Похожие презентации:
Profit tax from legal entities. Topic 4
1.
Bukhara State UniversityDepartment of Economics
Topic 4:
PROFIT TAX FROM LEGAL
ENTITIES
(2 hours)
2.
PLAN:1) Economic nature and importance of the profit
tax from legal entities.
2) Payers of profit tax from legal entities, the
object of taxation and the procedure for forming
the tax base.
3) Profit tax benefits and profit tax rates for
legal entities.
4) Procedure for calculation of profit tax from
legal entities and payment of tax.
3.
Economic nature and importance of the profit taxfrom legal entities
Profit as an economic category represents the net income created
in the course of business activity. Profit is the last financial result of
economic entities operating on a commercial basis, and is one of the
main financial sources of the state budget, as well as the main goal
of business activity.
When prices are stable, the increase in profit indicates that the
company is operating efficiently. The increase in the profit volume
expands the financial potential of the enterprise, the development of
production, and the opportunities for financial incentives for workers
and employees.
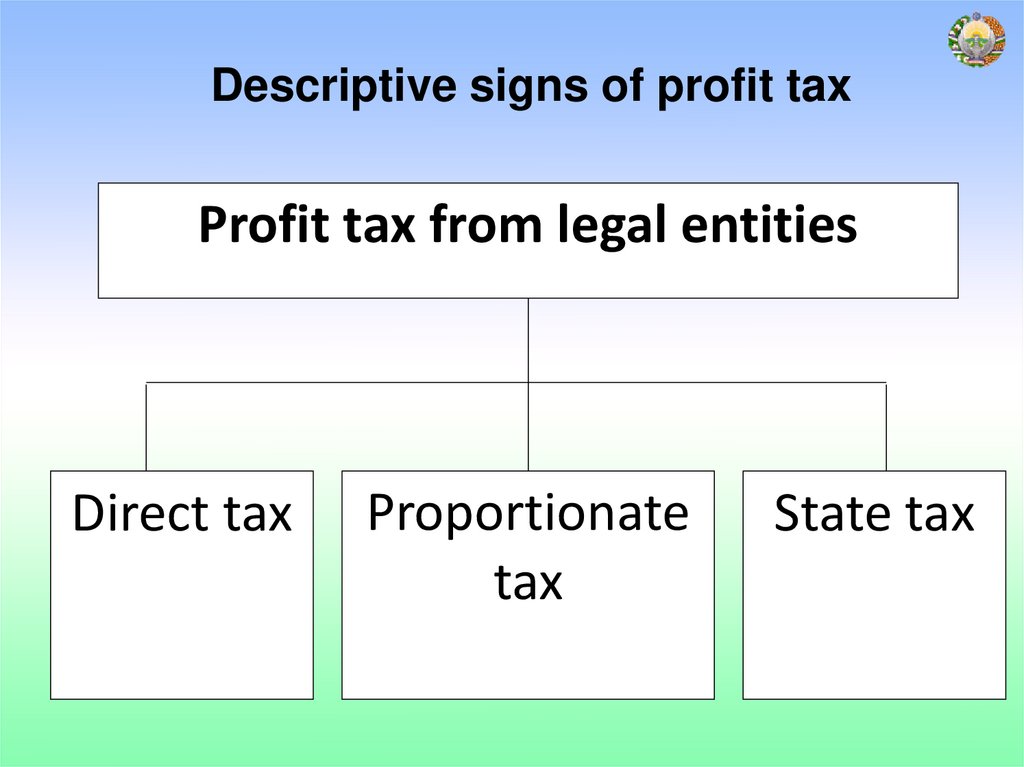
The profit tax collected from legal entities is a direct tax by its
essence, and a state tax according to the budget.
4.
Economic nature and importance of the profittax from legal entities
The essence of the profit tax is reflected in the financial relations
in the process of taxing the profits of legal entities and charging a
part of their profits to the budget.
The profit of legal entities is determined based on the procedure
for the formation of financial results specified in the accounting
legislation.
Income (profit) tax from legal entities was introduced on the basis
of the Law "On Taxes from Enterprises, Associations and
Organizations" dated February 15, 1991, and has been levied as an
income tax since 1992.
5.
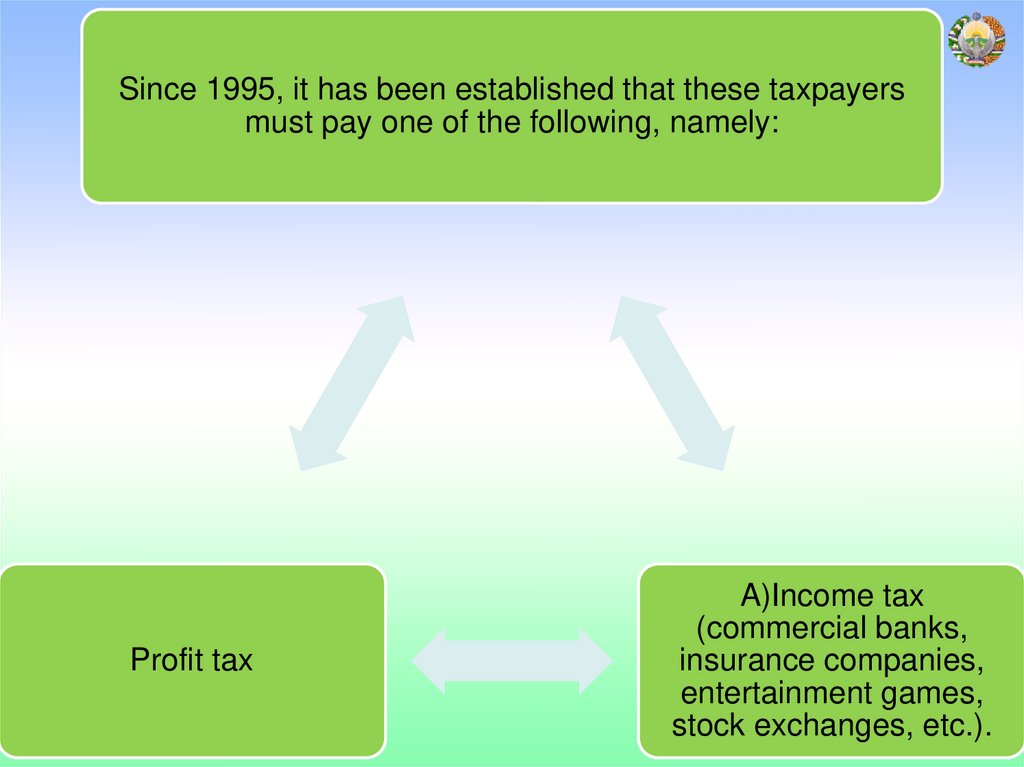
Since 1995, it has been established that these taxpayersmust pay one of the following, namely:
Profit tax
A)Income tax
(commercial banks,
insurance companies,
entertainment games,
stock exchanges, etc.).
