Похожие презентации:
Database normalization. Module 9
1.
Databasenormalization
• Module 9
2.
Agenda• What is normalization?
• First normal form
• Second normal form
• Third normal form
• Denormalization
2
3.
What is normalization?The process of organizing the columns and
tables of a relational database to minimize
data redundancy
“Abnormal” DB
(unnormalized form ,
UNF)
normalization
“Normal” DB
(normalized form, NF)
3
4.
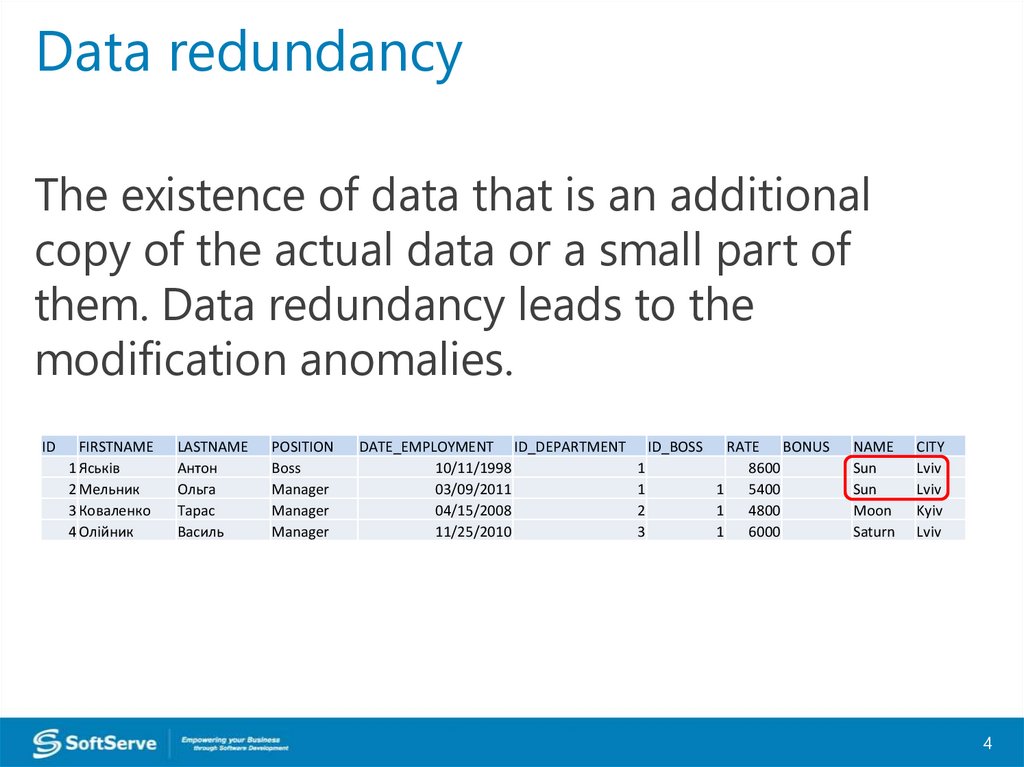
Data redundancyThe existence of data that is an additional
copy of the actual data or a small part of
them. Data redundancy leads to the
modification anomalies.
ID
FIRSTNAME
1 Яськів
2 Мельник
3 Коваленко
4 Олійник
LASTNAME
Антон
Ольга
Тарас
Василь
POSITION
Boss
Manager
Manager
Manager
DATE_EMPLOYMENT ID_DEPARTMENT
10/11/1998
03/09/2011
04/15/2008
11/25/2010
ID_BOSS
1
1
2
3
RATE BONUS
8600
1
5400
1
4800
1
6000
NAME
Sun
Sun
Moon
Saturn
CITY
Lviv
Lviv
Kyiv
Lviv
4
5.
Modification anomalies• Insert anomalies
• Update anomalies
• Delete anomalies
5
6.
Goals of the normalization• Free the DB of modification anomalies
• Minimize redesign when extending the DB
structure
• Make the DB more informative
• Make the DB suitable for querying
6
7.
Normal forms• First normal form (1NF)
• Second normal form (2NF)
• Third normal form (3NF)
• Other normal forms
Normal form of a DB is a set of rules which
the DB has to meet for decreasing the data
redundancy.
