Похожие презентации:
Anatomical & physiological features of urinary tract in children. Semiotics of urinary tract diseases. Renal failure
1. ZAPOROZHYE STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY PROPEDEUTICS OF PEDIATRICS DEPARTMENT O.G. Ivanko – M.D. & PH.D., Professor of pediatrics, the Head of propedeutics of pediatrics department
ZAPOROZHYE STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITYPROPEDEUTICS OF PEDIATRICS DEPARTMENT
O.G. Ivanko – M.D. & PH.D., Professor of pediatrics,
the Head of propedeutics of pediatrics department
ANATOMICAL & PHYSIOLOGICAL FEATURES
OF URINARY TRACT IN CHILDREN.
SEMIOTICS OF URINARY TRACT DISEASES.
RENAL FAILURE.
N.V. Kizima – M.D., associate professor
2.
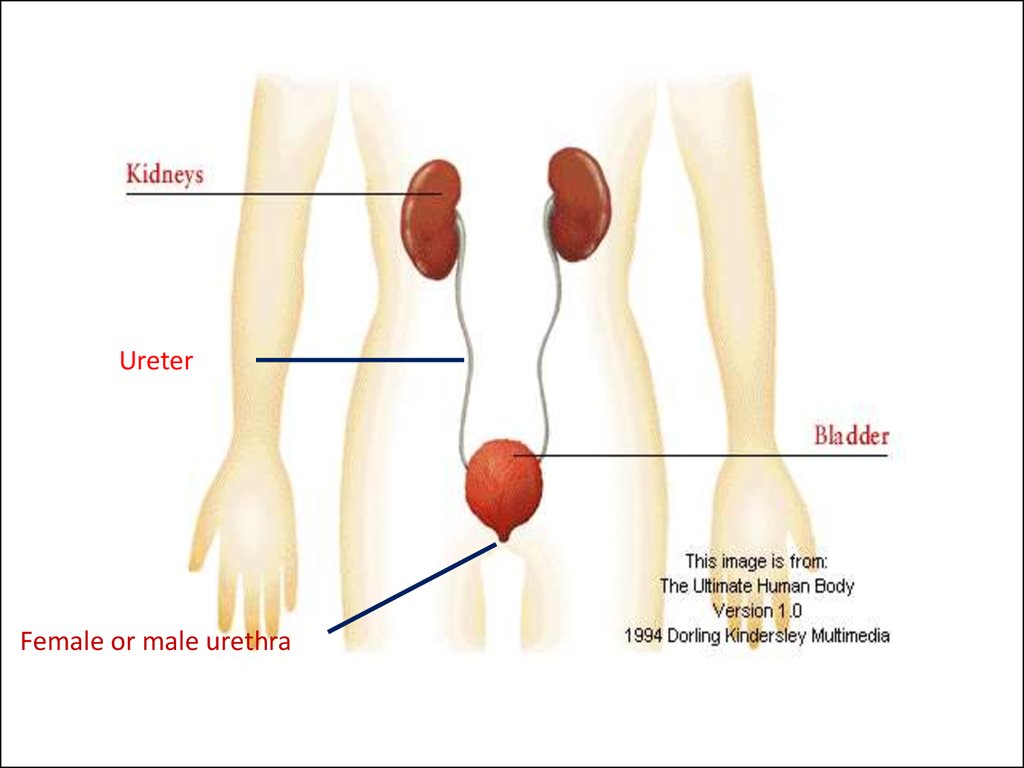
UreterFemale or male urethra
3.
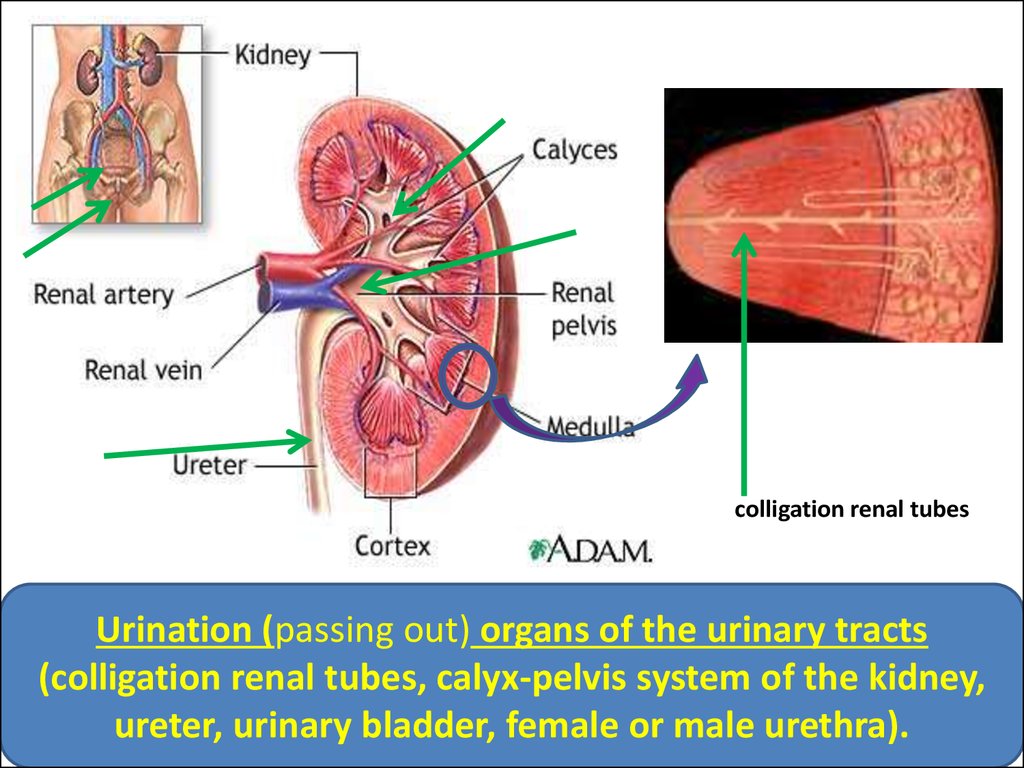
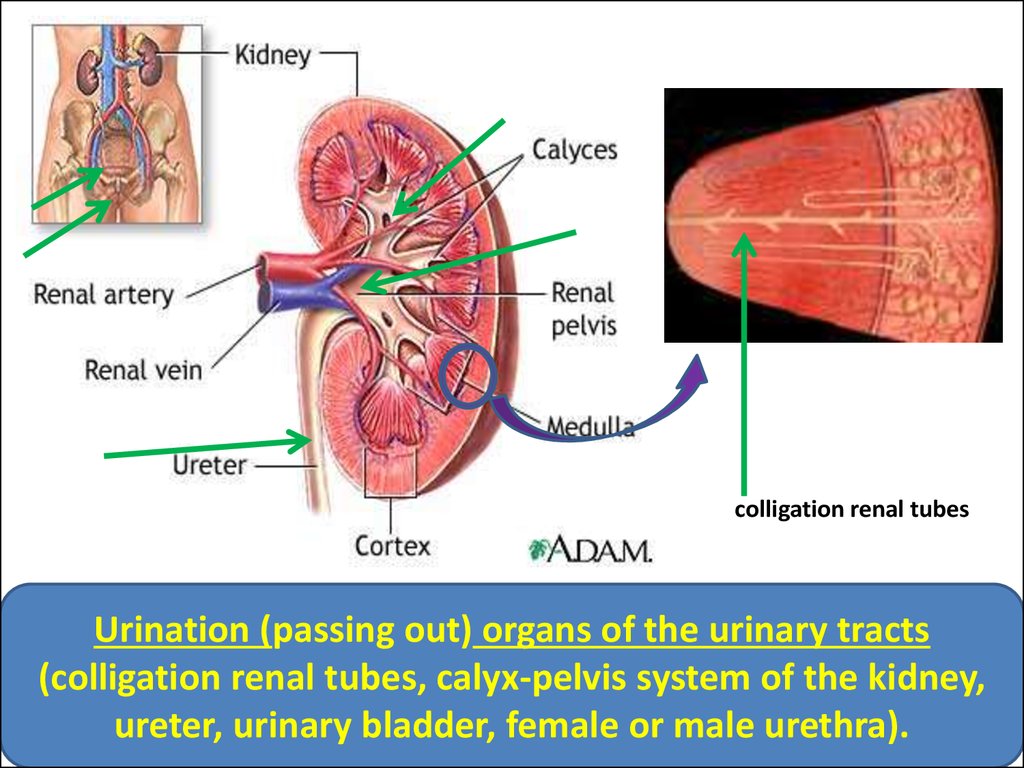
colligation renal tubesUrination (passing out) organs of the urinary tracts
(colligation renal tubes, calyx-pelvis system of the kidney,
ureter, urinary bladder, female or male urethra).
4.
THE URINARY SYSTEM EMBRYOGENESISUreter, Renal pelvis, Major and minor calyces, Collecting
tubules formed from Ureteric bud (metanephric diverticulum).
The urogenital sinus (also known as the persistent cloaca) is a part of the human
body only present in the development of the urinary and reproductive organs.