6.
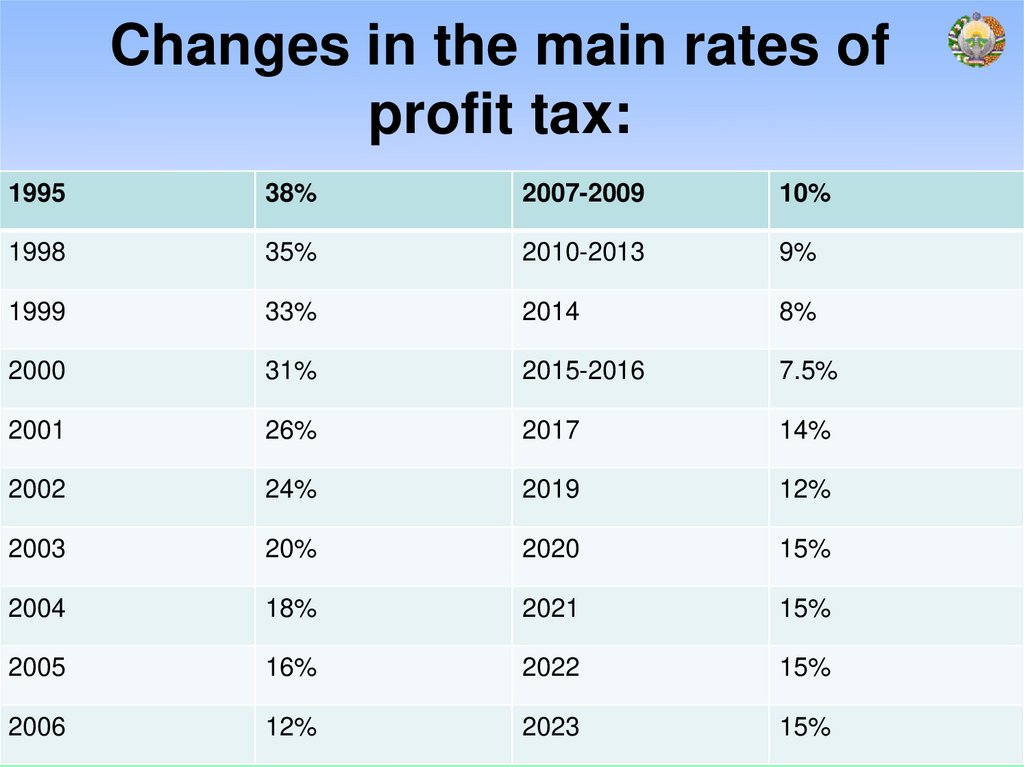
Changes in the main rates ofprofit tax:
1995
38%
2007-2009
10%
1998
35%
2010-2013
9%
1999
33%
2014
8%
2000
31%
2015-2016
7.5%
2001
26%
2017
14%
2002
24%
2019
12%
2003
20%
2020
15%
2004
18%
2021
15%
2005
16%
2022
15%
2006
12%
2023
15%
7.
Descriptive signs of profit taxProfit tax from legal entities
Direct tax
Proportionate
tax
State tax
8.