7
8.
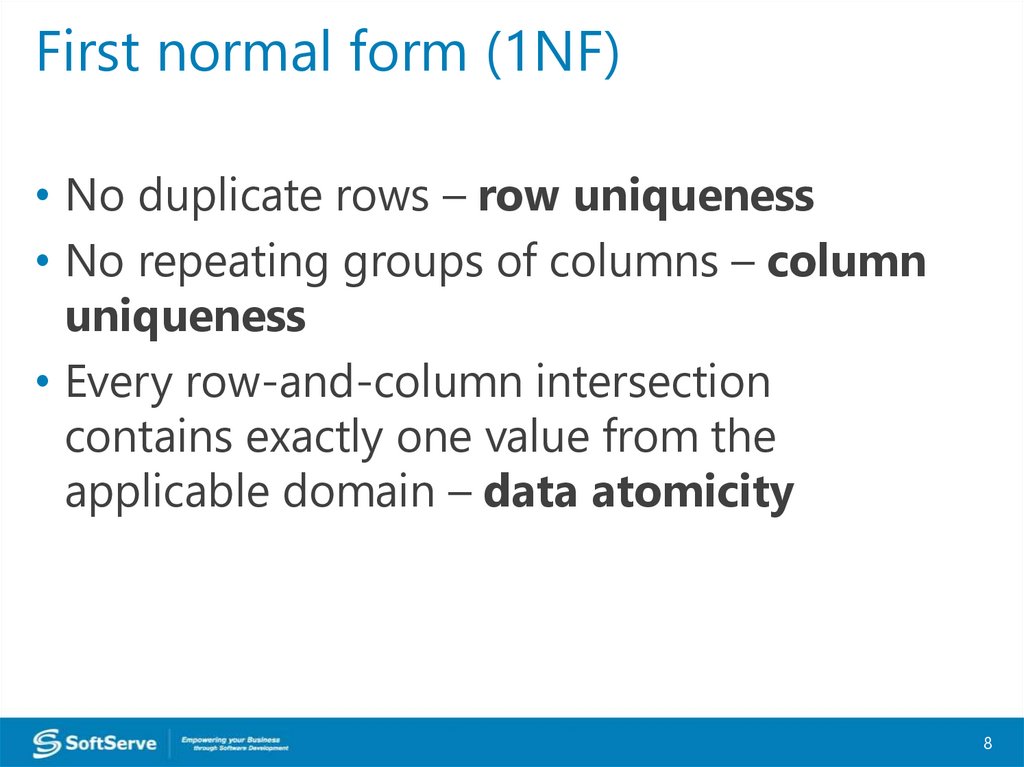
First normal form (1NF)• No duplicate rows – row uniqueness
• No repeating groups of columns – column
uniqueness
• Every row-and-column intersection
contains exactly one value from the
applicable domain – data atomicity
8
9.