The upper part of the urogenital sinus gives rise to the URINARY BLADDER.
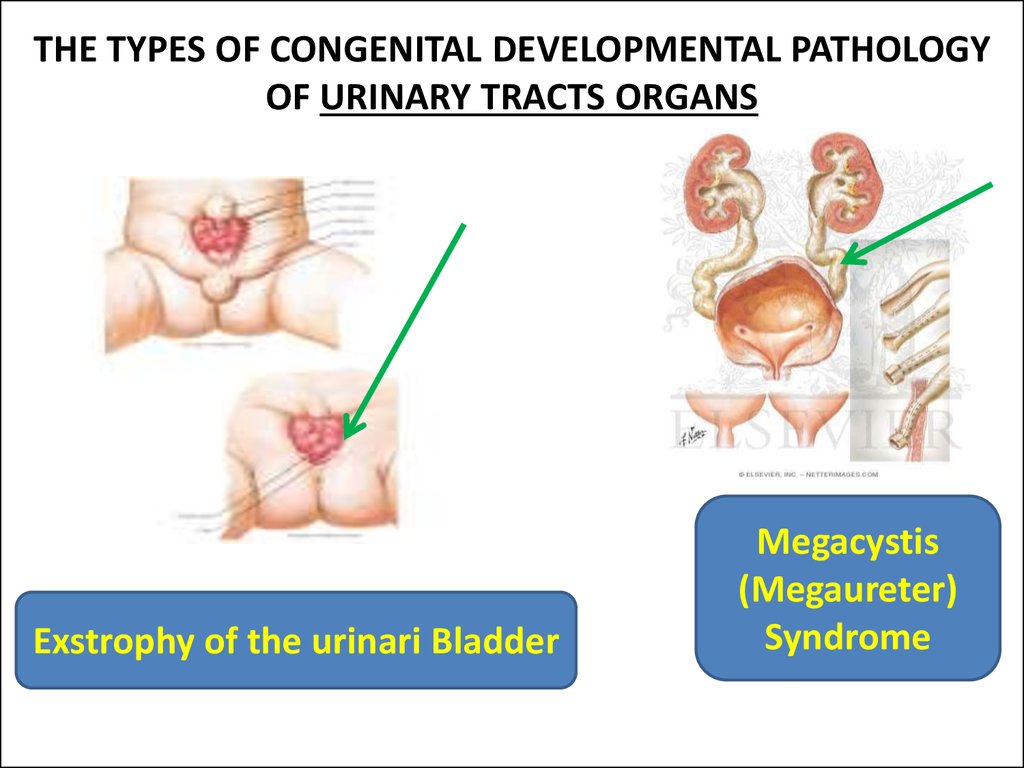
5. THE TYPES OF CONGENITAL DEVELOPMENTAL PATHOLOGY OF URINARY TRACTS ORGANS
Exstrophy of the urinari BladderMegacystis
(Megaureter)
Syndrome
6. THE TYPES OF CONGENITAL DEVELOPMENTAL PATHOLOGY OF URINARY TRACTS ORGANS
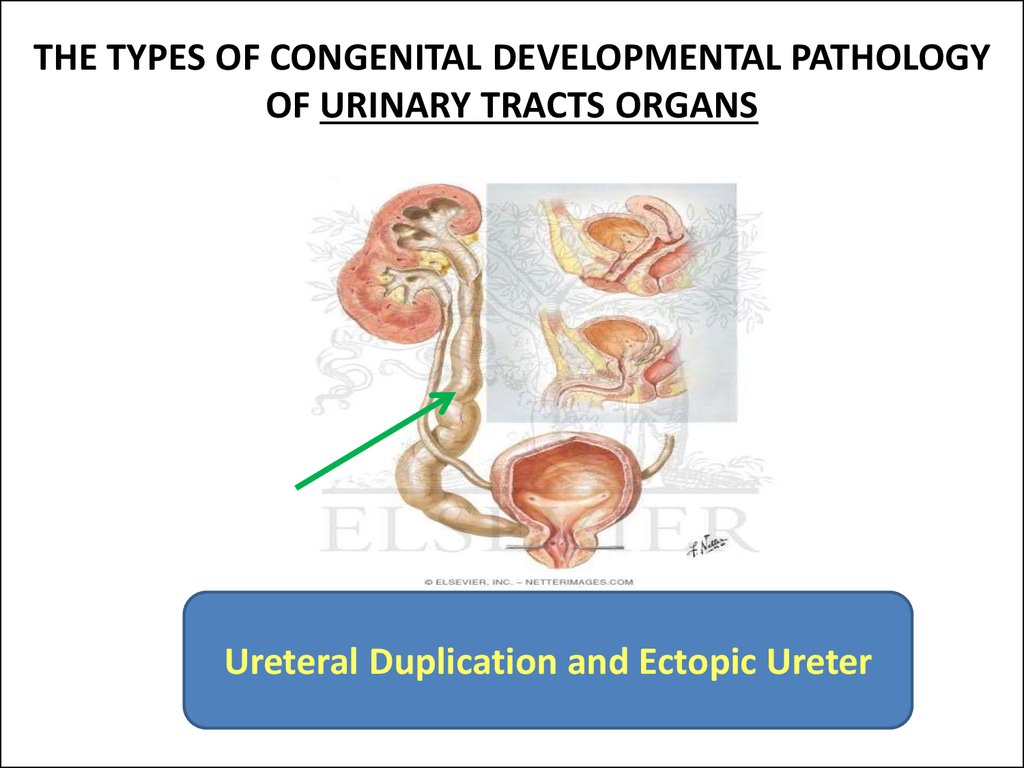
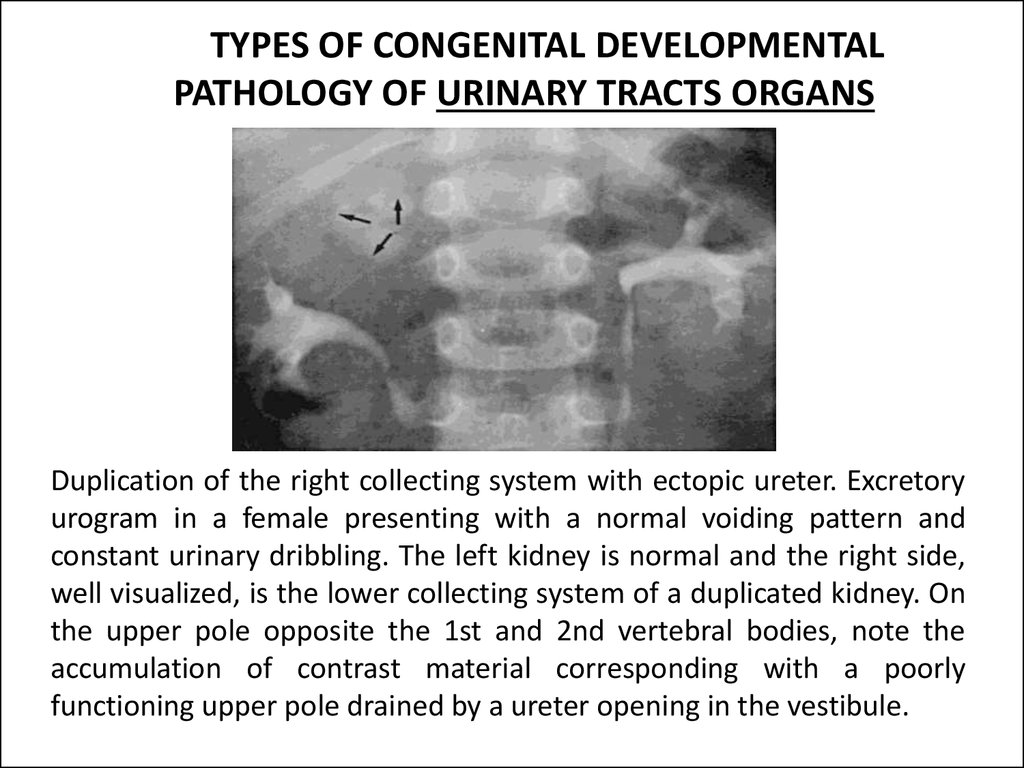
Ureteral Duplication and Ectopic Ureter7. Duplication of the right collecting system with ectopic ureter. Excretory urogram in a female presenting with a normal voiding pattern and constant urinary dribbling. The left kidney is normal and the right side, well visualized, is the lower collecting s
THE TYPESOF CONGENITAL DEVELOPMENTAL
PATHOLOGY OF URINARY TRACTS ORGANS
Duplication of the right collecting system with ectopic ureter. Excretory
urogram in a female presenting with a normal voiding pattern and
constant urinary dribbling. The left kidney is normal and the right side,
well visualized, is the lower collecting system of a duplicated kidney. On
the upper pole opposite the 1st and 2nd vertebral bodies, note the
accumulation of contrast material corresponding with a poorly
functioning upper pole drained by a ureter opening in the vestibule.
