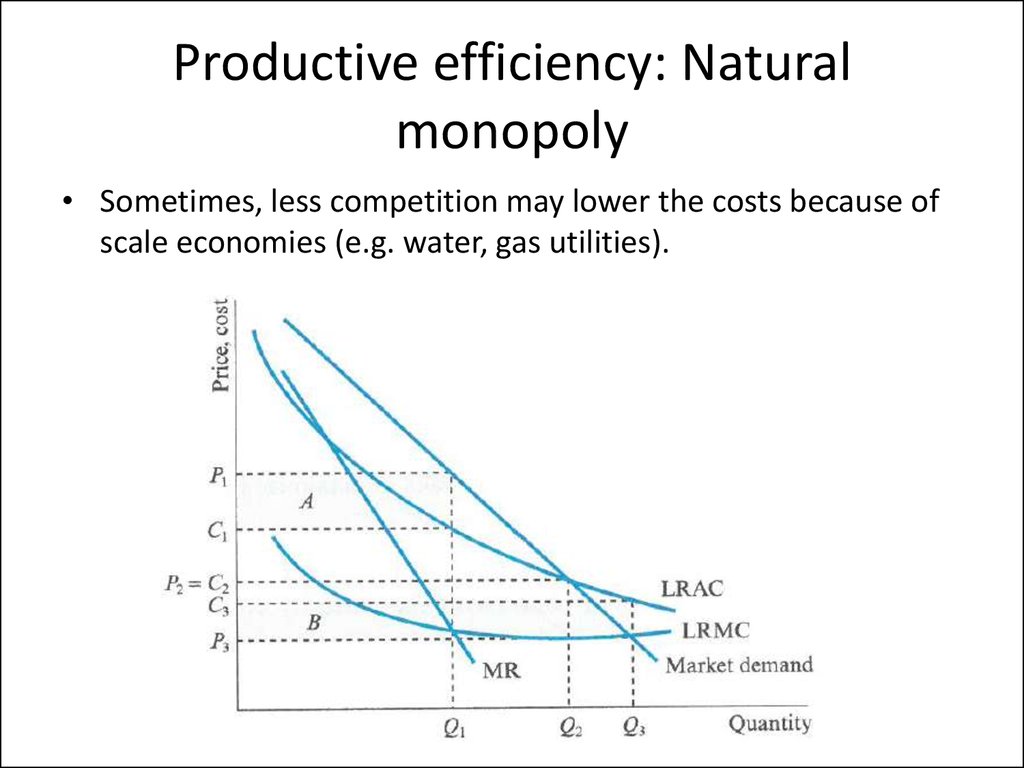
– Productive efficiency
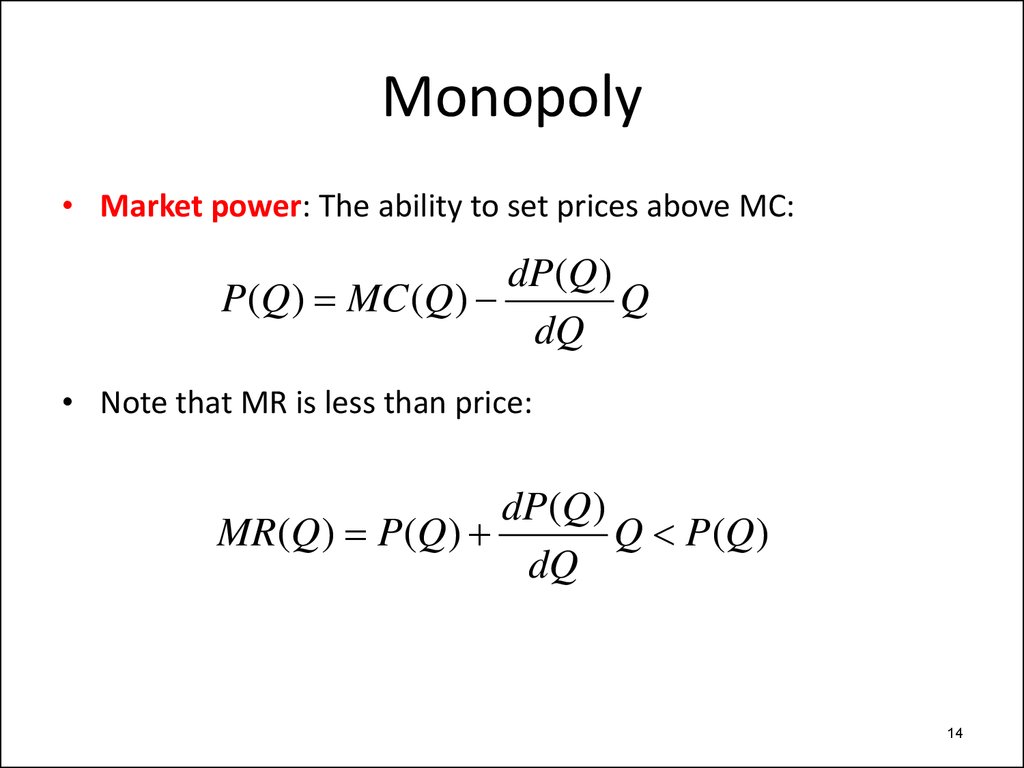
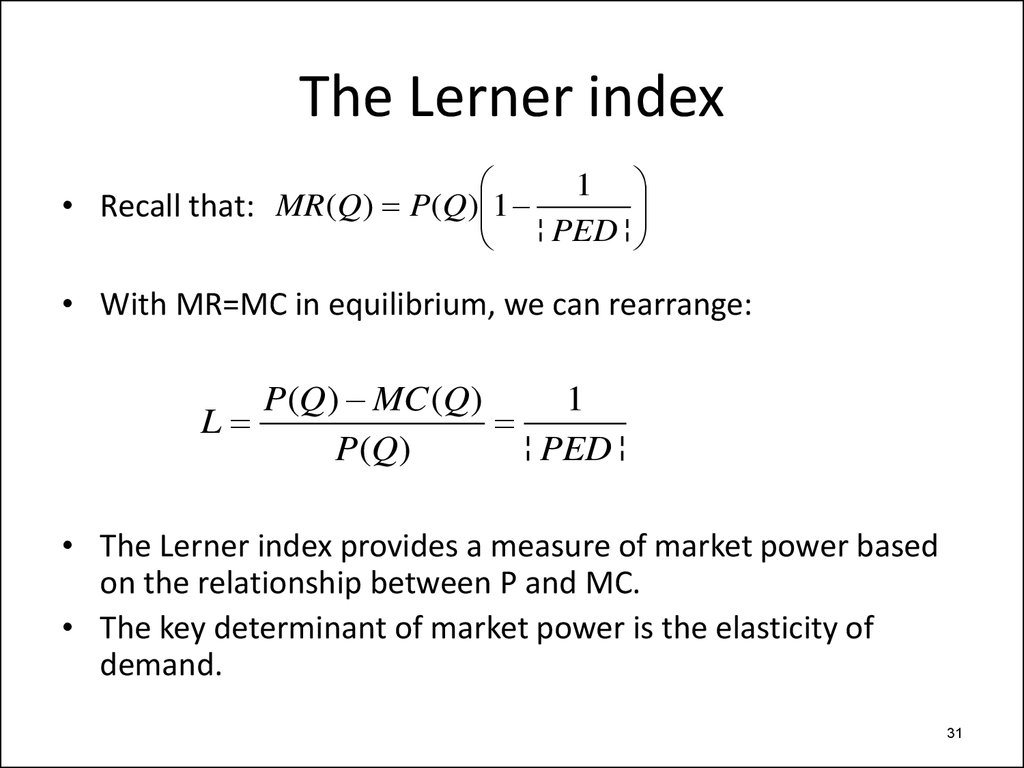
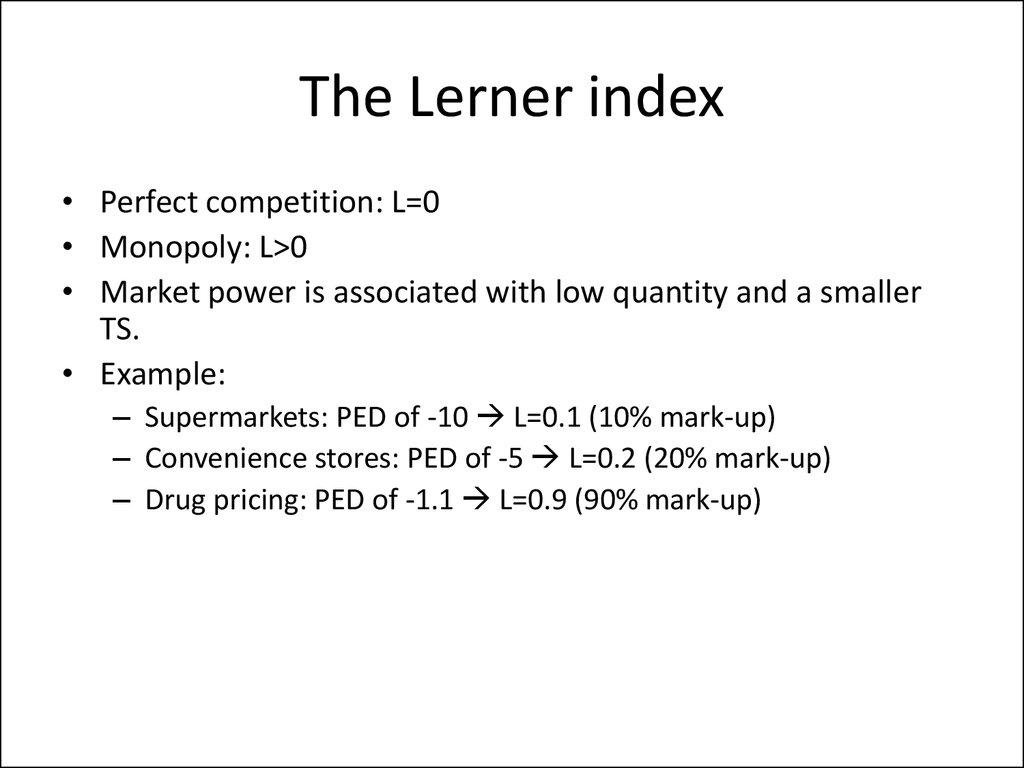
The Lerner index
Welfare: more than just quantity
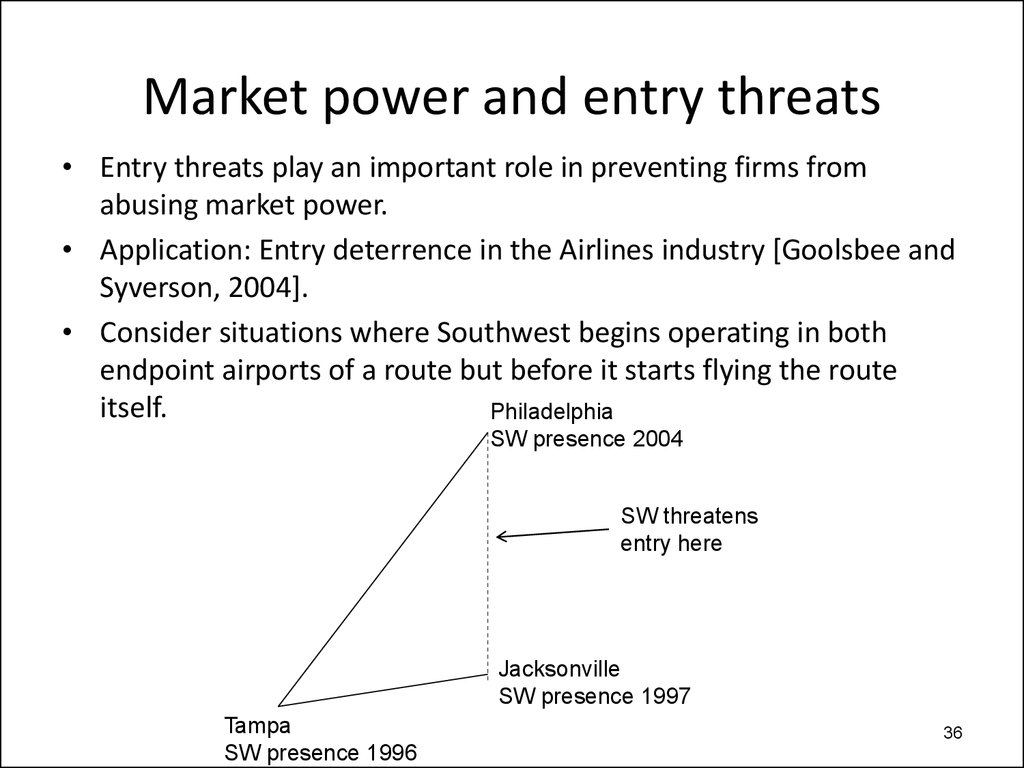