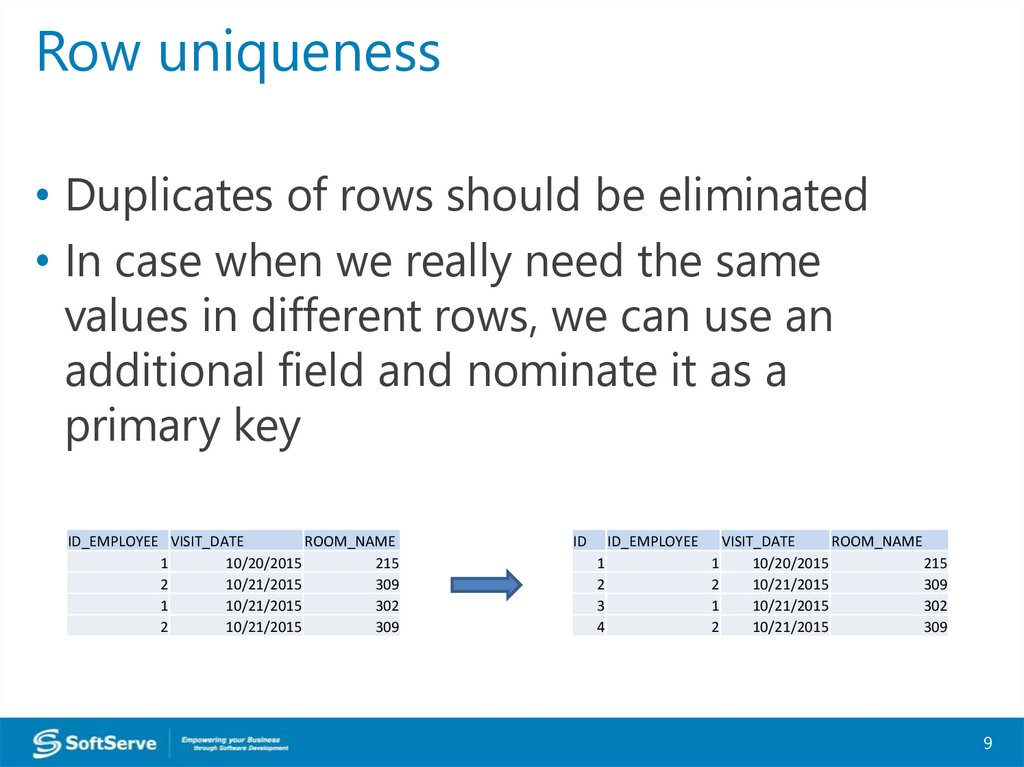
Row uniqueness• Duplicates of rows should be eliminated
• In case when we really need the same
values in different rows, we can use an
additional field and nominate it as a
primary key
ID_EMPLOYEE VISIT_DATE
ROOM_NAME
1
10/20/2015
215
2
10/21/2015
309
1
10/21/2015
302
2
10/21/2015
309
ID
ID_EMPLOYEE
1
2
3
4
1
2
1
2
VISIT_DATE
ROOM_NAME
10/20/2015
215
10/21/2015
309
10/21/2015
302
10/21/2015
309
9
10.
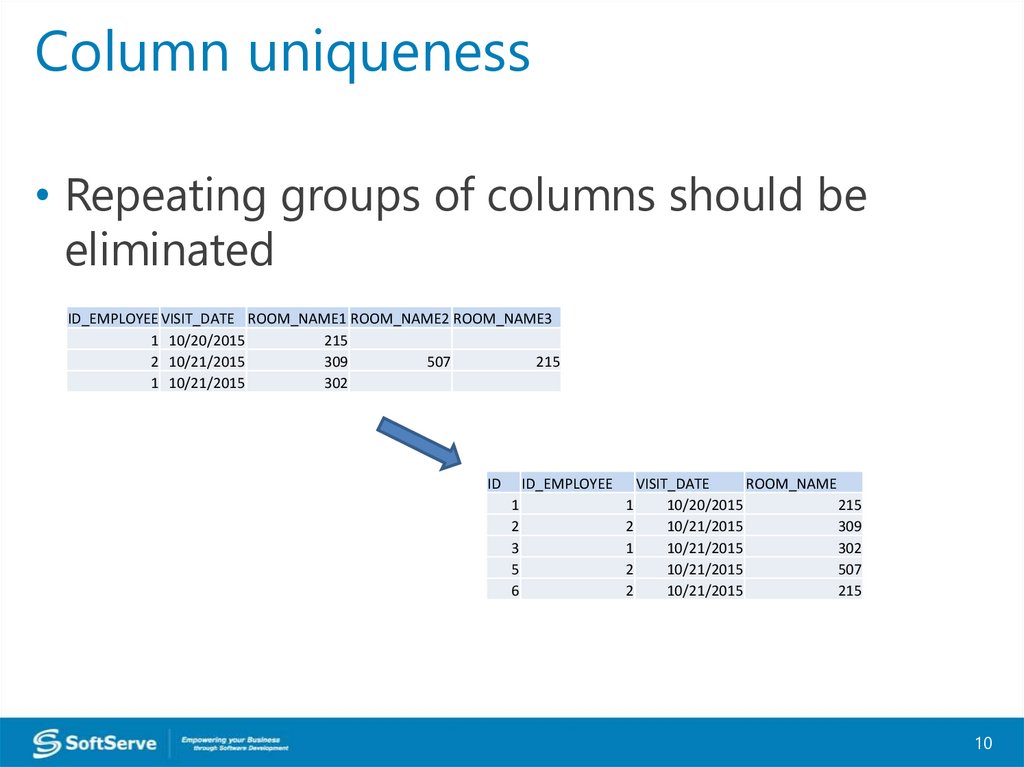
Column uniqueness• Repeating groups of columns should be
eliminated
ID_EMPLOYEE VISIT_DATE ROOM_NAME1 ROOM_NAME2 ROOM_NAME3
1 10/20/2015
215
2 10/21/2015
309
507
215
1 10/21/2015
302
ID
ID_EMPLOYEE
1
2
3
5
6
VISIT_DATE
ROOM_NAME
1
10/20/2015
215
2
10/21/2015
309
1
10/21/2015
302
2
10/21/2015
507
2
10/21/2015
215
10
11.