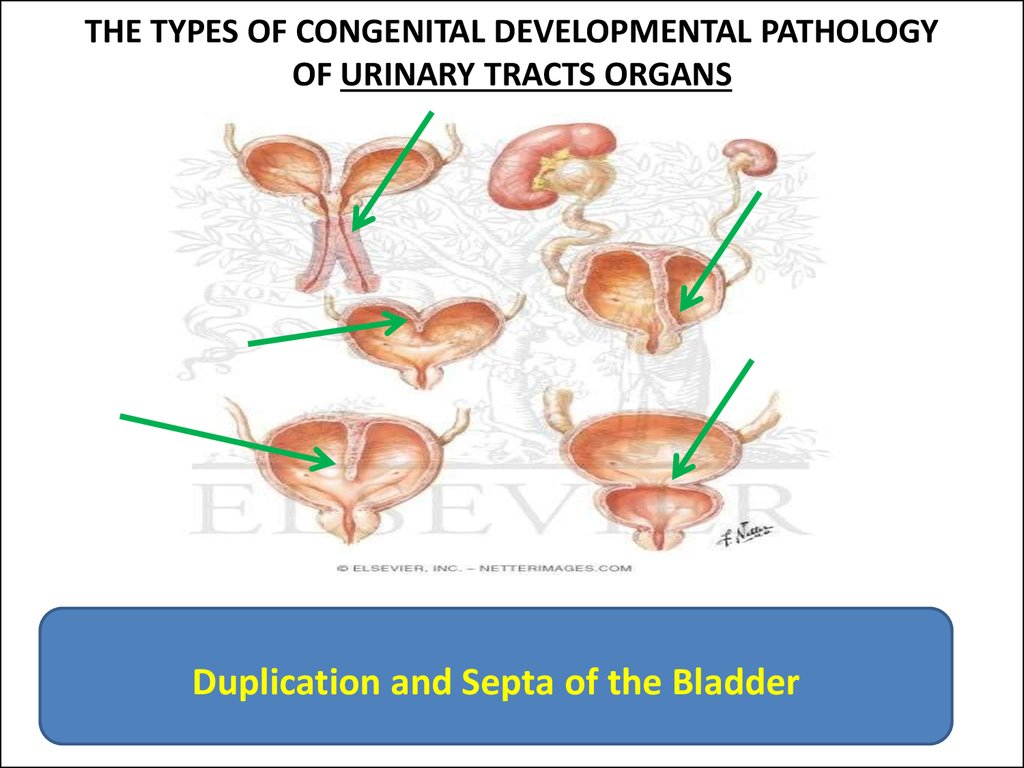
8. THE TYPES OF CONGENITAL DEVELOPMENTAL PATHOLOGY OF URINARY TRACTS ORGANS
Duplication and Septa of the Bladder9. THE TYPES OF CONGENITAL DEVELOPMENTAL PATHOLOGY OF URINARY TRACTS ORGANS
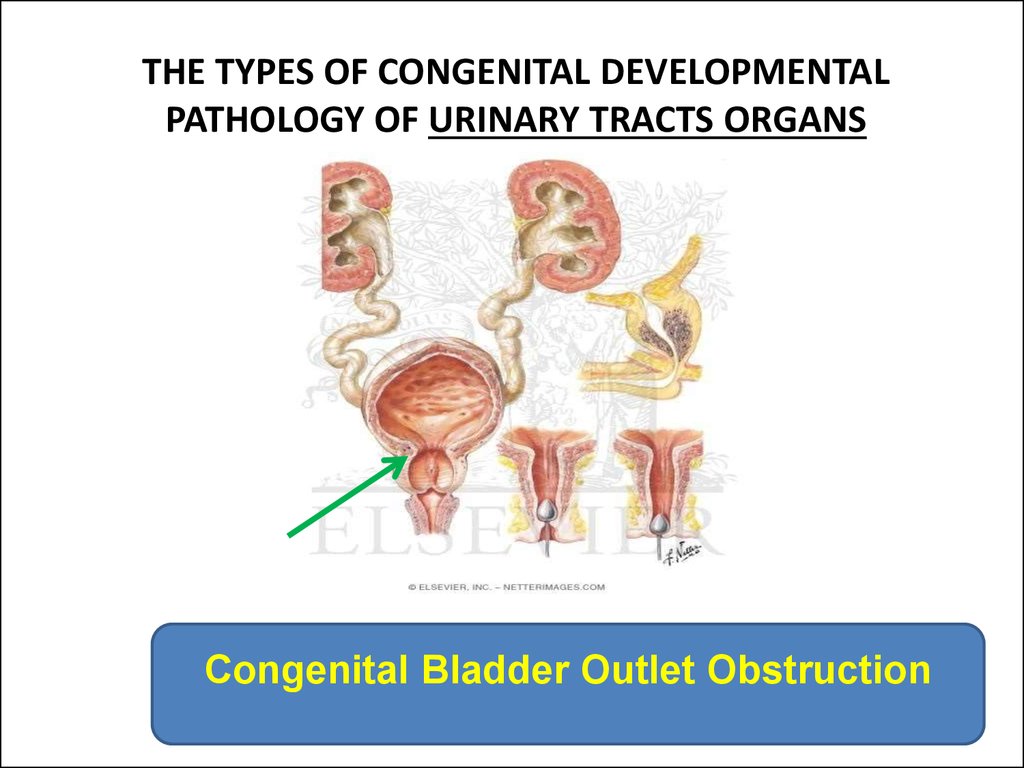
Congenital Bladder Outlet Obstruction10.
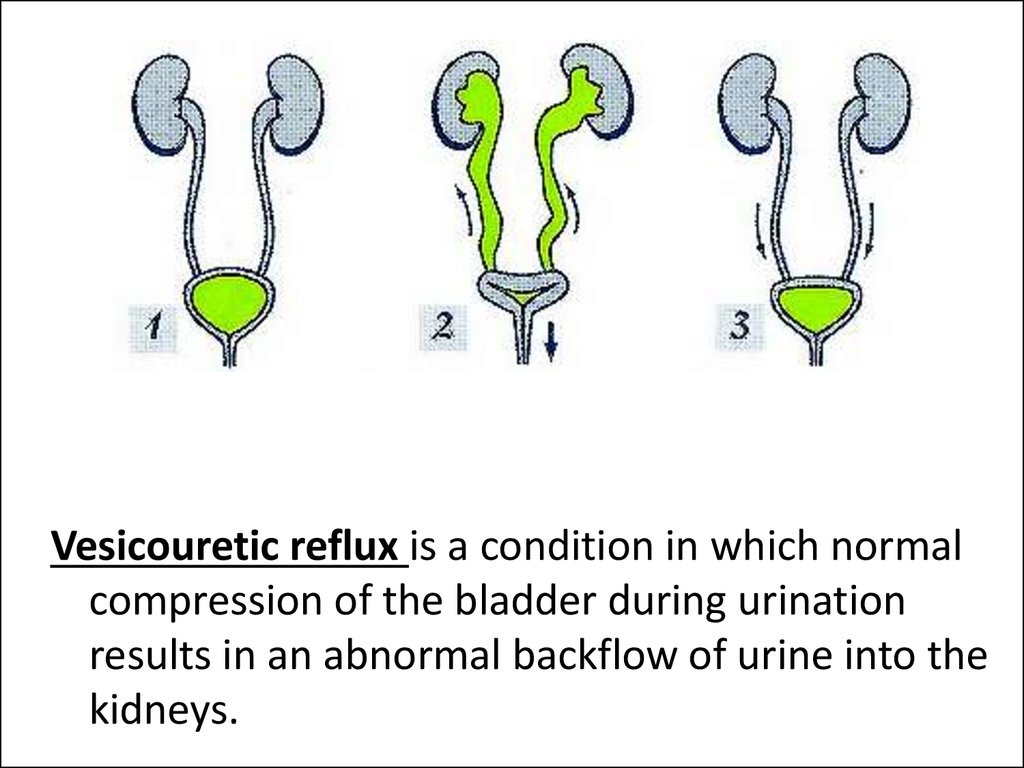
Vesicouretic reflux is a condition in which normalcompression of the bladder during urination
results in an abnormal backflow of urine into the
kidneys.
11.
colligation renal tubesUrination (passing out) organs of the urinary tracts
(colligation renal tubes, calyx-pelvis system of the kidney,
ureter, urinary bladder, female or male urethra).