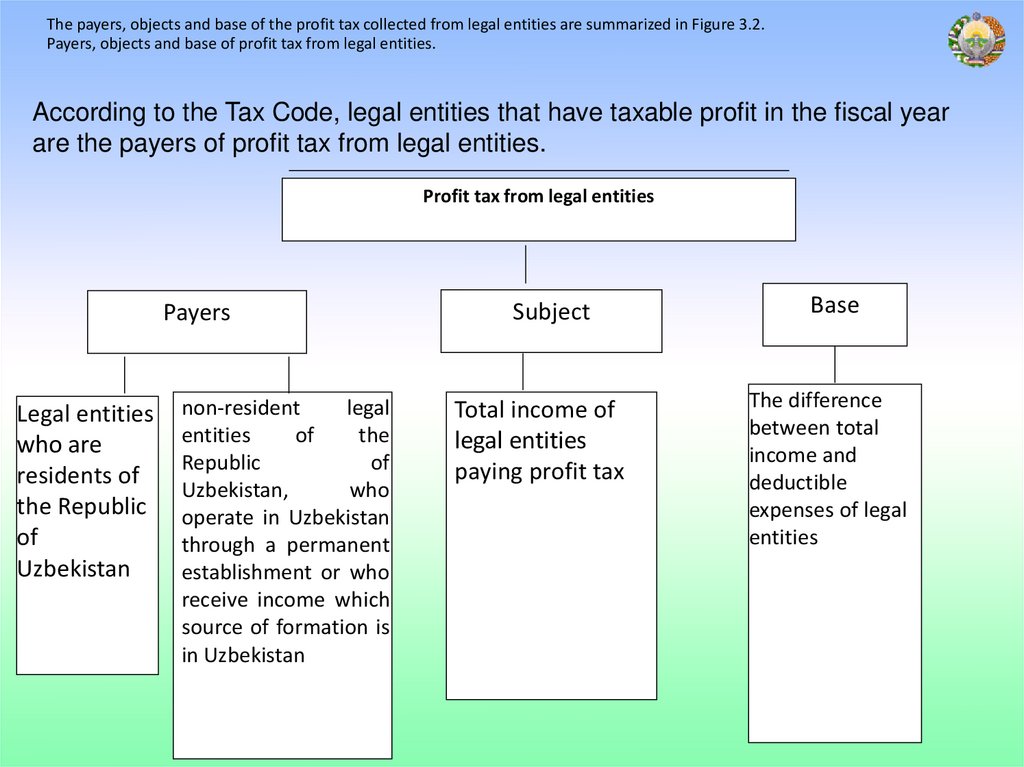
The payers, objects and base of the profit tax collected from legal entities are summarized in Figure 3.2.Payers, objects and base of profit tax from legal entities.
According to the Tax Code, legal entities that have taxable profit in the fiscal year
are the payers of profit tax from legal entities.
Profit tax from legal entities
Payers
Legal entities
who are
residents of
the Republic
of
Uzbekistan
non-resident
legal
entities
of
the
Republic
of
Uzbekistan,
who
operate in Uzbekistan
through a permanent
establishment or who
receive income which
source of formation is
in Uzbekistan
Subject
Base
Total income of
legal entities
paying profit tax
The difference
between total
income and
deductible
expenses of legal
entities
9.
The taxable base is determined on the basis of the calculatedtaxable profit, taking into account the reduction of the taxable profit
as the difference between the total income and the deductible
expenses. The profit tax base for legal entities is determined as
follows.
Profit tax base = Incomes - Expenditures + Non-deductible
expenses - Benefits
The profit of legal entities is determined in accordance with the
accounting legislation of our republic.
The single methodological basis for determining the costs of
production and sale of products (work, services) of economic subjectslegal entities in our republic is approved by the decision of the Cabinet of
Ministers of Uzbekistan No. 54 dated February 5, 1999 "On the
composition of Production (work, services) and sales expenses and the
procedure for forming financial results" and it is defined by the Regulation.
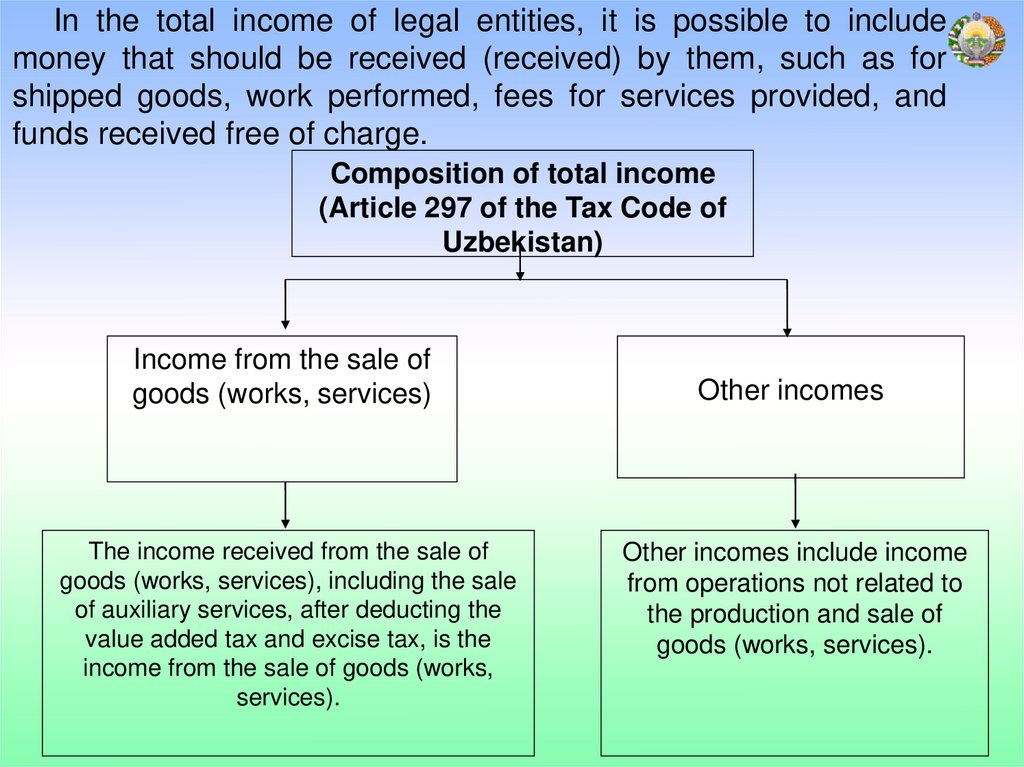
10.
In the total income of legal entities, it is possible to includemoney that should be received (received) by them, such as for
shipped goods, work performed, fees for services provided, and
funds received free of charge.