Data atomicity• There is a single value in each field of each
row.
• This value is from selected domain
• NULL values could be also allowed
ID_EMPLOYEE VISIT_DATE
ROOM_NAME
1
10/20/2015
215
2
10/21/2015 309, 507, 215
1
10/21/2015
302
ID
ID_EMPLOYEE
1
2
3
5
6
1
2
1
2
2
VISIT_DATE
ROOM_NAME
10/20/2015
215
10/21/2015
309
10/21/2015
302
10/21/2015
507
10/21/2015
215
11
12.
UNF->1NF• Eliminate duplicative columns from the
same table.
• Create separate tables for each group of
related data and identify each row with a
unique column or set of columns (the
primary key).
12
13.
Functional dependency• Describes relationship between columns in
a table.
• If A and B are columns of the table R, B is
functionally dependent on A (denoted
A→B), if each value of A in R is associated
with exactly one value of B in R.
ID→LASTNAME
ID→FIRSTNAME
LASTNAME → FIRSTNAME
13
14.
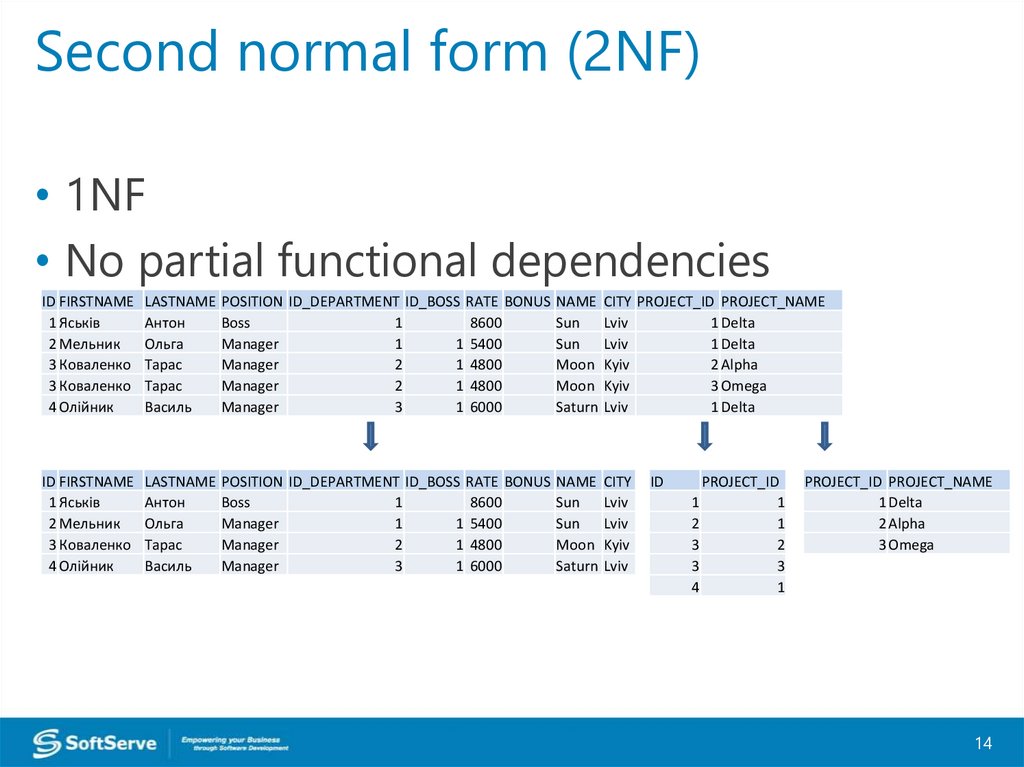
Second normal form (2NF)• 1NF
• No partial functional dependencies
ID FIRSTNAME LASTNAME POSITION ID_DEPARTMENT ID_BOSS RATE BONUS NAME CITY PROJECT_ID PROJECT_NAME
1 Яськів
Антон
Boss
1
8600
Sun
Lviv
1 Delta
2 Мельник
Ольга
Manager
1
1 5400
Sun
Lviv
1 Delta
3 Коваленко Тарас
Manager
2
1 4800
Moon Kyiv
2 Alpha
3 Коваленко Тарас
Manager
2
1 4800
Moon Kyiv
3 Omega
4 Олійник
Василь
Manager
3
1 6000
Saturn Lviv
1 Delta
ID FIRSTNAME LASTNAME POSITION ID_DEPARTMENT ID_BOSS RATE BONUS NAME CITY
1 Яськів
Антон
Boss
1
8600
Sun
Lviv
2 Мельник
Ольга
Manager
1
1 5400
Sun
Lviv
3 Коваленко Тарас
Manager
2
1 4800
Moon Kyiv
4 Олійник
Василь
Manager
3
1 6000
Saturn Lviv
ID
PROJECT_ID
1
1
2
1
3
2
3
3
4
1
PROJECT_ID PROJECT_NAME
1 Delta
2 Alpha
3 Omega
14
15.
1NF->2NF• Identify functional dependencies in the
table.
• If partial dependencies exist on the primary