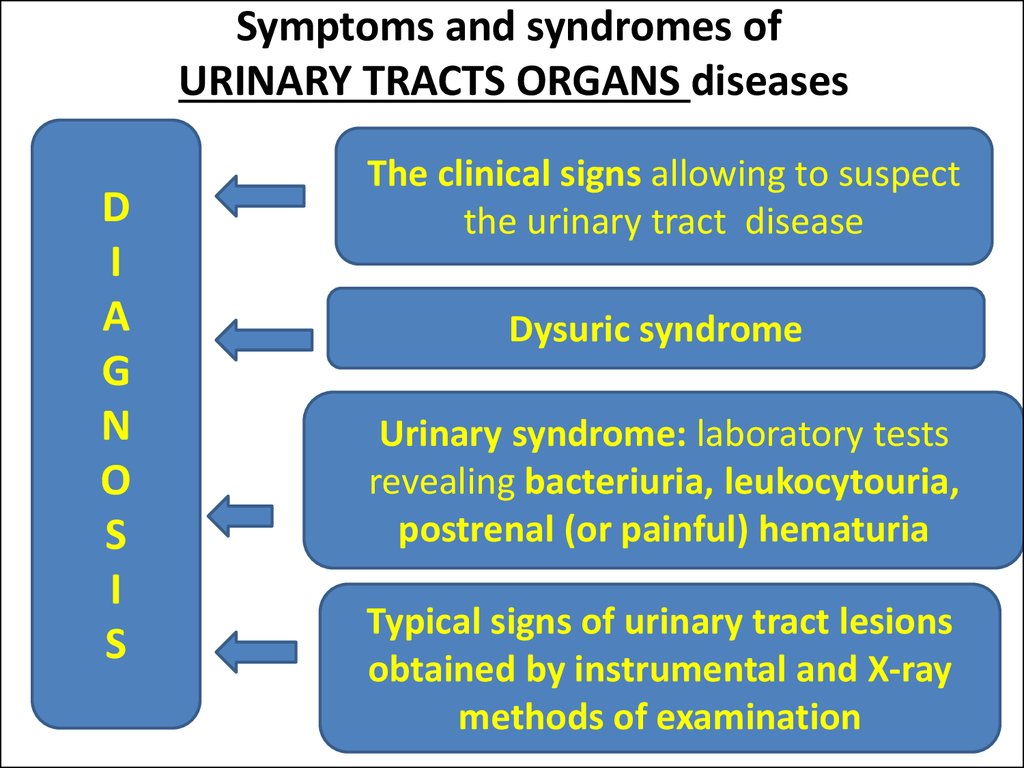
12. Symptoms and syndromes of URINARY TRACTS ORGANS diseases
DI
A
G
N
O
S
I
S
The clinical signs allowing to suspect
the urinary tract disease
Dysuric syndrome
Urinary syndrome: laboratory tests
revealing bacteriuria, leukocytouria,
postrenal (or painful) hematuria
Typical signs of urinary tract lesions
obtained by instrumental and X-ray
methods of examination
13.
The clinical signs allowing to suspect the urinarytract disease
Intoxication syndrome:
fever, anorexia (refusal of
meals), vomiting and
headache
Abdomen and loin pain
14.
The clinical signs allowing to suspect the urinarytract disease
Dysuric disorders
Anomalies of development of
urethra and urinary bladder.
15.
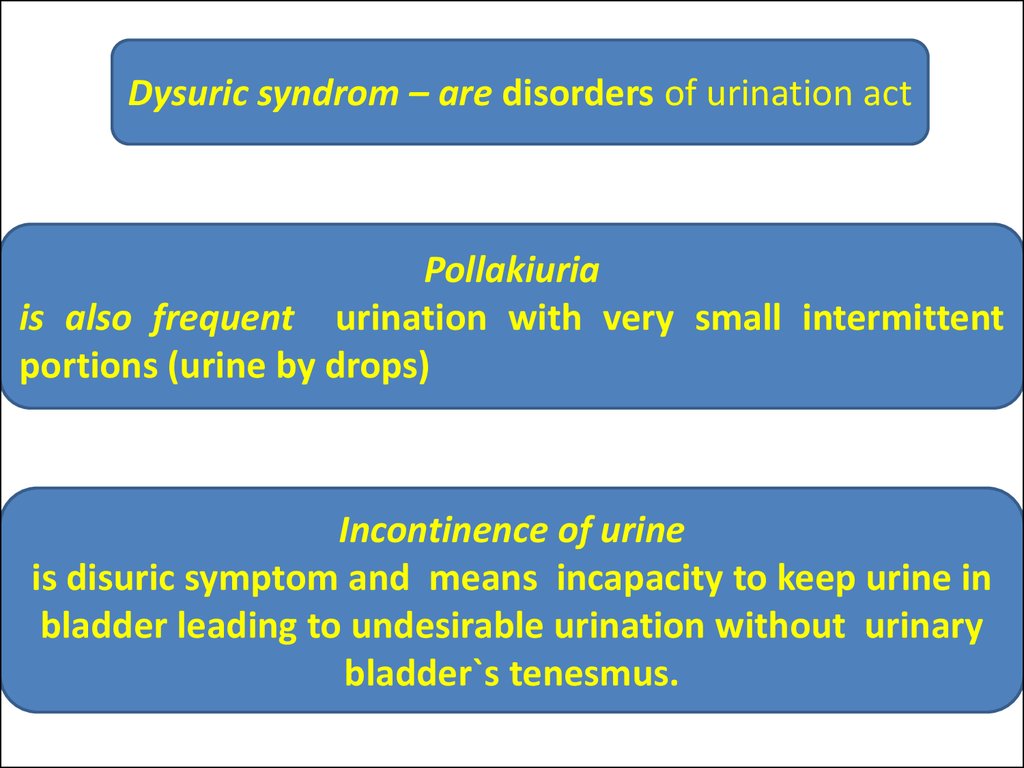
Dysuric syndrom – are disorders of urination actPollakiuria
is also frequent urination with very small intermittent
portions (urine by drops)
Incontinence of urine
is disuric symptom and means incapacity to keep urine in
bladder leading to undesirable urination without urinary
bladder`s tenesmus.
16.
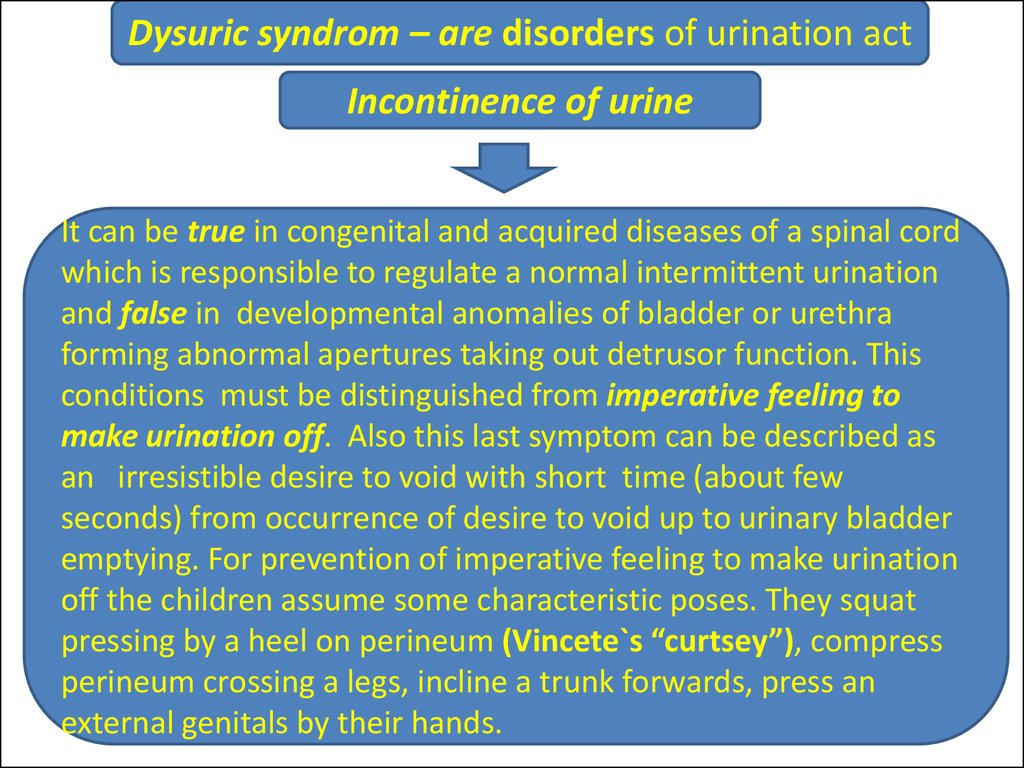
Dysuric syndrom – are disorders of urination actIncontinence of urine
It can be true in congenital and acquired diseases of a spinal cord
which is responsible to regulate a normal intermittent urination
and false in developmental anomalies of bladder or urethra
forming abnormal apertures taking out detrusor function. This
conditions must be distinguished from imperative feeling to
make urination off. Also this last symptom can be described as
an irresistible desire to void with short time (about few
seconds) from occurrence of desire to void up to urinary bladder
emptying. For prevention of imperative feeling to make urination
off the children assume some characteristic poses. They squat
pressing by a heel on perineum (Vincete`s “curtsey”), compress
perineum crossing a legs, incline a trunk forwards, press an
external genitals by their hands.
17. Dysuric syndrom – are disorders of urination act
Enuresis isurine incontinence during the sleeping and it is wide spread
in children.
The seldom urination
can be also a disuric symptom if it is not connected with
water intake restriction. It means that the quantity of
urination acts in day is less than normative date. The
normative parameters differ in a wide range from 25 times
per day in infants up to 6 times in adult children.