Market power and entry threats
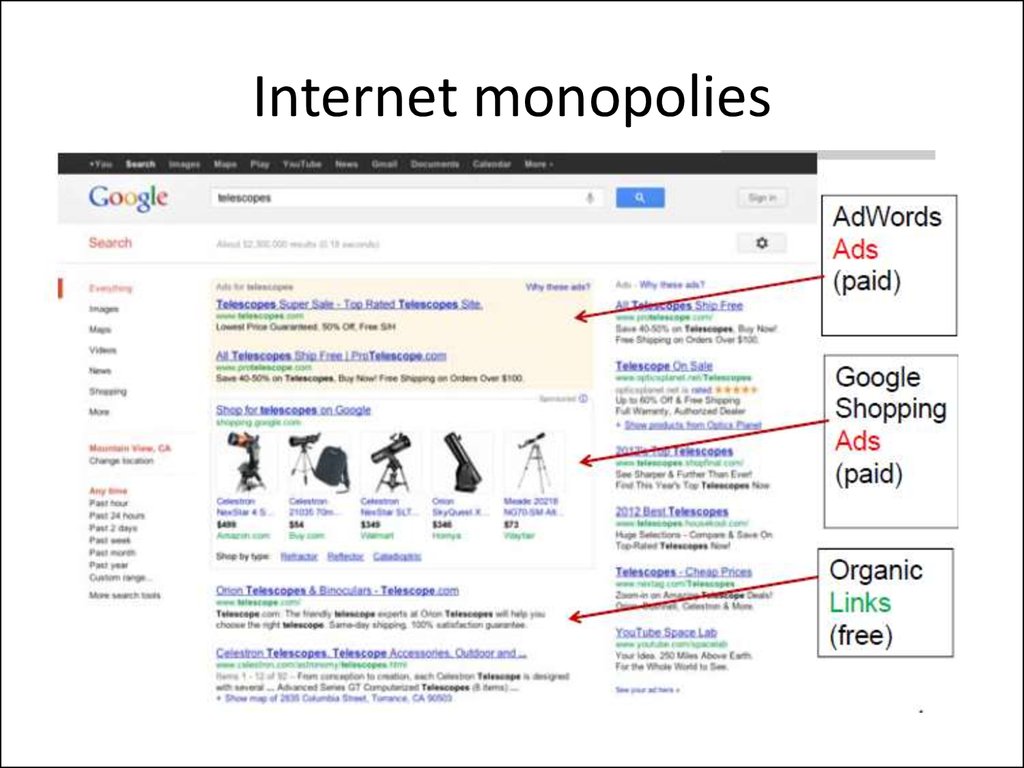
Application: Internet monopolies
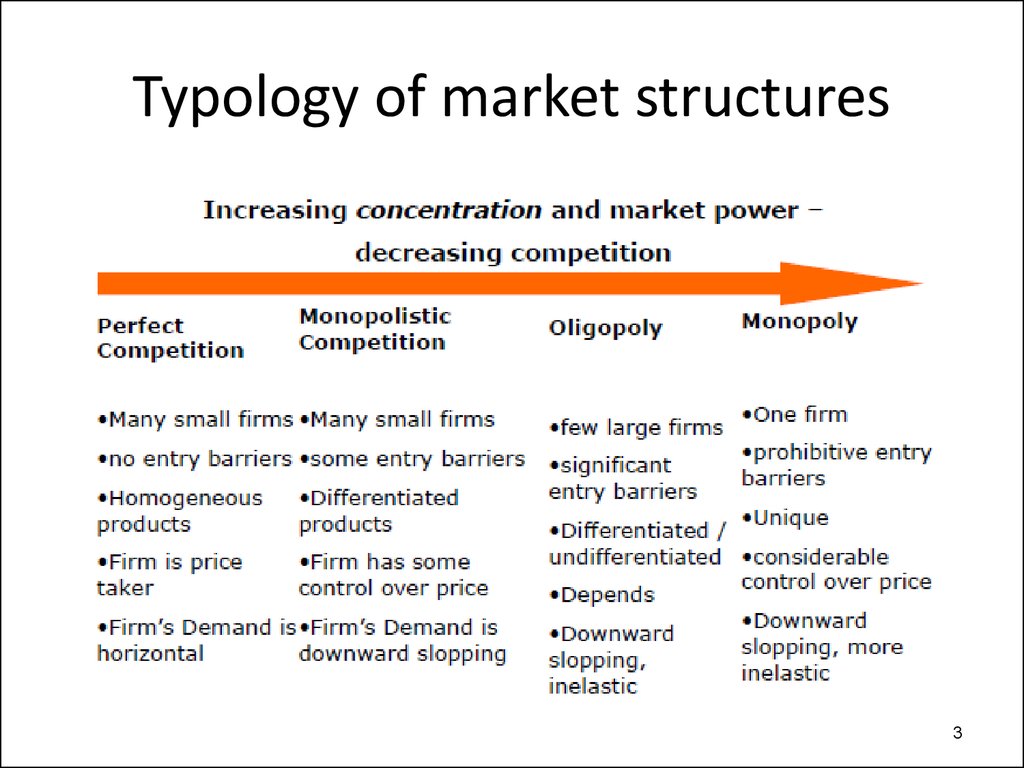
3. Typology of market structures
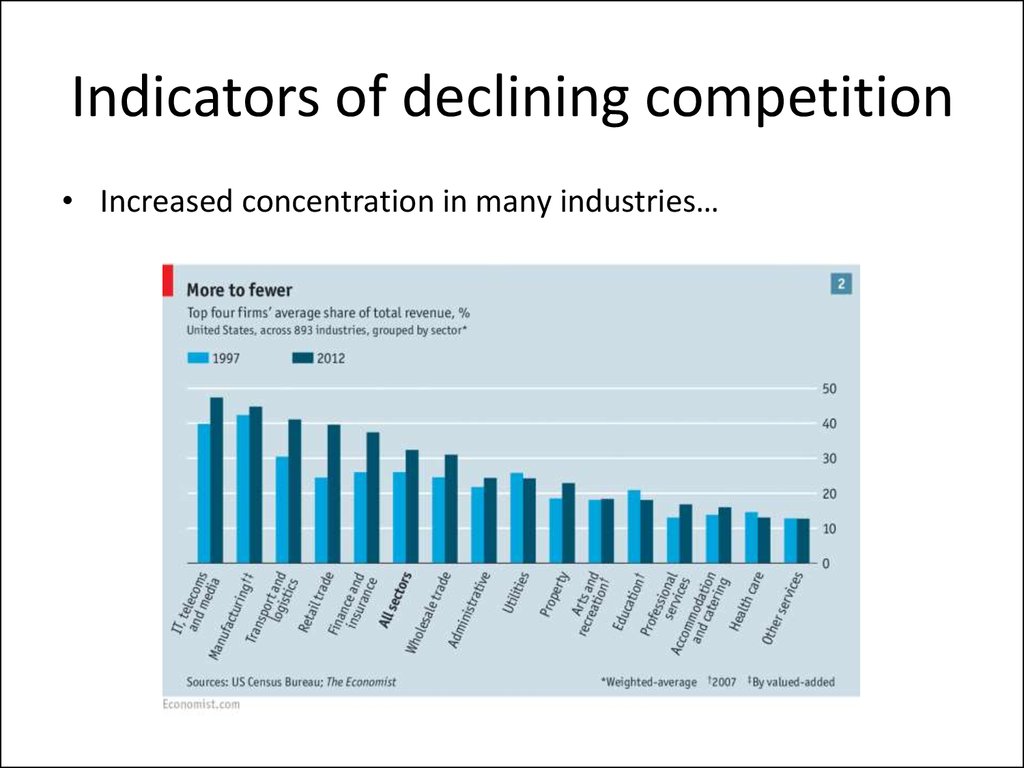
34. Indicators of declining competition
