Похожие презентации:
Data structure: String. Indexing and slicing
1.
Data structure:String. Indexing
and slicing
2.
Learning objectives:• 11.2.2.3 apply functions and string processing
methods;
• 11.2.2.1 perform access to the elements of strings,
lists, tuples;
• 11.2.2.2 use slicers to process the string;
• 11.2.3.6 determine the difference between different
data structures.
3.
A string is a sequence of characters.Strings are enclosed in quotes:
"Hello, World!"
'Python is fun!’
Strings are used to store and manipulate text in
Python.
fixed_word = 'Programming'
print(fixed_word)
4.
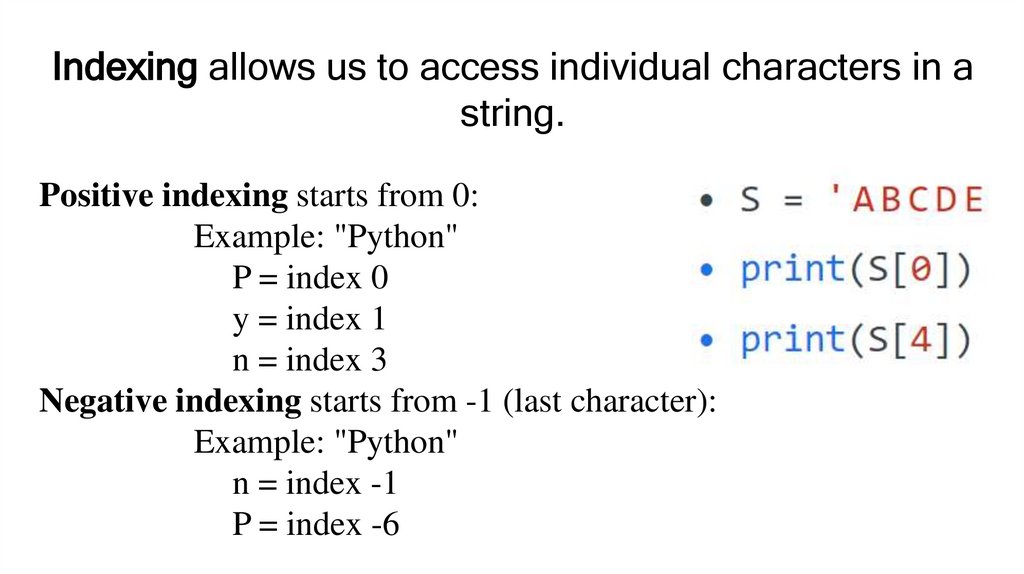
Indexing allows us to access individual characters in astring.
Positive indexing starts from 0:
Example: "Python"
P = index 0
y = index 1
n = index 3
Negative indexing starts from -1 (last character):
Example: "Python"
n = index -1
P = index -6
5.
Slicing is used to extract parts of a string.Syntax: string[start:end:step]
start: Starting index (inclusive)
end: Ending index (exclusive)
step: Interval between characters (optional)
6.
Given: word = "Python"1.word[0:2] → "Py"
2.word[2:5] → "tho"
3.word[::2] → "Pto" (every second character)
4.word[::-1] → "nohtyP" (reverses the string)
7.
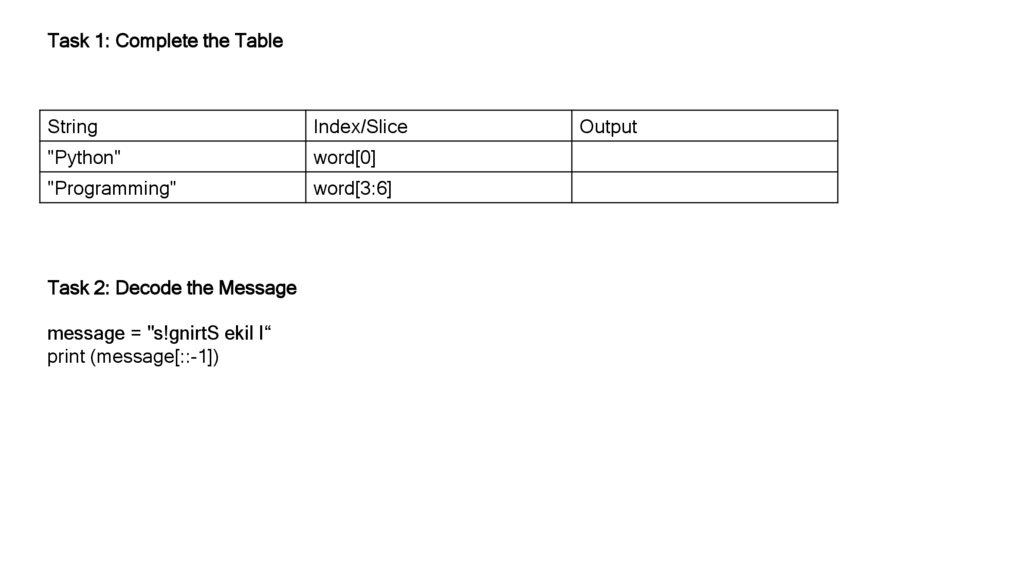
Task 1: Complete the TableString
Index/Slice
"Python"
word[0]
"Programming"
word[3:6]
Task 2: Decode the Message
message = "s!gnirtS ekil I“
print (message[::-1])
Output




 Программирование
Программирование Информатика
Информатика