18.
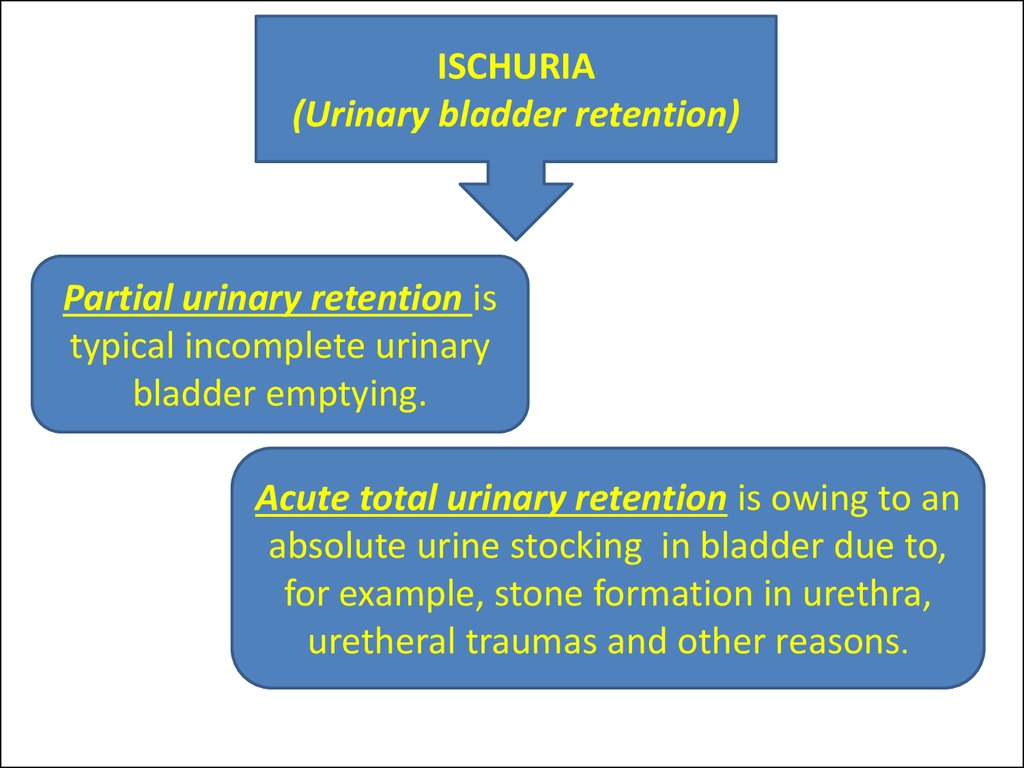
ISCHURIA(Urinary bladder retention)
Partial urinary retention is
typical incomplete urinary
bladder emptying.
Acute total urinary retention is owing to an
absolute urine stocking in bladder due to,
for example, stone formation in urethra,
uretheral traumas and other reasons.
19.
The reasons of dysuric disordersthe congenital and
acquired diseases of a
spinal cord,
peripheral nerves,
nerve plexus of a
urinary bladder
microbial inflammatory
processes in
urinary tract
the
structural
abnormality
of urinary
tract
Hypospadias
Classic bladder exstrophy in newborn
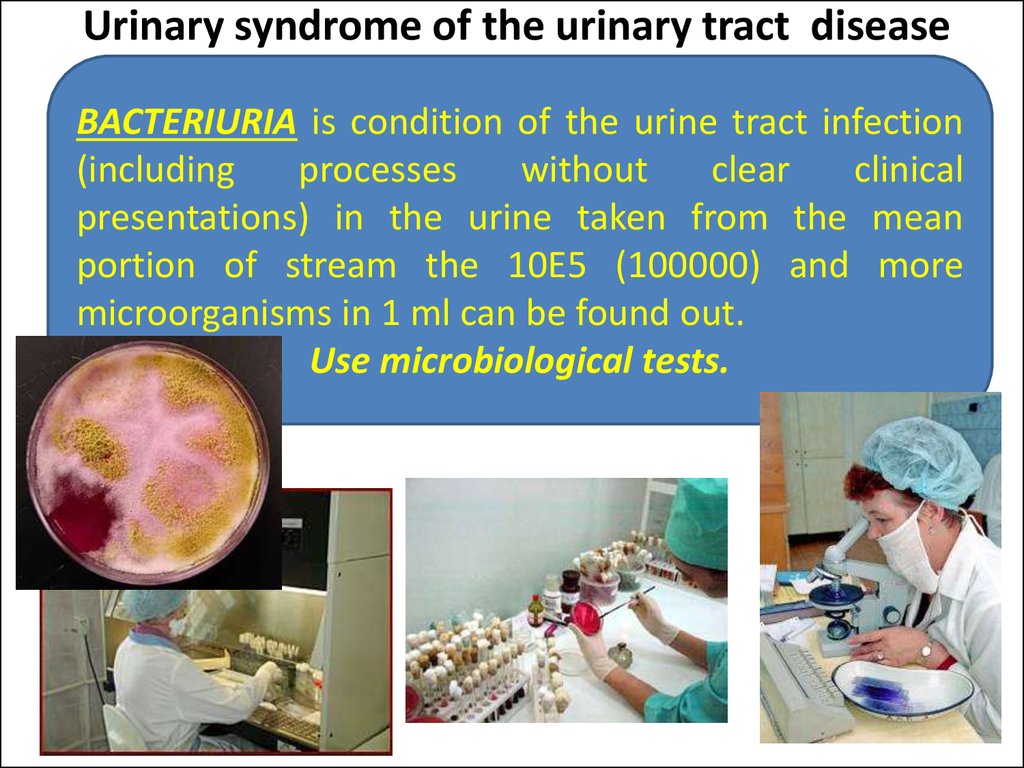
20. Urinary syndrome of the urinary tract disease
BACTERIURIA is condition of the urine tract infection(including
processes
without
clear
clinical
presentations) in the urine taken from the mean
portion of stream the 10Е5 (100000) and more
microorganisms in 1 ml can be found out.
Use microbiological tests.
21. Urinary syndrome of the urinary tract disease
The LEUKOCYTOURIAis the presence of more than 5 leukocytes in visual field
during the microscopic investigation of urine sediment.
You can use microscopic test of urine sediment for
diagnosis leukocytouria or
Quantity urinalyses:
Addis`s test: The test is positive and leukocytouria is
presented if more than 2 million (2000000 un.)
leukocytes per day. Nechiporenko`s test : The test is
positive and leukocytouria is presented if more than 2
thousand (2000 un.) leukocytes in 1 ml of urine.
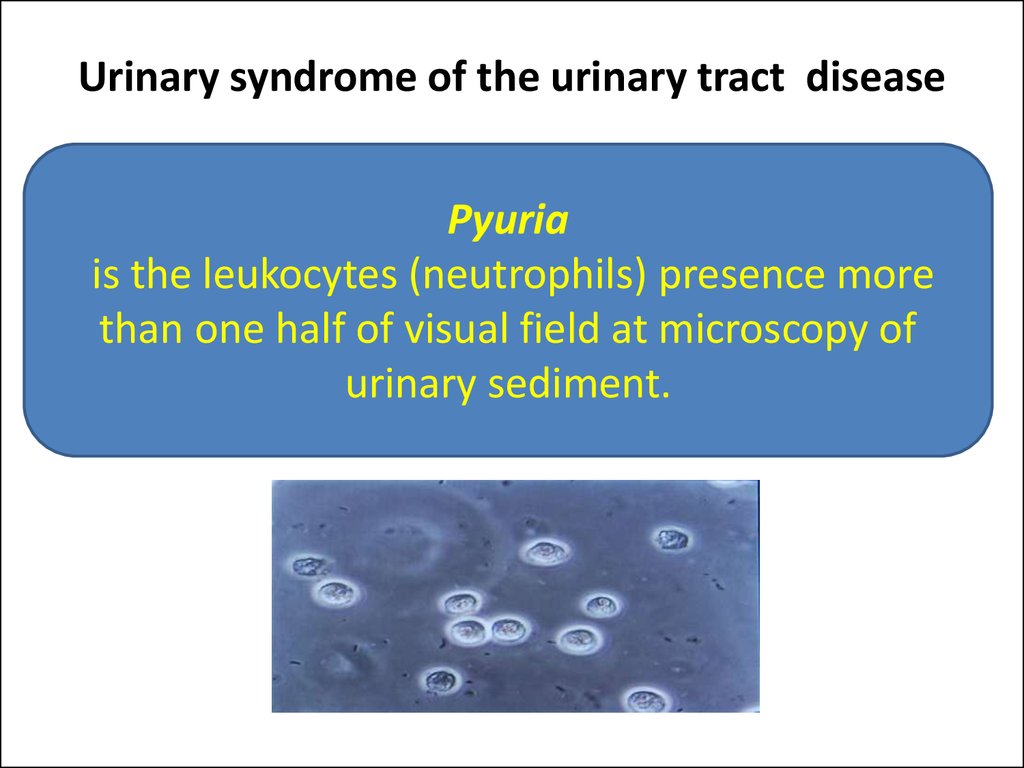
22. Urinary syndrome of the urinary tract disease
Pyuriais the leukocytes (neutrophils) presence more
than one half of visual field at microscopy of
urinary sediment.