Composition of total income
(Article 297 of the Tax Code of
Uzbekistan)
Income from the sale of
goods (works, services)
The income received from the sale of
goods (works, services), including the sale
of auxiliary services, after deducting the
value added tax and excise tax, is the
income from the sale of goods (works,
services).
Other incomes
Other incomes include income
from operations not related to
the production and sale of
goods (works, services).
11.
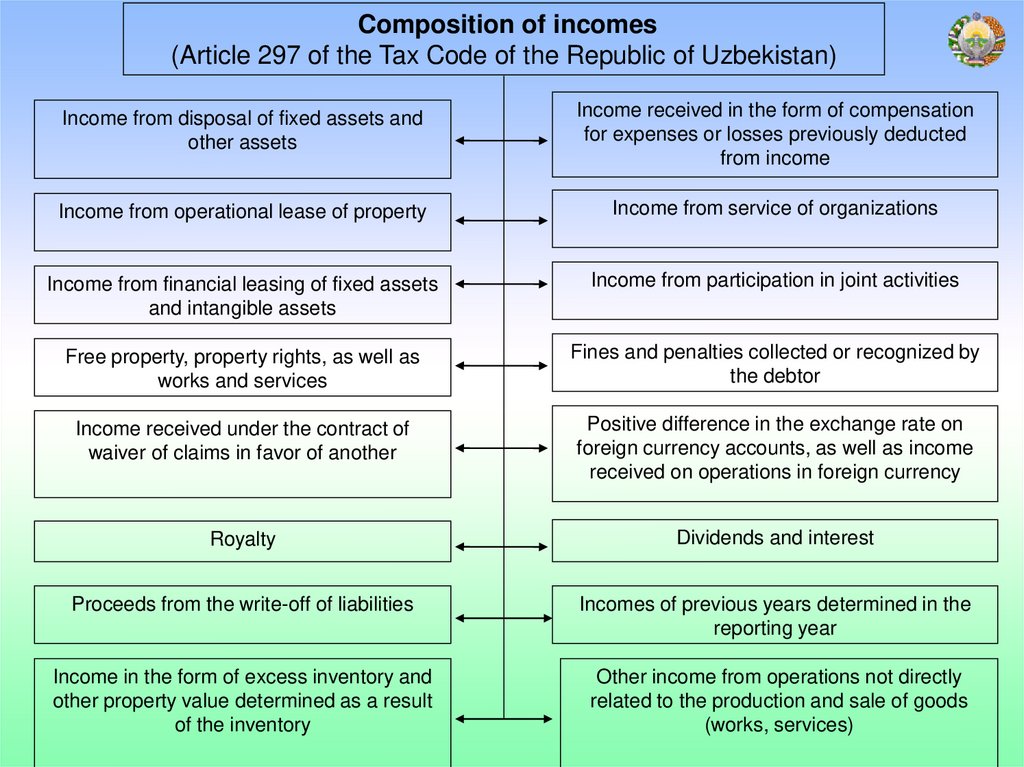
Composition of incomes(Article 297 of the Tax Code of the Republic of Uzbekistan)
Income from disposal of fixed assets and
other assets
Income received in the form of compensation
for expenses or losses previously deducted
from income
Income from operational lease of property
Income from service of organizations
Income from financial leasing of fixed assets
and intangible assets
Income from participation in joint activities
Free property, property rights, as well as
works and services
Fines and penalties collected or recognized by
the debtor
Income received under the contract of
waiver of claims in favor of another
Positive difference in the exchange rate on
foreign currency accounts, as well as income
received on operations in foreign currency
Royalty
Dividends and interest
Proceeds from the write-off of liabilities
Incomes of previous years determined in the
reporting year
Income in the form of excess inventory and
other property value determined as a result
of the inventory
Other income from operations not directly
related to the production and sale of goods
(works, services)
12.
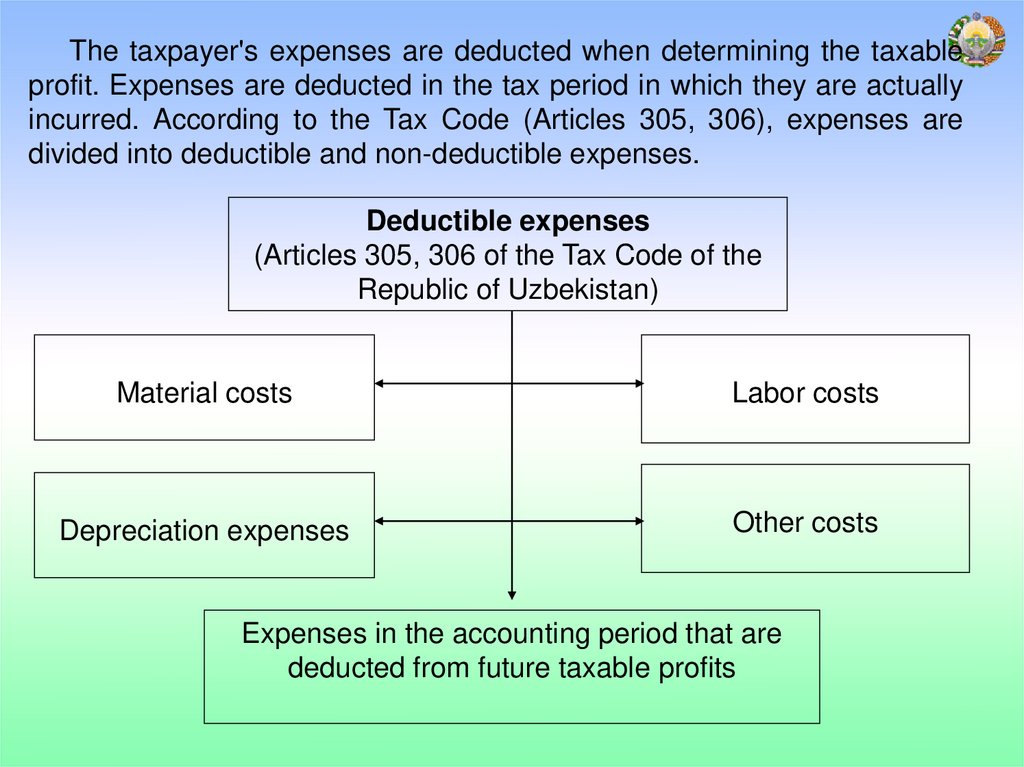
The taxpayer's expenses are deducted when determining the taxableprofit. Expenses are deducted in the tax period in which they are actually
incurred. According to the Tax Code (Articles 305, 306), expenses are
divided into deductible and non-deductible expenses.