• Increased concentration in many industries…5. Indicators of declining competition
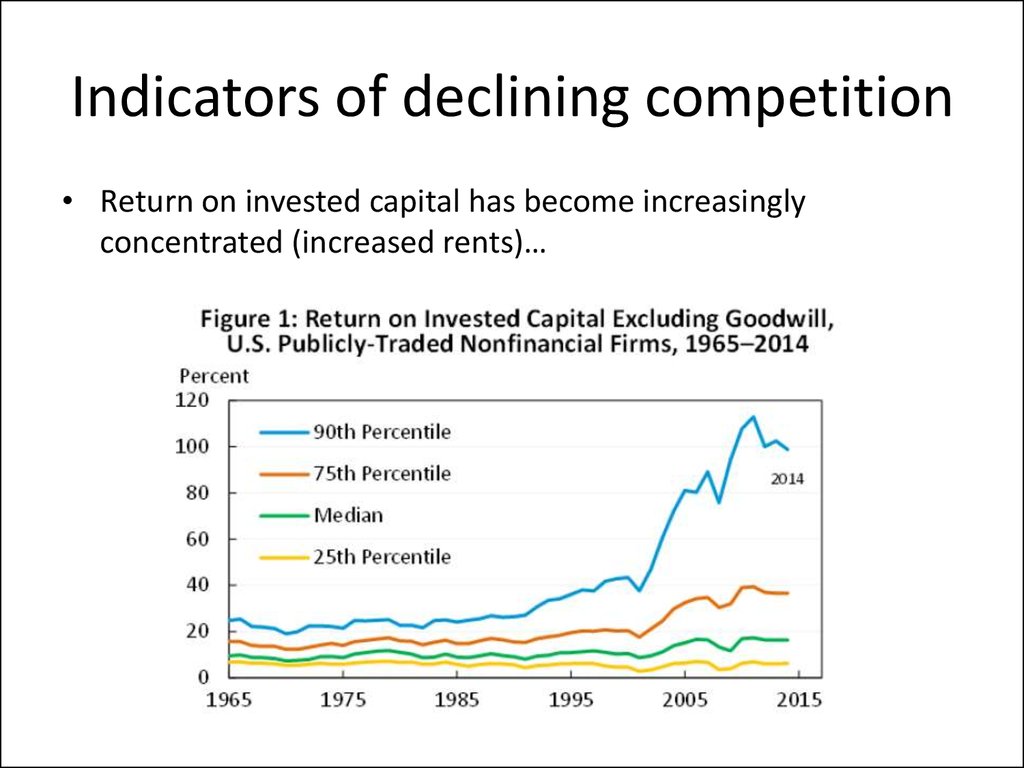
• Return on invested capital has become increasinglyconcentrated (increased rents)…
6. Indicators of declining competition