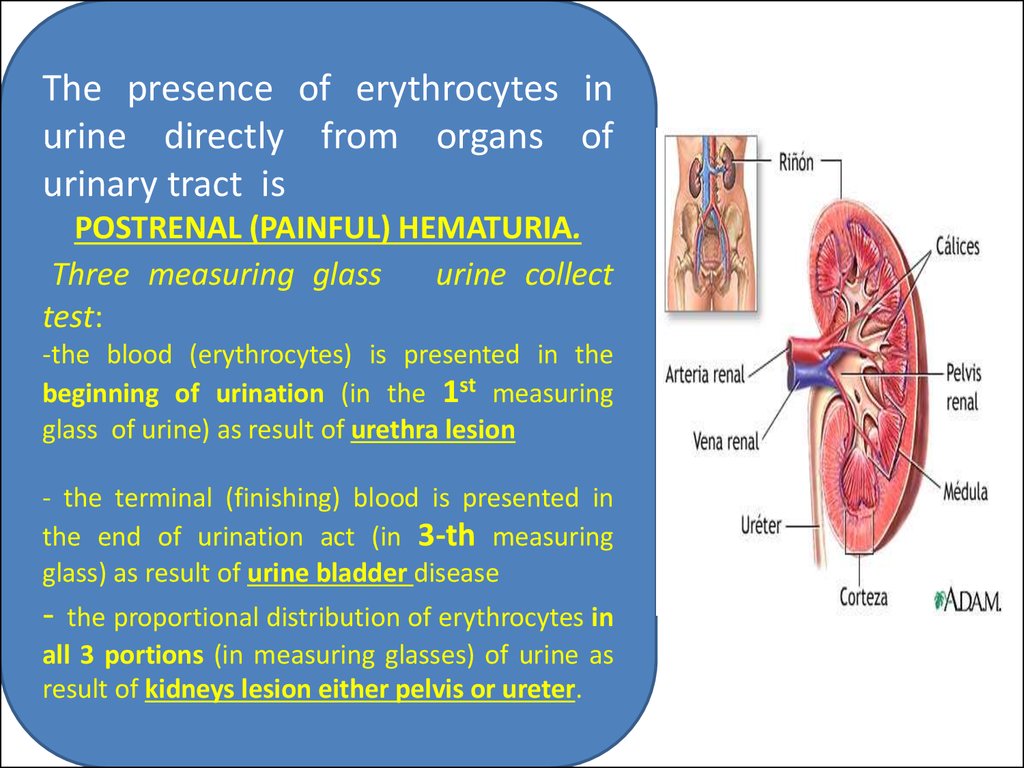
23.
The presence of erythrocytes inurine directly from organs of
urinary tract is
POSTRENAL (PAINFUL) HEMATURIA.
Three measuring glass
urine collect
test:
-the blood (erythrocytes) is presented in the
beginning of urination (in the 1st measuring
glass of urine) as result of urethra lesion
- the terminal (finishing) blood is presented in
the end of urination act (in 3-th measuring
glass) as result of urine bladder disease
-
the proportional distribution of erythrocytes in
all 3 portions (in measuring glasses) of urine as
result of kidneys lesion either pelvis or ureter.
24. The instrumental and radiological signs of urinary tract examination.
ULTRASONOGRAPHYIt helps to diagnose a quantity, position, sizes and
anatomical structure of kidneys as a pelvis dilation and
abnormal cavities or cysts. Also the ultrasonography is
used for calculi diagnosing in any part of urinary tract.
25.
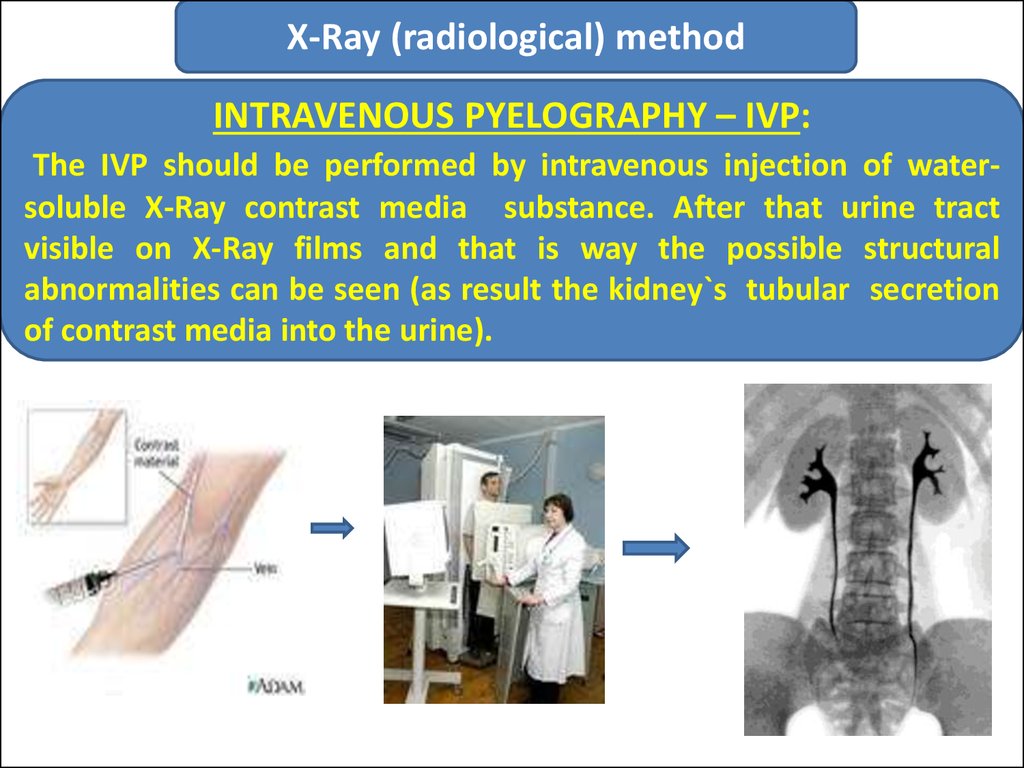
X-Ray (radiological) methodINTRAVENOUS PYELOGRAPHY – IVP:
The IVP should be performed by intravenous injection of watersoluble X-Ray contrast media substance. After that urine tract
visible on X-Ray films and that is way the possible structural
abnormalities can be seen (as result the kidney`s tubular secretion
of contrast media into the urine).
26.
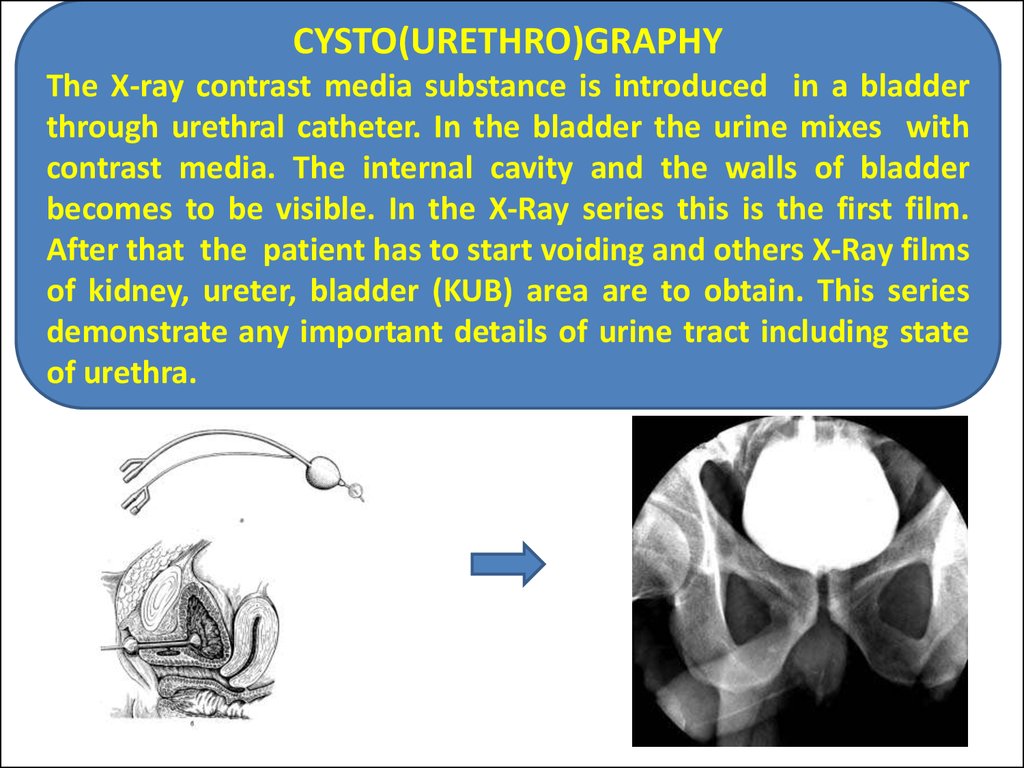
CYSTO(URETHRO)GRAPHYThe X-ray contrast media substance is introduced in a bladder
through urethral catheter. In the bladder the urine mixes with
contrast media. The internal cavity and the walls of bladder
becomes to be visible. In the X-Ray series this is the first film.