Deductible expenses
(Articles 305, 306 of the Tax Code of the
Republic of Uzbekistan)
Material costs
Labor costs
Depreciation expenses
Other costs
Expenses in the accounting period that are
deducted from future taxable profits
13.
NON-DEDUCTIBLE EXPENSESNon-deductible expenses in determining taxable profit
include:
- excessive losses and violations of the norms of natural
decrease of material values;
- expenses in excess of the established norms (service trips,
representation expenses, allowances for optional insurance
types);
- allocations to non-state pension funds;
- training costs for professions that are not required in the
taxpayer's activity;
- material support paid to employees;
- court rulings;
- thefts, the perpetrators of which have not been identified,
and damages caused when it is not possible to compensate
for the necessary sums due to a deficit or at the expense of
the guilty party, etc.
14.
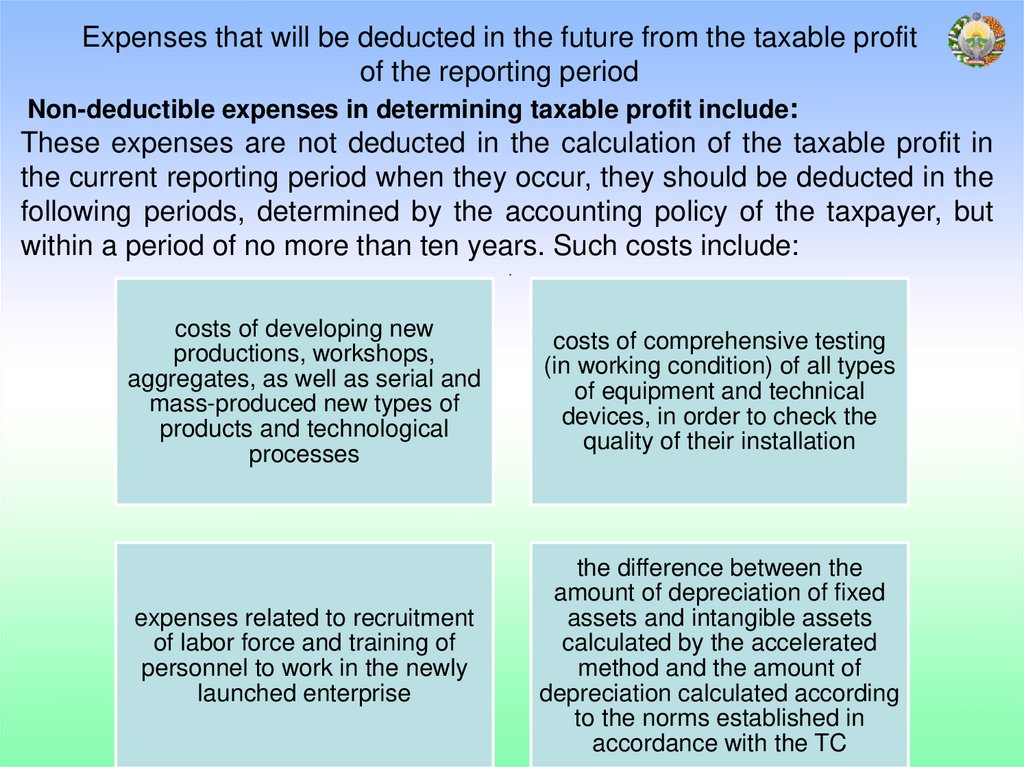
Expenses that will be deducted in the future from the taxable profitof the reporting period
Non-deductible expenses in determining taxable profit include:
These expenses are not deducted in the calculation of the taxable profit in
the current reporting period when they occur, they should be deducted in the
following periods, determined by the accounting policy of the taxpayer, but
within a period of no more than ten years. Such costs include:
costs of developing new
productions, workshops,
aggregates, as well as serial and
mass-produced new types of
products and technological
processes
costs of comprehensive testing
(in working condition) of all types
of equipment and technical
devices, in order to check the
quality of their installation
expenses related to recruitment
of labor force and training of
personnel to work in the newly
launched enterprise
the difference between the
amount of depreciation of fixed
assets and intangible assets
calculated by the accelerated
method and the amount of
depreciation calculated according
to the norms established in
accordance with the TC
15.