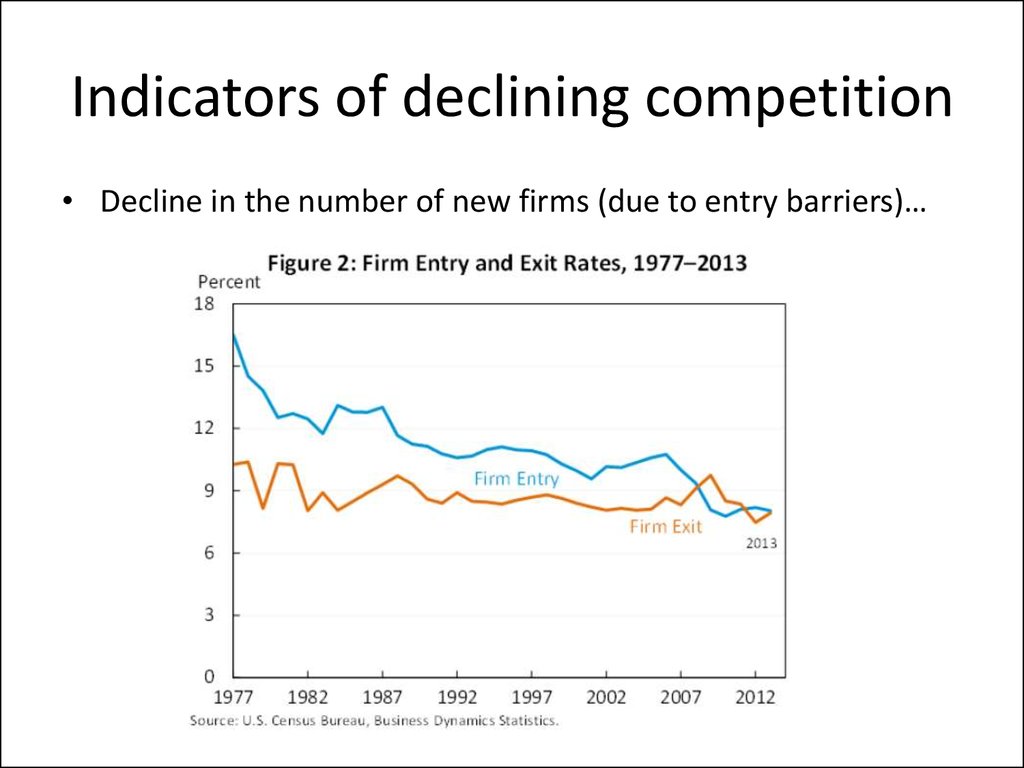
• Decline in the number of new firms (due to entry barriers)…7. Causes of declining competition
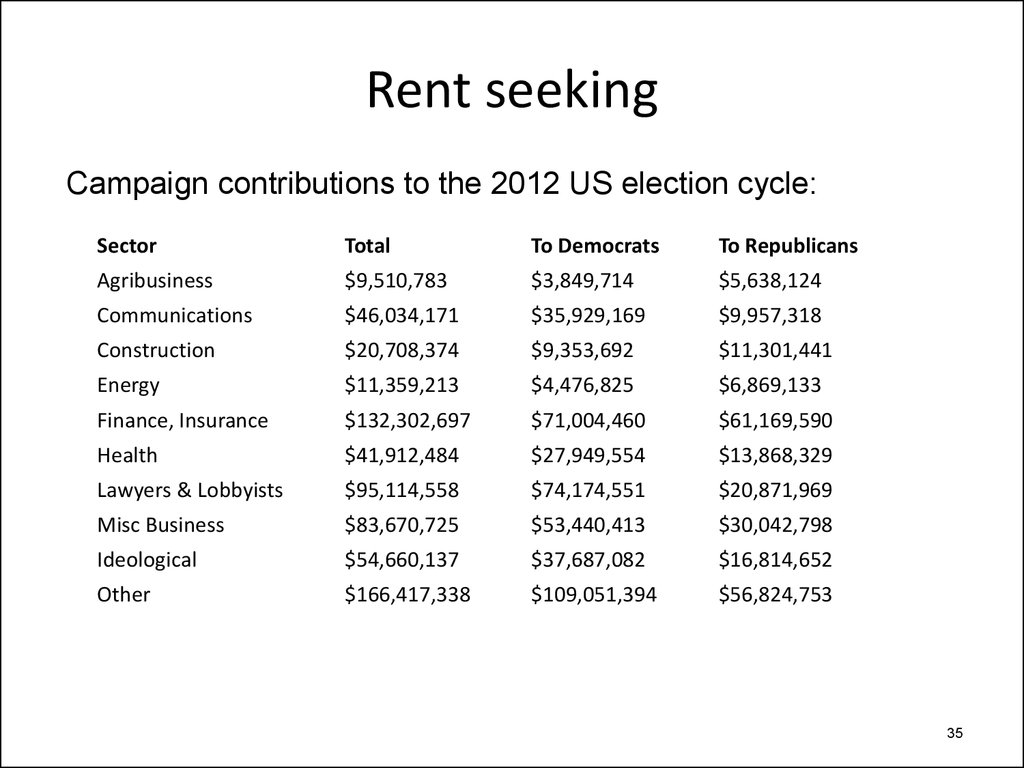
• Mergers: in 2015,– Global M&A volume hit $5 trillion, U.S. M&A made up 50% of