key remove them by placing them in a new
table along with copy of their determinant.
15
16.
Third normal form (3NF)• 2NF
• No transitive dependencies, i.e. no non-key
field depends upon another.
ID FIRSTNAME LASTNAME POSITION ID_DEPARTMENT ID_BOSS RATE BONUS NAME CITY
1 Яськів
Антон
Boss
1
8600
Sun
Lviv
2 Мельник
Ольга
Manager
1
1 5400
Sun
Lviv
3 Коваленко Тарас
Manager
2
1 4800
Moon Kyiv
4 Олійник
Василь
Manager
3
1 6000
Saturn Lviv
ID FIRSTNAME LASTNAME POSITION ID_BOSS RATE BONUS ID_DEPARTMENT
1 Яськів
Антон
Boss
8600
1
2 Мельник Ольга
Manager
1 5400
1
3 Коваленко Тарас
Manager
1 4800
2
4 Олійник
Василь
Manager
1 6000
3
ID_DEPARTMENT NAME CITY
1 Sun
Lviv
2 Moon Kyiv
3 Saturn Lviv
16
17.
2NF->3NF• Identify functional dependencies in the
table.
• If transitive dependencies exist on the
primary key remove them by placing them
in a new table along with copy of their
determinant.
17
18.
Normalization: questionHow does a normalization affect the
productivity of such operations:
• Insert
• Update
• Delete
• Select
?
18
19.
Denormalization• Denormalized databases fair well under
heavy read-load and when the application
is read intensive
• But because the data is duplicated, the
updates and inserts become complex and
costly
19
20.
More information• http://databases.about.com/od/specificpro
ducts/a/normalization.htm
• http://holowczak.com/databasenormalization/
• http://www.essentialsql.com/get-ready-tolearn-sql-database-normalizationexplained-in-simple-english/
• http://www.studytonight.com/dbms/datab
ase-normalization.php
20
21.
Thank you!US OFFICES
EUROPE OFFICES
Austin, TX
Fort Myers, FL
Lehi, UT
Newport Beach, CA
Waltham, MA
Bulgaria
Germany
Netherlands
Poland
Russia
Sweden
Ukraine
United Kingdom
www.softserveinc.com













 Базы данных
Базы данных