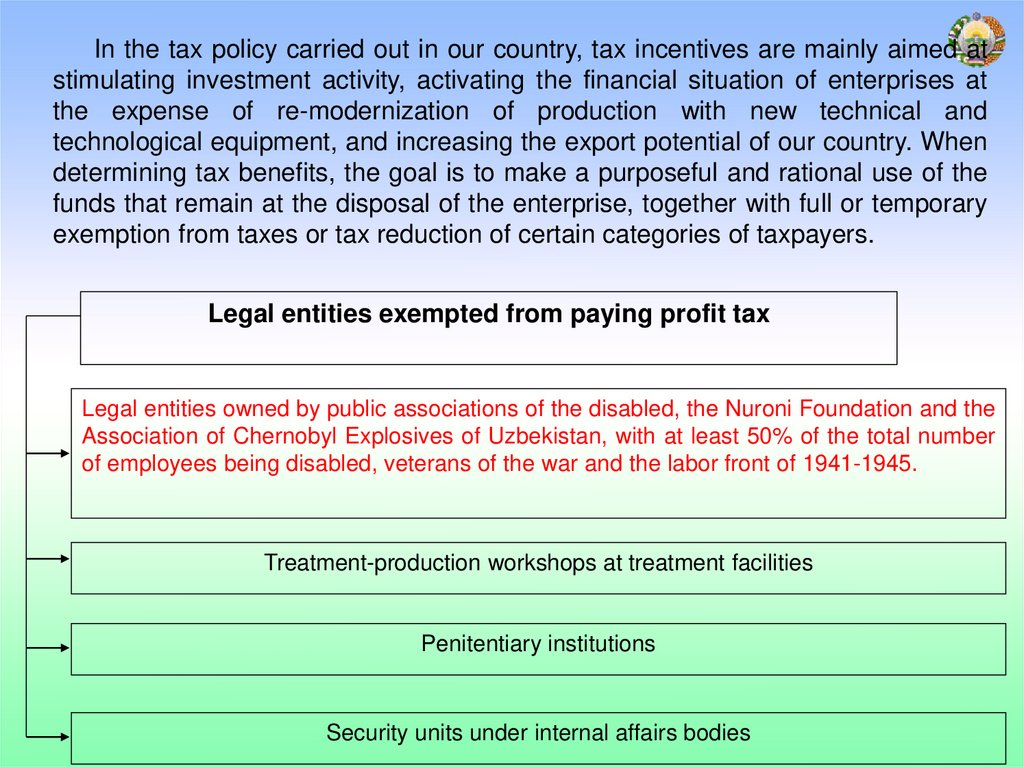
In the tax policy carried out in our country, tax incentives are mainly aimed atstimulating investment activity, activating the financial situation of enterprises at
the expense of re-modernization of production with new technical and
technological equipment, and increasing the export potential of our country. When
determining tax benefits, the goal is to make a purposeful and rational use of the
funds that remain at the disposal of the enterprise, together with full or temporary
exemption from taxes or tax reduction of certain categories of taxpayers.
Legal entities exempted from paying profit tax
Legal entities owned by public associations of the disabled, the Nuroni Foundation and the
Association of Chernobyl Explosives of Uzbekistan, with at least 50% of the total number
of employees being disabled, veterans of the war and the labor front of 1941-1945.
Treatment-production workshops at treatment facilities
Penitentiary institutions
Security units under internal affairs bodies
16.
The following profits of legal entities are exempted frompayment of profit tax from legal entities
Profit from the production of prosthetic-orthopedic goods, inventories for the disabled,
as well as the provision of orthopedic prosthetics services for the disabled, repair and
servicing of prosthetic-orthopedic goods and inventories intended for the disabled
Profit from the provision of services for the transportation of passengers in urban
passenger transport (except for taxis, including directional taxis)
Profit from the repair and restoration of historical and cultural monuments
The profit of investment funds directed to the purchase of shares of privatized
enterprises
The profit obtained by the Xalq banki from the use of funds in the personal savings
accounts of citizens
For legal entities with more than 3 percent of the total number of employees being
disabled, the amount of profit tax from legal entities is calculated on the basis of one
percent reduction of the amount of profit tax from legal entities for each percent of
disabled persons employed in excess of the norm specified in this part. is reduced
17.
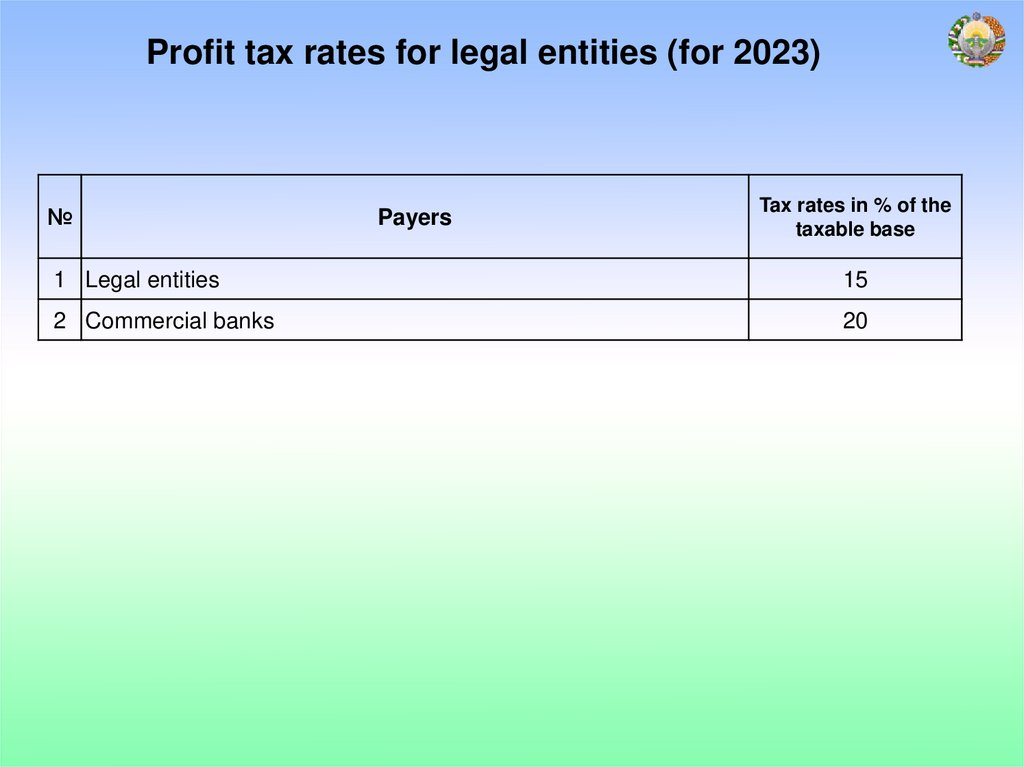
Profit tax rates for legal entities (for 2023)№
Payers
Tax rates in % of the
taxable base
1 Legal entities
15
2 Commercial banks
20
18.