the total.
– 69 deals over $10 billion, and 10 deals over $50 billion.
– Pfizer’s $160 billion acquisition of Allergan.
– Anheuser-Busch InBev’s $117 billion acquisition of SABMiller.
• Firm conduct
–
–
–
–
R&D
Advertising
Collusion
Erecting entry barriers
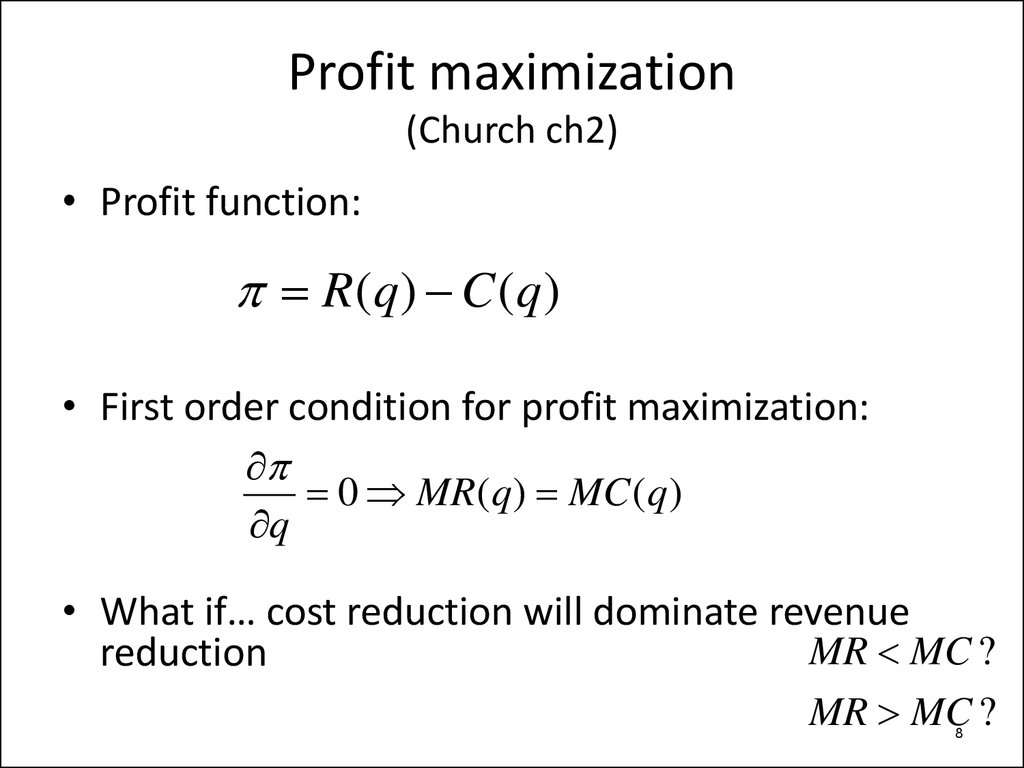
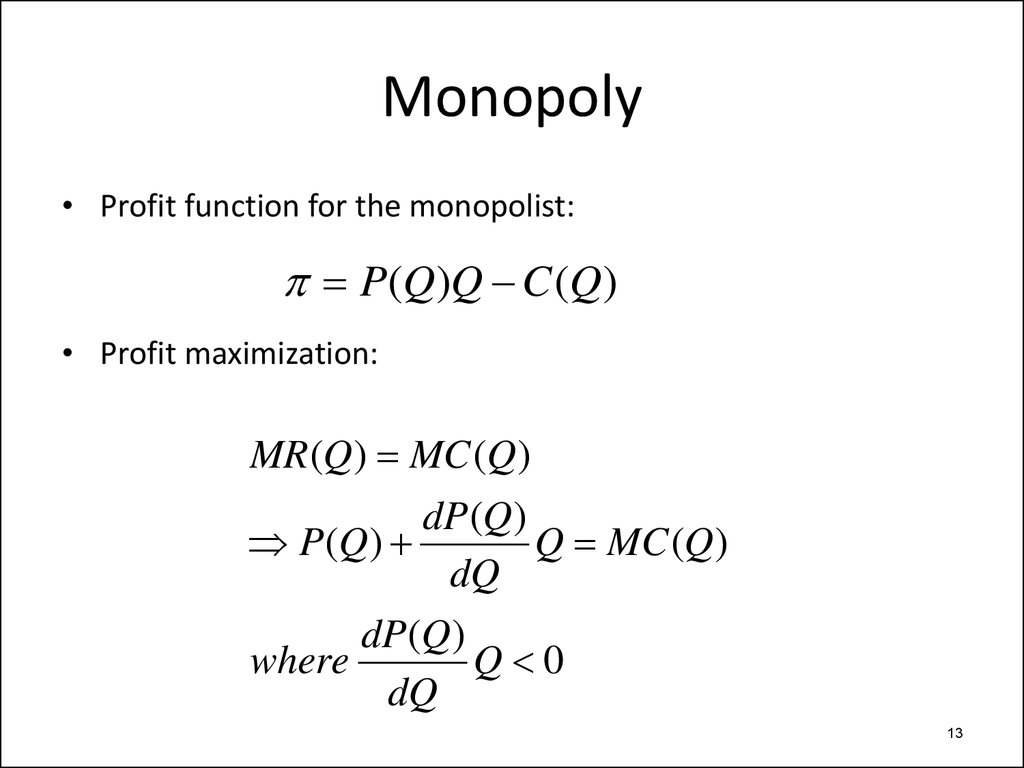
8. Profit maximization (Church ch2)
• Profit function:R(q) C (q)
• First order condition for profit maximization:
0 MR(q ) MC (q )
q
• What if… cost reduction will dominate revenue