After that the patient has to start voiding and others X-Ray films
of kidney, ureter, bladder (KUB) area are to obtain. This series
demonstrate any important details of urine tract including state
of urethra.
27. URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI):
85% - due to bacteria - gram negative bacilli - frompatients own normal flora of his/her gastrointestinal
system i.e. endogenous infection ( he/she is infecting
him/herself!!)
most common gram negative bacteria - E. coli ,
Proteus , Kliebsiella and enterobacter
two ways the bacteria can reach the kidney:
through the blood stream - hematogenous infection less common . Occurs in septicaemia , bacterial
endocarditis and immunocompromised patients
can start in early childhood (in infants)
28. The semiotics of common urine tract diseases in children
CYSTITIS microbe inflammation of urinary bladder- Pain in the inguinal region
of the abdomen
- Dysuria: frequent, painful
urination, urinary
incontinence
- Bacteriuria,
- Leukocyturia, pyuria
-Terminal according to test
of three measuring glass
microhematuria
29.
PYELONEPHRITIS –suppurative inflammation pelvis of kidneys, tubular
system in medullar substance of kidney caused by
bacterial infection
PREDISPOSING FACTORS
urinary obstruction - either congenital or acquired
vesicoureteric reflux
diabetes mellitus - due to increased susceptiblity to infection
immunodepression and immunodeficiency
The pyelonephritis it is the complicated form of urine tract infection.
In pyelonephritis the microbes contaminate the pelvis of
kidneys, tubular system in medullar substance of kidney.
30.
PYELONEPHRITISIntoxication syndrome:
Fever, vomiting, headache
Disuric syndrome
Pain syndrome:
Pain in abdomen and loin
31. PYELONEPHRITIS –
Urinary syndrome:- Bacteriuria
- Leukocyturia, pyuria
- Postrenal microhematuria
32.
The calculi are formed in a bladder or in kidneys pelvisis UROLITHIASIS.
The
cramping
pain,
hematuria, leukocytouria,
dysuria are characteristic for
UROLITHIASIS.
The acute retention of urine
in bladder occurs due to
urethra occlusion by a
calculus.
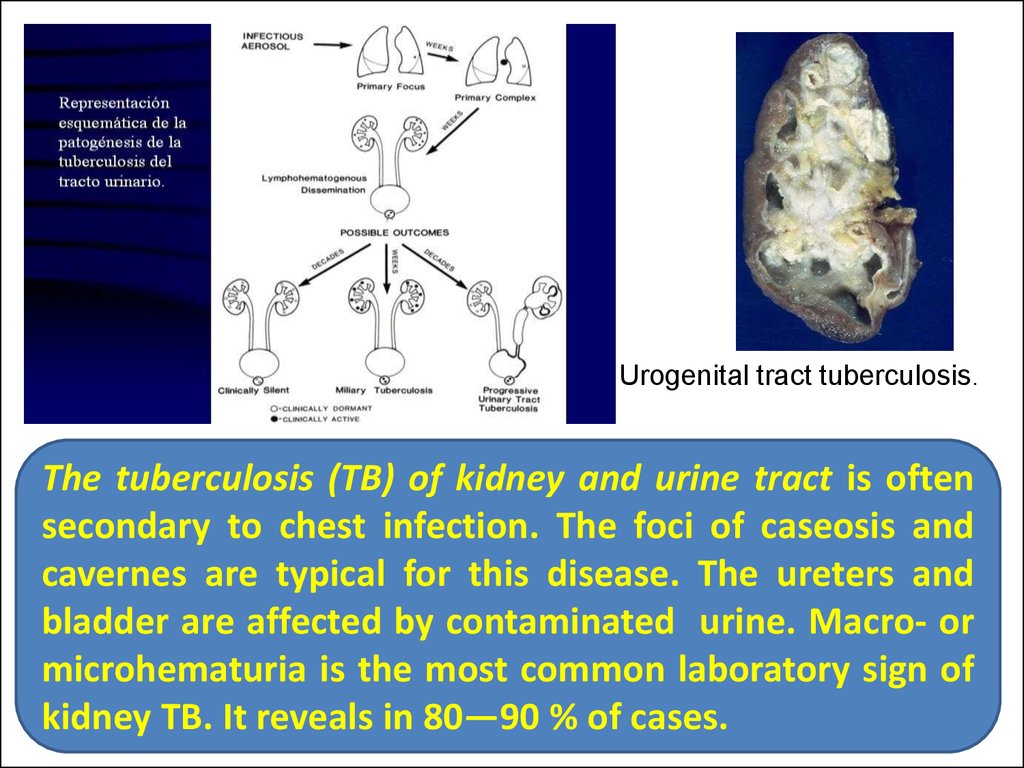
33.
Urogenital tract tuberculosis.The tuberculosis (TB) of kidney and urine tract is often
secondary to chest infection. The foci of caseosis and
cavernes are typical for this disease. The ureters and
bladder are affected by contaminated urine. Macro- or
microhematuria is the most common laboratory sign of
kidney TB. It reveals in 80—90 % of cases.
34.
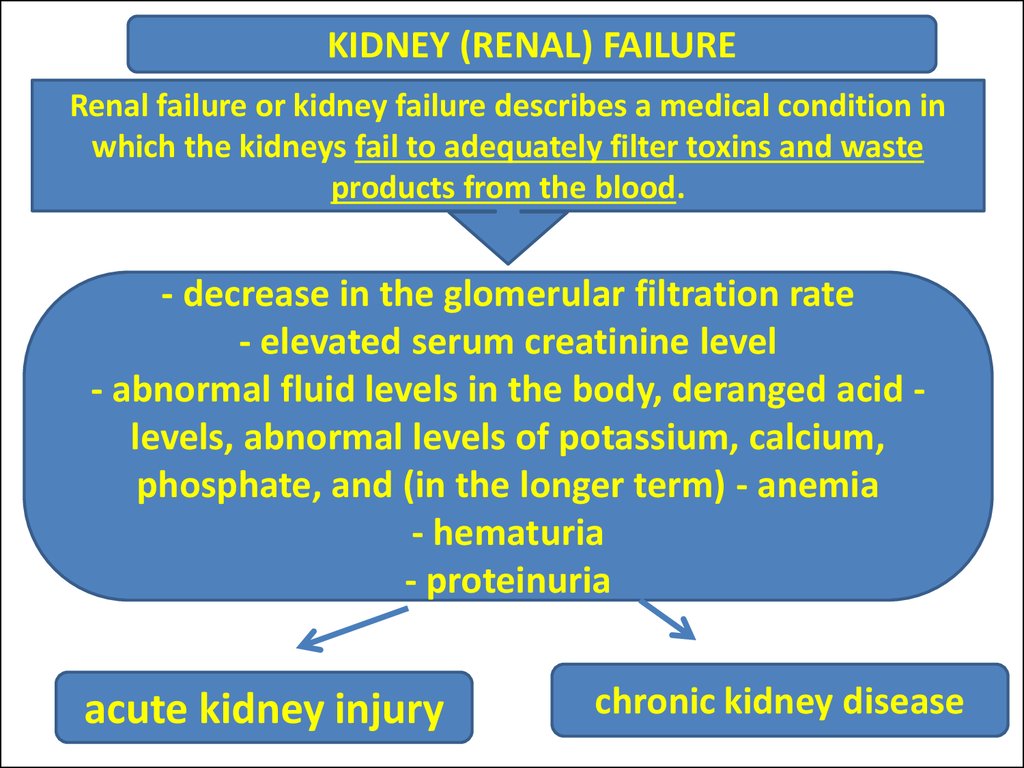
KIDNEY (RENAL) FAILURERenal failure or kidney failure describes a medical condition in
which the kidneys fail to adequately filter toxins and waste
products from the blood.
- decrease in the glomerular filtration rate
- elevated serum creatinine level
- abnormal fluid levels in the body, deranged acid levels, abnormal levels of potassium, calcium,
phosphate, and (in the longer term) - anemia
- hematuria
- proteinuria
acute kidney injury
chronic kidney disease
35.