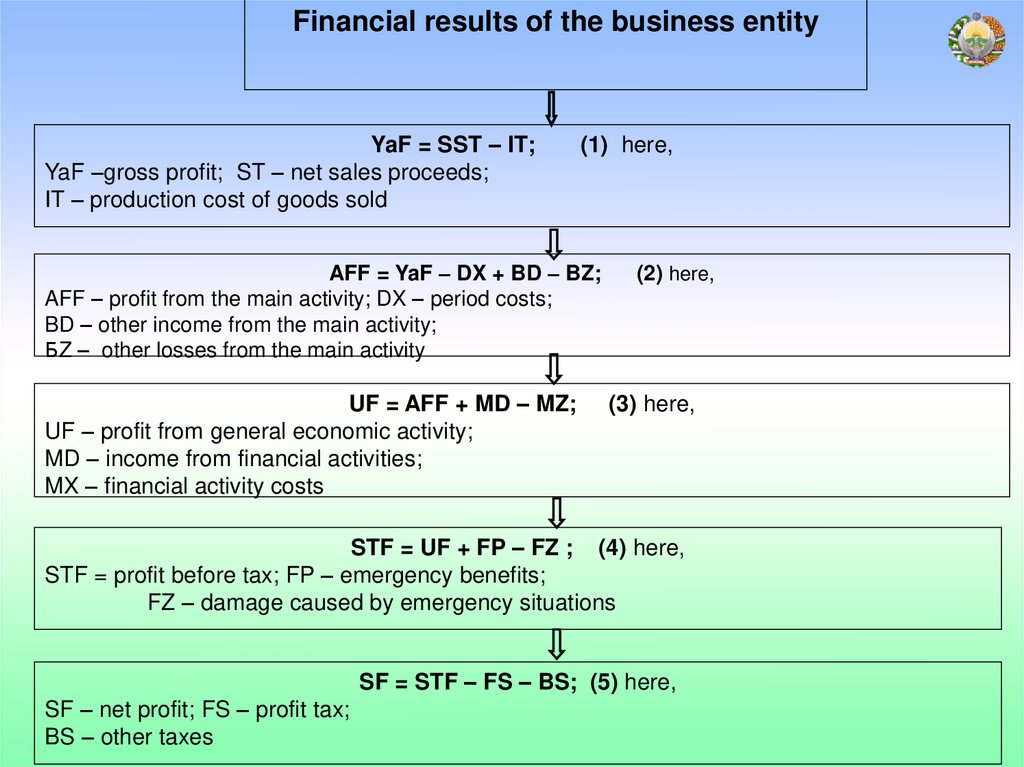
Financial results of the business entityYaF = SST – IT;
YaF –gross profit; ST – net sales proceeds;
IT – production cost of goods sold
(1) here,
AFF = YaF – DX + BD – BZ;
AFF – profit from the main activity; DX – period costs;
BD – other income from the main activity;
БZ – other losses from the main activity
UF = AFF + MD – MZ;
UF – profit from general economic activity;
MD – income from financial activities;
MX – financial activity costs
(2) here,
(3) here,
STF = UF + FP – FZ ; (4) here,
STF = profit before tax; FP – emergency benefits;
FZ – damage caused by emergency situations
SF = STF – FS – BS; (5) here,
SF – net profit; FS – profit tax;
BS – other taxes
19.
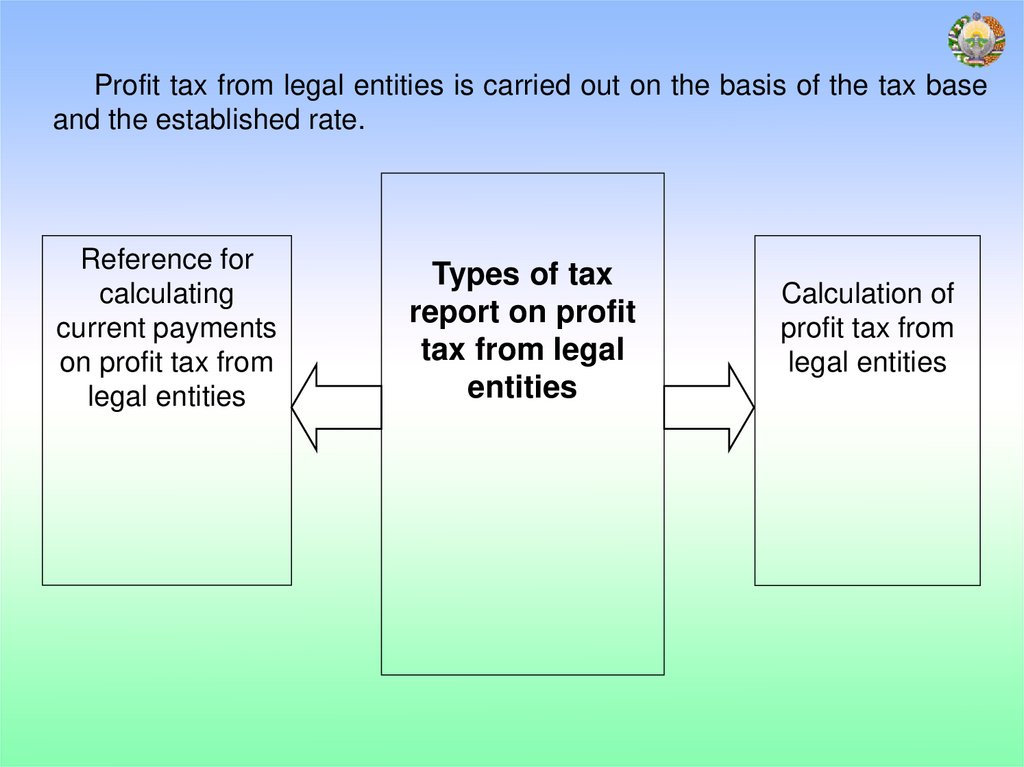
Profit tax from legal entities is carried out on the basis of the tax baseand the established rate.