MR MC ?
reduction
MR MC ?
8
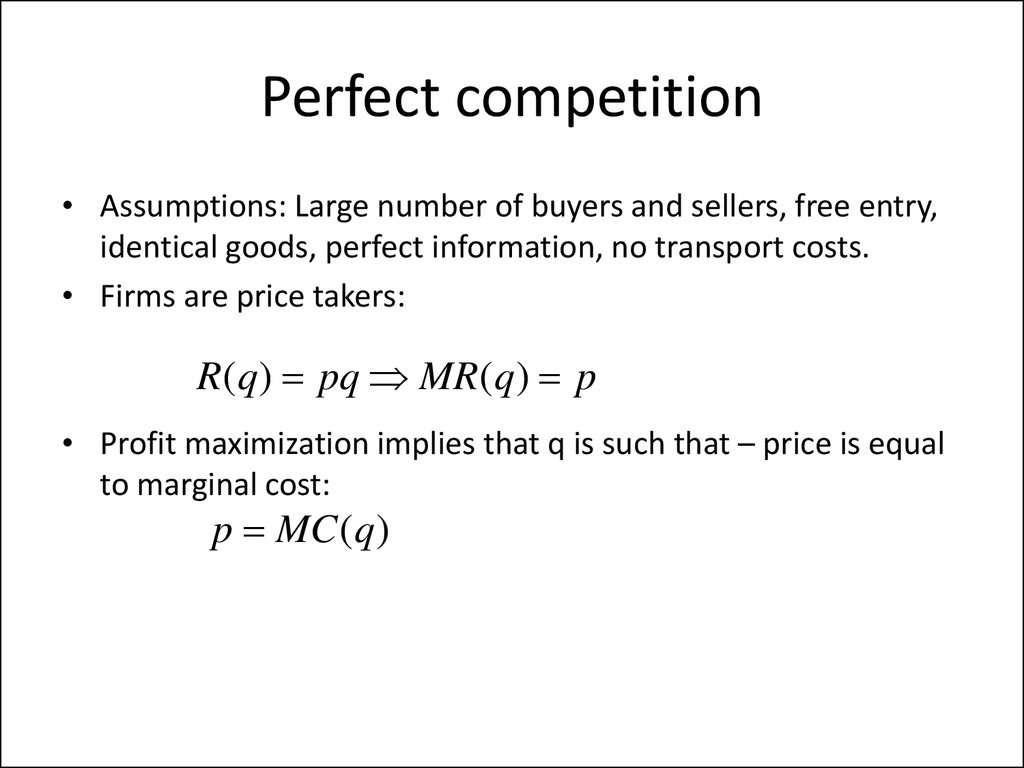
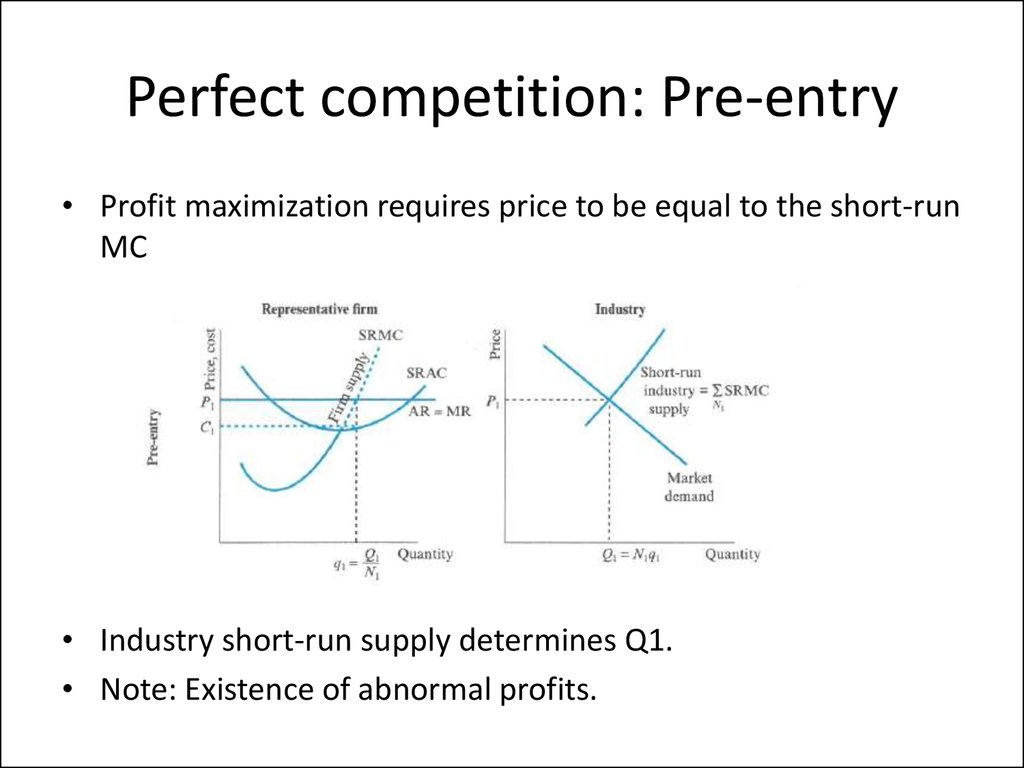
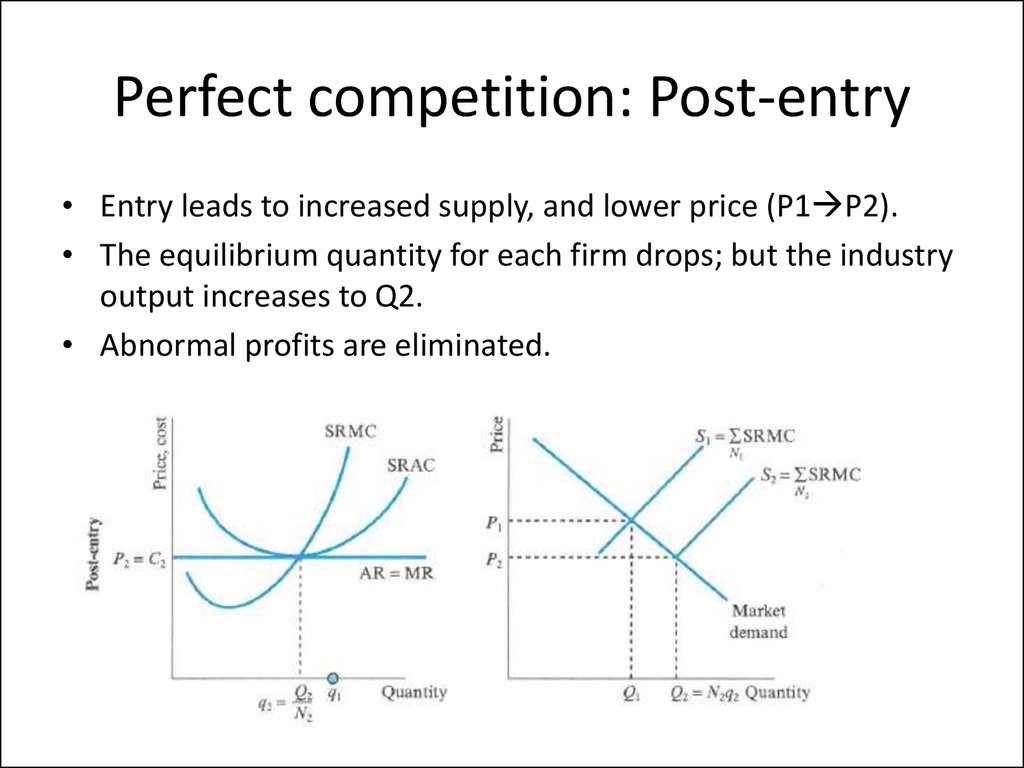
9. Perfect competition
• Assumptions: Large number of buyers and sellers, free entry,identical goods, perfect information, no transport costs.
• Firms are price takers:
R(q) pq MR(q) p
• Profit maximization implies that q is such that – price is equal
to marginal cost:
p MC (q)






























 Экономика
Экономика Менеджмент
Менеджмент Бизнес
Бизнес