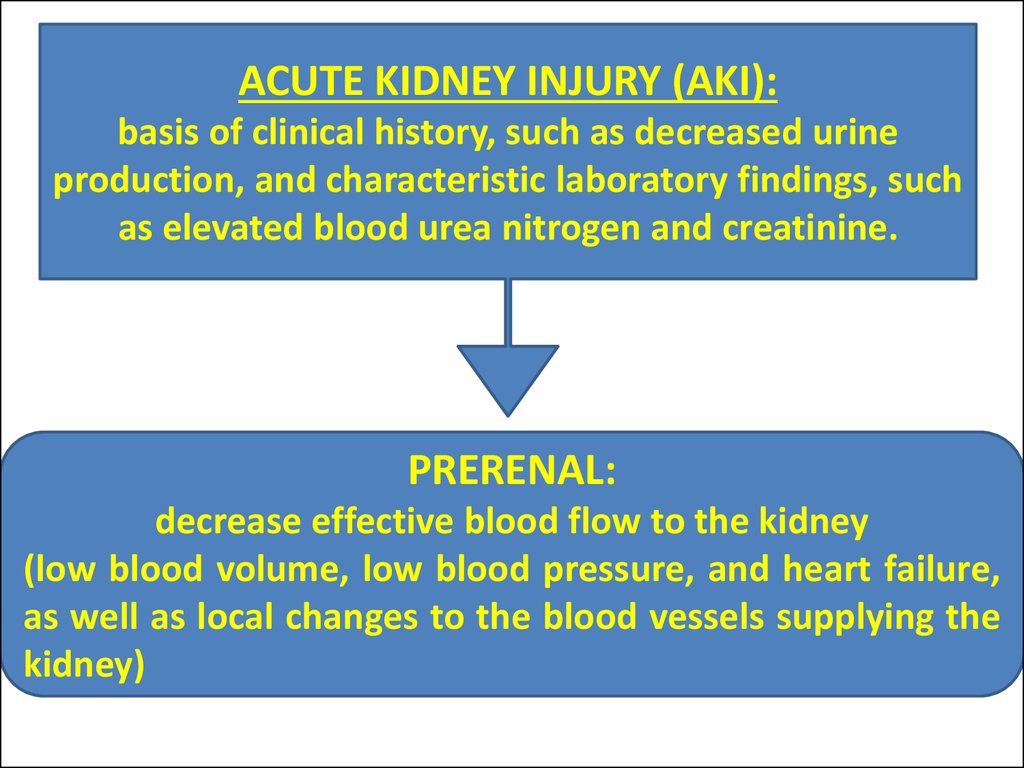
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY (AKI):basis of clinical history, such as decreased urine
production, and characteristic laboratory findings, such
as elevated blood urea nitrogen and creatinine.
PRERENAL:
decrease effective blood flow to the kidney
(low blood volume, low blood pressure, and heart failure,
as well as local changes to the blood vessels supplying the
kidney)
36.
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY (AKI):RENAL (INTRINSIC): damage to the kidney itself .
(to damage to the glomeruli, renal tubules, or interstitium.
Common causes of each are glomerulonephritis, acute
tubular necrosis (ATN), and acute interstitial nephritis (AIN)
POSTRENAL: consequence of urinary tract obstruction.
This may be related to benign kidney stones, obstructed
urinary catheter, bladder stone, bladder, ureteral or renal
malignancy. A renal ultrasound will demonstrate
hydronephrosis if present.
37.
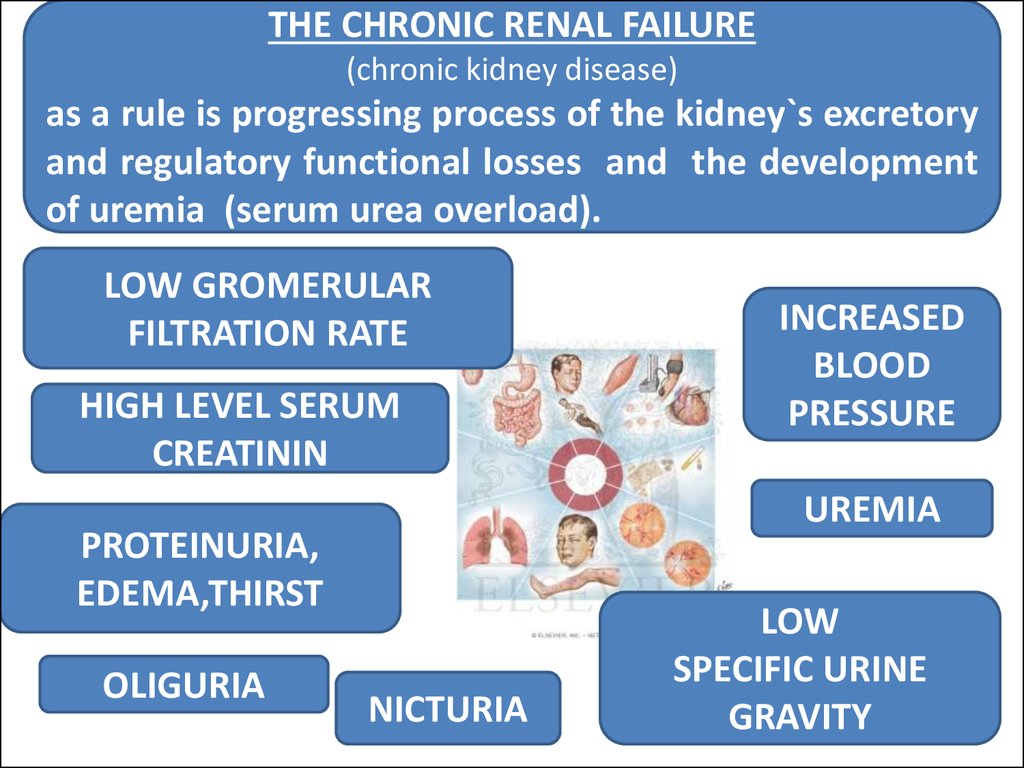
THE CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE(chronic kidney disease)
as a rule is progressing process of the kidney`s excretory
and regulatory functional losses and the development
of uremia (serum urea overload).
LOW GROMERULAR
FILTRATION RATE
HIGH LEVEL SERUM
CREATININ
UREMIA
PROTEINURIA,
EDEMA,THIRST
OLIGURIA
INCREASED
BLOOD
PRESSURE
NICTURIA
LOW
SPECIFIC URINE
GRAVITY
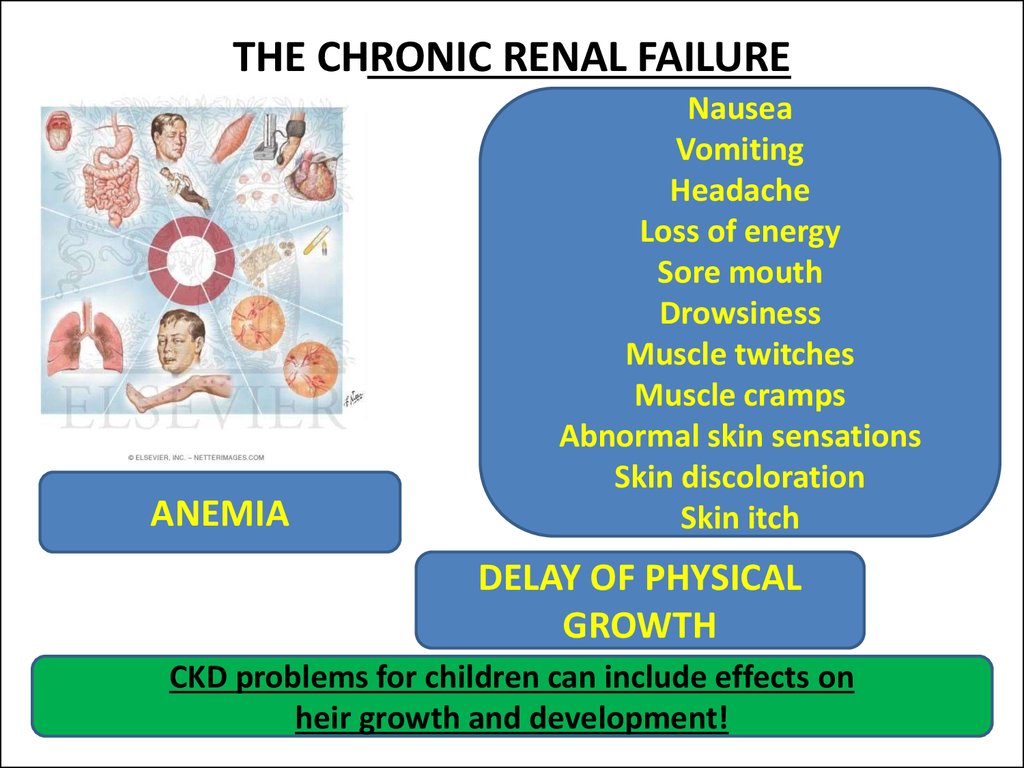
38. THE CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE
ANEMIANausea
Vomiting
Headache
Loss of energy
Sore mouth
Drowsiness
Muscle twitches
Muscle cramps
Abnormal skin sensations
Skin discoloration
Skin itch
DELAY OF PHYSICAL
GROWTH
CKD problems for children can include effects on
heir growth and development!
39.
HAEMODIALYSISis a method for removing waste products such as
creatinine and urea, as well as free water from the blood
when the kidneys are in renal failure.
40.
KIDNEY TRANSPLANTATIONis the organ transplant of a kidney into a patient
with end-stage renal disease.















 Медицина
Медицина