Reference for
calculating
current payments
on profit tax from
legal entities
Types of tax
report on profit
tax from legal
entities
Calculation of
profit tax from
legal entities
20.
The procedure for tax calculation andsubmission of calculations
Profit tax from legal entities is carried out on the
basis of the taxable base and the fixed rate.
The calculation of the profit tax from legal entities
is submitted to the state tax service authorities with
the increasing end every quarter of the year no later
than the 25th day of the month following the reporting
quarter, and at the end of the year, during the period
when the annual financial report is submitted.
21.
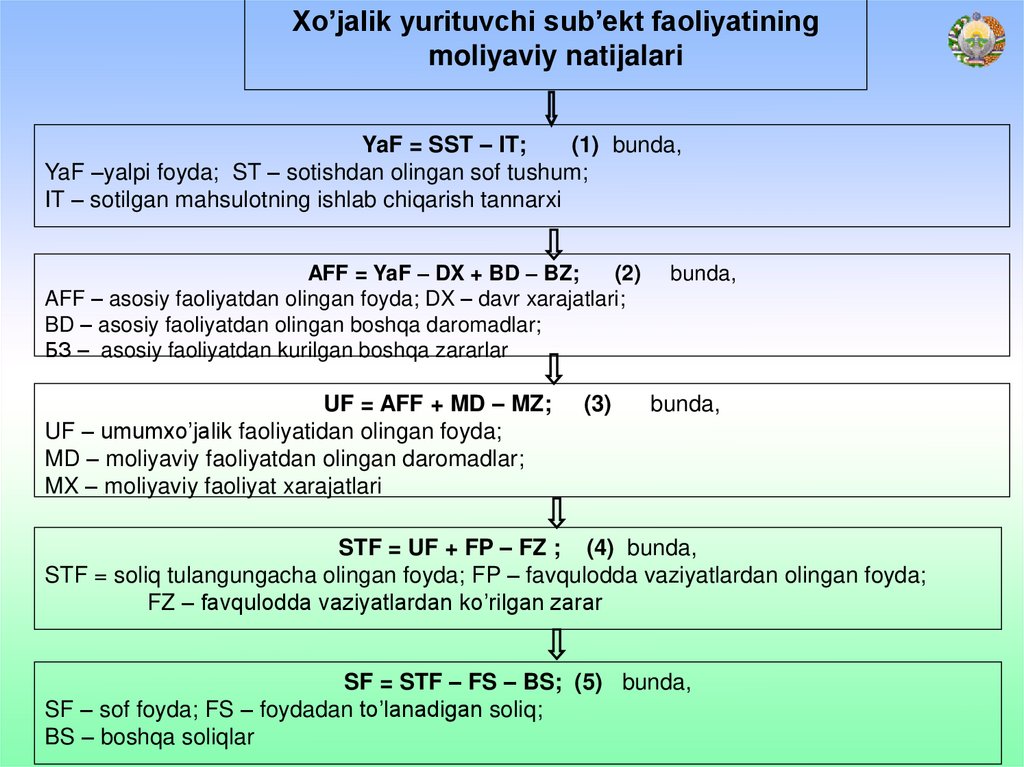
Xo’jalik yurituvchi sub’ekt faoliyatiningmoliyaviy natijalari
YaF = SST – IT;
(1) bunda,
YaF –yalpi foyda; ST – sotishdan olingan sof tushum;
IT – sotilgan mahsulotning ishlab chiqarish tannarxi
AFF = YaF – DX + BD – BZ;
(2)
AFF – asosiy faoliyatdan olingan foyda; DX – davr xarajatlari;
BD – asosiy faoliyatdan olingan boshqa daromadlar;
БЗ – asosiy faoliyatdan kurilgan boshqa zararlar
UF = AFF + MD – MZ;
UF – umumxo’jalik faoliyatidan olingan foyda;
MD – moliyaviy faoliyatdan olingan daromadlar;
MX – moliyaviy faoliyat xarajatlari
(3)
bunda,
bunda,
STF = UF + FP – FZ ; (4) bunda,
STF = soliq tulangungacha olingan foyda; FP – favqulodda vaziyatlardan olingan foyda;
FZ – favqulodda vaziyatlardan ko’rilgan zarar
SF = STF – FS – BS; (5) bunda,
SF – sof foyda; FS – foydadan to’lanadigan soliq;
BS – boshqa soliqlar








 Финансы
Финансы Право
Право








